HSTS-based super cookies will track you even in private mode
For several years, all browsers have been offering settings for private browsing. In private mode, they may not save cookies, page history and temporary files. People who value privacy rely on this opportunity. But recently another method has been proposed to track the user even in this case, if he does not take special measures.
The irony is that this tracking system is facilitated by a mechanism called HTTP Strict Transport Security. It is needed so that sites can make sure that the user works with their servers only via the HTTPS protocol. If the server adds the corresponding flag to the headers, then according to the HSTS rules, all connections to the server should be encrypted. Thus, the user is protected from various possible attacks.
Sam Greenkhalh, a consultant for RadicalResearch, thought of how to turn this safety feature into a user tracking function. He called his concept HSTS Super Cookies. Like regular cookies, supercooks track a user and can identify him if he returns to the site in the future. One of the features of superkuk - they work even in private mode. Another - these cookies can be read from other domain names, and not just from the fact that they set.
')
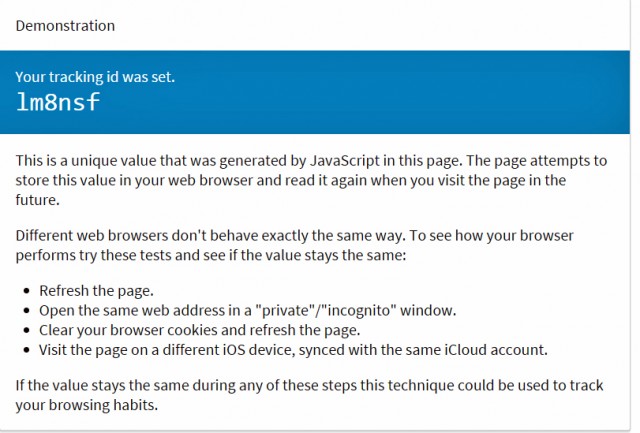
For a single site, HSTS can contain one binary value — on or off. To circumvent this limitation, Greenhalch puts together 32 sites, adds all their binary values and stores the result as one number. As a result, it is possible to create more than two billion variants of browsers. For simplicity, the decimal number is converted to base36, so 169ze7 represents 71009647, or lm8nsf represents 1307145327.
When you enter the hacker's site as usual, the script checks your HSTS settings for different sites and calculates the identifier. A unique identifier is set and saved, even if you later turn on private mode. Moreover, other sites will be able to read the ID, thus tracking the user when visiting different sites. Usually, people expect a reverse behavior from private mode. In addition, regular cookies can only be read from the domain that set them.
Fortunately, all but Safari users on the iPhone or iPad can remove these flags used for tracking by deleting all cookies. Usually, browsers reset the HSTS flags with this operation. In addition, if you visited a site that is trying to track you, only in private mode, then this flag will not be cocked.
HSTS Super Cookies is a good example of how new features can turn into security holes. The whole point of HSTS is that the browser always uses HTTPS when querying sites that support this protocol. Browser developers obviously wanted to provide increased security for their users, but now they will have to think about their decision again.
Note: after the publication of the article, it was reviewed by the developers of Chrome and Firefox. The former decided to change nothing in their attempts to “strike a balance between privacy and security.” The latter, starting with version 34, excluded the possibility of transferring flag settings to private mode.
The irony is that this tracking system is facilitated by a mechanism called HTTP Strict Transport Security. It is needed so that sites can make sure that the user works with their servers only via the HTTPS protocol. If the server adds the corresponding flag to the headers, then according to the HSTS rules, all connections to the server should be encrypted. Thus, the user is protected from various possible attacks.

Sam Greenkhalh, a consultant for RadicalResearch, thought of how to turn this safety feature into a user tracking function. He called his concept HSTS Super Cookies. Like regular cookies, supercooks track a user and can identify him if he returns to the site in the future. One of the features of superkuk - they work even in private mode. Another - these cookies can be read from other domain names, and not just from the fact that they set.
')
How it works
For a single site, HSTS can contain one binary value — on or off. To circumvent this limitation, Greenhalch puts together 32 sites, adds all their binary values and stores the result as one number. As a result, it is possible to create more than two billion variants of browsers. For simplicity, the decimal number is converted to base36, so 169ze7 represents 71009647, or lm8nsf represents 1307145327.
When you enter the hacker's site as usual, the script checks your HSTS settings for different sites and calculates the identifier. A unique identifier is set and saved, even if you later turn on private mode. Moreover, other sites will be able to read the ID, thus tracking the user when visiting different sites. Usually, people expect a reverse behavior from private mode. In addition, regular cookies can only be read from the domain that set them.
Fortunately, all but Safari users on the iPhone or iPad can remove these flags used for tracking by deleting all cookies. Usually, browsers reset the HSTS flags with this operation. In addition, if you visited a site that is trying to track you, only in private mode, then this flag will not be cocked.
HSTS Super Cookies is a good example of how new features can turn into security holes. The whole point of HSTS is that the browser always uses HTTPS when querying sites that support this protocol. Browser developers obviously wanted to provide increased security for their users, but now they will have to think about their decision again.
Note: after the publication of the article, it was reviewed by the developers of Chrome and Firefox. The former decided to change nothing in their attempts to “strike a balance between privacy and security.” The latter, starting with version 34, excluded the possibility of transferring flag settings to private mode.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/252433/
All Articles