City Wi-Fi on the example of Moscow University dormitories
Hi, Habr! Today we will deviate a little from the usual course and tell you not about the video surveillance system, but about how Wi-Fi works in Moscow.
At once we will say that the publication will be without hardcore technical details, for one simple reason: the Internet is provided according to the “service model”. Simply put, the customer places demands on the necessary communication services, and performers provide these communication services on a competitive basis. Currently, two major operators, VimpelCom and MGTS, selected on the basis of competitive procedures, are involved in providing communications in Moscow as part of the Wi-Fi in Hostels project. The quality and operability of the network depend on the work of these two operators.
Wireless Internet access in hostels is part of the City Wi-Fi urban project, which includes other public facilities: city parks, cultural objects, and pedestrian and bicycle lanes. Dormitory universities are one of the main parts of the project, and we will talk about them in today's article.
')
At the time of this writing, a total of two operators have installed 5561 radio access points, all of them are located in the 121 dormitory buildings of the universities of Moscow, where about 77 thousand students live.
There are many requirements for the work of operators, and one of them is stable operation of at least 10-15 subscribers at each of the points. At the same time, 10-15 people are not the maximum number of subscribers (the upper threshold has not yet been established), but an approximate number of people who should be serviced steadily (there are places where up to 30 subscribers are stably served).
SMS authorization will soon be available for all zones of the City Wi-Fi city project, which will function using the Unified mobile platform. In the meantime, this has not happened, authorization is implemented on the networks of the operator.
As an example, let us consider in more detail the model of rendering communication services for hostels from the MGTS operator.
MGTS network deployed using solutions from the company Hewlett-Packard. Wi-Fi access points operating in the 2.4 and 5 GHz bands are connected via aggregating switching equipment to the main communication channel based on GPON technology. To provide centralized management, two geographically dispersed clusters are used, consisting of HP 870 Unified Wired-WLAN Appliance hardware controllers and connected according to the N + M scheme in combination with the HP iMC Wireless Services Manager control system.
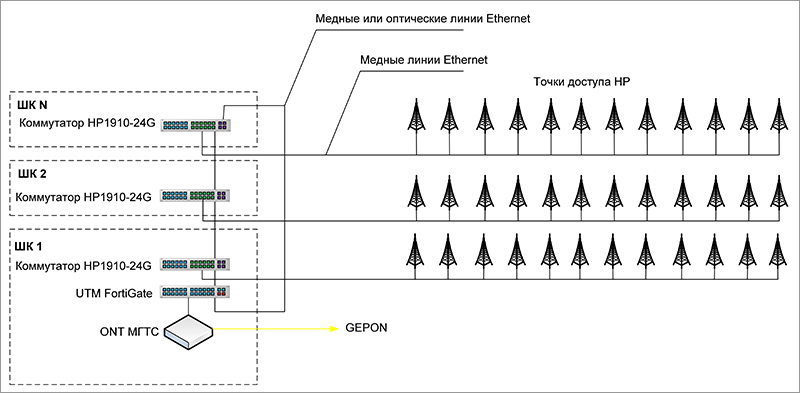
Client Access Layout
As access points, HP4xx series products with two radio interfaces supporting two 2.4 and 5 GHz bands are selected. This allows you to start the service at each access point simultaneously at 2.4 GHz (the most popular, but at the same time the “noisy” range itself) and at 5 GHz. Radio Resource Management (RRM) technology helps connect user devices with 5 GHz support (or both bands) primarily in these frequencies, which improves the communication quality for the user. RRM also constantly analyzes the environment and automatically adjusts the radiation power of all access points, achieving optimal coverage. Thanks to seamless roaming, the user can move around the hostel without disconnecting. Balancing clients between access points retains a high-quality connection for all connected users, not allowing to overload individual access points in the presence of neighboring free points.
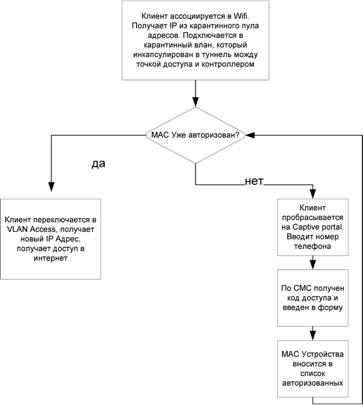
When trying to connect to the network, the user is redirected to the web-portal for authorization by the mobile phone number. After entering the password received via SMS, the user gets access to the Internet. At the moment, the system supports up to 15,000 concurrent users. The portal is implemented on the basis of the User Access Manager (UAM) software module of the HP iMC management system; this module also performs the function of a RADIUS server. A single solution management interface is provided by the HP iMC Wireless Service Manager (WSM) module. This module allows operators to see the wireless network map, equipment coverage areas and the location of the equipment on the floor plan, create, launch or disable services. In general, for solving management and authorization tasks on such a scale (more than 2,300 access points and 15,000 simultaneous users), 10 9th generation HP servers are used: 5 each under the active system and 5 under the backup one.
To ensure the best coverage, specialists carried out a comprehensive radio survey, which resulted in the selection of optimal access points with both built-in and remote antennas. All access points are connected using PoE technology, and the power supply of the aggregation and channel-forming equipment is guaranteed by uninterruptible power supplies. This scheme ensures the proper operation of the network during short-term outages or drops in the power supply network.
In those schools where access is already provided, there are information signs with contact information, so if you live in a dormitory at a university with city wireless access, and something suddenly does not work, feel free to call the specified phones: the operator will accept the application, it is processed Must be within 4 hours.
Device Authorization Scheme:
If suddenly you are a Wi-FI user in a dormitory of some Moscow university or you just have any questions (or even better - suggestions) on the operation of this service, then we will be happy to see them in the comments.
And yet a couple of words about video surveillance :) The work is actively continued with your help, we want to say again thanks for the feedback that you send as part of testing our system on a joint special project .
We want to note one important change. When testing, we had a limited number of accounts, while the number of people willing to take part in the test exceeded all our expectations. Therefore, we made a decision to do the following: if you have an account on the Moscow portal of State services , you can leave a request for testing on the page of the special project using the login of the portal. We will try to process your application as quickly as possible and provide access for tests.
And the last. The main goal of the special project is not just to let the professional community play around with the cameras, but to help you make our service better (so that you can play around with the cameras more conveniently in the future). Therefore, after you make your opinion about the service, we ask you to share with us your impressions and ideas on how to improve it. Any feedback about the service is useful to us: from the interface texts and layout, to bugs at work, or even vulnerability information. During the special project, many useful wishes were sent (some of which have already been taken into account), but here, as in a joke, I want pills for greed, but more, more!
We really appreciate your opinion.
Thanks for attention!
Read also in our blog on Habré:
» 130 thousand security cameras - how to make them work?
» Habraeffect for 130,000 Moscow cameras
» Information technology feeds more than 750 thousand people in Moscow
» Blog of the Department of Information Technology of the city of Moscow on" Habrahabr "

At once we will say that the publication will be without hardcore technical details, for one simple reason: the Internet is provided according to the “service model”. Simply put, the customer places demands on the necessary communication services, and performers provide these communication services on a competitive basis. Currently, two major operators, VimpelCom and MGTS, selected on the basis of competitive procedures, are involved in providing communications in Moscow as part of the Wi-Fi in Hostels project. The quality and operability of the network depend on the work of these two operators.
Wireless Internet access in hostels is part of the City Wi-Fi urban project, which includes other public facilities: city parks, cultural objects, and pedestrian and bicycle lanes. Dormitory universities are one of the main parts of the project, and we will talk about them in today's article.
')
At the time of this writing, a total of two operators have installed 5561 radio access points, all of them are located in the 121 dormitory buildings of the universities of Moscow, where about 77 thousand students live.
There are many requirements for the work of operators, and one of them is stable operation of at least 10-15 subscribers at each of the points. At the same time, 10-15 people are not the maximum number of subscribers (the upper threshold has not yet been established), but an approximate number of people who should be serviced steadily (there are places where up to 30 subscribers are stably served).
SMS authorization will soon be available for all zones of the City Wi-Fi city project, which will function using the Unified mobile platform. In the meantime, this has not happened, authorization is implemented on the networks of the operator.
As an example, let us consider in more detail the model of rendering communication services for hostels from the MGTS operator.
MGTS network deployed using solutions from the company Hewlett-Packard. Wi-Fi access points operating in the 2.4 and 5 GHz bands are connected via aggregating switching equipment to the main communication channel based on GPON technology. To provide centralized management, two geographically dispersed clusters are used, consisting of HP 870 Unified Wired-WLAN Appliance hardware controllers and connected according to the N + M scheme in combination with the HP iMC Wireless Services Manager control system.

Client Access Layout
As access points, HP4xx series products with two radio interfaces supporting two 2.4 and 5 GHz bands are selected. This allows you to start the service at each access point simultaneously at 2.4 GHz (the most popular, but at the same time the “noisy” range itself) and at 5 GHz. Radio Resource Management (RRM) technology helps connect user devices with 5 GHz support (or both bands) primarily in these frequencies, which improves the communication quality for the user. RRM also constantly analyzes the environment and automatically adjusts the radiation power of all access points, achieving optimal coverage. Thanks to seamless roaming, the user can move around the hostel without disconnecting. Balancing clients between access points retains a high-quality connection for all connected users, not allowing to overload individual access points in the presence of neighboring free points.
When trying to connect to the network, the user is redirected to the web-portal for authorization by the mobile phone number. After entering the password received via SMS, the user gets access to the Internet. At the moment, the system supports up to 15,000 concurrent users. The portal is implemented on the basis of the User Access Manager (UAM) software module of the HP iMC management system; this module also performs the function of a RADIUS server. A single solution management interface is provided by the HP iMC Wireless Service Manager (WSM) module. This module allows operators to see the wireless network map, equipment coverage areas and the location of the equipment on the floor plan, create, launch or disable services. In general, for solving management and authorization tasks on such a scale (more than 2,300 access points and 15,000 simultaneous users), 10 9th generation HP servers are used: 5 each under the active system and 5 under the backup one.
A more detailed description of the solution.
The scheme consists of three main functional blocks:
- The core of the wireless network
- Transport network between core and objects
- LAN at the facility
The core is geographically distributed. Each site consists of Wi-Fi controllers, an HP IMC management server, a captive portal server with an SMS gateway, and authentication servers (RADIUS). Wi-Fi controllers provide centralized access point management, radio resource management and user session management. Unauthorized user device traffic passes through the controller to an isolated VLAN. Authorized user traffic is switched to local VLANs on sites with Internet access.
To provide access to the Internet for all users, the carrier solution Cisco Carrier Grade NAT is used, implemented on the basis of high-performance CGSE + modules installed in the Cisco CRS-3 ASBR. The stated performance of the CGSE + module is up to 80 Gbit / s half-duplex and 80 million NAT translations.
Last mile on objects - GPON. 3 objects are connected to each object in the tagged interface on the ONT.
Consists of access points, switches and a multifunction device named UTM Fortigate. L2 is a collection of switches interconnected into a ring. Fortigate is also part of the ring.
Contains 3 VLANs. VLAN MGMT, VLAN WIFI-HP-CONTROL, VLAN INTERNET to which authorized devices are connected.
UTM Fortigate contains a dhcp-relay to Wi-Fi core and CG NAT. It can potentially be used as DPI, webfilter, mail inspection, ssl inspection, device recognition, etc. FSTEC is approved with a low encryption license.
- The core of the wireless network
- Transport network between core and objects
- LAN at the facility
Wireless core
The core is geographically distributed. Each site consists of Wi-Fi controllers, an HP IMC management server, a captive portal server with an SMS gateway, and authentication servers (RADIUS). Wi-Fi controllers provide centralized access point management, radio resource management and user session management. Unauthorized user device traffic passes through the controller to an isolated VLAN. Authorized user traffic is switched to local VLANs on sites with Internet access.
To provide access to the Internet for all users, the carrier solution Cisco Carrier Grade NAT is used, implemented on the basis of high-performance CGSE + modules installed in the Cisco CRS-3 ASBR. The stated performance of the CGSE + module is up to 80 Gbit / s half-duplex and 80 million NAT translations.
Transportation network
Last mile on objects - GPON. 3 objects are connected to each object in the tagged interface on the ONT.
- VLAN WIFI-HP-CONTROL connects to the appropriate VRF and serves two purposes: control devices (switches and gateways) from the core of the wireless network. Installing CAPWAP tunnels from access points to controllers in which point control traffic and unauthorized device traffic pass.
- VLAN WIFI-HP-INET-DPI connects to the appropriate VRF and serves to pass Internet traffic with the appropriate rules (QoS, and so on).
- The MGMT VLAN connects to the appropriate VRF and serves to control switches and gateways from the operator’s network.
LAN at the facility
Consists of access points, switches and a multifunction device named UTM Fortigate. L2 is a collection of switches interconnected into a ring. Fortigate is also part of the ring.
Contains 3 VLANs. VLAN MGMT, VLAN WIFI-HP-CONTROL, VLAN INTERNET to which authorized devices are connected.
UTM Fortigate contains a dhcp-relay to Wi-Fi core and CG NAT. It can potentially be used as DPI, webfilter, mail inspection, ssl inspection, device recognition, etc. FSTEC is approved with a low encryption license.
To ensure the best coverage, specialists carried out a comprehensive radio survey, which resulted in the selection of optimal access points with both built-in and remote antennas. All access points are connected using PoE technology, and the power supply of the aggregation and channel-forming equipment is guaranteed by uninterruptible power supplies. This scheme ensures the proper operation of the network during short-term outages or drops in the power supply network.
In those schools where access is already provided, there are information signs with contact information, so if you live in a dormitory at a university with city wireless access, and something suddenly does not work, feel free to call the specified phones: the operator will accept the application, it is processed Must be within 4 hours.
Device Authorization Scheme:

If suddenly you are a Wi-FI user in a dormitory of some Moscow university or you just have any questions (or even better - suggestions) on the operation of this service, then we will be happy to see them in the comments.
And yet a couple of words about video surveillance :) The work is actively continued with your help, we want to say again thanks for the feedback that you send as part of testing our system on a joint special project .
We want to note one important change. When testing, we had a limited number of accounts, while the number of people willing to take part in the test exceeded all our expectations. Therefore, we made a decision to do the following: if you have an account on the Moscow portal of State services , you can leave a request for testing on the page of the special project using the login of the portal. We will try to process your application as quickly as possible and provide access for tests.
And the last. The main goal of the special project is not just to let the professional community play around with the cameras, but to help you make our service better (so that you can play around with the cameras more conveniently in the future). Therefore, after you make your opinion about the service, we ask you to share with us your impressions and ideas on how to improve it. Any feedback about the service is useful to us: from the interface texts and layout, to bugs at work, or even vulnerability information. During the special project, many useful wishes were sent (some of which have already been taken into account), but here, as in a joke, I want pills for greed, but more, more!
We really appreciate your opinion.
Thanks for attention!
Read also in our blog on Habré:
» 130 thousand security cameras - how to make them work?
» Habraeffect for 130,000 Moscow cameras
» Information technology feeds more than 750 thousand people in Moscow
» Blog of the Department of Information Technology of the city of Moscow on" Habrahabr "
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/253567/
All Articles