Streaming audio in iOS using Yandex.Disk as an example
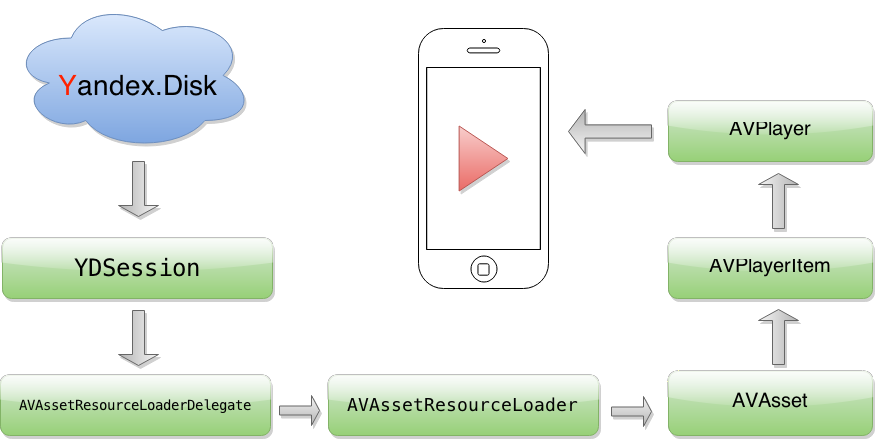
While working on the project for streaming audio, it was necessary to add support for new services, such as Yandex.Disk. Working with audio in the application is implemented through AVPlayer, which plays files by url and supports standard schemes such as file, http, https. Everything works fine for services in which the authorization token is sent to the url of the request, among them DropBox, Box, Google Drive. For services such as Yandex.Disk, the authorization token is passed in the request header and AVPlayer does not provide access to it.
Finding solutions to this problem among the available APIs led to the use of the resourceLoader object in AVURLAsset. With it, we provide access to a file hosted on a remote resource for AVPlayer. This works on the principle of a local HTTP proxy but with maximum simplification for use.
It is necessary to understand that AVPlayer uses resourceLoader in those cases when he himself does not know how to download the file. Therefore, we create a url with a custom scheme and initialize the player with this url. AVPlayer, without knowing how to load a resource, transfers control to resourceLoader.
')
AVAssetResourceLoader works through AVAssetResourceLoaderDelegate for which you need to implement two methods:
- (BOOL)resourceLoader:(AVAssetResourceLoader *)resourceLoader shouldWaitForLoadingOfRequestedResource:(AVAssetResourceLoadingRequest *)loadingRequest; - (void)resourceLoader:(AVAssetResourceLoader *)resourceLoader didCancelLoadingRequest:(AVAssetResourceLoadingRequest *)loadingRequest; The first is called when the AVAssetResourceLoader starts loading the resource and sends us the AVAssetResourceLoadingRequest. In this case, we memorize the request and begin loading the data. If the request is no longer relevant, then AVAssetResourceLoader calls the second method and we cancel the data loading.
To begin, create an AVPlayer using the url with a custom scheme, assign AVAssetResourceLoaderDelegate and the queue on which the delegate methods will be called:
AVURLAsset *asset = [AVURLAsset URLAssetWithURL:[NSURL URLWithString:@"customscheme://host/myfile.mp3"] options:nil]; [asset.resourceLoader setDelegate:self queue:dispatch_get_main_queue()]; AVPlayerItem *item = [AVPlayerItem playerItemWithAsset:asset]; [self addObserversForPlayerItem:item]; self.player = [AVPlayer playerWithPlayerItem:playerItem]; [self addObserversForPlayer]; Some class LSFilePlayerResourceLoader will be engaged in resource loading. It is initialized with the url of the resource being loaded and the YDSession, which will directly download the file from the server. We will store the LSFilePlayerResourceLoader objects in the NSDictionary, and the key will be the url of the resource.
When loading a resource from an unknown source, AVAssetResourceLoader will invoke delegate methods.
AVAssetResourceLoaderDelegate
- (BOOL)resourceLoader:(AVAssetResourceLoader *)resourceLoader shouldWaitForLoadingOfRequestedResource:(AVAssetResourceLoadingRequest *)loadingRequest{ NSURL *resourceURL = [loadingRequest.request URL]; if([resourceURL.scheme isEqualToString:@"customscheme"]){ LSFilePlayerResourceLoader *loader = [self resourceLoaderForRequest:loadingRequest]; if(loader==nil){ loader = [[LSFilePlayerResourceLoader alloc] initWithResourceURL:resourceURL session:self.session]; loader.delegate = self; [self.resourceLoaders setObject:loader forKey:[self keyForResourceLoaderWithURL:resourceURL]]; } [loader addRequest:loadingRequest]; return YES; } return NO; } - (void)resourceLoader:(AVAssetResourceLoader *)resourceLoader didCancelLoadingRequest:(AVAssetResourceLoadingRequest *)loadingRequest{ LSFilePlayerResourceLoader *loader = [self resourceLoaderForRequest:loadingRequest]; [loader removeRequest:loadingRequest]; } At the beginning of the boot method, we check that the scheme corresponds to ours. Next, take the LSFilePlayerResourceLoader from the cache or create a new one and add a request to load the resource to it.
The interface of our LSFilePlayerResourceLoader looks like this:
LSFilePlayerResourceLoader
@interface LSFilePlayerResourceLoader : NSObject @property (nonatomic,readonly,strong)NSURL *resourceURL; @property (nonatomic,readonly)NSArray *requests; @property (nonatomic,readonly,strong)YDSession *session; @property (nonatomic,readonly,assign)BOOL isCancelled; @property (nonatomic,weak)id<LSFilePlayerResourceLoaderDelegate> delegate; - (instancetype)initWithResourceURL:(NSURL *)url session:(YDSession *)session; - (void)addRequest:(AVAssetResourceLoadingRequest *)loadingRequest; - (void)removeRequest:(AVAssetResourceLoadingRequest *)loadingRequest; - (void)cancel; @end @protocol LSFilePlayerResourceLoaderDelegate <NSObject> @optional - (void)filePlayerResourceLoader:(LSFilePlayerResourceLoader *)resourceLoader didFailWithError:(NSError *)error; - (void)filePlayerResourceLoader:(LSFilePlayerResourceLoader *)resourceLoader didLoadResource:(NSURL *)resourceURL; @end It contains methods for adding / removing a request to the queue and a method for canceling all requests. LSFilePlayerResourceLoaderDelegate will report when the resource is fully loaded or an error occurred during the download.
When adding a request to the queue by calling addRequest, we store it in pendingRequests and start the data load operation:
Add request
- (void)addRequest:(AVAssetResourceLoadingRequest *)loadingRequest{ if(self.isCancelled==NO){ NSURL *interceptedURL = [loadingRequest.request URL]; [self startOperationFromOffset:loadingRequest.dataRequest.requestedOffset length:loadingRequest.dataRequest.requestedLength]; [self.pendingRequests addObject:loadingRequest]; } else{ if(loadingRequest.isFinished==NO){ [loadingRequest finishLoadingWithError:[self loaderCancelledError]]; } } } In the beginning, we created a new data load operation for each incoming request. The result was that the file was loaded into three or four threads while the data overlapped. But then they found out that as soon as AVAssetResourceLoader starts a new query, the previous ones are no longer relevant for it. This gives us the opportunity to safely cancel all ongoing data load operations as soon as we start a new one, which saves traffic.
The operation of loading data from the server is divided into two. The first (contentInfoOperation) gets information about the size and type of the file. The second (dataOperation) - receives the data of the file with the offset. We subtract the offset and size of the requested data from the object of the AVAssetResourceLoadingDataRequest class.
Data load operation
- (void)startOperationFromOffset:(unsigned long long)requestedOffset length:(unsigned long long)requestedLength{ [self cancelAllPendingRequests]; [self cancelOperations]; __weak typeof (self) weakSelf = self; void(^failureBlock)(NSError *error) = ^(NSError *error) { [weakSelf performBlockOnMainThreadSync:^{ if(weakSelf && weakSelf.isCancelled==NO){ [weakSelf completeWithError:error]; } }]; }; void(^loadDataBlock)(unsigned long long off, unsigned long long len) = ^(unsigned long long offset,unsigned long long length){ [weakSelf performBlockOnMainThreadSync:^{ NSString *bytesString = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"bytes=%lld-%lld",offset,(offset+length-1)]; NSDictionary *params = @{@"Range":bytesString}; id<YDSessionRequest> req = [weakSelf.session partialContentForFileAtPath:weakSelf.path withParams:params response:nil data:^(UInt64 recDataLength, UInt64 totDataLength, NSData *recData) { [weakSelf performBlockOnMainThreadSync:^{ if(weakSelf && weakSelf.isCancelled==NO){ LSDataResonse *dataResponse = [LSDataResonse responseWithRequestedOffset:offset requestedLength:length receivedDataLength:recDataLength data:recData]; [weakSelf didReceiveDataResponse:dataResponse]; } }]; } completion:^(NSError *err) { if(err){ failureBlock(err); } }]; weakSelf.dataOperation = req; }]; }; if(self.contentInformation==nil){ self.contentInfoOperation = [self.session fetchStatusForPath:self.path completion:^(NSError *err, YDItemStat *item) { if(weakSelf && weakSelf.isCancelled==NO){ if(err==nil){ NSString *mimeType = item.path.mimeTypeForPathExtension; CFStringRef contentType = UTTypeCreatePreferredIdentifierForTag(kUTTagClassMIMEType,(__bridge CFStringRef)(mimeType),NULL); unsigned long long contentLength = item.size; weakSelf.contentInformation = [[LSContentInformation alloc] init]; weakSelf.contentInformation.byteRangeAccessSupported = YES; weakSelf.contentInformation.contentType = CFBridgingRelease(contentType); weakSelf.contentInformation.contentLength = contentLength; [weakSelf prepareDataCache]; loadDataBlock(requestedOffset,requestedLength); weakSelf.contentInfoOperation = nil; } else{ failureBlock(err); } } }]; } else{ loadDataBlock(requestedOffset,requestedLength); } } After receiving information about the file on the server, we create a temporary file in which we will write data from the network and read it as needed.
Disk cache initialization
- (void)prepareDataCache{ self.cachedFilePath = [[self class] pathForTemporaryFile]; NSError *error = nil; if ([[NSFileManager defaultManager] fileExistsAtPath:self.cachedFilePath] == YES){ [[NSFileManager defaultManager] removeItemAtPath:self.cachedFilePath error:&error]; } if (error == nil && [[NSFileManager defaultManager] fileExistsAtPath:self.cachedFilePath] == NO) { NSString *dirPath = [self.cachedFilePath stringByDeletingLastPathComponent]; [[NSFileManager defaultManager] createDirectoryAtPath:dirPath withIntermediateDirectories:YES attributes:nil error:&error]; if (error == nil) { [[NSFileManager defaultManager] createFileAtPath:self.cachedFilePath contents:nil attributes:nil]; self.writingFileHandle = [NSFileHandle fileHandleForWritingAtPath:self.cachedFilePath]; @try { [self.writingFileHandle truncateFileAtOffset:self.contentInformation.contentLength]; [self.writingFileHandle synchronizeFile]; } @catch (NSException *exception) { NSError *error = [[NSError alloc] initWithDomain:LSFilePlayerResourceLoaderErrorDomain code:-1 userInfo:@{NSLocalizedDescriptionKey:@"can not write to file"}]; [self completeWithError:error]; return; } self.readingFileHandle = [NSFileHandle fileHandleForReadingAtPath:self.cachedFilePath]; } } if (error != nil) { [self completeWithError:error]; } } After receiving the data packet, we first cache it to disk and update the size of the received data stored in the receivedDataLength variable. At the end we notify requests queued for a new portion of data.
Receive data packet
- (void)didReceiveDataResponse:(LSDataResonse *)dataResponse{ [self cacheDataResponse:dataResponse]; self.receivedDataLength=dataResponse.currentOffset; [self processPendingRequests]; } The caching method writes data to a file with the desired offset.
Data caching
- (void)cacheDataResponse:(LSDataResonse *)dataResponse{ unsigned long long offset = dataResponse.dataOffset; @try { [self.writingFileHandle seekToFileOffset:offset]; [self.writingFileHandle writeData:dataResponse.data]; [self.writingFileHandle synchronizeFile]; } @catch (NSException *exception) { NSError *error = [[NSError alloc] initWithDomain:LSFilePlayerResourceLoaderErrorDomain code:-1 userInfo:@{NSLocalizedDescriptionKey:@"can not write to file"}]; [self completeWithError:error]; } } The reading method does the reverse operation.
Reading data from the cache
- (NSData *)readCachedData:(unsigned long long)startOffset length:(unsigned long long)numberOfBytesToRespondWith{ @try { [self.readingFileHandle seekToFileOffset:startOffset]; NSData *data = [self.readingFileHandle readDataOfLength:numberOfBytesToRespondWith]; return data; } @catch (NSException *exception) {} return nil; } To notify requests that are in the queue about a new piece of data, we first write information about the content, and then the data from the cache. If all the data for the request has been recorded, then we remove it from the queue.
Request Alerts
- (void)processPendingRequests{ NSMutableArray *requestsCompleted = [[NSMutableArray alloc] init]; for (AVAssetResourceLoadingRequest *loadingRequest in self.pendingRequests){ [self fillInContentInformation:loadingRequest.contentInformationRequest]; BOOL didRespondCompletely = [self respondWithDataForRequest:loadingRequest.dataRequest]; if (didRespondCompletely){ [loadingRequest finishLoading]; [requestsCompleted addObject:loadingRequest]; } } [self.pendingRequests removeObjectsInArray:requestsCompleted]; } In the method of filling information about the content, we set the size, type, flag of access to an arbitrary range of data.
Filling in content information
- (void)fillInContentInformation:(AVAssetResourceLoadingContentInformationRequest *)contentInformationRequest{ if (contentInformationRequest == nil || self.contentInformation == nil){ return; } contentInformationRequest.byteRangeAccessSupported = self.contentInformation.byteRangeAccessSupported; contentInformationRequest.contentType = self.contentInformation.contentType; contentInformationRequest.contentLength = self.contentInformation.contentLength; } And the main method in which we read data from the cache and pass it to requests from the queue.
Filling data
- (BOOL)respondWithDataForRequest:(AVAssetResourceLoadingDataRequest *)dataRequest{ long long startOffset = dataRequest.requestedOffset; if (dataRequest.currentOffset != 0){ startOffset = dataRequest.currentOffset; } // Don't have any data at all for this request if (self.receivedDataLength < startOffset){ return NO; } // This is the total data we have from startOffset to whatever has been downloaded so far NSUInteger unreadBytes = self.receivedDataLength - startOffset; // Respond with whatever is available if we can't satisfy the request fully yet NSUInteger numberOfBytesToRespondWith = MIN(dataRequest.requestedLength, unreadBytes); BOOL didRespondFully = NO; NSData *data = [self readCachedData:startOffset length:numberOfBytesToRespondWith]; if(data){ [dataRequest respondWithData:data]; long long endOffset = startOffset + dataRequest.requestedLength; didRespondFully = self.receivedDataLength >= endOffset; } return didRespondFully; } This is the end of the work with the loader It remains to slightly change the Yandex.Disk SDK so that we can load arbitrary range data from a file on the server. There are only three changes.
The first is to add the ability to cancel for each request in YDSession. To do this, we add the new protocol YDSessionRequest and set it as the return value in the requests.
YDSession.h
@protocol YDSessionRequest <NSObject> - (void)cancel; @end - (id<YDSessionRequest>)fetchDirectoryContentsAtPath:(NSString *)path completion:(YDFetchDirectoryHandler)block; - (id<YDSessionRequest>)fetchStatusForPath:(NSString *)path completion:(YDFetchStatusHandler)block; Second, we add a method for loading data of arbitrary range from a file on the server.
YDSession.h
- (id<YDSessionRequest>)partialContentForFileAtPath:(NSString *)srcRemotePath withParams:(NSDictionary *)params response:(YDDidReceiveResponseHandler)response data:(YDPartialDataHandler)data completion:(YDHandler)completion; YDSession.m
- (id<YDSessionRequest>)partialContentForFileAtPath:(NSString *)srcRemotePath withParams:(NSDictionary *)params response:(YDDidReceiveResponseHandler)response data:(YDPartialDataHandler)data completion:(YDHandler)completion{ return [self downloadFileFromPath:srcRemotePath toFile:nil withParams:params response:response data:data progress:nil completion:completion]; } - (id<YDSessionRequest>)downloadFileFromPath:(NSString *)path toFile:(NSString *)aFilePath withParams:(NSDictionary *)params response:(YDDidReceiveResponseHandler)responseBlock data:(YDPartialDataHandler)dataBlock progress:(YDProgressHandler)progressBlock completion:(YDHandler)completionBlock{ NSURL *url = [YDSession urlForDiskPath:path]; if (!url) { completionBlock([NSError errorWithDomain:kYDSessionBadArgumentErrorDomain code:0 userInfo:@{@"getPath": path}]); return nil; } BOOL skipReceivedData = NO; if(aFilePath==nil){ aFilePath = [[self class] pathForTemporaryFile]; skipReceivedData = YES; } NSURL *filePath = [YDSession urlForLocalPath:aFilePath]; if (!filePath) { completionBlock([NSError errorWithDomain:kYDSessionBadArgumentErrorDomain code:1 userInfo:@{@"toFile": aFilePath}]); return nil; } YDDiskRequest *request = [[YDDiskRequest alloc] initWithURL:url]; request.fileURL = filePath; request.params = params; request.skipReceivedData = skipReceivedData; [self prepareRequest:request]; NSURL *requestURL = [request.URL copy]; request.callbackQueue = _callBackQueue; request.didReceiveResponseBlock = ^(NSURLResponse *response, BOOL *accept) { if(responseBlock){ responseBlock(response); } }; request.didGetPartialDataBlock = ^(UInt64 receivedDataLength, UInt64 expectedDataLength, NSData *data){ if(progressBlock){ progressBlock(receivedDataLength,expectedDataLength); } if(dataBlock){ dataBlock(receivedDataLength,expectedDataLength,data); } }; request.didFinishLoadingBlock = ^(NSData *receivedData) { if(skipReceivedData){ [[self class] removeTemporaryFileAtPath:aFilePath]; } NSDictionary *userInfo = @{@"URL": requestURL, @"receivedDataLength": @(receivedData.length)}; [[NSNotificationCenter defaultCenter] postNotificationInMainQueueWithName:kYDSessionDidDownloadFileNotification object:self userInfo:userInfo]; completionBlock(nil); }; request.didFailBlock = ^(NSError *error) { if(skipReceivedData){ [[self class] removeTemporaryFileAtPath:aFilePath]; } NSDictionary *userInfo = @{@"URL": requestURL}; [[NSNotificationCenter defaultCenter] postNotificationInMainQueueWithName:kYDSessionDidFailToDownloadFileNotification object:self userInfo:userInfo]; completionBlock([NSError errorWithDomain:error.domain code:error.code userInfo:userInfo]); }; [request start]; NSDictionary *userInfo = @{@"URL": request.URL}; [[NSNotificationCenter defaultCenter] postNotificationInMainQueueWithName:kYDSessionDidStartDownloadFileNotification object:self userInfo:userInfo]; return (id<YDSessionRequest>)request; } And the third thing to be corrected is to change the queue of callbacks from parallel to serial, otherwise the data blocks will not arrive in the order we requested, and the user will hear jerks when playing music.
YDSession.m
- (instancetype)initWithDelegate:(id<YDSessionDelegate>)delegate callBackQueue:(dispatch_queue_t)queue{ self = [super init]; if (self) { _delegate = delegate; _callBackQueue = queue; } return self; } YDDiskRequest *request = [[YDDiskRequest alloc] initWithURL:url]; request.fileURL = filePath; request.params = params; [self prepareRequest:request]; request.callbackQueue = _callBackQueue; The source code of the example on GitHub .
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/249605/
All Articles