HGST drives in RAID arrays
Good afternoon, friends and colleagues. Today we would like to talk about the benefits of using HGST disks in RAID arrays and how our solutions help ensure the smooth operation of data centers by minimizing financial and reputational risks.
Corporate users prefer to configure systems with RAID arrays for reliable data protection, minimizing downtime and maintaining performance. That is why they choose HGST enterprise-class drives, which provide best-in-class reliability, constant throughput and power. However, even the most reliable disks in the world cannot completely eliminate the risks of data loss. RAID systems have come a long way towards minimizing these risks, but, nevertheless, recovery processes that occur as a result of a disk failure are inevitable. In this regard, a number of problems arise: loss of time, productivity and data integrity are tasks that HGST plans to cope with thanks to the Rebuild Assist function.
')
No storage technology is immune to errors. Disk and flash memory may suffer from improper use.
HGST uses a number of diagnostic functions to evaluate possible errors, information about which is sent to the RAID controller for further analysis and identification of possible corrective actions.
HGST discs minimize the possibility of errors, as evidenced by the average time between failures equal to 2 hours. Minor errors can often be corrected or redistributed, leading to the absence or minimization of data loss. However, a disk that is full of data may exhibit significant errors that can be identified as a disk failure. In this case, the RAID controller must take action: disk errors will be taken offline, and the array will be placed in reduced functionality mode to reduce the possibility of additional data loss as a result of long-term malfunction. While the data is reconstructed in a reinstalled disk or in a hot-swap disk, the RAID controller continues to provide data access using the parity data from the remaining disks in the array through a recovery process known as XOR operation.
And it really works. The disadvantage is that recovering the contents of a disk can take a long time. Although the array is operating in a slow state, it must recover the data and at the same time still respond to their requests. In terms of performance, RAID configurations are often used as shared storage. This means that the decrease in productivity caused by recovery can affect the productivity of many workers.
RAID rebuild. Not all RAID users understand how high the risk of data loss is, which is possible during a secondary failure during the recovery process. Reducing recovery times can reduce this risk.
Why the time of adjustment is increasing
At a time when the capacity of arrays was calculated in megabytes and gigabytes, the time needed to rebuild RAID arrays was considered acceptable. Nevertheless, the practical consequences of switching to terabyte arrays quickly become noticeable, given the basic formula for calculating the time required for rebuilding:
Capacity (MB) / Average Transmission Rate (MB / s) = Tuning Time (s)
When it comes to rebuilding a 3TB volume on a conventional 3.5-inch hard disk with an average data transfer rate of 110MB / s, it will take 19,108 seconds (or 5.3 hours) to rebuild. This is a typical situation for a RAID 1 array. If that doesn’t scare you, remember that more complex array options work in “reduced functionality mode” when one of the drives is disabled. This reduces the performance of the volumes and further increases the tuning time. In practice, RAID 5 rebuild speeds can quietly drop to around 10Mb / s, so this process will take days, and this is unacceptable for most data storage centers that must follow certain guarantees of the end-user service level.
As disk capacity grows, both the time of their rebuilding and the risk of data loss increase. For example, using the program for estimating the tuning time for a RAID 5 array consisting of 12 disks with a single high-speed automatic switch-on device consisting of 3TB disks against 5TB disks and a decent rebuild speed of 40Mb / s, it can be established that the annual probability of data loss is 54% higher on 5TB more capacious disk array, mainly because it will take approximately 13 hours more to rebuild *. If a second disk fails in a RAID array that does not provide additional redundancy, the contents of the volume will be lost, often irrevocably. RAID 6 is often used to reduce the risk of a second disk failure.
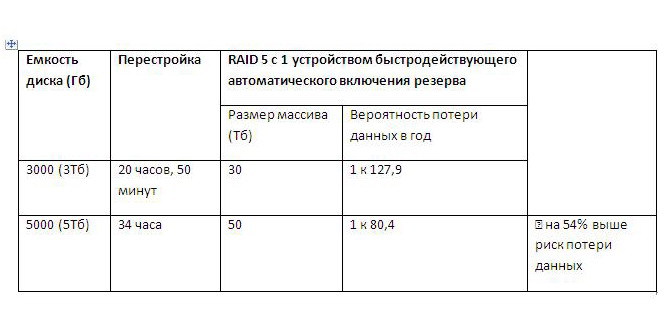
* The example is modeled using a realignment time calculator located at: www.memset.com/tools/raid-calculator
Simulation conditions: averaged data transfer rate of 40Mb / s, 12 disks in the array (including a parity disk and a device for high-speed automatic switching on of the reserve), a five-year warranty and the ability to replace the disk for 7 days.
Summing up, it should be noted that there is a direct relationship between the disk capacity and the restructuring time, or more precisely, the larger the capacity, the longer the restructuring process takes in working in the mode of limited array functionality. To solve this problem, HGST has provided support for its industry-standard Rebuild Assist feature on its latest corporate devices. It not only reduces the time required to rebuild arrays, but also reduces the risk of data loss, quickly restoring the full functionality of the array.
Corporate users prefer to configure systems with RAID arrays for reliable data protection, minimizing downtime and maintaining performance. That is why they choose HGST enterprise-class drives, which provide best-in-class reliability, constant throughput and power. However, even the most reliable disks in the world cannot completely eliminate the risks of data loss. RAID systems have come a long way towards minimizing these risks, but, nevertheless, recovery processes that occur as a result of a disk failure are inevitable. In this regard, a number of problems arise: loss of time, productivity and data integrity are tasks that HGST plans to cope with thanks to the Rebuild Assist function.
')
No storage technology is immune to errors. Disk and flash memory may suffer from improper use.
HGST uses a number of diagnostic functions to evaluate possible errors, information about which is sent to the RAID controller for further analysis and identification of possible corrective actions.
HGST discs minimize the possibility of errors, as evidenced by the average time between failures equal to 2 hours. Minor errors can often be corrected or redistributed, leading to the absence or minimization of data loss. However, a disk that is full of data may exhibit significant errors that can be identified as a disk failure. In this case, the RAID controller must take action: disk errors will be taken offline, and the array will be placed in reduced functionality mode to reduce the possibility of additional data loss as a result of long-term malfunction. While the data is reconstructed in a reinstalled disk or in a hot-swap disk, the RAID controller continues to provide data access using the parity data from the remaining disks in the array through a recovery process known as XOR operation.
And it really works. The disadvantage is that recovering the contents of a disk can take a long time. Although the array is operating in a slow state, it must recover the data and at the same time still respond to their requests. In terms of performance, RAID configurations are often used as shared storage. This means that the decrease in productivity caused by recovery can affect the productivity of many workers.
RAID rebuild. Not all RAID users understand how high the risk of data loss is, which is possible during a secondary failure during the recovery process. Reducing recovery times can reduce this risk.
Why the time of adjustment is increasing
At a time when the capacity of arrays was calculated in megabytes and gigabytes, the time needed to rebuild RAID arrays was considered acceptable. Nevertheless, the practical consequences of switching to terabyte arrays quickly become noticeable, given the basic formula for calculating the time required for rebuilding:
Capacity (MB) / Average Transmission Rate (MB / s) = Tuning Time (s)
When it comes to rebuilding a 3TB volume on a conventional 3.5-inch hard disk with an average data transfer rate of 110MB / s, it will take 19,108 seconds (or 5.3 hours) to rebuild. This is a typical situation for a RAID 1 array. If that doesn’t scare you, remember that more complex array options work in “reduced functionality mode” when one of the drives is disabled. This reduces the performance of the volumes and further increases the tuning time. In practice, RAID 5 rebuild speeds can quietly drop to around 10Mb / s, so this process will take days, and this is unacceptable for most data storage centers that must follow certain guarantees of the end-user service level.
As disk capacity grows, both the time of their rebuilding and the risk of data loss increase. For example, using the program for estimating the tuning time for a RAID 5 array consisting of 12 disks with a single high-speed automatic switch-on device consisting of 3TB disks against 5TB disks and a decent rebuild speed of 40Mb / s, it can be established that the annual probability of data loss is 54% higher on 5TB more capacious disk array, mainly because it will take approximately 13 hours more to rebuild *. If a second disk fails in a RAID array that does not provide additional redundancy, the contents of the volume will be lost, often irrevocably. RAID 6 is often used to reduce the risk of a second disk failure.

* The example is modeled using a realignment time calculator located at: www.memset.com/tools/raid-calculator
Simulation conditions: averaged data transfer rate of 40Mb / s, 12 disks in the array (including a parity disk and a device for high-speed automatic switching on of the reserve), a five-year warranty and the ability to replace the disk for 7 days.
Summing up, it should be noted that there is a direct relationship between the disk capacity and the restructuring time, or more precisely, the larger the capacity, the longer the restructuring process takes in working in the mode of limited array functionality. To solve this problem, HGST has provided support for its industry-standard Rebuild Assist feature on its latest corporate devices. It not only reduces the time required to rebuild arrays, but also reduces the risk of data loss, quickly restoring the full functionality of the array.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/250359/
All Articles