EMC VMAX 3: Enterprise Data Management Platform

In the light of the global development trend of various social, mobile and cloud platforms, most modern companies need an IT infrastructure that can provide instant access to large amounts of information characteristic of the new generation of hybrid cloud environments. EMC introduces the VMAX 3 family of storage systems that implement a range of approaches designed to simplify information lifecycle management.
The new line of storage systems is a high-end storage system for business critical loads of the first level. At the same time, the solution allows customers to have full control over data services in terms of SLA and infrastructure where applications are located - in the data processing center or in the public cloud. In fact, such capabilities make EMC VMAX 3 a corporate management platform, because if previously this was possible only with the integration of third-party data management services and external software, now control over the life cycle of information, as well as the implementation of the “data storage as a service” model in a hybrid cloud is possible using basic system functions.
')
The EMC VMAX 3 model range consists of three storage systems - VMAX 100K, 200K and 400K. All storage systems are based on a fundamentally new architecture based on the HYPERMAX OS and the Dynamic Virtual Matrix. HYPERMAX OS combines the storage hypervisor and operating system, which allows embedding the storage infrastructure services directly into an array into the VMAX 3. Dynamic Virtual Matrix allows you to dynamically allocate computing resources to improve performance and ensure predictable levels of service across a large enterprise. All this makes it possible to increase the level of efficiency and consolidate the data center by reducing the occupied space and reducing energy consumption.
Despite the fact that for building data storage services, server architectures such as Vsan or ScaleIO are increasingly used and middle-class systems have achieved performance enough for any application, there is still room for using multi-controller Hi-END systems:
1) These are multi-user databases that require transactional performance, the size of which is constantly growing and it will be quite expensive to locate them only on SSD.
2) This is a virtualization environment where many virtual machines with very different performance requirements can actually generate a decent load.
In both cases, everything is stored on the same storage system. Accordingly, it is necessary that this system provides a very high availability of services, as well as the flexibility of the online redistribution of resources in accordance with the load that changes with time.
3) A solution is needed to organize a second or third backup site, with minimal impact of replication on application performance and recovery of service on this site with minimal or no data loss.
Architecture features
The new version of VMAX, like all previous ones, is built on the INTEL multi-controller hardware architecture. Only this time the storage controllers are connected by a fault-tolerant data bus - Infiniband 56 Gbit / s. The total coherent cache reaches 16 TB in older models, the number of processing cores reaches 384.

VMAX 3 has seen many design changes. Controllers, disk shelves have changed, and the racks themselves have changed. VMAX 3 is now supplied in standard 19-inch cabinets and allows support from third-party racks. Thus, it is not necessary to plan the VMAX placement especially, which is especially important for large data centers. VMAX no longer separates system bay and storage bay. All racks are fully equal. Each rack can accommodate from 1 to 2 Engine (1 Engine or 2 controllers), interconnect and a certain number of disk shelves. There are two options for disk shelves - both with dense placement: 60 in 3.5 inch format and 120 in 2.5 inch format.
Due to this, the overall density of the array has increased: in one rack you can put 720 disks and two controllers (1 Engine) or 480 disks and four controllers (2 Engine). The maximum array configuration is placed in 8 cabinets: 5760 disks and 8 Engine.
Racks VMAX can be spread to a distance of 25 meters from the first, which is installed internal switching.
 The possibility of separation racks VMAX up to 25 meters from System Bay
The possibility of separation racks VMAX up to 25 meters from System BayVMAX 3 supports I / O interfaces:
- FC 8 and 16 Gbit / s;
- FCoE / iSCSI 10 Gb / s.
The range of disks is constantly expanding, and the following types of drives are currently supported:
- SSD 200, 400, 800 GB;
- SAS 15K 300 GB;
- SAS 10K 300, 600, 1200 GB;
- NL-SAS 7K 2, 4 TB.
For the first time, Vault to flash technology has been applied to protect the cache. Previously, a special partition on vault hard drives was provided for this purpose, but now it is a separate Flash memory installed in the controllers themselves. This has reduced the capacity of the batteries used to protect the cache: maintaining the health of hard drives vault is no longer necessary.
The main operating system of the array has changed its name to HYPERMAX (previously Enginuity), and the name is not chosen by chance. The thing is that, in addition to the operating system, a specialized hypervisor works on the controllers, which allows you to run a large number of additional services, such as: monitoring, management, file access. Of particular note is the ability to integrate the virtual version of VPLEX to create disaster-resistant infrastructures without the need for additional equipment.
There is a dynamic internal load balancing. If earlier in Enginuity there was a hard binding of the processor cores to the input-output ports, then it disappeared in HYPERMAX, and the computational power is balanced between the Front-end, Back-end and the built-in hypervisor.
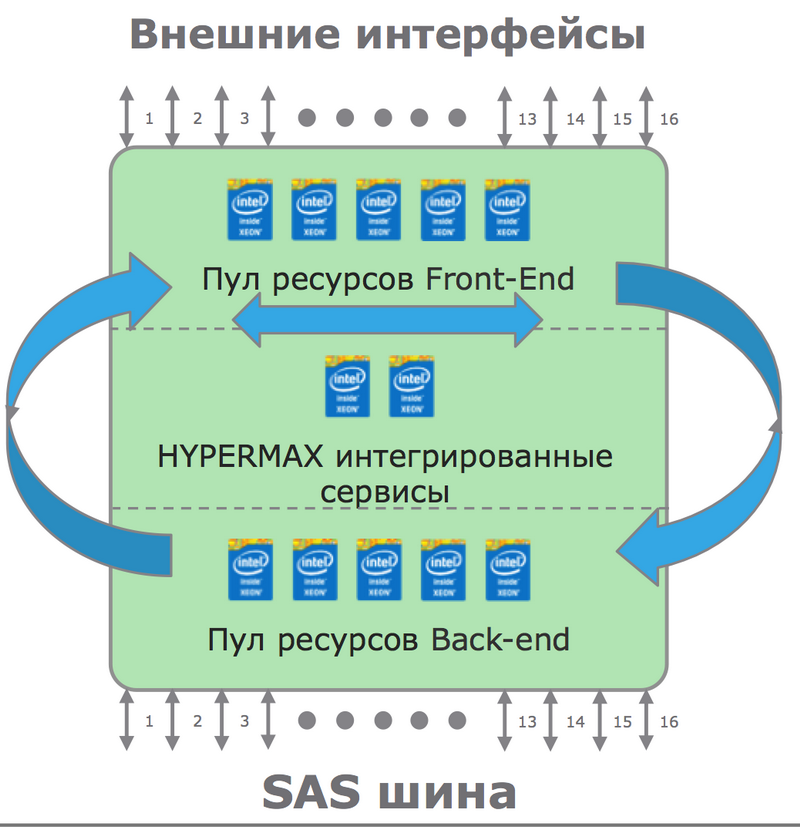 Dynamic balancing of processor cores between tasks
Dynamic balancing of processor cores between tasksGiven the huge amount of resources (VMAX 400K in the maximum configuration supports 384 Intel cores and 16 TB of cache), combined with the incredible flexibility of dynamic redistribution of resources, we can talk about the new VMAX as one of the most powerful high-end storage systems today.
Resource planning
In the new version, the approach to system sizing and dynamic resource allocation has changed fundamentally. If earlier the implementation and configuration of the VMAX system could be compared with a whole small project, now VMAX is delivered in a fully configured state broken down by RAID, with pre-configured virtual resource pools and a simplified management interface. Pre-configuration with compliance with SLA levels is collected at the factory in full compliance with the load profile, which was agreed with the customer at the stage of sizing and planning. At the stage of final implementation at the customer site, you just need to connect the pre-configured logical volumes to the applications, and you can start working with a guaranteed SLA level!
Several SLA levels are offered as standard: DIAMOND, PLATINUM, GOLD, SILVER, BRONZE (more precisely, in the VMAX terminology, this is called SLO - Service Level Objective), which is divided by the allowable response time and application profile for the application. The following parameters are taken into account:
- average response time;
- reading / writing ratio;
- the load profile is sequential / random;
- average read / write unit;
- data volume.
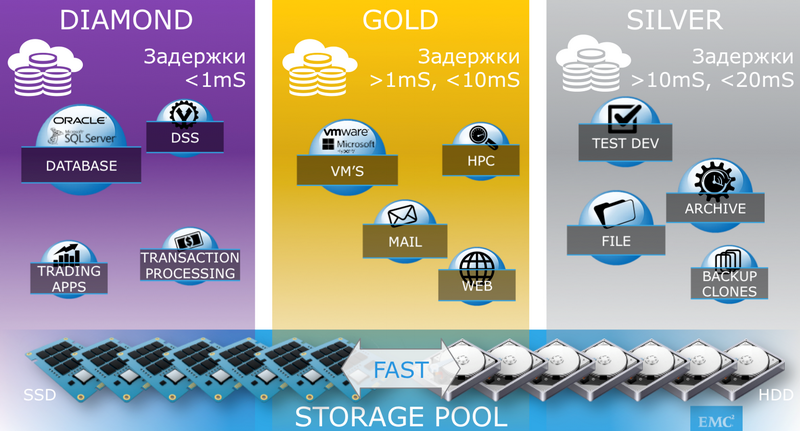 SLO levels with response time classification
SLO levels with response time classificationIf you plan to run several different tasks on the system, you need to predetermine the load profile of each of them. The lack of interference is fully guaranteed by the basic HYPERMAX services.
The more information about the load was known at the design stage, the more precisely VMAX will be able to plan its resources predicting bottlenecks. In other words, the VMAX 3 setup does not start from the moment the system is connected to the customer’s data center, but from the moment information is collected before ordering the system.
Federated storage
One of the key features that appeared in VMAX some time ago is Federated Tiered Storage (FTS), which in the new version has been significantly expanded and expanded.
FTS, firstly, allows you to consolidate arrays of different manufacturers on the basis of VMAX, and secondly, to extend technologies such as FAST, SRDF, TimeFinder to the connected pool of arrays. The key difference between FTS and similar implementations of other manufacturers is that when writing data to a third-party array, VMAX necessarily performs a check reading and CRC control.
The use of FTS is very diverse. This includes the use of third-party arrays as part of multi-level FAST storage, and the storage of Timefinder snapshots together with SRDF for remote replication. An interesting implementation in conjunction with VPLEX is to create Active / Active configurations with continuous access to data and full stability against the failure of one of the entire data centers.
Together with VPLEX, data mobility is increased, and it also becomes possible to work with a single geographically distributed cross-platform pool of resources.
VMAX 3 has a completely new technology based on FTS algorithms - EMC ProtectPoint, which allows you to connect an EMC DataDomain (DD) backup system like Federated Tiered Storage and back up and restore data directly from DD.
All this works as follows: the database is suspended, the ProtectPoint agent gives the command to take a TimeFinder snapshot, the database is restored. After that, in the background, VMAX copies the snapshot content to DD.
From the point of view of the database and applications, with the introduction of ProtectPoint, the backup procedure does not change, and everything looks very much like regular backup using snapshots, except that traffic is not run across the entire network between the application server and the server, but is localized between VMAX and DD.
Data recovery is also performed by the command of the ProtectPoint agent installed on the application / database server. The administrator, manually or through any supported backup software, selects the desired breakpoint: the data recovery process starts from the backup DD. The key feature of ProtectPoint is that you can use the recovered volume immediately after initiating the recovery procedure, without waiting for the data to be copied. All requested blocks will be priority read from DD and provided to the application. Of course, this will cause additional delays, but the period until the physical recovery of the volume can be spent on the service functions of checking content, access rights, compatibility, etc.
Together with the high speed of the channel between DD and VMAX, this greatly reduces the recovery time after a crash.
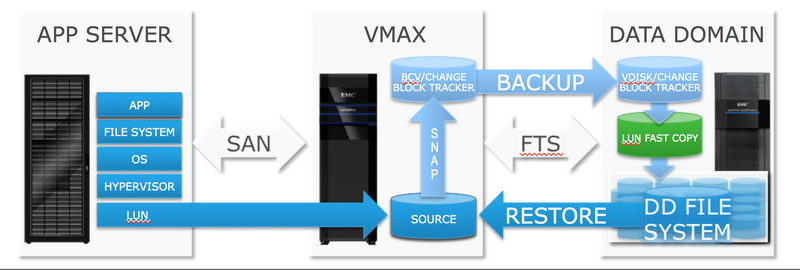
Multi-level storage
Multi-level storage has remained the strongest side of EMC arrays for the past 6 years, when in 2008, the corporation first on the market offered Flash disks for use as part of one of the media types in VMAX.
The algorithms that move data between storage levels are aimed at maintaining a predetermined SLA (SLO). If earlier the decision to move between levels was dictated by the frequency of requests of a block, now the decision is made on the basis of maintaining a predetermined response time and other parameters (provided that they are predefined).
Data analysis and movement between storage levels now runs 24x7 continuously. This does not affect performance, as VMAX is endowed with enormous computational resources, even in minimal configuration.

Service Level Objective (SLO) and virtual pools
Another important change in FAST is that if previously the center for deciding whether to move between levels was located directly in the VMAX core, now agents installed on application and database servers are helping. Agents receive information on the most requested data areas and possible changes in the load profile. FAST on VMAX has become proactive.
DBMS Performance Analysis
Now, using Unisphere, you can not only manage the array, but also analyze database performance: the DBclassify utility has been added to the interface, which can collect information directly from the database server and transfer it to Unisphere. This allows Unisphere to be viewed as a single point of performance monitoring, both from the array side and from the application server side. DBclassify can compare the IO response time on the storage system side and the response time on the application / database side and conclude whether there is a bottleneck inside the array or to look for it somewhere outside: in the network stack, file system, etc. DBclassify gives a tabular view, so you can see the “bottleneck” in a particular database area, and with the help of FAST technologies give the command to move the table to another resource pool. DBclassify is primarily aimed at Oracle, but support is expected for other databases.
Unisphere, DBclassify and all built-in functions for monitoring and system management are located in the core of the HYPERMAX OS and do not require third-party management servers.
We distribute EMC solutions in Ukraine and Belarus . Prices, questions - write: abo@muk.ua, or in a personal.
Catalog of all solutions and services of the distributor MUK
EMC Authorized Training Courses
Translation of the review into Tajik
Translation of the review into Belarusian
MUK-Service - all types of IT repair: warranty, non-warranty repair, sale of spare parts, contract service
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/249931/
All Articles