Online Arbitration or Arbitration Court on the Internet
Making purchases on the Internet there is always a risk to fall on the unscrupulous seller or buyer and will face the fact that the solution of the problems encountered will fall on your shoulders. Even if you make a deal through the already known sites of online trading, then you may still have questions to the decision makers in your dispute.
Therefore, the idea arose of creating a likeness of an arbitration court in Internet commerce, when the parties, before the transaction, choose arbitrators, submit the dispute for their consideration and undertake to obey the decision of the latter.

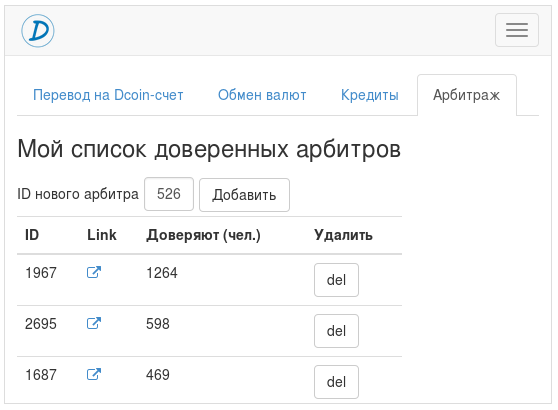
First of all, the buyer needs to select arbitrators with whom he is willing to entrust the decision of possible disputes with sellers.
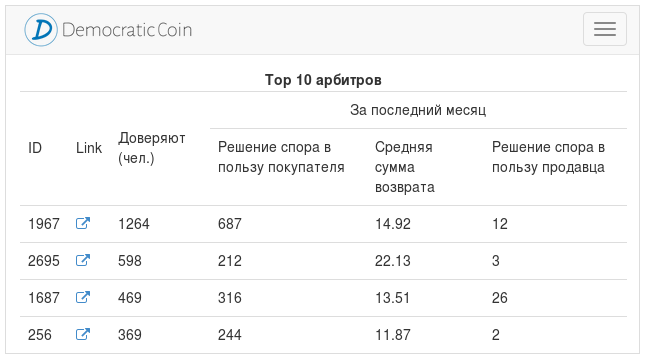
Any action of the arbitrator is recorded and stored in the blockchain. Thus, information about the activities of the arbitrator is publicly available. However, for anti-cheat protection, statistics are issued only by identified users .
')
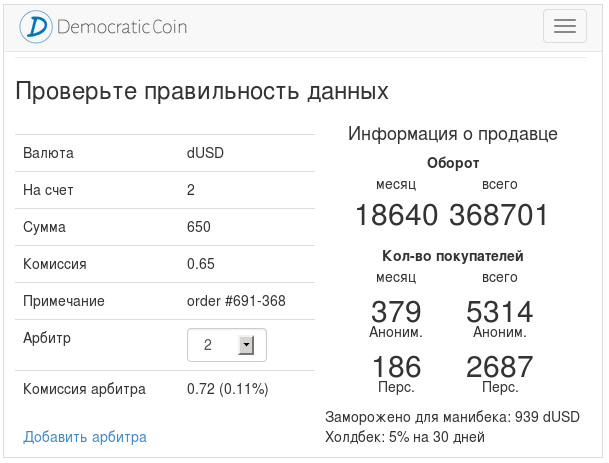
When transferring coins, the user selects an arbitrator from the list of arbitrators who are trusted both by him and the seller, then presses “send”.
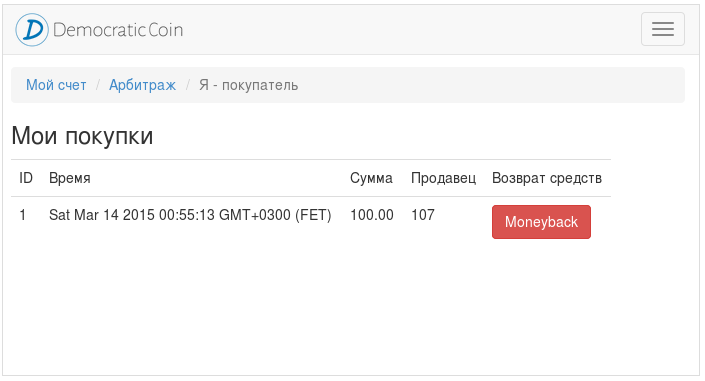
If the buyer has a claim to the seller, he enters the shopping list, presses "Manibek", indicates your email, which is encrypted with the public key of the arbitrator (s) and the seller, and waits for him to be contacted to clarify the circumstances.
First a couple of words about Dcoin
In Dcoin there are no central servers, just as in Bitcoin, each node stores a complete copy of the database . The exchange of new data between nodes takes place using blocks . Each block contains a hash of the previous block. All transactions originating from the user contain a unique signature that proves that the transaction was created by this user.

Unlike Bitcoin, Dcoin has not one, but 66 types of transactions , thanks to which Dcoin can exist in the form in which it is presented.
Example transaction structure:
All transactions have a header (TYPE, TIME, USER_ID) and SIGN, and all other fields vary depending on the purpose of the transaction.
Block structure:
A more detailed description of the work of Dcoin can be found in the wiki .
Pro mining in Dcoin
Mining in Dcoin is not mining in its pure form, to which everyone is accustomed using the example of other cryptocurrencies. Production of new coins does not require any effort from users. Dcoin-coins are created with each new block and distributed among all participants. For anonymous users, the growth in the volume of coins in their accounts is about 0.0004% / unit. The percentage value is determined by the identified users by voting.
One identified user can create a limited number of coins from nothing. Those. Users who have proven that they are not bots are responsible for creating the initial money supply. In addition, each such user is a cash exchange point for coins offline. For simplicity, the identified users I call miners.
There are periods of reduction in the volume of coins , when the created coins turned out to be more than the market needs. The reduction is triggered based on the data from the blockchain and can be predicted based on the number of miners, the number of coins created and the number of promised amounts. While the number of miners and the amount of the promised amounts increase, reductions do not occur. In more detail about the periods of reduction and the periods of reproduction can be read here . And about the identification of users - here .
Dcoin makes it possible to attach up to 5 arbitrators to a single transaction. In case the buyer requests a manibek, his request will be able to satisfy any of the selected arbitrators. After the transaction is sealed in the blockchain, it becomes impossible to change the list of arbitrators for this transaction. Each arbitrator who is attached to the transaction is charged a commission.
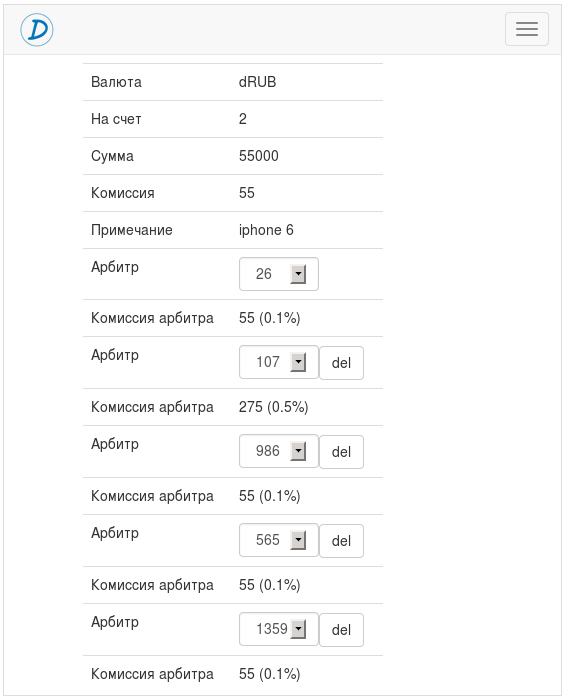
In order for the transaction to take place, both the buyer and the seller must have at least one general arbiter.

The arbitrator can set different conditions for each currency. Maximum - 0. This means without restrictions.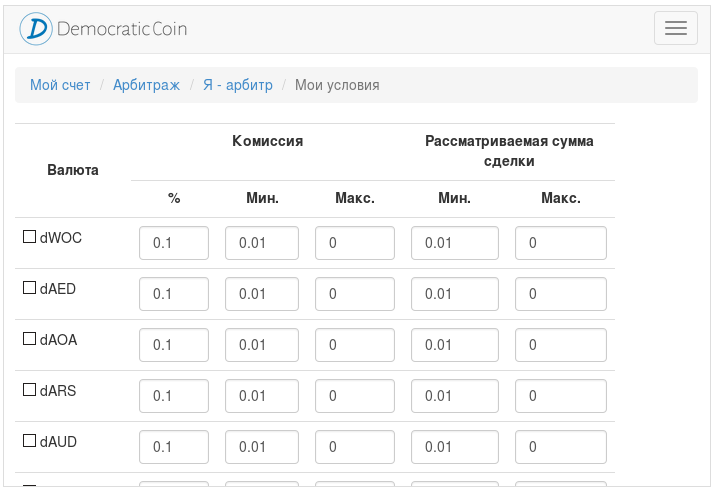
The seller can specify the number of days during which the buyer will be able to request the money back, as well as a percentage of the purchase amount, which is frozen on the seller’s account for the previously specified number of days.
For a pizza making and delivery company, it will be logical to specify 3 days and about 10% of holdback.
But for the seller who sells something for the first time, for example, through a service similar to ebay.com, it is better to specify 30 days and 100% holdback. Then gradually lower the% of holdback when reputation appears. 100% holdback means that the entire amount paid by the buyer is frozen on the seller’s account for 30 days and can be returned to the buyer at any time if the arbitrator makes such a decision.

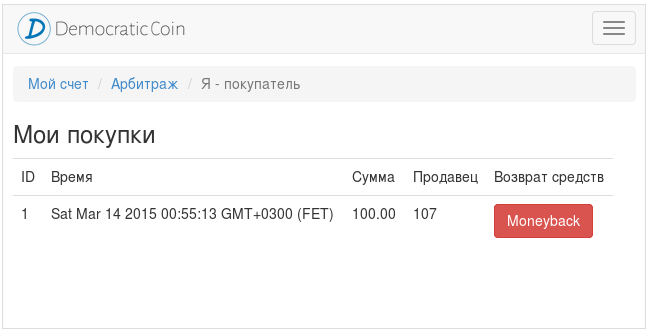
The buyer may request a money back during the time specified by the seller at the time of the transaction.
The request of the moneyback is seen by both the seller and the arbitrator. If the seller was able to negotiate with the buyer before the arbitrator made the decision, he can make a refund on his own. If the seller did not make a full money back, then an arbitrator can do it. To make a money back in an amount greater than the amount of the transaction is impossible.
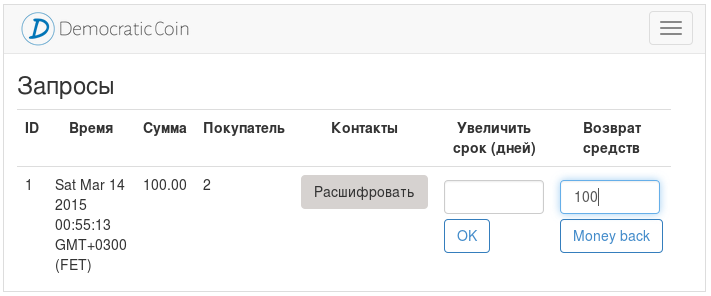
The time during which manibek is possible may not be enough to make an informed decision by the arbitrator. Therefore, he has the opportunity to increase this period once up to 180 days.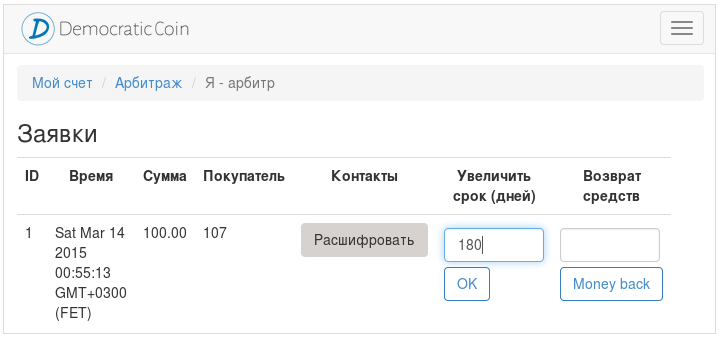
The main disadvantage of arbitration is that arbitrators must have a high degree of trust among sellers / buyers and have a reputation as fair judges who do not save time on carrying out full investigations of each dispute so that they can safely trust and not worry about anything.
As a result, to all the charms of independence, which gives the decentralization of electronic money, added one of the main advantages of classical payment instruments - the ability to challenge the transaction.
There are 20 dUSD on my account, which I am ready to distribute for tests (1 dUSD each), write to the PM. About 50 dUSD are on the stock exchange.
web-wallet and exe , source
List of services already accepting Dcoins:
racktech.ru
m4host.net
steadyhost.ru
komtet.ru (their chief engineer suggested the idea of arbitration, for which many thanks to him)
I don’t have much usability and interfaces, so I’ll be grateful for advice on where things can be improved.
Therefore, the idea arose of creating a likeness of an arbitration court in Internet commerce, when the parties, before the transaction, choose arbitrators, submit the dispute for their consideration and undertake to obey the decision of the latter.

At first, briefly about what I got in the end
- Arbitrators can not take away either the buyer's money or the seller's money. They can only decide on the withdrawal of funds from the seller’s account in the event that the buyer has received a complaint. For their services, arbitrators receive commissions - a percentage of each transaction, where they are listed as arbitrators.
- In order for the transaction to take place, both the buyer and the seller must have at least one general arbiter.
- A buyer can attach up to 5 arbitrators to a single transaction. All arbitrators have equal rights, each of them can exercise manibek.
- Before transferring funds, the buyer is provided with information about the seller: turnover, number of buyers (anonymous, not anonymous), etc.

First of all, the buyer needs to select arbitrators with whom he is willing to entrust the decision of possible disputes with sellers.

Any action of the arbitrator is recorded and stored in the blockchain. Thus, information about the activities of the arbitrator is publicly available. However, for anti-cheat protection, statistics are issued only by identified users .
')

When transferring coins, the user selects an arbitrator from the list of arbitrators who are trusted both by him and the seller, then presses “send”.

If the buyer has a claim to the seller, he enters the shopping list, presses "Manibek", indicates your email, which is encrypted with the public key of the arbitrator (s) and the seller, and waits for him to be contacted to clarify the circumstances.
And now the details
First a couple of words about Dcoin
In Dcoin there are no central servers, just as in Bitcoin, each node stores a complete copy of the database . The exchange of new data between nodes takes place using blocks . Each block contains a hash of the previous block. All transactions originating from the user contain a unique signature that proves that the transaction was created by this user.

Unlike Bitcoin, Dcoin has not one, but 66 types of transactions , thanks to which Dcoin can exist in the form in which it is presented.
Example transaction structure:
| Field | Description | The size |
|---|---|---|
| TYPE | Transaction type | |
| TIME | Transaction time | |
| USER_ID | ID of the user who created the transaction | |
| CURRENCY_ID | Currency ID | |
| AMOUNT | The size of the promised amount | |
| VIDEO_TYPE | youtube, vimeo, youku, null | |
| VIDEO_URL_ID | ID from video hosting | |
| PAYMENT_SYSTEMS_IDS | Payment systems id | 1-24 bytes |
| SIGN | From 1 to 3 signatures (TYPE, TIME, USER_ID, CURRENCY_ID, AMOUNT, VIDEO_TYPE, VIDEO_URL_ID, PAYMENT_SYSTEMS_IDS) from USER_ID | 128 to 4096 bytes |
Block structure:
| Field | Description | The size |
|---|---|---|
| BLOCK_ID | Block sequence number | 4 bytes |
| TIME | The time when the block was created | 4 bytes |
| USER_ID | ID of the user who signed the block | 5 bytes |
| LEVEL | The level at which the miner was at the time of block creation | 2 bytes |
| SIGN | Signature from (TYPE, BLOCK_ID, PREV_BLOCK_HASH, TIME, USER_ID, LEVEL, MRKL_ROOT) made with the node-key | from 128 bytes to 512 bytes |
| TRANSACTIONS | Transaction list | Up to 3Mb |
Pro mining in Dcoin
Mining in Dcoin is not mining in its pure form, to which everyone is accustomed using the example of other cryptocurrencies. Production of new coins does not require any effort from users. Dcoin-coins are created with each new block and distributed among all participants. For anonymous users, the growth in the volume of coins in their accounts is about 0.0004% / unit. The percentage value is determined by the identified users by voting.
One identified user can create a limited number of coins from nothing. Those. Users who have proven that they are not bots are responsible for creating the initial money supply. In addition, each such user is a cash exchange point for coins offline. For simplicity, the identified users I call miners.
There are periods of reduction in the volume of coins , when the created coins turned out to be more than the market needs. The reduction is triggered based on the data from the blockchain and can be predicted based on the number of miners, the number of coins created and the number of promised amounts. While the number of miners and the amount of the promised amounts increase, reductions do not occur. In more detail about the periods of reduction and the periods of reproduction can be read here . And about the identification of users - here .
Read more about arbitration
Multi arbitration
Dcoin makes it possible to attach up to 5 arbitrators to a single transaction. In case the buyer requests a manibek, his request will be able to satisfy any of the selected arbitrators. After the transaction is sealed in the blockchain, it becomes impossible to change the list of arbitrators for this transaction. Each arbitrator who is attached to the transaction is charged a commission.

List of trusted arbitrators
In order for the transaction to take place, both the buyer and the seller must have at least one general arbiter.

What it looks like from the inside
Transaction example
Transaction structure
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| TYPE | Transaction type |
| TIME | Transaction time |
| USER_ID | ID of the user who created the transaction |
| TRUST_LIST | List of referees trusted by the user |
| SIGN | From 1 to 3 signatures (TYPE, TIME, USER_ID, TRUST_LIST) from the user USER_ID |
Transaction example
(
[type] => 62
[time] => 1408470908
[user_id] => 1
[arbitration_trust_list] => [2,107,269]
[Sign] => 82010085c558dd411e816f589d57e48a02bf9231c9dcc55994568e0e00a7db3980c7005d91e88815e5e5a3dc5908a7c4f97c1f973f7ba576c86621f59b608e9d84ce9595710050a42a72e12fa78eb6dd12f8ff90f7004d8b8426a7cf714d7707899e8aafd9dc4534b94292fe849cce765ca975af88f2524874e22439716a59d1473baf115da4d67193320a33f36a442aa1c9711c3145c7499c207fbcc2846f9712bb0dc96c6c59708fd8d25e36a631213679a060a728473be8f23b8f8591bce50b64c67cca00d970fce93a714d2678119b1e67324e9b462986d11239337532a179a6f455f68d3a2e59df24f34590bc032b7c8cc5d633add4bef4c8c18efe7100a5a873
) Terms of the arbitrator
The arbitrator can set different conditions for each currency. Maximum - 0. This means without restrictions.

What it looks like from the inside
Transaction example
Transaction structure
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| TYPE | Transaction type |
| TIME | Transaction time |
| USER_ID | ID of the user who created the transaction |
| CONDITIONS | Commission: min, max,%; min, max amount for each currency the arbitrator works with |
| URL | The address of the site of the arbitrator, where he can show some information about himself |
| SIGN | From 1 to 3 signatures (TYPE, TIME, USER_ID, CONDITIONS, URL) from user USER_ID |
Transaction example
(
[type] => 62
[time] => 1408470908
[user_id] => 1
[conditions] => {"23": ["0.01", "0", "0.01", "0", "0.1"], "72": ["0.01", "0", "0.01", " 0 "," 0.1 "]}
[url] => http://arbitr.ru
[Sign] => 82010085c558dd411e816f589d57e48a02bf9231c9dcc55994568e0e00a7db3980c7005d91e88815e5e5a3dc5908a7c4f97c1f973f7ba576c86621f59b608e9d84ce9595710050a42a72e12fa78eb6dd12f8ff90f7004d8b8426a7cf714d7707899e8aafd9dc4534b94292fe849cce765ca975af88f2524874e22439716a59d1473baf115da4d67193320a33f36a442aa1c9711c3145c7499c207fbcc2846f9712bb0dc96c6c59708fd8d25e36a631213679a060a728473be8f23b8f8591bce50b64c67cca00d970fce93a714d2678119b1e67324e9b462986d11239337532a179a6f455f68d3a2e59df24f34590bc032b7c8cc5d633add4bef4c8c18efe7100a5a873
) Holdback
The seller can specify the number of days during which the buyer will be able to request the money back, as well as a percentage of the purchase amount, which is frozen on the seller’s account for the previously specified number of days.
For a pizza making and delivery company, it will be logical to specify 3 days and about 10% of holdback.
But for the seller who sells something for the first time, for example, through a service similar to ebay.com, it is better to specify 30 days and 100% holdback. Then gradually lower the% of holdback when reputation appears. 100% holdback means that the entire amount paid by the buyer is frozen on the seller’s account for 30 days and can be returned to the buyer at any time if the arbitrator makes such a decision.

What it looks like from the inside
Transaction example
Transaction structure
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| TYPE | Transaction type |
| TIME | Transaction time |
| USER_ID | ID of the user who created the transaction |
| ARBITRATION_DAYS_REFUND | The number of days during which the buyer will be able to request a money back |
| HOLD_BACK_PCT | % holdback |
| SIGN | From 1 to 3 signatures (TYPE, TIME, USER_ID, ARBITRATION_DAYS_REFUND, HOLD_BACK_PCT) from user USER_ID |
Transaction example
(
[type] => 62
[time] => 1408470908
[user_id] => 545
[arbitration_days_refund] => 30
[hold_back_pct] => 10
[Sign] => 82010085c558dd411e816f589d57e48a02bf9231c9dcc55994568e0e00a7db3980c7005d91e88815e5e5a3dc5908a7c4f97c1f973f7ba576c86621f59b608e9d84ce9595710050a42a72e12fa78eb6dd12f8ff90f7004d8b8426a7cf714d7707899e8aafd9dc4534b94292fe849cce765ca975af88f2524874e22439716a59d1473baf115da4d67193320a33f36a442aa1c9711c3145c7499c207fbcc2846f9712bb0dc96c6c59708fd8d25e36a631213679a060a728473be8f23b8f8591bce50b64c67cca00d970fce93a714d2678119b1e67324e9b462986d11239337532a179a6f455f68d3a2e59df24f34590bc032b7c8cc5d633add4bef4c8c18efe7100a5a873
) Request for moneyback
The buyer may request a money back during the time specified by the seller at the time of the transaction.

What it looks like from the inside
Transaction example
Transaction structure
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| TYPE | Transaction type |
| TIME | Transaction time |
| USER_ID | ID of the user who created the transaction |
| ORDER_ID | ID of the order by which the user wants manibek |
| ARBITRATOR0_ENC_TEXT | User contact details encrypted with an open RSA arbiter key 1 |
| ARBITRATOR1_ENC_TEXT | User contact information encrypted with RSA public key 2 |
| ARBITRATOR2_ENC_TEXT | User contact details encrypted with RSA public key 3 |
| ARBITRATOR3_ENC_TEXT | User contact details encrypted with RSA public key 4 |
| ARBITRATOR4_ENC_TEXT | User contact details encrypted with RSA public key 5 |
| SELLER_ENC_TEXT | User contact details encrypted with RSA public key |
| SIGN | 1 to 3 of signatures (TYPE, TIME, USER_ID, ORDER_ID, ARBITRATOR0_ENC_TEXT, ARBITRATOR1_ENC_TEXT, ARBITRATOR2_ENC_TEXT, ARBITRATOR3_ENC_TEXT, ARBITRATOR4_ENC_TEXT) from the user USER_ID |
Transaction example
(
[type] => 62
[time] => 1408470908
[user_id] => 6589
[order_id] => 2725
[Arbitrator0_enc_text] => 4440b7abc674354aeb85a3e56e32e3a844a75571e12e516b35db27d6bab71813dd6b05deb36a27c074305476218810944c81f11f6f6fe53957daaa167cf533d06dfe5c5c98d26f004996bd1462cb775a9d8512c4494fb8326894a9e7038d1c073397a7ada2d22ed75118d0aaeba1b2721656320dd4d181fdddcf59a0fb66c3bf
[Arbitrator1_enc_text] => 73e87240c492d500436fcae4932050cb649c82da95f35b2bc00dadff840c52b4c1ab5ffa55fa1382549c6ae606f569e86e48fec2abefdf5efac92a736e3ec84e481718c003c510de314080c26842c6752051221c9bb27b45e146505e30f760f54284cc8e2b5c9d01999cc4314ccffbb77fcf4a02d35cec5c1efd61af3733b81b
[Arbitrator2_enc_text] => ec022338af265ffe077d42edc5f7bb62efabaa4a68760209e62ba323a9ac6bcf8a118564475538c18ed13ce4a56d3d67c2354c3a7f8e3f4a283bdcc78532968715715acab73a48943943e2e444e6f474230c1ee8391ee34cbcfa368a4be2f918724dc9c31e6ea10d5ba3e248708de8e9e00341887df22e6c1eccda8ea8db9942
[Arbitrator3_enc_text] => 6a73044d9b3ae670a29598dbfe057490e68d21f67b691b8a3132debefbee46dc124a0c6a900702a00238e658df1250284c3477e23cfffef05fcd589f025bb1a589fe3689582010ab77318e2498483fe8855d314c2799215117c67402401fcf851563ab2e5421849b888ab3298795a8fc12fa32259a264382383c4f8b4d95fbb1
[Arbitrator4_enc_text] => a4513ed3b369fd85dae21e5561aa13d52886b63171321d686dd8d083ae0db8e64cfd8a19419973e83fa275cc037962633d7694097bf56944d1e78ebd4ecbf321678a095ec27df9ff5555194b6df697ba37f9fd6f7dfa3781202473b908c471e507838d0a7cda04b2502cf276d229b2c0d4fed5329ec8421d4aec86b18f33c502
[Seller_enc_text] => 54b0c7b193aee7fea8cf30a0bff179b41b65b083c3e9cb5562940ee3cd7490fc0d7c17b5bf577798bde829da7d8fa264afb9f6e96242057edd4a04446da2660ef36675f0161f452685fd6cb45e170f4de282dc4913c16a59428053df4a283e96fb77f7d9e6b1d0942bc9e1fac72127bfebba48d3cf0eca4846f32106d3523adf
[Sign] => 82010085c558dd411e816f589d57e48a02bf9231c9dcc55994568e0e00a7db3980c7005d91e88815e5e5a3dc5908a7c4f97c1f973f7ba576c86621f59b608e9d84ce9595710050a42a72e12fa78eb6dd12f8ff90f7004d8b8426a7cf714d7707899e8aafd9dc4534b94292fe849cce765ca975af88f2524874e22439716a59d1473baf115da4d67193320a33f36a442aa1c9711c3145c7499c207fbcc2846f9712bb0dc96c6c59708fd8d25e36a631213679a060a728473be8f23b8f8591bce50b64c67cca00d970fce93a714d2678119b1e67324e9b462986d11239337532a179a6f455f68d3a2e59df24f34590bc032b7c8cc5d633add4bef4c8c18efe7100a5a873
) Satisfying a Moneyback Request
The request of the moneyback is seen by both the seller and the arbitrator. If the seller was able to negotiate with the buyer before the arbitrator made the decision, he can make a refund on his own. If the seller did not make a full money back, then an arbitrator can do it. To make a money back in an amount greater than the amount of the transaction is impossible.

What it looks like from the inside
Transaction example
Transaction structure
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| TYPE | Transaction type |
| TIME | Transaction time |
| USER_ID | ID of the user who created the transaction |
| ORDER_ID | ID of the order for which the money back is made |
| AMOUNT | Sum of money back |
| SIGN | From 1 to 3 signatures (TYPE, TIME, USER_ID, ORDER_ID, AMOUNT) from the user USER_ID |
Transaction example
(
[type] => 62
[time] => 1408470908
[user_id] => 7569
[order_id] => 2725
[amount] => 50.99
[Sign] => 82010085c558dd411e816f589d57e48a02bf9231c9dcc55994568e0e00a7db3980c7005d91e88815e5e5a3dc5908a7c4f97c1f973f7ba576c86621f59b608e9d84ce9595710050a42a72e12fa78eb6dd12f8ff90f7004d8b8426a7cf714d7707899e8aafd9dc4534b94292fe849cce765ca975af88f2524874e22439716a59d1473baf115da4d67193320a33f36a442aa1c9711c3145c7499c207fbcc2846f9712bb0dc96c6c59708fd8d25e36a631213679a060a728473be8f23b8f8591bce50b64c67cca00d970fce93a714d2678119b1e67324e9b462986d11239337532a179a6f455f68d3a2e59df24f34590bc032b7c8cc5d633add4bef4c8c18efe7100a5a873
) Changing the time of the dispute
The time during which manibek is possible may not be enough to make an informed decision by the arbitrator. Therefore, he has the opportunity to increase this period once up to 180 days.

What it looks like from the inside
Transaction example
Transaction structure
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| TYPE | Transaction type |
| TIME | Transaction time |
| USER_ID | ID of the user who created the transaction |
| ORDER_ID | ID of the order for which the time increase is made |
| ADD_TIME | Number of days for which the request will be extended |
| SIGN | From 1 to 3 signatures (TYPE, TIME, USER_ID, ORDER_ID, ADD_TIME) from the user USER_ID |
Transaction example
(
[type] => 62
[time] => 1408470908
[user_id] => 1
[order_id] => 2725
[add_time] => 180
[Sign] => 82010085c558dd411e816f589d57e48a02bf9231c9dcc55994568e0e00a7db3980c7005d91e88815e5e5a3dc5908a7c4f97c1f973f7ba576c86621f59b608e9d84ce9595710050a42a72e12fa78eb6dd12f8ff90f7004d8b8426a7cf714d7707899e8aafd9dc4534b94292fe849cce765ca975af88f2524874e22439716a59d1473baf115da4d67193320a33f36a442aa1c9711c3145c7499c207fbcc2846f9712bb0dc96c6c59708fd8d25e36a631213679a060a728473be8f23b8f8591bce50b64c67cca00d970fce93a714d2678119b1e67324e9b462986d11239337532a179a6f455f68d3a2e59df24f34590bc032b7c8cc5d633add4bef4c8c18efe7100a5a873
) disadvantages
The main disadvantage of arbitration is that arbitrators must have a high degree of trust among sellers / buyers and have a reputation as fair judges who do not save time on carrying out full investigations of each dispute so that they can safely trust and not worry about anything.
Total
As a result, to all the charms of independence, which gives the decentralization of electronic money, added one of the main advantages of classical payment instruments - the ability to challenge the transaction.
Tests
There are 20 dUSD on my account, which I am ready to distribute for tests (1 dUSD each), write to the PM. About 50 dUSD are on the stock exchange.
web-wallet and exe , source
List of services already accepting Dcoins:
racktech.ru
m4host.net
steadyhost.ru
komtet.ru (their chief engineer suggested the idea of arbitration, for which many thanks to him)
PS
I don’t have much usability and interfaces, so I’ll be grateful for advice on where things can be improved.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/247685/
All Articles