Mathcad Express is a free math editor that few people know about.
First of all, I welcome the first visitors of my blog. This is my first article on Habré and I hope that I can tell you a lot of useful things here.
Mathcad RS is a typical example of mathematical software designed to perform both numerical and analytical calculations using formulas and visualizing their results in the form of graphs. Over the past years, Mathcad has become very popular, and, in my opinion, it can rightly be considered the number one mathematical package in the world.
First, a few facts about Mathcad, of course, known to most readers, because We have been using Mathcad for more than a dozen years in university training, scientific and engineering calculations. Most likely, you used the "old" version of Mathcad (the latter - behind number 15), which has changed little since the last century. Nowadays, it coexists quite successfully with the younger Mathcad family, which bears the name of Mathcad Prime. Thus, the developers a few years ago completely rewrote the program code, but did not care about 100% compatibility. Therefore, now they safely support both families - the “old” Mathcad and the “new” Mathcad Prime. Further in this article, and in my blog, we will talk about Mathcad Prime.
')
I’ll say right away that you can download the Russian -language distribution kit, a fully functional 30-day version of Mathcad Prime from the site of the Russian reseller RTS . If you are already going to try it in your work, my advice is to take the time in the Installation Wizard to agree to the inclusion of a test 30-day period. The fact is that Mathcad Prime, along with a powerful full-featured version (the window of which you see from above) has a free limited version called Mathcad Express. A feature of Mathcad Express is that most of the features in this version are turned off and unavailable. Nevertheless, the program Mathcad Express is quite rich in functionality, sufficient, at least, in order to study mathematics at school and in the 1st year of a technical university.

Formulas can be entered into documents either from the keyboard (if there are suitable characters on it), or using the Math menu. For the sake of example, let's calculate the integral of the function cos (x). To do this, select the integral symbol, and then - in the appropriate placeholders, enter (from the keyboard) the limits of integration and the integrand cos (x). It remains to press the "equal" key to get an answer immediately.

We need to be well aware of what happens when we enter an equal sign. Namely, the corresponding numerical algorithm for calculating the integral is launched: the integration interval is divided into a certain number of segments, at certain points of which the array of values of the integrand is calculated, which is then converted into a corresponding approximation of the integral sum. Thus, most of the calculations are hidden and occur "behind the scenes", and only the final result is displayed on the screen.
The key tools of Mathcad are operators and functions. For example, in our calculations we used the integration operator and the cosine function. To select the desired built-in function is convenient to use the Options menu.
Let's now define a custom function f (t), which will depend on the variable t. We will use the assignment operator intended for this purpose in Mathcad (colon with the equal sign).
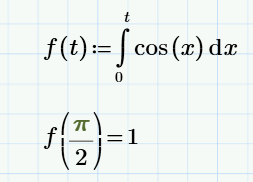
We defined the function f (t) as our integral of cos (x) with a variable upper limit t. After we have defined the function f (t), we can calculate its values in points (for which it is enough to enter the argument and press the "equal" key to output the answer to the document). To enter a constant, for example π, use either the Symbols menu or the Constants menu.
As an argument, you can use not only a scalar, but also a vector variable. You can define it as follows:

Then the result of calculating the function will be the corresponding vector.
Finally, one of the important features of Mathcad Express is the ability to plot graphs in a document. Let's select the place in the document and insert the XY-graph (i.e. Cartesian graph) into this place of our function f (x).
We denote the variable name on the x-axis (not to be confused with the previously used x and t), and the y-axis is the name of the function f (z), a function that, as you remember, we defined as the cosine integral of course , sin (z). As a result, we get a graph of this function.
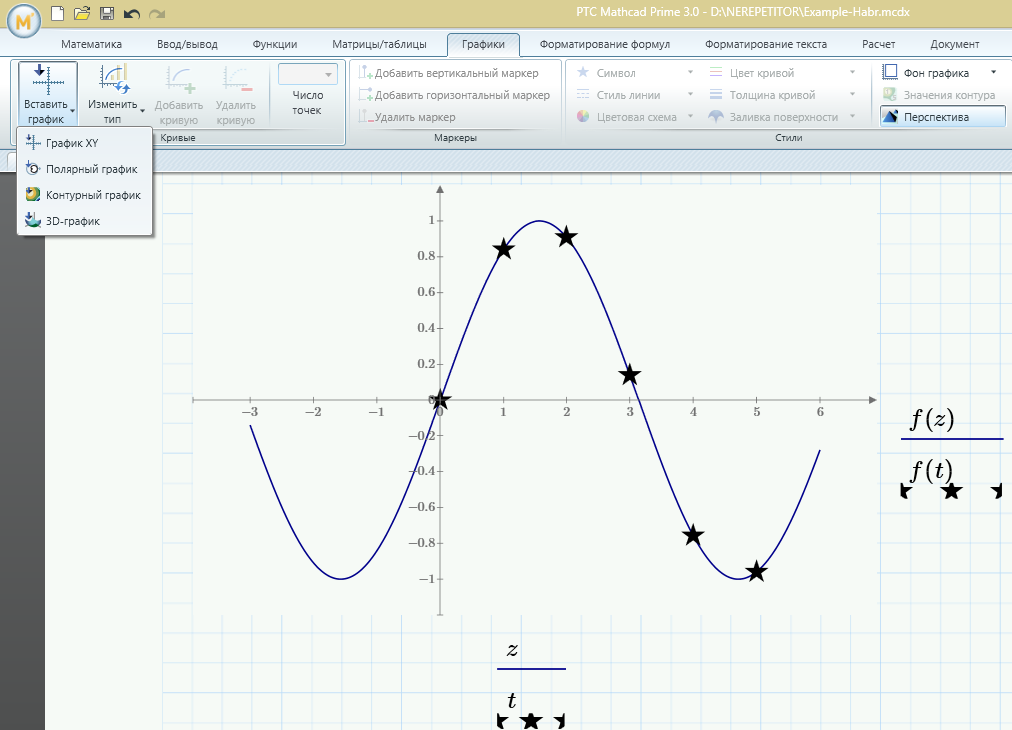
I will also say that matrix operations are still available in Mathcad Express (possibly due to a developer's oversight). Therefore, Mathcad Express is quite a powerful tool for solving linear algebra problems.

Moving up and down the document, we can view our calculations, and you can manage them using the Calculation menu. By default, the option of automatic calculation is enabled (as the formulas are entered into the document, these formulas are immediately calculated). If this option is disabled, then in order to calculate the document manually, just click the Calculate button.
Let me dwell on this, assuming that the task of familiarizing the reader with Mathcad Express has been solved, and in the next blog articles, when it comes to mathematics, I can use the calculations in Mathcad, without delving into its interface.
In conclusion, I am directing the interested reader to his video course on mathematical analysis , which was held in the format of the MEP on the INTUIT portal in 2014. All laboratory work was done at Mathcad Prime and can be downloaded here . All these materials on the site Nerepetitor.ru free, registration is not required.
Ps. To my surprise, faced with a few negative comments, I note several shortcomings of Mathcad (again, from my point of view):
Mathcad RS is a typical example of mathematical software designed to perform both numerical and analytical calculations using formulas and visualizing their results in the form of graphs. Over the past years, Mathcad has become very popular, and, in my opinion, it can rightly be considered the number one mathematical package in the world.
First, a few facts about Mathcad, of course, known to most readers, because We have been using Mathcad for more than a dozen years in university training, scientific and engineering calculations. Most likely, you used the "old" version of Mathcad (the latter - behind number 15), which has changed little since the last century. Nowadays, it coexists quite successfully with the younger Mathcad family, which bears the name of Mathcad Prime. Thus, the developers a few years ago completely rewrote the program code, but did not care about 100% compatibility. Therefore, now they safely support both families - the “old” Mathcad and the “new” Mathcad Prime. Further in this article, and in my blog, we will talk about Mathcad Prime.
')

I’ll say right away that you can download the Russian -language distribution kit, a fully functional 30-day version of Mathcad Prime from the site of the Russian reseller RTS . If you are already going to try it in your work, my advice is to take the time in the Installation Wizard to agree to the inclusion of a test 30-day period. The fact is that Mathcad Prime, along with a powerful full-featured version (the window of which you see from above) has a free limited version called Mathcad Express. A feature of Mathcad Express is that most of the features in this version are turned off and unavailable. Nevertheless, the program Mathcad Express is quite rich in functionality, sufficient, at least, in order to study mathematics at school and in the 1st year of a technical university.

Formulas can be entered into documents either from the keyboard (if there are suitable characters on it), or using the Math menu. For the sake of example, let's calculate the integral of the function cos (x). To do this, select the integral symbol, and then - in the appropriate placeholders, enter (from the keyboard) the limits of integration and the integrand cos (x). It remains to press the "equal" key to get an answer immediately.

We need to be well aware of what happens when we enter an equal sign. Namely, the corresponding numerical algorithm for calculating the integral is launched: the integration interval is divided into a certain number of segments, at certain points of which the array of values of the integrand is calculated, which is then converted into a corresponding approximation of the integral sum. Thus, most of the calculations are hidden and occur "behind the scenes", and only the final result is displayed on the screen.
The key tools of Mathcad are operators and functions. For example, in our calculations we used the integration operator and the cosine function. To select the desired built-in function is convenient to use the Options menu.
Let's now define a custom function f (t), which will depend on the variable t. We will use the assignment operator intended for this purpose in Mathcad (colon with the equal sign).
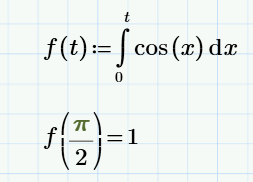
We defined the function f (t) as our integral of cos (x) with a variable upper limit t. After we have defined the function f (t), we can calculate its values in points (for which it is enough to enter the argument and press the "equal" key to output the answer to the document). To enter a constant, for example π, use either the Symbols menu or the Constants menu.
As an argument, you can use not only a scalar, but also a vector variable. You can define it as follows:

Then the result of calculating the function will be the corresponding vector.
Finally, one of the important features of Mathcad Express is the ability to plot graphs in a document. Let's select the place in the document and insert the XY-graph (i.e. Cartesian graph) into this place of our function f (x).
We denote the variable name on the x-axis (not to be confused with the previously used x and t), and the y-axis is the name of the function f (z), a function that, as you remember, we defined as the cosine integral of course , sin (z). As a result, we get a graph of this function.

I will also say that matrix operations are still available in Mathcad Express (possibly due to a developer's oversight). Therefore, Mathcad Express is quite a powerful tool for solving linear algebra problems.

Moving up and down the document, we can view our calculations, and you can manage them using the Calculation menu. By default, the option of automatic calculation is enabled (as the formulas are entered into the document, these formulas are immediately calculated). If this option is disabled, then in order to calculate the document manually, just click the Calculate button.

Let me dwell on this, assuming that the task of familiarizing the reader with Mathcad Express has been solved, and in the next blog articles, when it comes to mathematics, I can use the calculations in Mathcad, without delving into its interface.
In conclusion, I am directing the interested reader to his video course on mathematical analysis , which was held in the format of the MEP on the INTUIT portal in 2014. All laboratory work was done at Mathcad Prime and can be downloaded here . All these materials on the site Nerepetitor.ru free, registration is not required.
Ps. To my surprise, faced with a few negative comments, I note several shortcomings of Mathcad (again, from my point of view):
- only Windows version available
- resource-intensive, slower "past» Mathcad
- the interface could be more convenient
- can not save the document in the previous version (eg from the 3rd in the format of the 2nd)
- documents from the "past" Mathcad do not always manage to import into Prime
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/247999/
All Articles