IT rounded shapes as a factor
It is no secret that engineers often draw their inspiration from the nature around us, studying its harsh and fair laws. Over the years of evolution, according to some estimates, this process lasts for about 3.5 billion years, the contours of biological structures have increasingly acquired a thorough look, these forms are not only pleasing to the eye, but often are good examples for deliberate inheritance in technology. The IT industry is no exception here, it can be seen in many examples. The Internet itself reminds us of a huge cobweb that has enveloped the entire planet, which in fact has found its morphological mapping in the commonly understood phrase “Internet cobweb”.

Industrial designs - as a crown of human thought, with its angular surfaces and overly straight lines, more and more often began to take on forms more streamlined, rounded, repeating the bends that filled the world of nature. In addition to subjective aesthetics, the progressive movement in this direction can bring a lot of excellent design solutions and optimization of engineering tasks that the IT sector abounds in. In the article below, we will try to shed light on the design solutions that are not too standard at this time, which are used in the construction of data centers, especially paying attention to what advantages, in comparison with existing technologies, in terms of efficiency they can to conclude.
')
Historically, a modern data center has actually become a rectangular monument. At all levels of an IT site, we can meet a huge number of rectangular projections, starting from the building itself, where the entire IT economy is located, right up to the most trivial data storage devices. The structures that are familiar to us, convenient for production, storage, for transportation, are not always the most successful for efficient operation in data centers. The rectangular contours of the building also define the internal space, imposing a certain type of placement of server cabinets, which, by the way, are also rectangular.

Once in the server room of a large data center, you usually see rows of server cabinets in front of you, between which hot and cold corridors alternate. Such an organization of the process is far from rational, but it is probably impossible to change anything with the current realities, but the engineering thought does not stand still and already there are some very interesting solutions. The basis for such decisions was the change of forms.
The last few years have brought changes to the understanding by engineers of the approach to the organization of the internal space of data centers and components that fill it. At different levels, very interesting solutions arise that look very contrast against the background of classic designs.
Cylindrical structures, both new and often refitted, former industrial facilities, gave engineers the opportunity to look at the problem of the efficient use of the internal space of future data centers from a new angle. The commonly used "corridor" arrangement of server racks under certain conditions turned out to be completely unsuitable, as will become clear a little further, and not at all necessary.
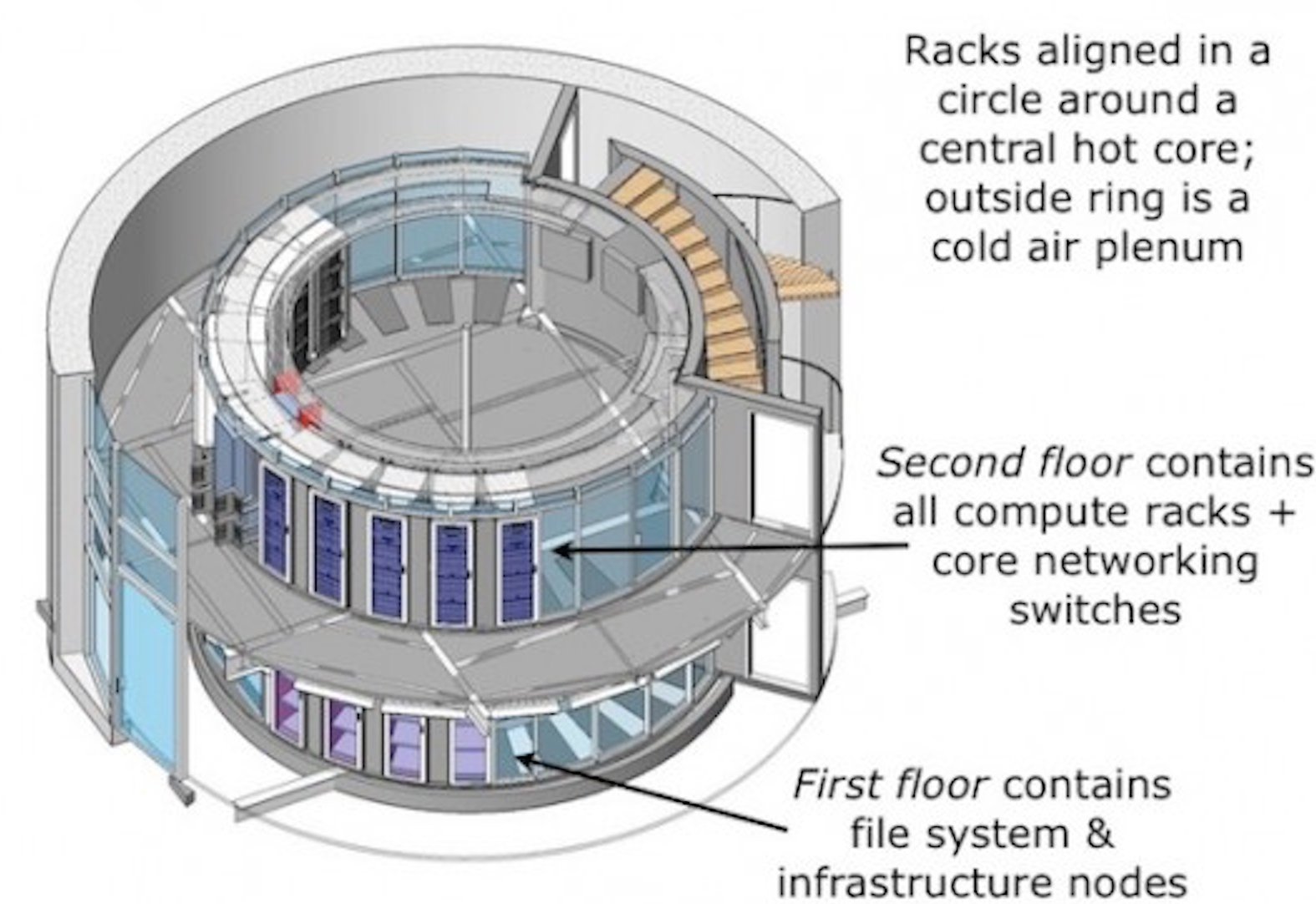
An interesting experience in this direction has been obtained by Sun Microsystems, having placed its data center - CLUMEQ (Consortium Laval UQAM McGill and Eastern Quebec) in a cylindrical building. The dimensions of the building are 11 meters in diameter and 20 meters in height. The total computational power of the equipment it houses is 86 teraflops, while it allows you to allocate a total of more than 1 petabyte of data.
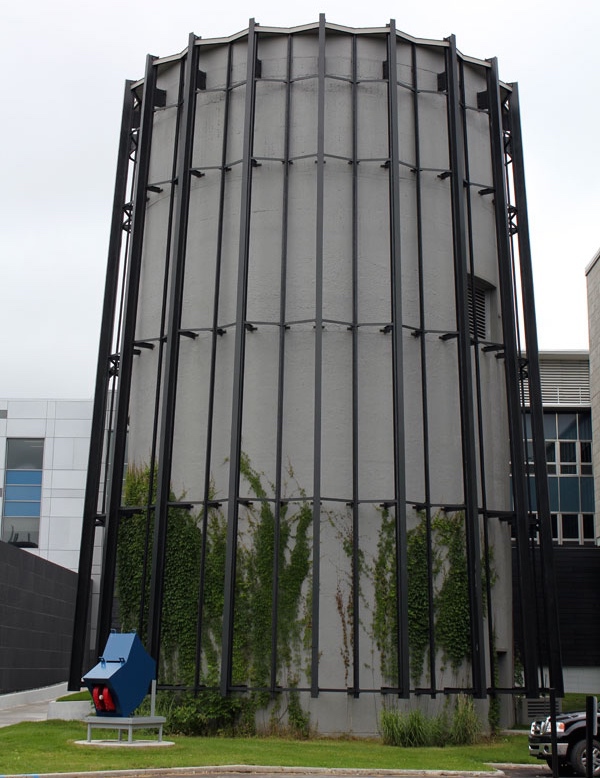

On each of the floors, server racks form a closed ring of racks. A special feature here is that the hot side is directed inside the “ring”, thereby forming a hot core in the central part of the building, respectively, the outer ring is cold. Such an arrangement of racks makes it possible to organize highly efficient centralized heat removal from equipment. The fans installed at the basement level direct the flow of cold air along the outer contour of the ring of racks, reaching the top the cooled flow is independently discharged through the central space of the building, thereby ensuring a comfortable temperature condition in the data center with minimal energy consumption.
The cylindrical building is interesting, but no less creative was the decision of the Vapor IO company to develop cylindrical server racks. Placing in the familiar server rooms, filled with network equipment columns, according to the engineers Vapor, they can save during the operation of substantial funds.
“At the time of cloud services and huge data centers, which were in fact continuously loaded with ever increasing data flows, the issue of energy efficiency is particularly acute and the rack design itself has become a significant contribution to its increase, it’s strange that such an obvious understanding didn’t find its technical condition for so long commercially successful implementation, ”said one of the developers of the server colony. Let's take a closer look at what the old solution in the new shell is.
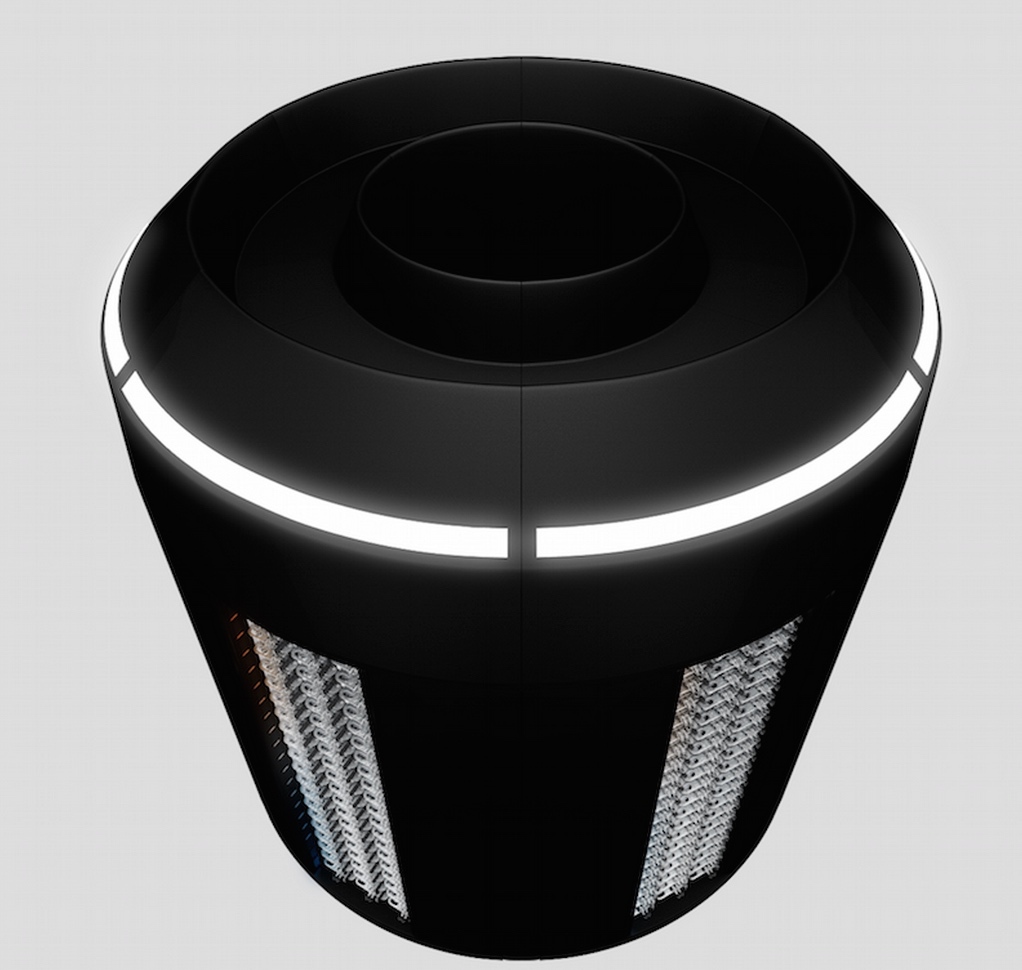

Sealed rack housing almost completely eliminates unauthorized heat exchange with the surrounding space. All the heat generated by the equipment accumulates the internal space of the “columns”, but due to the installed in it, at the base level, the fan and the hole in its upper part, the excess heat can be easily removed. Such an arrangement not only reduces the cost of maintaining an acceptable temperature throughout the room, but also makes it possible to more efficiently collect the air heated by the racks and direct it to further commercial use as a free energy source.
The first model of the server rack from Vapor IO is actually formed from six 25 kV racks, the effective heat dissipation from equipment allows us to concentrate more equipment than in the well-known 42U rack. If we continue the topic of efficiency further, thanks to the individual ventilation system in the server column, the savings are realized not only due to the individual operation of the ventilation system in it, but also due to the greater concentration of the cylindrical cabinets themselves in the server room. According to the marketing department of Vapor IO, thanks to the thermal insulation of their solutions, it was possible to place more production capacity on the very area of the building, without deteriorating the operating conditions of the servers, than was possible earlier. An example is the classic layout of 42U racks, while respecting the correct configuration of hot and cold corridors, in an area where you can fit 120 racks with a total power of 4.32 MW, 36 new server columns capable of supporting equipment with a total capacity of 5.4 MW can fit.

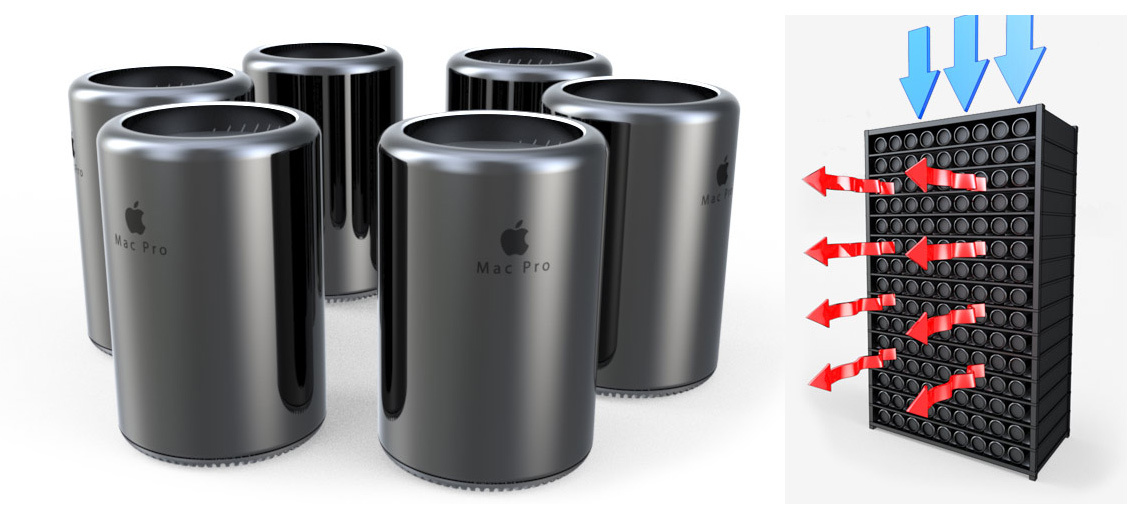
For a person who has come across server hardware, manufacturers such as Dell, HP, Lenovo / IBM, Fujitsu will be new, but perhaps the mention of Apple in this series may surprise. In fact, the creation of a data center based on Apple products is certainly not new, small data centers have been around for more than a year. The rarity of such infrastructure is due to its high cost, while most potential consumers do not see expediency in it. Nevertheless, there are such solutions, and sometimes they can be very competitive. In this context, it is impossible not to recall the Mac Pro workstation. In addition to the high-performance, energy-efficient stuffing in the crown of Apple Corporation, the Mac Pro body itself also has very non-trivial forms. Actually why not a cylinder? Apparently, such questions were asked by designers from Apple.
It was this non-standard design of Mac Pro that prompted MacStadium employees to develop a new type of server rack specifically for it, which would allow more efficient use of the cylindrical shape of the device.
The presented rack, outwardly, resembles the familiar 42U already known to us, but it has its own peculiarities. Chilled air is supplied through a hole in the upper part of the rack, after which the air masses, bending around the smooth lines of the Mac Pro, are removed by gravity through the open walls of the rack and the heat generated by the equipment. When placed in the hall of such racks there are no “cold” corridors, which somewhat simplifies the thermoregulation in the room. Access to equipment in cabinets is very easy, and this makes working with equipment simple and pleasant. By the way, in a rack it is possible to place up to 270 Mac Pro, which gives the concentration of equipment an order of magnitude higher than that of existing server cabinets analogues.

You can often hear the saying “You don’t need to reinvent the bicycle” in everyday life, saying that why waste energy on searching for new forms and solutions under the already established order of things? Why revise the existing standards, because it will undoubtedly be incurred in addition to the fact that additional costs, at the first stage of implementation, and simply rejection of the conservative part of potential consumers. But the obvious inefficiency of established technologies will sooner or later give way to progress, which bears in itself cost-effectiveness, high productivity and, of course, ease of operation. It is obvious that enthusiasts who invent the “bicycle”, as before, are not going anywhere and will continue to be one of the engines of progress. Using the article as an example, we looked at a few cases where, in the era of high-tech manufacturing, nanotechnology, quite simple upgrades, innovative vision, can reduce the end-user costs. And this, in turn, may be the impetus for the entry into the IT equipment market of new, relatively small manufacturers, which in the foreseeable future will be able to tear a substantial chunk away from the market.

Industrial designs - as a crown of human thought, with its angular surfaces and overly straight lines, more and more often began to take on forms more streamlined, rounded, repeating the bends that filled the world of nature. In addition to subjective aesthetics, the progressive movement in this direction can bring a lot of excellent design solutions and optimization of engineering tasks that the IT sector abounds in. In the article below, we will try to shed light on the design solutions that are not too standard at this time, which are used in the construction of data centers, especially paying attention to what advantages, in comparison with existing technologies, in terms of efficiency they can to conclude.
')
Vicious rectangle
Historically, a modern data center has actually become a rectangular monument. At all levels of an IT site, we can meet a huge number of rectangular projections, starting from the building itself, where the entire IT economy is located, right up to the most trivial data storage devices. The structures that are familiar to us, convenient for production, storage, for transportation, are not always the most successful for efficient operation in data centers. The rectangular contours of the building also define the internal space, imposing a certain type of placement of server cabinets, which, by the way, are also rectangular.

Once in the server room of a large data center, you usually see rows of server cabinets in front of you, between which hot and cold corridors alternate. Such an organization of the process is far from rational, but it is probably impossible to change anything with the current realities, but the engineering thought does not stand still and already there are some very interesting solutions. The basis for such decisions was the change of forms.
Roundness - the answer of time
The last few years have brought changes to the understanding by engineers of the approach to the organization of the internal space of data centers and components that fill it. At different levels, very interesting solutions arise that look very contrast against the background of classic designs.
Cylindrical structures, both new and often refitted, former industrial facilities, gave engineers the opportunity to look at the problem of the efficient use of the internal space of future data centers from a new angle. The commonly used "corridor" arrangement of server racks under certain conditions turned out to be completely unsuitable, as will become clear a little further, and not at all necessary.
An interesting experience in this direction has been obtained by Sun Microsystems, having placed its data center - CLUMEQ (Consortium Laval UQAM McGill and Eastern Quebec) in a cylindrical building. The dimensions of the building are 11 meters in diameter and 20 meters in height. The total computational power of the equipment it houses is 86 teraflops, while it allows you to allocate a total of more than 1 petabyte of data.

On each of the floors, server racks form a closed ring of racks. A special feature here is that the hot side is directed inside the “ring”, thereby forming a hot core in the central part of the building, respectively, the outer ring is cold. Such an arrangement of racks makes it possible to organize highly efficient centralized heat removal from equipment. The fans installed at the basement level direct the flow of cold air along the outer contour of the ring of racks, reaching the top the cooled flow is independently discharged through the central space of the building, thereby ensuring a comfortable temperature condition in the data center with minimal energy consumption.

Server column from Vapor IO
The cylindrical building is interesting, but no less creative was the decision of the Vapor IO company to develop cylindrical server racks. Placing in the familiar server rooms, filled with network equipment columns, according to the engineers Vapor, they can save during the operation of substantial funds.
“At the time of cloud services and huge data centers, which were in fact continuously loaded with ever increasing data flows, the issue of energy efficiency is particularly acute and the rack design itself has become a significant contribution to its increase, it’s strange that such an obvious understanding didn’t find its technical condition for so long commercially successful implementation, ”said one of the developers of the server colony. Let's take a closer look at what the old solution in the new shell is.

Sealed rack housing almost completely eliminates unauthorized heat exchange with the surrounding space. All the heat generated by the equipment accumulates the internal space of the “columns”, but due to the installed in it, at the base level, the fan and the hole in its upper part, the excess heat can be easily removed. Such an arrangement not only reduces the cost of maintaining an acceptable temperature throughout the room, but also makes it possible to more efficiently collect the air heated by the racks and direct it to further commercial use as a free energy source.
The first model of the server rack from Vapor IO is actually formed from six 25 kV racks, the effective heat dissipation from equipment allows us to concentrate more equipment than in the well-known 42U rack. If we continue the topic of efficiency further, thanks to the individual ventilation system in the server column, the savings are realized not only due to the individual operation of the ventilation system in it, but also due to the greater concentration of the cylindrical cabinets themselves in the server room. According to the marketing department of Vapor IO, thanks to the thermal insulation of their solutions, it was possible to place more production capacity on the very area of the building, without deteriorating the operating conditions of the servers, than was possible earlier. An example is the classic layout of 42U racks, while respecting the correct configuration of hot and cold corridors, in an area where you can fit 120 racks with a total power of 4.32 MW, 36 new server columns capable of supporting equipment with a total capacity of 5.4 MW can fit.

Apple's server hardware
For a person who has come across server hardware, manufacturers such as Dell, HP, Lenovo / IBM, Fujitsu will be new, but perhaps the mention of Apple in this series may surprise. In fact, the creation of a data center based on Apple products is certainly not new, small data centers have been around for more than a year. The rarity of such infrastructure is due to its high cost, while most potential consumers do not see expediency in it. Nevertheless, there are such solutions, and sometimes they can be very competitive. In this context, it is impossible not to recall the Mac Pro workstation. In addition to the high-performance, energy-efficient stuffing in the crown of Apple Corporation, the Mac Pro body itself also has very non-trivial forms. Actually why not a cylinder? Apparently, such questions were asked by designers from Apple.
It was this non-standard design of Mac Pro that prompted MacStadium employees to develop a new type of server rack specifically for it, which would allow more efficient use of the cylindrical shape of the device.
The presented rack, outwardly, resembles the familiar 42U already known to us, but it has its own peculiarities. Chilled air is supplied through a hole in the upper part of the rack, after which the air masses, bending around the smooth lines of the Mac Pro, are removed by gravity through the open walls of the rack and the heat generated by the equipment. When placed in the hall of such racks there are no “cold” corridors, which somewhat simplifies the thermoregulation in the room. Access to equipment in cabinets is very easy, and this makes working with equipment simple and pleasant. By the way, in a rack it is possible to place up to 270 Mac Pro, which gives the concentration of equipment an order of magnitude higher than that of existing server cabinets analogues.

findings
You can often hear the saying “You don’t need to reinvent the bicycle” in everyday life, saying that why waste energy on searching for new forms and solutions under the already established order of things? Why revise the existing standards, because it will undoubtedly be incurred in addition to the fact that additional costs, at the first stage of implementation, and simply rejection of the conservative part of potential consumers. But the obvious inefficiency of established technologies will sooner or later give way to progress, which bears in itself cost-effectiveness, high productivity and, of course, ease of operation. It is obvious that enthusiasts who invent the “bicycle”, as before, are not going anywhere and will continue to be one of the engines of progress. Using the article as an example, we looked at a few cases where, in the era of high-tech manufacturing, nanotechnology, quite simple upgrades, innovative vision, can reduce the end-user costs. And this, in turn, may be the impetus for the entry into the IT equipment market of new, relatively small manufacturers, which in the foreseeable future will be able to tear a substantial chunk away from the market.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/254143/
All Articles