First look at VMware 6
I offer the readers of Habrakhabr a translation of the article “First look: VMware vSphere 6 keeps its edge” .
More recently, VMware has long held a leading leadership in server virtualization, offering kernel features that were simply incomparable with other products. In recent years, virtualization competition has been fierce, competing parties have been close to vmware functionality, and the company didn’t have many opportunities to distinguish themselves from others.
Competition could go on and on, and VMware could not be included in the leading lines as it did. With improvements in some key features, namely, the combination of backup and recovery functions that were previously only available separately, vSphere 6 is a worthy addition to the vSphere line. This suggests that most newer versions of version 6, such as remote use of vMotion, will strongly attract the customer, which in turn will lead to an increase in vSphere sales.
Big changes in vSphere 6 revolve around expanding resource limits, increasing vMotion capabilities, a more complete version of the linux-based vCenter Server Appliance module, offloading memory, and innovations to the web client. In addition, VMware has built-in specific technologies in the vSphere 6, such as the vCenter Director content library, which stores ISO images, templates, scripts, OVF files, and other elements and automatically distributes them through multiple vCenter servers. On top of that, advanced data protection capabilities were incorporated through backup and recovery.
')
VMware vSphere 6 offers improvements in the pre-installed failsafe feature (Fault Tolerance). This technology allows one virtual machine to exist on several physical servers at the same time. If one of the active system images is stopped, the second image can be launched immediately. Without using this technology, the virtual machine can be automatically restarted on another host, but in this case it takes time to determine the failure in the system and load the new machine. With Fault Tolerance, this step can be skipped.
In previous versions of vSphere, Fault Tolerance supported only one vCPU for one virtual machine and four fault-tolerant virtual machines per host. In vSphere 6, these limits are extended to four vCPUs per virtual machine and 8 vCPUs or four virtual machines per host.

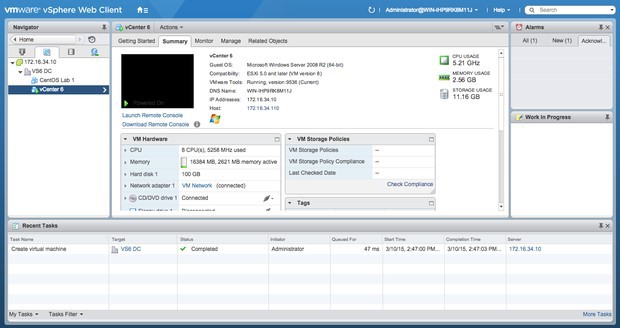
A screenshot of the new vSphere web client looks more like a Windows window. It is worth noting that the history of the frequent tasks is at the bottom of this window.
Improving vMotion will be the most appropriate improvement for those who work with a large number of data centers geographically separated. The previous vSphere 6 migration of virtual machines over long distances was complicated by some problems and required a large bandwidth as well as a small delay for successful migration. The new version of vSphere 6 introduced lower requirements for network connections, vMotions can be used for connections with a delay of 100 ms or less, and also require a channel of 250 megabits per single vMotion.
In addition, virtual machines can be transferred between vCenter servers, and with the right infrastructure, vMotions can be transferred without the use of steamed vaults. However, there are some limitations with the expansion of capabilities, mainly in the form of a correct network diagram on each side in order to ensure proper communication between virtual machines for each network.
The ESXi 6.0 hypervisor in vSphere 6 can support up to 64 physical hosts per cluster, increasing this number from 32. Also, each image can support up to 480 CPUs, 12 TB RAM and 1000 virtual machines. Each virtual machine can work with 128 vCPU and use 4 TB RAM with the ability to hot add vNUMA memory.
From the management side, the vCenter Server Appliance is now fully functional at its copy level on Windows. Previously, you had to start a Linux-based vCenter Server Appliance and manage ESXi hosts, but some of the more advanced features (especially the update manager) from the Windows-based vCenter Server were not available. As for vSphere 6, an application can perform all the possible tasks that a Windows-based application performs.
Those who run vCenter Server on Windows may note that the installation procedure is greatly simplified, but you still need to perform some actions before completing the installation. All the installation steps that vCenter Server performs are now formed in one installation program, including the new controller services platform, which includes SSO, license and certificate management. The vCenter Server can be deployed with all components on one system, or it can be distributed across multiple systems with a platform controller and installed separate.
Both the vCenter Server for Winows and the vCenter Server Appliance now use the local PostgreSQL database by default, although the addition of the MicrosoftSQL database and Oracle are also supported. Switching to PostgreSQL will be very important for those who work with local databases on earlier versions of vSphere, because the restriction from previous Microsoft databases is no longer present; thus, local databases can support up to 1000 hosts and 10 thousand virtual machines.

vSphere web-client, right-click opens the context menu, which is still slow, but still faster than before.
The first version of the vSphere web client was slow, incomplete, and not as transparent as the Windows client, and most users refused to work with it. In vSphere 5.5, we see improvements in the web client, but so far it does not reach the Windows client. In vSphere 6, new features and accelerated work of the web interface makes the web client more interesting in that it provides the use of more supported browsers and operating systems. Client-integrated tools that allow you to work with important utilities, such as console VM access, are now available for most platforms, including Mac OS X.
Users who will work with the web interface will note that it is very similar to the Windows client, including the panel with recent tasks at the bottom of the screen, which shows what recent activities have been done on the infrastructure. Further, the context menu is available through a right-click, it is now compiled faster and all navigation through the web client works better than in previous versions of the web client.
The success of the web client is very important for VMware. Companies are very concerned that the management of a separate client management will be discontinued soon for some software implementations and is currently frustrated that using a single client will limit the functionality of vSphere for version 5.0. Features and features from vSphere 5.5 are no longer available for the Windows client.

Creating a new virtual machine in vSphere 6 using the web client
VMware introduces a new vSphere 6 storage integration system called Virtual Volumes. This is the most dense integration with SAN and NAS devices for managing storage operations at the virtual disk level. Virtual volumes are designed to eliminate the need to shut down a large number of LUNs or volumes with virtualized hosts, as well as to offload operations related to storage management for compatible arrays, divided at the virtual disk level.
Intuition includes vSphere policy-oriented storage management, which uses the VMware API to communicate with the storage array, as well as to connect to virtual machines and storage through the vSphere user interface. Thus, policies can be created and applied to virtual machines via vCenter, while the functions will be initially supported by arrays.
VMware now includes vSphere data protection with vSphere Essential Plus or higher versions of vSphere 6. It is a backup and restore tool, previously known as vSphere Data Protection Advanced and was a separate feature. This tool can be used to support software-based virtual machine backup and recovery, including support for Microsoft SQL Server, Microsoft Exchange to the mail level, as well as other popular databases and applications.
View of the new vSphere web client
Starting with vSphere 6, VMware offers a set of initial features that are now connected more as separate products. A number of already installed features have appeared and the installation process has been streamlined. The web client may still be the subject of discontent for those who previously used an individual client from the very beginning, but the web client has become much better than its previous versions.
Improvements in vMotion and other cross-directional capabilities are limited by the need to use large bandwidth for a large number of connected data centers to maintain core capabilities. But VMware reduces bandwidth and latency requirements, meaning the viability of the system features provided.
There is no doubt that VMware continues to hold a leading position in server virtualization, but with the fact that the future is setting the best vendors, the convergence continues and the competing solutions continue to become more complete. All this leads to the fact that in the near future we can see the interbreeding of functional and simplified licensing. And vSphere 6 supports itself among the cream of this society.
More recently, VMware has long held a leading leadership in server virtualization, offering kernel features that were simply incomparable with other products. In recent years, virtualization competition has been fierce, competing parties have been close to vmware functionality, and the company didn’t have many opportunities to distinguish themselves from others.
Competition could go on and on, and VMware could not be included in the leading lines as it did. With improvements in some key features, namely, the combination of backup and recovery functions that were previously only available separately, vSphere 6 is a worthy addition to the vSphere line. This suggests that most newer versions of version 6, such as remote use of vMotion, will strongly attract the customer, which in turn will lead to an increase in vSphere sales.
Big changes in vSphere 6
Big changes in vSphere 6 revolve around expanding resource limits, increasing vMotion capabilities, a more complete version of the linux-based vCenter Server Appliance module, offloading memory, and innovations to the web client. In addition, VMware has built-in specific technologies in the vSphere 6, such as the vCenter Director content library, which stores ISO images, templates, scripts, OVF files, and other elements and automatically distributes them through multiple vCenter servers. On top of that, advanced data protection capabilities were incorporated through backup and recovery.
')
VMware vSphere 6 offers improvements in the pre-installed failsafe feature (Fault Tolerance). This technology allows one virtual machine to exist on several physical servers at the same time. If one of the active system images is stopped, the second image can be launched immediately. Without using this technology, the virtual machine can be automatically restarted on another host, but in this case it takes time to determine the failure in the system and load the new machine. With Fault Tolerance, this step can be skipped.
In previous versions of vSphere, Fault Tolerance supported only one vCPU for one virtual machine and four fault-tolerant virtual machines per host. In vSphere 6, these limits are extended to four vCPUs per virtual machine and 8 vCPUs or four virtual machines per host.

A screenshot of the new vSphere web client looks more like a Windows window. It is worth noting that the history of the frequent tasks is at the bottom of this window.
VMotion remote control
Improving vMotion will be the most appropriate improvement for those who work with a large number of data centers geographically separated. The previous vSphere 6 migration of virtual machines over long distances was complicated by some problems and required a large bandwidth as well as a small delay for successful migration. The new version of vSphere 6 introduced lower requirements for network connections, vMotions can be used for connections with a delay of 100 ms or less, and also require a channel of 250 megabits per single vMotion.
In addition, virtual machines can be transferred between vCenter servers, and with the right infrastructure, vMotions can be transferred without the use of steamed vaults. However, there are some limitations with the expansion of capabilities, mainly in the form of a correct network diagram on each side in order to ensure proper communication between virtual machines for each network.
The ESXi 6.0 hypervisor in vSphere 6 can support up to 64 physical hosts per cluster, increasing this number from 32. Also, each image can support up to 480 CPUs, 12 TB RAM and 1000 virtual machines. Each virtual machine can work with 128 vCPU and use 4 TB RAM with the ability to hot add vNUMA memory.
Enhancements in the vSphere Environments Management Environment (VMware vCenter Server)
From the management side, the vCenter Server Appliance is now fully functional at its copy level on Windows. Previously, you had to start a Linux-based vCenter Server Appliance and manage ESXi hosts, but some of the more advanced features (especially the update manager) from the Windows-based vCenter Server were not available. As for vSphere 6, an application can perform all the possible tasks that a Windows-based application performs.
Those who run vCenter Server on Windows may note that the installation procedure is greatly simplified, but you still need to perform some actions before completing the installation. All the installation steps that vCenter Server performs are now formed in one installation program, including the new controller services platform, which includes SSO, license and certificate management. The vCenter Server can be deployed with all components on one system, or it can be distributed across multiple systems with a platform controller and installed separate.
Both the vCenter Server for Winows and the vCenter Server Appliance now use the local PostgreSQL database by default, although the addition of the MicrosoftSQL database and Oracle are also supported. Switching to PostgreSQL will be very important for those who work with local databases on earlier versions of vSphere, because the restriction from previous Microsoft databases is no longer present; thus, local databases can support up to 1000 hosts and 10 thousand virtual machines.

vSphere web-client, right-click opens the context menu, which is still slow, but still faster than before.
Frontend improvements
The first version of the vSphere web client was slow, incomplete, and not as transparent as the Windows client, and most users refused to work with it. In vSphere 5.5, we see improvements in the web client, but so far it does not reach the Windows client. In vSphere 6, new features and accelerated work of the web interface makes the web client more interesting in that it provides the use of more supported browsers and operating systems. Client-integrated tools that allow you to work with important utilities, such as console VM access, are now available for most platforms, including Mac OS X.
Users who will work with the web interface will note that it is very similar to the Windows client, including the panel with recent tasks at the bottom of the screen, which shows what recent activities have been done on the infrastructure. Further, the context menu is available through a right-click, it is now compiled faster and all navigation through the web client works better than in previous versions of the web client.
The success of the web client is very important for VMware. Companies are very concerned that the management of a separate client management will be discontinued soon for some software implementations and is currently frustrated that using a single client will limit the functionality of vSphere for version 5.0. Features and features from vSphere 5.5 are no longer available for the Windows client.

Creating a new virtual machine in vSphere 6 using the web client
Virtual Volumes in VMware
VMware introduces a new vSphere 6 storage integration system called Virtual Volumes. This is the most dense integration with SAN and NAS devices for managing storage operations at the virtual disk level. Virtual volumes are designed to eliminate the need to shut down a large number of LUNs or volumes with virtualized hosts, as well as to offload operations related to storage management for compatible arrays, divided at the virtual disk level.
Intuition includes vSphere policy-oriented storage management, which uses the VMware API to communicate with the storage array, as well as to connect to virtual machines and storage through the vSphere user interface. Thus, policies can be created and applied to virtual machines via vCenter, while the functions will be initially supported by arrays.
VMware now includes vSphere data protection with vSphere Essential Plus or higher versions of vSphere 6. It is a backup and restore tool, previously known as vSphere Data Protection Advanced and was a separate feature. This tool can be used to support software-based virtual machine backup and recovery, including support for Microsoft SQL Server, Microsoft Exchange to the mail level, as well as other popular databases and applications.

View of the new vSphere web client
Upgrade with vSphere 5.5
Starting with vSphere 6, VMware offers a set of initial features that are now connected more as separate products. A number of already installed features have appeared and the installation process has been streamlined. The web client may still be the subject of discontent for those who previously used an individual client from the very beginning, but the web client has become much better than its previous versions.
Improvements in vMotion and other cross-directional capabilities are limited by the need to use large bandwidth for a large number of connected data centers to maintain core capabilities. But VMware reduces bandwidth and latency requirements, meaning the viability of the system features provided.
There is no doubt that VMware continues to hold a leading position in server virtualization, but with the fact that the future is setting the best vendors, the convergence continues and the competing solutions continue to become more complete. All this leads to the fact that in the near future we can see the interbreeding of functional and simplified licensing. And vSphere 6 supports itself among the cream of this society.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/253307/
All Articles