New GHOST vulnerability threatens popular Linux distributions

Vulnerability in common Linux distributions could allow an attacker to gain remote control over the system. The users of Debian 7 (wheezy), Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 & 7, CentOS 6 & 7, Ubuntu 12.04 were under attack. Zend Framework v2, Wordpress and a number of other popular applications are also vulnerable.
A new vulnerability information ( CVE-2015-0235 ) in the glibc library (GNU C Library) was first published in the French ezine . Some experts believe that this was done by mistake, since by that time no one had time to prepare the updates.
')
A detailed technical description of the vulnerability and an exploit for the vulnerability can be found on the Openwall , and the first descriptions were published in the Rapid 7 community.
What is the problem
The specialists who discovered the vulnerability managed to prepare a specially crafted email message that exploits the vulnerability in the Exim mail server running the vulnerable version of Glibc. It is worth noting that Exim is very widespread and in some operating systems is the default mail server. But beyond that, other applications can potentially be exploited:
- SSH servers that use DNS requests for authentication with allow / deny.
- Mail servers with reverse DNS queries.
- Numerous web applications that perform DNS queries based on user input.
- MySQL DBMS that authenticates by domain name (MySQL privileges).
GHOST vulnerability was discovered in the library (glibc - gethostbyname () and gethostbyname2 () functions), which are an integral part of Linux - there are not so many desktop computers running this OS, but the server population is very large This means that the network infrastructure of most technological projects may be at risk. In other libc implementations (such as uclibc, musl) there is no vulnerability.
The error was given the name GHOST (“ghost”) - an abbreviation that beats the names of the vulnerable functions gethostbyname () and gethostbyname2 ().
According to one of the versions based on the analysis of the metadata of the red-ghost logo , experts knew about this vulnerability at least since October 2, 2014 and complied with the conditions of responsible disclosure, while the developers corrected the error.
What is the difference from Heartbleed and Shellshock
Unlike the OpenSSL Heartbleed vulnerability, which allowed attackers to read server memory, the GHOST error allows you to take control of the operating system using remote code execution (RCE). Since servers are primarily at risk, the problem should not affect such a wide range of users as in the case of Heartbleed, but the infrastructure of most Internet companies is at risk.
Compared to another well-known Shellshock vulnerability, GHOST is more difficult to operate because it allows you to execute binary instructions, rather than console commands, which means that you need to bypass the protection mechanisms of the Linux kernel to operate.
How to protect
In order to secure your servers, you need to install a patch (patch) issued by the supplier of the corresponding Linux distribution. Vulnerability information appeared on January 27, so today (January 28) the first patches should appear.
In addition, Cyberciti.biz has published instructions on how to detect all services, applications and executable files in the distribution associated with the vulnerable glibc library (GNU C Library), as well as fixing the error.
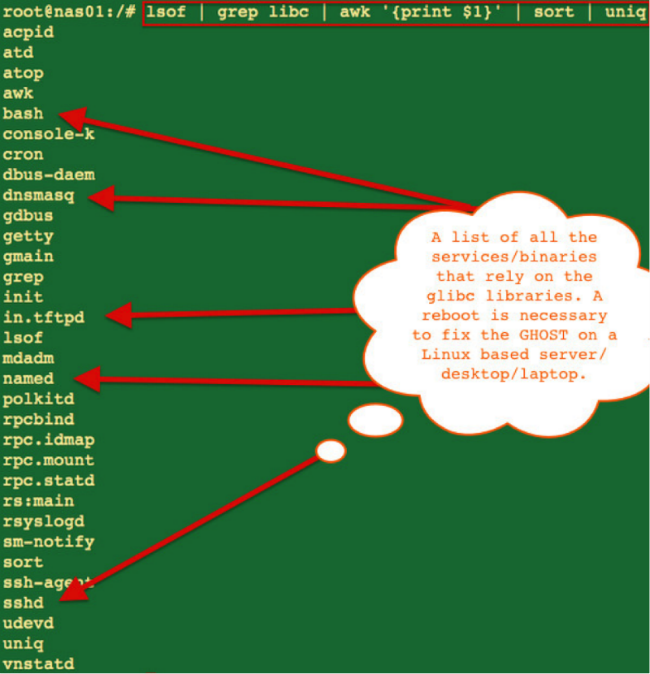
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/249097/
All Articles