Implementing MSA in a virtualized enterprise environment
Virtualization has become the number one topic in modern IT. According to VMware, the level of server virtualization in Russia increased in 2014 to 30%, having doubled in three years. As a result, server utilization efficiency increases: according to various estimates, the average load factor is now from 50% to 80%, which means a reduction in the need for physical servers. Not surprisingly, virtualization technology is increasingly being used not only by large companies and organizations, but also by small businesses. First of all, we are talking about server virtualization.

Virtualization gives significant advantages not only in large data centers with hundreds of virtual machines, but also in the case when several VMs are running on one server. Among them - the benefits of server consolidation, ease of deployment, easy and convenient allocation of resources and standardization of equipment, getting rid of the "zoo" systems. Ultimately, all of this translates into lower IT costs and lower total cost of ownership ( TCO ).
Meanwhile, when introducing virtualization, a critical issue is the choice of storage systems. Virtualization increases the load on the storage system; therefore, before its implementation, planning and proper choice of a disk array are necessary. Storage should not become a bottleneck in a virtual environment with high I / O performance and latency requirements. For the successful deployment of server virtualization, this is even more important than the power of the processors and the memory capacity of the servers.
')
Small companies that are committed to server virtualization and data storage consolidation need reliable, but at the same time inexpensive and easy-to-maintain storage systems. HP offers these customers the MSA entry-level disk arrays. They are designed for businesses with a limited budget who want to get the most out of their IT investments.
MSA is one of the most successful HP disk array series. In the world, more than 400,000 MSA arrays have already been sold, which are considered among the best entry-level storage systems on Fiber Channel. These storage systems provide high performance, reliability and ease of management, are well suited for companies representing small and medium-sized businesses (SMB). The HP MSA 1040 and MSA 2040 arrays can be managed from within Windows Server 2012, which is an added plus, since the Windows platform is often used in small organizations.
The MSA system supports a large number of virtual environments, allows you to consolidate diverse IT resources and, in combination with virtualization, increase the efficiency of their use. According to HP statistics, in 60% of installations, MSA arrays are deployed in a virtual environment, which speaks for itself. Four times higher MSA performance compared to the previous generation of these SAN disk arrays means that the system can support more VMs, the response time in applications decreases. The performance of the MSA 1040 is 29,000 IOPS, and the MSA 2040 is 82,000 IOPS with random reading, and the throughput is 3.1 and 6.2 GB / s, respectively.
Due to its performance and functionality, the HP MSA 1040/2040 arrays provide a solution that deserves attention when planning deployment of virtual environments, especially in combination with HP ProLiant servers . Model 1040 is a suitable option for the first virtualization project, and the array 2040 can be used to deploy high-performance virtual environments in companies that have already gained some experience with virtual servers. HP MSA offers features that simplify the management of a virtual environment, its deployment and support, as well as implementing the necessary services for working with data.
Small and medium-sized companies, like large corporations, are forced to constantly look for ways to reduce costs. Over the past decade, data storage technologies have significantly increased the efficiency and flexibility of storage. However, these improvements, until recently, were implemented only in disk arrays of the middle and senior classes, which made them inaccessible to small and medium-sized businesses.
At the end of 2014, HP introduced software updates for MSA arrays with advanced virtualization features - new software reduces the cost of data storage and makes management much easier. Updates include dynamic data optimization features, improved performance through the use of SSD flash drives and intelligent storage automation using the capabilities of the fourth generation HP MSA hardware architecture.
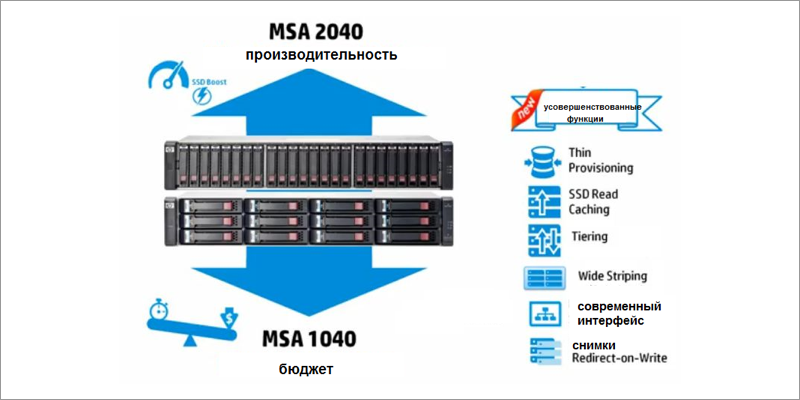
Advanced MSA virtualization features: Thin Provisioning (dynamic allocation of capacity), SSD Read Cache (read cache on SSDs), Automated Tiering (automatically move data through storage levels), Redirect on Write Snapshot (redirected write images) and Wide Striping (virtual pool with distribution on HDD).
Thin provisioning
This feature provides flexible use of capacity and its expansion as needed. Thin Provisioning - the creation of logical volumes that initially use a little space and "grow" as data is written to them. Dynamic allocation of disk space allows you to quickly allocate storage resources to virtual servers and eliminate the reservation of more capacity than is necessary. Thin Provisioning is supported by popular server virtualization environments, and, according to VMware information, its impact on performance is negligible.
Thin Provisioning means reducing the cost of storage resources that would otherwise have to be allocated in excess. Administrators can allocate large virtual volumes to applications — even with more physical capacity. In reality, a VM uses as much disk space as is currently needed. The system itself warns the administrator that the purchase of additional capacity will be required soon. Another useful quality is the “thin rebuild” of RAID (Thin Rebuild), when in the process of RAID reorganization after a disk crashes or when RAID levels change, only already allocated blocks participate in the consoles. This significantly reduces the time of this procedure.
It is also important to note that, in contrast to the HP StoreVirtual line, MSA supports not only dynamic allocation, but also freeing up of capacity (T10-Unmap): the system releases data blocks after receiving a command to delete files from the file system. This is important for effective use of Thin Provisioning.
SSD caching
The SSD Read Cache feature, available in MSA 2040 (MSA 1040 model does not support SSD), means the ability to cache data on solid-state drives when reading. MSA supports the installation of up to two SSD drives up to 1.6TB as a read cache. SSD Read Cache increases the performance of storage at random reading. Under laboratory conditions, with read operations, the response time of the disk system is improved up to 80%, which is reflected in a noticeable acceleration of the virtual environment.
Automatic storage tiering
This feature allows you to optimize the use of expensive SSD drives - they store “hot” data that is frequently accessed, that is, the data with the most read / write operations. Automated Tiering moves hot blocks (4 MB pages) to fast SSD drives, which speeds up operations with them. The “archival tiring” works similarly: rarely used (“cold”) data is transferred from SAS disks to slower MDL SAS disks. Tiring helps to find the best balance between the cost of the system and its performance. According to HP, automatic tearing saves 70-80% in dollars per gigabyte. The reading and reading cache are complementary technologies in the data management approach: the reading cache works almost instantly and speeds up the work during the so-called “activity surges”, while the tearing moves the blocks based on the generated time reporting of the system.
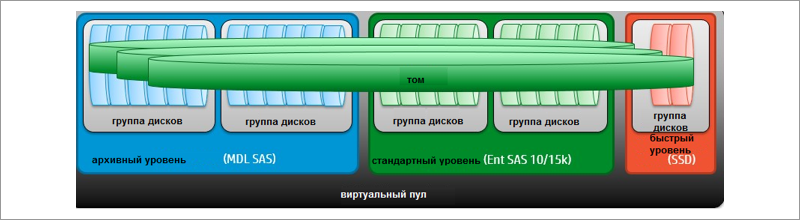
As storage levels in tearing, SAS disks of different classes (in MSA 1040) or SAS and SSD (in MSA 2040) can be used.
Wide striping
This feature actually means storage virtualization within the MSA. It allows you to organize existing physical disks into a storage pool and use their capacity to create virtual disks (V-disk). In this case, the V-disk can be distributed throughout the pool. The former limitation of 16 physical disks per virtual disk is removed, the volume capacity is increased. Distributing a virtual disk to physical drives improves performance, i.e. virtual volume can use disk resources of all disks used in the pool.
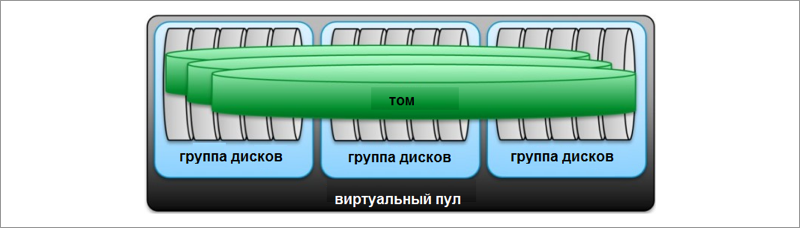
Wide Striping improves the efficiency of disk array usage and reduces response time by distributing the V-disk volume data among all disks.
Improved snapshot mechanism
More efficient snapshot functions simplify management and improve performance when creating copies, making disaster recovery possible in more complex cases. Snapshots in the new release now work on the principle of Redirect-on-Write, which improves the performance of operations as compared to traditional Copy-on-Write (less input-output operations are required at the back-end level). Simplified setting snapshots.
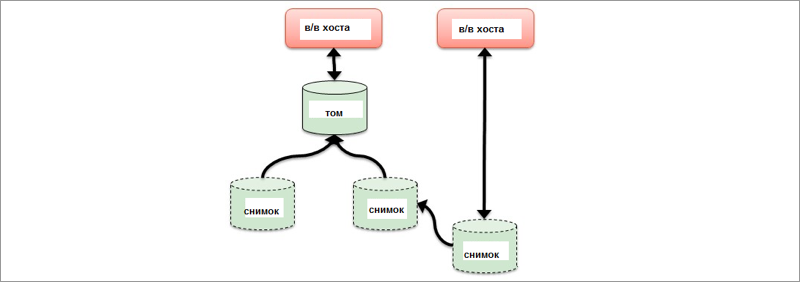
The new version of the MSA firmware has the ability to create "snapshots", which is used by software developers to debug versions.
Improved web interface and advanced management
The management interface has been updated, now HTML5 is used as a platform. The new interface simplifies and speeds up administration, especially in a server virtualization environment, where management may be complicated by a rapid increase in the number of VMs, reduces the likelihood of errors. Sorting, searching, filtering and grouping features make it easy to manage a large number of hosts and volumes. You can also manage MSA arrays directly from popular virtual environment management systems, for example, in VMware vCenter — you can create logical volumes (LUNs), assign them to servers, etc.
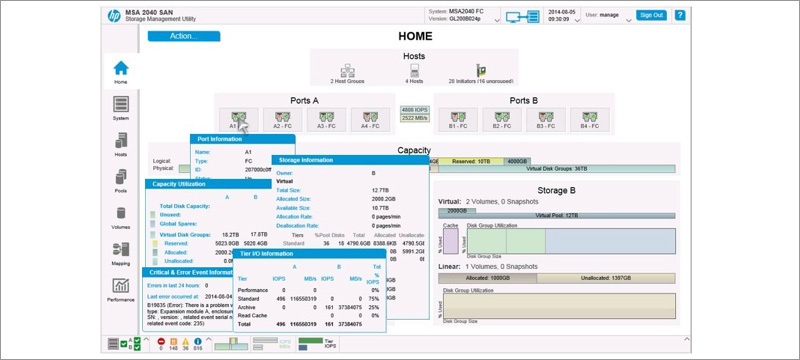
The new interface of the utility SMU (Storage Management Utility).
What does Microsoft Exchange virtualization do? Such an environment is easy to scale, allocating resources (for example, memory and processor power) to virtual machines. More efficient use of equipment reduces operational costs, including power, cooling, storage infrastructure, and storage management. Increases system reliability: virtualization allows administrators to create Database Availability Group (DAG) groups and use Exchange database replication tools, leveraging the minimum of hardware resources. You can configure the fault tolerance level of the entire Exchange architecture and protect yourself from system component failure. In addition, you can update the software without disconnecting users from the mail server.
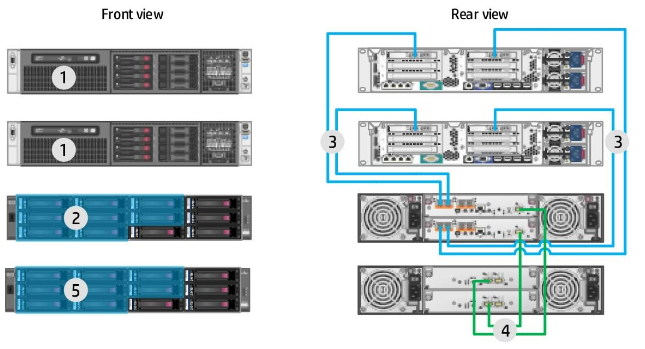
An example of a reference architecture for deploying a virtual Exchange environment (front and back view):
1. Two HP ProLiant DL380p Gen8 servers.
2. Array of HP MSA 2040 with 8 disks 2 TB SAS LFF, allocated for Exchange databases and logs. The remaining disks are used as backup.
3. Primary and secondary connection FC 16 Gbit / s.
4. Primary and secondary connection SAS 6 Gb / s.
5. HP MSA 2040 LFF disk shelf with 8 2 TB SAS LFF disks allocated for Exchange databases and logs.
HP MSA 2040 can be scaled with an increase in the number of users connecting disk shelves. Two system controllers operating in active / active mode, dual port drives and redundant components reduce the likelihood of storage failure to a minimum. HP MSA 2040 also allows you to select different connectivity options to meet your SAN configuration requirements. Built-in tools simplify array deployment and administration.
Exchange 2013 virtualization guidelines are available on the Microsoft website .
When virtualizing Microsoft Exchange 2013 using Microsoft Hyper-V and HP MSA 2040 arrays, you can host additional virtualized applications on the same server. For example, the HP ProLiant DL380p Gen8 server can easily handle not only the workload of Exchange, but also other virtual servers at the same time. Reducing the number of physical servers simplifies administration, reduces support costs.
Microsoft Exchange on HP ProLiant servers and HP MSA storage systems is a cost-effective, reliable and scalable messaging solution. In the Microsoft Windows Server 2012 Hyper-V virtual environment, on ProLiant DL380p Gen8 servers with HP MSA 2040 disk arrays, you can support approximately 750 Exchange 2013 mailboxes.
A suitable use case is also the use of the MSA 2040 array for the SQL server 2012 environment, where the MSA 2040 array showed itself well in working with sequential and random read and write loads.

MSA 2040 Reference Architecture for SQL Server 2012
HP MSA 1040/2040 arrays are the right solution for deploying a virtual environment in SMB. These systems have enough flexibility, are easy to manage / administer, and allow you to choose the best option for cost or performance.
Read on:
» Best practices for working with MSA 1040/2040 arrays
" Up to 1.2GB / s performance on MSA array
» Best Practices for Working with MSA Array in VMware Environment
Our previous publications:
» HP MSA Disk Arrays as a Basis for Data Consolidation
» Multivendor corporate network: myths and reality
» Available HP ProLiant server models (10 and 100 series)
» Convergence based on HP Networking. Part 1
» HP ProLiant ML350 Gen9 - server with insane extensibility
Thank you for your attention, we are ready to answer your questions in the comments.

SMB Virtualization
Virtualization gives significant advantages not only in large data centers with hundreds of virtual machines, but also in the case when several VMs are running on one server. Among them - the benefits of server consolidation, ease of deployment, easy and convenient allocation of resources and standardization of equipment, getting rid of the "zoo" systems. Ultimately, all of this translates into lower IT costs and lower total cost of ownership ( TCO ).
Meanwhile, when introducing virtualization, a critical issue is the choice of storage systems. Virtualization increases the load on the storage system; therefore, before its implementation, planning and proper choice of a disk array are necessary. Storage should not become a bottleneck in a virtual environment with high I / O performance and latency requirements. For the successful deployment of server virtualization, this is even more important than the power of the processors and the memory capacity of the servers.
')
Small companies that are committed to server virtualization and data storage consolidation need reliable, but at the same time inexpensive and easy-to-maintain storage systems. HP offers these customers the MSA entry-level disk arrays. They are designed for businesses with a limited budget who want to get the most out of their IT investments.
MSA is one of the most successful HP disk array series. In the world, more than 400,000 MSA arrays have already been sold, which are considered among the best entry-level storage systems on Fiber Channel. These storage systems provide high performance, reliability and ease of management, are well suited for companies representing small and medium-sized businesses (SMB). The HP MSA 1040 and MSA 2040 arrays can be managed from within Windows Server 2012, which is an added plus, since the Windows platform is often used in small organizations.
The MSA system supports a large number of virtual environments, allows you to consolidate diverse IT resources and, in combination with virtualization, increase the efficiency of their use. According to HP statistics, in 60% of installations, MSA arrays are deployed in a virtual environment, which speaks for itself. Four times higher MSA performance compared to the previous generation of these SAN disk arrays means that the system can support more VMs, the response time in applications decreases. The performance of the MSA 1040 is 29,000 IOPS, and the MSA 2040 is 82,000 IOPS with random reading, and the throughput is 3.1 and 6.2 GB / s, respectively.
Due to its performance and functionality, the HP MSA 1040/2040 arrays provide a solution that deserves attention when planning deployment of virtual environments, especially in combination with HP ProLiant servers . Model 1040 is a suitable option for the first virtualization project, and the array 2040 can be used to deploy high-performance virtual environments in companies that have already gained some experience with virtual servers. HP MSA offers features that simplify the management of a virtual environment, its deployment and support, as well as implementing the necessary services for working with data.
HP MSA Advanced Features
Small and medium-sized companies, like large corporations, are forced to constantly look for ways to reduce costs. Over the past decade, data storage technologies have significantly increased the efficiency and flexibility of storage. However, these improvements, until recently, were implemented only in disk arrays of the middle and senior classes, which made them inaccessible to small and medium-sized businesses.
At the end of 2014, HP introduced software updates for MSA arrays with advanced virtualization features - new software reduces the cost of data storage and makes management much easier. Updates include dynamic data optimization features, improved performance through the use of SSD flash drives and intelligent storage automation using the capabilities of the fourth generation HP MSA hardware architecture.

Advanced MSA virtualization features: Thin Provisioning (dynamic allocation of capacity), SSD Read Cache (read cache on SSDs), Automated Tiering (automatically move data through storage levels), Redirect on Write Snapshot (redirected write images) and Wide Striping (virtual pool with distribution on HDD).
Thin provisioning
This feature provides flexible use of capacity and its expansion as needed. Thin Provisioning - the creation of logical volumes that initially use a little space and "grow" as data is written to them. Dynamic allocation of disk space allows you to quickly allocate storage resources to virtual servers and eliminate the reservation of more capacity than is necessary. Thin Provisioning is supported by popular server virtualization environments, and, according to VMware information, its impact on performance is negligible.
Thin Provisioning means reducing the cost of storage resources that would otherwise have to be allocated in excess. Administrators can allocate large virtual volumes to applications — even with more physical capacity. In reality, a VM uses as much disk space as is currently needed. The system itself warns the administrator that the purchase of additional capacity will be required soon. Another useful quality is the “thin rebuild” of RAID (Thin Rebuild), when in the process of RAID reorganization after a disk crashes or when RAID levels change, only already allocated blocks participate in the consoles. This significantly reduces the time of this procedure.
It is also important to note that, in contrast to the HP StoreVirtual line, MSA supports not only dynamic allocation, but also freeing up of capacity (T10-Unmap): the system releases data blocks after receiving a command to delete files from the file system. This is important for effective use of Thin Provisioning.
SSD caching
The SSD Read Cache feature, available in MSA 2040 (MSA 1040 model does not support SSD), means the ability to cache data on solid-state drives when reading. MSA supports the installation of up to two SSD drives up to 1.6TB as a read cache. SSD Read Cache increases the performance of storage at random reading. Under laboratory conditions, with read operations, the response time of the disk system is improved up to 80%, which is reflected in a noticeable acceleration of the virtual environment.
Automatic storage tiering
This feature allows you to optimize the use of expensive SSD drives - they store “hot” data that is frequently accessed, that is, the data with the most read / write operations. Automated Tiering moves hot blocks (4 MB pages) to fast SSD drives, which speeds up operations with them. The “archival tiring” works similarly: rarely used (“cold”) data is transferred from SAS disks to slower MDL SAS disks. Tiring helps to find the best balance between the cost of the system and its performance. According to HP, automatic tearing saves 70-80% in dollars per gigabyte. The reading and reading cache are complementary technologies in the data management approach: the reading cache works almost instantly and speeds up the work during the so-called “activity surges”, while the tearing moves the blocks based on the generated time reporting of the system.

As storage levels in tearing, SAS disks of different classes (in MSA 1040) or SAS and SSD (in MSA 2040) can be used.
Wide striping
This feature actually means storage virtualization within the MSA. It allows you to organize existing physical disks into a storage pool and use their capacity to create virtual disks (V-disk). In this case, the V-disk can be distributed throughout the pool. The former limitation of 16 physical disks per virtual disk is removed, the volume capacity is increased. Distributing a virtual disk to physical drives improves performance, i.e. virtual volume can use disk resources of all disks used in the pool.

Wide Striping improves the efficiency of disk array usage and reduces response time by distributing the V-disk volume data among all disks.
Improved snapshot mechanism
More efficient snapshot functions simplify management and improve performance when creating copies, making disaster recovery possible in more complex cases. Snapshots in the new release now work on the principle of Redirect-on-Write, which improves the performance of operations as compared to traditional Copy-on-Write (less input-output operations are required at the back-end level). Simplified setting snapshots.

The new version of the MSA firmware has the ability to create "snapshots", which is used by software developers to debug versions.
Improved web interface and advanced management
The management interface has been updated, now HTML5 is used as a platform. The new interface simplifies and speeds up administration, especially in a server virtualization environment, where management may be complicated by a rapid increase in the number of VMs, reduces the likelihood of errors. Sorting, searching, filtering and grouping features make it easy to manage a large number of hosts and volumes. You can also manage MSA arrays directly from popular virtual environment management systems, for example, in VMware vCenter — you can create logical volumes (LUNs), assign them to servers, etc.

The new interface of the utility SMU (Storage Management Utility).
Virtualization on the example of Microsoft Exchange
What does Microsoft Exchange virtualization do? Such an environment is easy to scale, allocating resources (for example, memory and processor power) to virtual machines. More efficient use of equipment reduces operational costs, including power, cooling, storage infrastructure, and storage management. Increases system reliability: virtualization allows administrators to create Database Availability Group (DAG) groups and use Exchange database replication tools, leveraging the minimum of hardware resources. You can configure the fault tolerance level of the entire Exchange architecture and protect yourself from system component failure. In addition, you can update the software without disconnecting users from the mail server.

An example of a reference architecture for deploying a virtual Exchange environment (front and back view):
1. Two HP ProLiant DL380p Gen8 servers.
2. Array of HP MSA 2040 with 8 disks 2 TB SAS LFF, allocated for Exchange databases and logs. The remaining disks are used as backup.
3. Primary and secondary connection FC 16 Gbit / s.
4. Primary and secondary connection SAS 6 Gb / s.
5. HP MSA 2040 LFF disk shelf with 8 2 TB SAS LFF disks allocated for Exchange databases and logs.
HP MSA 2040 can be scaled with an increase in the number of users connecting disk shelves. Two system controllers operating in active / active mode, dual port drives and redundant components reduce the likelihood of storage failure to a minimum. HP MSA 2040 also allows you to select different connectivity options to meet your SAN configuration requirements. Built-in tools simplify array deployment and administration.
Exchange 2013 virtualization guidelines are available on the Microsoft website .
When virtualizing Microsoft Exchange 2013 using Microsoft Hyper-V and HP MSA 2040 arrays, you can host additional virtualized applications on the same server. For example, the HP ProLiant DL380p Gen8 server can easily handle not only the workload of Exchange, but also other virtual servers at the same time. Reducing the number of physical servers simplifies administration, reduces support costs.
Microsoft Exchange on HP ProLiant servers and HP MSA storage systems is a cost-effective, reliable and scalable messaging solution. In the Microsoft Windows Server 2012 Hyper-V virtual environment, on ProLiant DL380p Gen8 servers with HP MSA 2040 disk arrays, you can support approximately 750 Exchange 2013 mailboxes.
A suitable use case is also the use of the MSA 2040 array for the SQL server 2012 environment, where the MSA 2040 array showed itself well in working with sequential and random read and write loads.

MSA 2040 Reference Architecture for SQL Server 2012
HP MSA 1040/2040 arrays are the right solution for deploying a virtual environment in SMB. These systems have enough flexibility, are easy to manage / administer, and allow you to choose the best option for cost or performance.
Read on:
» Best practices for working with MSA 1040/2040 arrays
" Up to 1.2GB / s performance on MSA array
» Best Practices for Working with MSA Array in VMware Environment
Our previous publications:
» HP MSA Disk Arrays as a Basis for Data Consolidation
» Multivendor corporate network: myths and reality
» Available HP ProLiant server models (10 and 100 series)
» Convergence based on HP Networking. Part 1
» HP ProLiant ML350 Gen9 - server with insane extensibility
Thank you for your attention, we are ready to answer your questions in the comments.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/252857/
All Articles