Tree - killer JSON, XML, YAML and their ilk
Hello, my name is Dmitry Karlovsky and I ... thought a lot. I thought about what was wrong with XML and why it was recently traded for stupid JSON. The result of these inventions was the new data format standard , which incorporated the flexibility of XML, the simplicity of JSON and the visibility of YAML.
 Tree is a two-dimensional binary-safe format for representing structured data. Easily readable by both human and computer. Simple, compact, fast, expressive and extensible. Comparing it with other popular formats, you can make the following comparison table:
Tree is a two-dimensional binary-safe format for representing structured data. Easily readable by both human and computer. Simple, compact, fast, expressive and extensible. Comparing it with other popular formats, you can make the following comparison table:
JSON and XML allow arbitrary formatting of output with spaces and line breaks. However, often for various reasons (the main ones are smaller, easier to implement) they are formatted in one line and then they become extremely unreadable.
, JSON — , escape- .
, XML , « », «» .
« », escape-. XML . Tree, , .

JSON XML , . . — , . , , Tree, .
INI .
XML — , , , .
JSON YAML «» «». . , AST, .
Tree . , .
(30 ), .
(90 ), , sgml.
(210 ). , , , .
(8 ), , (--).
(10 ), , , .
, .
. YAML , JSON, XML - .
Tree — .
: github.com/nin-jin/tree.d/tree/master/formats
, XML, . JSON YAML - . — INI, Tree JSON.
, , . — . — , .
XML JSON — , .
. Tree — , ( unix- , , ).
XML , . JSON, , . INI , . YAML , « , , ». Tree .
XML JSON . YAML . INI , . Tree , IDEA .
, . Tree — D TypeScript/JavaScript.
• . .
• . Tree .
• . API Tree.
Tree — , : , , . , 3 :
• — . . , .
• — . . — .
• — , . . , .
Tree , XML. JSON YAML. , INI. , Tree.
Tree- , (0x0D). , . . . - . - – , .
-, - , . . – -. , - .
, .
, , …
Tree , , Tree:
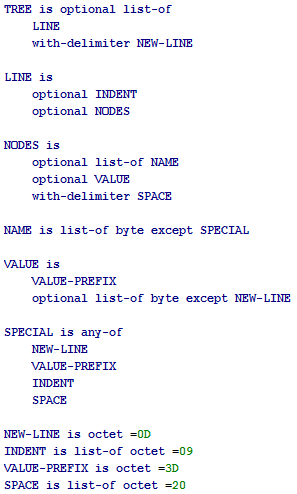
. , .
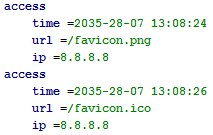
"---" , .
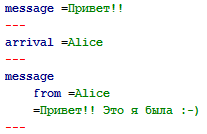
DSL Tree XML . xml.tree xml «@», «!» «?» , .

, . , DSL .

. NodeJS AST — JSON.
, JS:
, AST - :
, , . , , , — :
Tree :
Tree , . , XML — Tree.
? , Tree . , , , , XML , xml.tree , , , XML.
JSON "JSON pipes ". : linux , . JSON, , . Tree , .
Tree Lisp — . Lisp , Tree — . AST, DSL , .
D 50 , — 20. — 15. , 100 : github.com/nin-jin/tree.d
:
:
:
:
Tree IDEA, , . Tree , .
, Alex222 SynWrite
Tree. . . . — . .
( , ), .
:
":", "\".
 Tree is a two-dimensional binary-safe format for representing structured data. Easily readable by both human and computer. Simple, compact, fast, expressive and extensible. Comparing it with other popular formats, you can make the following comparison table:
Tree is a two-dimensional binary-safe format for representing structured data. Easily readable by both human and computer. Simple, compact, fast, expressive and extensible. Comparing it with other popular formats, you can make the following comparison table:| More is better | Json | XML | Yaml | INI | Tree |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Human comprehension | 3 | one | four | five | five |
| Easy editing | 3 | one | four | five | five |
| Arbitrary hierarchy | 3 | 3 | 3 | one | five |
| Ease of implementation | 3 | 2 | one | five | five |
| Speed parsing / serialization | 3 | one | one | five | five |
| Serialized Size | 3 | one | four | five | five |
| Threading support | 0 | 0 | five | five | five |
| Binary security | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | five |
| Prevalence | five | five | 3 | 3 | 0 |
| Editors support | five | five | 3 | five | one |
| Support programming languages | five | five | 3 | five | one |
Format Comparison
Human comprehension
JSON and XML allow arbitrary formatting of output with spaces and line breaks. However, often for various reasons (the main ones are smaller, easier to implement) they are formatted in one line and then they become extremely unreadable.
{ "users" : [ { "name" : "Alice" , age : 20 } ] }
<users><user><name>Alice</name><age>20</age></user></users>
, JSON — , escape- .
{ "description" : "Hello, Alice!\nHow do you do?" }
, XML , « », «» .
<greeting>
Hello, <b>Alice</b>!<br/>
How do you do?
</greeting>
<greeting>
Hello, <a href="http://example.org/user/alice?ref=xe3o7rubvo283xb">Alice</a>!<br/>
How do you do?
</greeting>
« », escape-. XML . Tree, , .
<title>"Rock&roll" = life</title>
{ "title" : "\"Rock&roll\" = life" }

JSON XML , . . — , . , , Tree, .
INI .
XML — , , , .
JSON YAML «» «». . , AST, .
Tree . , .
JSON
(30 ), .
XML
(90 ), , sgml.
YAML
(210 ). , , , .
INI
(8 ), , (--).
Tree
(10 ), , , .
/
, .
. YAML , JSON, XML - .
Tree — .
: github.com/nin-jin/tree.d/tree/master/formats
, XML, . JSON YAML - . — INI, Tree JSON.
, , . — . — , .
XML JSON — , .
. Tree — , ( unix- , , ).
XML , . JSON, , . INI , . YAML , « , , ». Tree .
XML JSON . YAML . INI , . Tree , IDEA .
, . Tree — D TypeScript/JavaScript.
Tree
• . .
• . Tree .
• . API Tree.
Tree — , : , , . , 3 :
• — . . , .
• — . . — .
• — , . . , .
Tree , XML. JSON YAML. , INI. , Tree.
Tree- , (0x0D). , . . . - . - – , .
-, - , . . – -. , - .
, .
, , …
Tree
Tree , , Tree:

grammar.tree
, .
. , .

STATEMENT «», « ».
(8 ) .
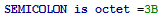
SEMICOLON . , .
.

: . .
.

( ).

DELIMITER .
. , , .

EXPRESSION « ».

( « »), « ».
, .
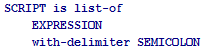
SCRIPT , .
is
. , .

STATEMENT «», « ».
octet
(8 ) .
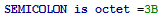
SEMICOLON . , .
optional
.

: . .
any-of
.

list-of
( ).

DELIMITER .
except
. , , .

EXPRESSION « ».

( « »), « ».
with-delimiter
, .

SCRIPT , .
-
. , .

"---" , .

-
DSL Tree XML . xml.tree xml «@», «!» «?» , .

xml.tree
QName – . – .

QName , «@».

. , , XML .
Tree , c «%». , XML. XML .

"--". , , xml.tree.

"?" - , -.


<html>
<head>
<title> & </title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>!</h1>
<p>, ?</p>
</body>
</html>
QName , «@».

<script type="text/javascript" src="index.js" />
. , , XML .
Tree , c «%». , XML. XML .

<link
rel="canonical"
href="/?article=rock%26roll&author=Nin+Jin"
/>
"--". , , xml.tree.

<!--<a href="/">top</a>-->
"?" - , -.

<?xml version="1.0" stanalone="yes" ololo?>
, . , DSL .

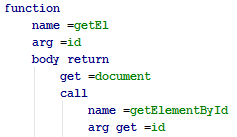
. NodeJS AST — JSON.
, JS:
function getEl( id ){
return document.getElementById( id )
}
, AST - :
[
{ "function": {
"name": "getEl",
"args": [ "id" ],
"body": [
{ "return": [
{ "get": "document" },
{ "call": {
"name": "getElementById",
"args": [
{ "get": "id" }
]
}}
]}
]
}}
]
, , . , , , — :
[ [ "function",
"getEl",
[ "id" ],
[ "return",
[ [ "get",
"document" ],
[ "call",
"getElementById",
[ "get", "id" ]
]
]
]
]
]
Tree :

, Tree
Tree , . , XML — Tree.
? , Tree . , , , , XML , xml.tree , , , XML.
UNIX-
JSON "JSON pipes ". : linux , . JSON, , . Tree , .
Tree Lisp — . Lisp , Tree — . AST, DSL , .
D 50 , — 20. — 15. , 100 : github.com/nin-jin/tree.d
:
string data = cast(string) read( "path/to/file.tree" ); // read from file
Tree tree = Tree.parse( data , "http://example.org/source/uri" ); // parse to tree
:
Tree userNames = tree.select( "user name" ); // returns name-nodes
Tree userNamesValues = tree.select( "user name " ); // returns value-nodes
:
string name = userNames[0].name; // get node name
string stringValue = userNames[0].value; // get value as string with "\n" as delimiter
uint intValue = userNames[0].value!uint; // get value converted from string to another type
Tree[] childs = tree.childs; // get child nodes array
string uri = tree.uri; // get uri like "http://example.org/source/uri#3:2"
:
string data = tree.toString(); // returns string representation of tree
tree.pipe( stdout ); // prints tree to output buffer
Tree IDEA, , . Tree , .
, Alex222 SynWrite
Tree. . . . — . .
2016-09-11
( , ), .
:
! City : table
ID : field
type : int 11
null : false
unique : true
Name : field
type : char 35
null : true
unique : false
City
ID : 1
Name : \Kabul
City
ID : 4079
Name : \Rafah
City
ID : 23023
Name : \Moscow
":", "\".
')
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/248147/
All Articles