Configure autoscaling in InfoboxCloud
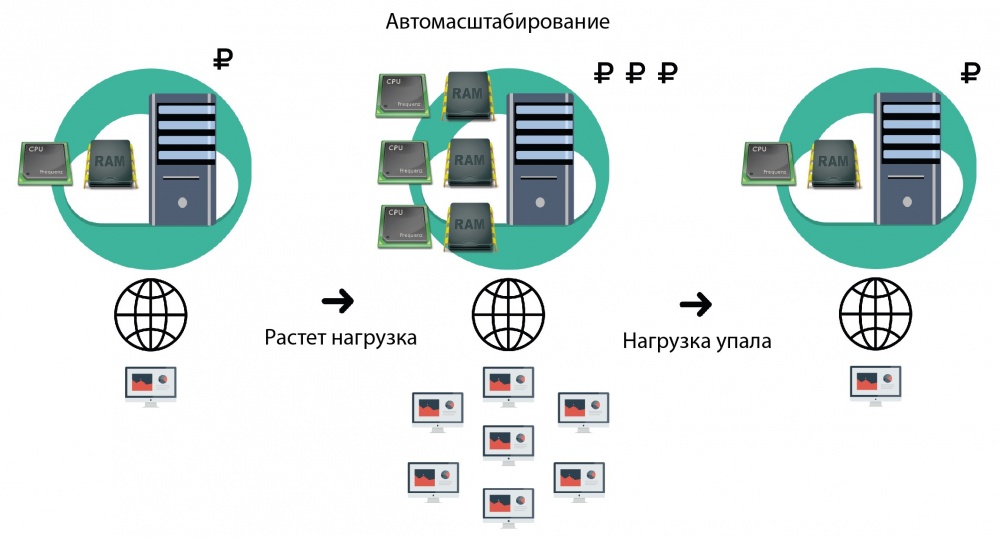
InfoboxCloud cloud infrastructure allows you to automatically scale the resources of your cloud servers in response to changing loads. Autoscaling helps maximize the use of cloud resources and save money: increase resources with increasing load and decrease while decreasing.
Uneven load on the server is a frequent occurrence. For example, at night the server may be idle, and in the morning the load may increase. Useful autoscaling during advertising campaigns, reporting companies through the Internet, to ensure the operation of online stores before the holidays and in the software development process.
When autoscaling is enabled, server resources are monitored. Changes to the available resources and the pitch of these changes depends on the rules configured by the user and the purpose of autoscaling. For some projects, it is more important to be able to quickly scale, for others, to save more money.
')
In this article, we will look at how to configure autoscaling in InfoboxCloud .
We hope that you already have an account on InfoboxCloud . If not yet, create it .
Log into the control panel . Create a cloud server.

When creating a server, you need to pay attention to the flag " I will manage the OS kernel ." In InfoboxCloud, autoscaling by CPU and memory works for containers (servers using OS-level virtualization). For virtual machines (servers using hardware virtualization), autoscaling is possible only by CPU. If you want to use memory autoscaling, do not set the flag “I will manage the OS kernel” when creating the server.

In the next step, select the required OS and complete the server creation process.
After creation, click on the server in the control panel.

You will be taken to the server management section. As you can see below, autoscaling is disabled. In order to understand the current server resource consumption, go to the "Performance" section.

Charts are updated 1 time in 5 minutes. In order to see the consumption for the required period of time, select the area on the lower graph of each resource.

The red line on the chart - set resource limits in the control panel. Blue - current resource consumption.

Both on the processor performance graph and on the memory consumption graph, the difference between the limit and the resources actually consumed is large. So idle computing resources, and users - pay extra money.
You reduce the amount of resources consumed by the server in the server management section "Summary". Autoscaling will not be involved.

This is a good way if you clearly know how much resources the server will consume.
If the load is less predictable or changes - use autoscaling.
To configure, go to the appropriate section "Autoscaling".

You can turn on auto-scaling by processor frequency and memory. You cannot scale by processor cores — guest operating systems require a reboot when the number of cores changes.
After the creation of the server, it is recommended that you first install the software that will be used, make sure that it works correctly, and determine the amount of resource consumption under different loads (autoscaling boundaries). Then you can turn on autoscaling and test its operation so that the result for industrial use is appropriate and expected.
Sliders (sliders) set the minimum and maximum value of the resource allowed for working without autoscaling (as a percentage of occupied resources). If the resource load is greater than the set value by the slider “if used more”, the resource will be added. If the resource value is less than the set value “if used less”, the resource will be reduced.
For processor autoscaling, the resource is the processor frequency, for memory, the amount of RAM.

The period for assessing the amount of resources used is indicated in the “within” fields. Auto scaling up and down is possible only after evaluating the resources used (building a performance graph) for each cloud server. The minimum period is 5 minutes.
The boundaries of the autoscale - the "increase to" and "reduce to". This is the maximum and minimum amount of the resource to which autoscaling is possible. It is recommended to set the minimum amount of a resource not less than specified in the minimum system requirements of the software used or not less than the minimum operational value for your use case.
The autoscaling step is indicated in the “Step” field. This is the value by which the amount of available resources changes when autoscaling: increases or decreases.
The autoscaling rate is the number of steps that the autoscaling must go through in order to change the amount of resources from minimum to maximum. This is the inverse of the autoscaling speed.
The pace can be calculated like this:

To apply the autoscaling rules correctly, the tempo, pitch and autoscaling boundaries must be integers! You cannot take half a step, but you can take a small step of at least 1 MHz.
Let's look at an example: let's say we want the minimum frequency of the processor to be 200 MHz, the maximum - 2000 MHz. Suppose we use autoscaling periods of 5 minutes to increase the amount of resources and to reduce them. The load increases. If the autoscaling step is set to 200 MHz:

The autoscaling rate is 9. We define the time over which the processor frequency will increase from 200 MHz to 2000 MHz with a significantly increased load.

Maximum autoscale time = 9 * 5 = 45 minutes.
Need to auto scale faster? Increase the pitch, but so that the tempo is still an integer.
For example, you can set the lower limit of autoscaling to 500 MHz, the upper limit to 2000 MHz, a step of 500 MHz, the periods will remain 5 minutes each.
Then the tempo = (2000-500) / 500 = 3.
Maximum autoscaling time = 3 * 5 = 15 minutes.
The same calculation is made for memory.
Suppose the lower limit is 1024 MB, the upper limit is 65536 MB. Periods - 5 minutes. Step - 1024 MB. Then the tempo = (65536-1024) / 1024 = 63.
The maximum autoscaling time from 1 GB of memory to 64 GB = 63 * 5 = 315 minutes.
This is evident from the calculations, autoscaling does not work instantly, which is associated with the cost of computing resources and the amount of service traffic needed to build graphs of the load of cloud servers. This means that the lower limit of autoscaling should be set with a margin sufficient to withstand the load with the expected increase in load for 5 minutes (before the autoscaling operation is performed). This will provide a predictable server performance with increasing load.
A useful feature of autoscaling is the ability to maximize resource savings. With the help of autoscaling, you can reduce the amount of resources available to the server to less than it is possible to install directly from the control panel. For example, values such as a 25 MHz processor and 48 megabytes of memory for an unvisited personal blog or a git – repository are quite a reality. This opens up the possibility for users to use the cloud cheaply, without overpaying for extra resources, as much as possible reducing the payment for the cloud server.
A feature of autoscaling InfoboxCloud is precise control of the process by the administrator. You define the process of autoscaling and the result is predictable, since all the parameters are set and the operation algorithm is clear. Autoscaling is not a panacea, but a very useful tool that allows you to use resources more efficiently and save money.
If you find an error in the article, the author will gladly correct it. Please write in the LAN or in the mail about it. Write questions in the comments or email. If you can not leave comments on Habré - write to us in the InfoboxCloud Community .
Successful work!
Uneven load on the server is a frequent occurrence. For example, at night the server may be idle, and in the morning the load may increase. Useful autoscaling during advertising campaigns, reporting companies through the Internet, to ensure the operation of online stores before the holidays and in the software development process.
When autoscaling is enabled, server resources are monitored. Changes to the available resources and the pitch of these changes depends on the rules configured by the user and the purpose of autoscaling. For some projects, it is more important to be able to quickly scale, for others, to save more money.
')

In this article, we will look at how to configure autoscaling in InfoboxCloud .
What we need to configure
We hope that you already have an account on InfoboxCloud . If not yet, create it .
Log into the control panel . Create a cloud server.

When creating a server, you need to pay attention to the flag " I will manage the OS kernel ." In InfoboxCloud, autoscaling by CPU and memory works for containers (servers using OS-level virtualization). For virtual machines (servers using hardware virtualization), autoscaling is possible only by CPU. If you want to use memory autoscaling, do not set the flag “I will manage the OS kernel” when creating the server.

In the next step, select the required OS and complete the server creation process.
After creation, click on the server in the control panel.

You will be taken to the server management section. As you can see below, autoscaling is disabled. In order to understand the current server resource consumption, go to the "Performance" section.

Charts are updated 1 time in 5 minutes. In order to see the consumption for the required period of time, select the area on the lower graph of each resource.

The red line on the chart - set resource limits in the control panel. Blue - current resource consumption.

Both on the processor performance graph and on the memory consumption graph, the difference between the limit and the resources actually consumed is large. So idle computing resources, and users - pay extra money.
You reduce the amount of resources consumed by the server in the server management section "Summary". Autoscaling will not be involved.

This is a good way if you clearly know how much resources the server will consume.
If the load is less predictable or changes - use autoscaling.
To configure, go to the appropriate section "Autoscaling".

You can turn on auto-scaling by processor frequency and memory. You cannot scale by processor cores — guest operating systems require a reboot when the number of cores changes.
After the creation of the server, it is recommended that you first install the software that will be used, make sure that it works correctly, and determine the amount of resource consumption under different loads (autoscaling boundaries). Then you can turn on autoscaling and test its operation so that the result for industrial use is appropriate and expected.
Autoscale setting
Sliders (sliders) set the minimum and maximum value of the resource allowed for working without autoscaling (as a percentage of occupied resources). If the resource load is greater than the set value by the slider “if used more”, the resource will be added. If the resource value is less than the set value “if used less”, the resource will be reduced.
For processor autoscaling, the resource is the processor frequency, for memory, the amount of RAM.

The period for assessing the amount of resources used is indicated in the “within” fields. Auto scaling up and down is possible only after evaluating the resources used (building a performance graph) for each cloud server. The minimum period is 5 minutes.
The boundaries of the autoscale - the "increase to" and "reduce to". This is the maximum and minimum amount of the resource to which autoscaling is possible. It is recommended to set the minimum amount of a resource not less than specified in the minimum system requirements of the software used or not less than the minimum operational value for your use case.
The autoscaling step is indicated in the “Step” field. This is the value by which the amount of available resources changes when autoscaling: increases or decreases.
The autoscaling rate is the number of steps that the autoscaling must go through in order to change the amount of resources from minimum to maximum. This is the inverse of the autoscaling speed.
The pace can be calculated like this:

To apply the autoscaling rules correctly, the tempo, pitch and autoscaling boundaries must be integers! You cannot take half a step, but you can take a small step of at least 1 MHz.
Let's look at an example: let's say we want the minimum frequency of the processor to be 200 MHz, the maximum - 2000 MHz. Suppose we use autoscaling periods of 5 minutes to increase the amount of resources and to reduce them. The load increases. If the autoscaling step is set to 200 MHz:

The autoscaling rate is 9. We define the time over which the processor frequency will increase from 200 MHz to 2000 MHz with a significantly increased load.

Maximum autoscale time = 9 * 5 = 45 minutes.
Need to auto scale faster? Increase the pitch, but so that the tempo is still an integer.
For example, you can set the lower limit of autoscaling to 500 MHz, the upper limit to 2000 MHz, a step of 500 MHz, the periods will remain 5 minutes each.
Then the tempo = (2000-500) / 500 = 3.
Maximum autoscaling time = 3 * 5 = 15 minutes.
The same calculation is made for memory.
Suppose the lower limit is 1024 MB, the upper limit is 65536 MB. Periods - 5 minutes. Step - 1024 MB. Then the tempo = (65536-1024) / 1024 = 63.
The maximum autoscaling time from 1 GB of memory to 64 GB = 63 * 5 = 315 minutes.
This is evident from the calculations, autoscaling does not work instantly, which is associated with the cost of computing resources and the amount of service traffic needed to build graphs of the load of cloud servers. This means that the lower limit of autoscaling should be set with a margin sufficient to withstand the load with the expected increase in load for 5 minutes (before the autoscaling operation is performed). This will provide a predictable server performance with increasing load.
A useful feature of autoscaling is the ability to maximize resource savings. With the help of autoscaling, you can reduce the amount of resources available to the server to less than it is possible to install directly from the control panel. For example, values such as a 25 MHz processor and 48 megabytes of memory for an unvisited personal blog or a git – repository are quite a reality. This opens up the possibility for users to use the cloud cheaply, without overpaying for extra resources, as much as possible reducing the payment for the cloud server.
A feature of autoscaling InfoboxCloud is precise control of the process by the administrator. You define the process of autoscaling and the result is predictable, since all the parameters are set and the operation algorithm is clear. Autoscaling is not a panacea, but a very useful tool that allows you to use resources more efficiently and save money.
Conclusion
If you find an error in the article, the author will gladly correct it. Please write in the LAN or in the mail about it. Write questions in the comments or email. If you can not leave comments on Habré - write to us in the InfoboxCloud Community .
Successful work!
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/250755/
All Articles