Evolution of Zeus. Part III
The previous part is here .
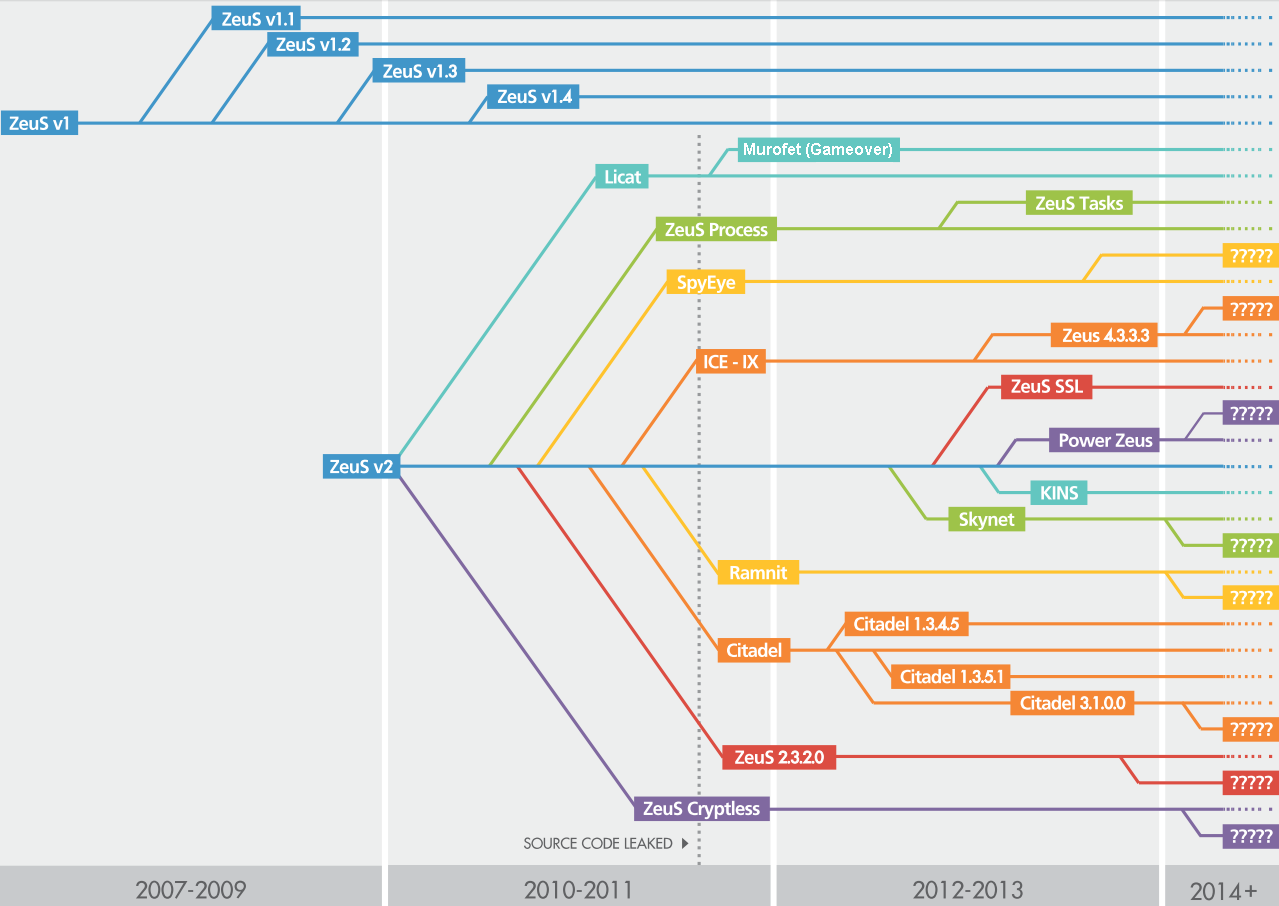
At the end of March 2012, Microsoft conducted a set of activities, codenamed Operation b71 , aimed at disabling some elements of the Zeus infrastructure, as well as SpyEye and Ice IX (a project based on the source code of Zeus). As a result, the work of the command servers on two hosting sites was terminated: in the cities of Scranton (Pennsylvania) and Lombard (Illinois). Also, two IP addresses and about 800 domains were removed from the botnet management structure.
This operation has been heavily criticized by the IT security community. In particular, Fox-IT specialists noted that Microsoft in its reporting documents not only disclosed information about suspects, including authors and individual users, but also completely unrelated persons. At the same time, all these data were the property of the IT security community and were not subject to disclosure in connection with the conduct of operational search activities. In addition, some domain names belonged to legal, but hacked resources. Among other things, it was found that, despite the statement by Microsoft that a disconnection simply occurred for the domain names that were withdrawn, this was not the case and the syncholy process went at full speed, that is, during it not only the IP addresses of the victims were saved, but also recorded HTTP requests with all the headers, which, in fact, could include various confidential information, including user names, email addresses, passwords, etc.
In addition, this operation almost did not affect the Zeus Gameover botnet. This is how Microsoft works, a lot of PR plus a lot of its colleagues in the workshop for a minute of glory. The materials feature Slavik and Gribodemon, to whose personalities we will return.
')
Nevertheless, while promoting the chain of links of cybercriminals, the experts also took the Trojan Citadel and its developer AquaBox under the scope. He, clearly noticing close attention to his person, at the end of 2012 lay down and stopped the open sale of his product.
The decisive impact on the infrastructure of Citadel was dealt in May-June 2013 during the Operation b54 event held jointly by Microsoft and the FBI. The essence of the operation was to remove 4,000 domain names that were used by Citadel. In fact, 1462 domain names were withdrawn, redirection to Microsoft servers for synchol was made for them. According to experts of the whole Trojan, Citadel infected about 5 million computers, mainly in the USA, Europe, Hong Kong, Singapore, India and Australia.
But here, Microsoft could not help but fix it. As it turned out , about 1000 domain names belonged to other security companies and were used specifically for monitoring. This circumstance was noticed by the owner of the tracker abuse.ch Roman Hüssi, who simultaneously lost about 300 domain names used for syncholy.
The ultimate goal of management interception is the distribution of specially configured Microsoft configuration files for Citadel, in which antivirus companies' websites were blocked. This feature, redirect for sites from the black list, was distinctive for Citadel, it appeared in version 1.3.5.1 of the Rain Edition, it was not in the original Zeus. And then a natural ethical question arises, and which other commands could potentially be given to Microsoft through “its” config? In general, it is strange that the Citadel developers have not implemented a digital signature mechanism for the configuration file.
Meanwhile, Citadel developers continued closed sales. In June 2013, Trend Micro experts discovered Citadel version 3.1.0.0, which had the function of distributing via USB devices. And in July, there were reports in the press that the banking systems of Japan were attacked with just this version. Nine command servers were identified and accessed from about 20,000 unique IP addresses, with 96% of the infected systems located in Japan.
While the security men were struggling with numerous variations of Zeus version 2 (a small digression - information about the x64 version of Zeus 2 with C & C on the TOR network from December 2013 here ), KINS - Kasper Internet Non Security appeared on the underground scene. According to Fox-IT, the private version of KINS, based almost entirely on Zeus source codes, has been used since December 2011 to attack the banking systems of Germany and the Netherlands. And then some confusion begins. The fact is that close attention to KINS was paid much later, in 2013.
As already mentioned here, in 2012-2013, a wave of operations against banking Trojans took place. In addition to Operation b71 and Operation b54, in 2012, mass arrests of cyber-group members using Carberp, which ended with the arrest of Carberp developers in Ukraine in March 2013, were made. One way or another, the underground since 2012 has become an urgent need for another tool with appropriate support for bank robberies.
Apparently, the name KINS later began to be used as a kind of brand, that is, in 2013 they released a relatively new product, which the security officers began to call after the old one - KINS. However, it is more correct to call this version a PowerZeus or ZeusVM.
Distinctive features of this version:
In addition, it is noticeable that the base for the dropper served as PowerLoader 2 (hence the PowerZeus). In fact, it uses the source code of the Zeus and SpyEye grabbers as a dll as modules. The French researcher Xylitol conducted his KINS study on the basis of source codes, and came to the conclusion that KINS = Zeus 2.0.8.9 + Power Loader 2.0 + SpyEye Plugins. Interestingly, in the course of his research, Xylitol came out on the KINS developer, he got his Jabber from the hacked KINS test admin. A rather interesting dialogue took place with the developer.
During the dialogue, it turned out that he was hired to develop KINS, but then "something went wrong." All his work was stolen during hacking, and that KINS source code, which was merged into the network, is a very raw alpha of the final product. Anyway, the development and closed sale of KINS is underway, and KINS and ZeusVM have become forks being developed by different teams.
ZeusVM, in particular, was used during the attacks of the Polish RB systems in the summer of 2013. A distinctive feature of the attack was that the config with web injections was not downloaded from the Internet (although the URL to the config URL was), but was entirely contained inside one of the sections of the PE file.
During the development of ZeusVM, additional features such as the use of steganography (November 2013) were implemented, when the config after processing xor, rc4 and base64 was introduced into the jpg image, as well as the change of the hook installation mechanism (May 2014) borrowed from Carberp. The last change, many rushed to announce, as another super cool Zeus and Carberp hybrid called Zberp , but in reality this is just another buggy.
The current state of affairs shows that, for the most part, cybercriminals have switched from using Citadel to ZeusVM.
As you can see, several Zeus forks are developed in parallel by several teams of intruders. Let's go back to the “main” Zeus branch called GameOver (aka Murofet). In total, there are three versions of it:
Version 3 appeared after another operation called “Tovar”, conducted from April to June 2014 jointly by the FBI, Europol and a number of companies working in the field of information security, such as CrowdStrike, Dell SecureWorks, Symantec, Trend Micro and McAfee. In the course of the investigation, it was established that Zeus GameOver was managed with the help of more than ten servers, which were located on the bulletproof site of one of the hosting providers in Odessa. Thus, the main control center was deactivated.
As a result of the disclosure of the hacker grouping Zeus GameOver, one of the alleged organizers was named - 30-year-old resident of Russia Yevgeny Bogachyov, he was put on the wanted list by the FBI. He was charged in absentia on the basis of intercepted negotiations in one of the chats. In them, Bogachev, writing under the nicknames Lucky12345 and Slavik, confesses to the interlocutor that he is the creator of the Zeus Trojan.
By the way, in 2013, the US authorities announced the arrest of a Russian citizen Alexander Panin, who was detained on June 28 by Interpol officers and extradited from the Dominican Republic to the United States. January 28, 2014 at the trial in Atlanta Panin admitted that he was one of the SpyEye developers and his pseudonym - Gribodemon. How to know if it was not through Panin that the law enforcement agencies came to Bogachev?
According to Interpol, more than 1 million computers worldwide have been infected with Zeus GameOver, the cumulative financial damage from theft from RBS systems is estimated at 75 million euros. In addition, through Zeus GameOver, 234,000 computers were installed with the malicious software CryptoLocker, with which the ransom was collected in the amount of 27 million US dollars. For distribution of Zeus GameOver, the power of the Cutwail botnet and the PonyLoader bootloader were used.
In August 2013, experts at the Dell SecureWorks Counter Threat Unit discovered that in addition to the PonyLoader, cybercriminals use the new Upatre loader to distribute the Zeus GameOver. Its file is small and extremely simple. Upatre uses an SSL connection to download and run the necessary malicious file, whose URL is hard-coded inside the loader code. Like the Pony Loader, Upatre was distributed via the Cutwail spam botnet as an attachment, which is a zip archive.
Since the end of January, the scheme has been slightly improved, the Zeus GameOver executable file has been compressed, encrypted with the xor operation using a 32-bit key, and the resulting file has the extension .enc. When decrypting, the updated version of Upatre reverses this process and gets the original executable file.
Since February 2014, Zeus GameOver has gotten a Necurs rootkit to hide its presence. The dropper contained x86 and x64 versions of the kernel mode driver. To raise the privileges, if there are no administrator rights required to install the driver, use the CVE-2010-4398 exploit. The x64 driver is signed, but since the certificate is not on the list of trusted ones, to bypass PathGuard, the regular bcdedit.exe utility is called to set the TESTSIGNING boot option.
Anyway, after the operation “Tovar” Zeus GameOver has not disappeared anywhere. Its next version , without P2P, Necurs and with Fast Flux support continues to spread by cybercriminals.
In December 2014, Kaspersky Lab employees announced the discovery of a new version of Zeus, called Chthonic . This version is a kind of hybrid bootloader Andromeda and ZeusVM. Chthonic has a modular structure, the following modules have been discovered to date:
By the version number you can see that the evolution of Zeus is in full swing. Moreover, in the summer of 2014, new players in the field of banking Trojans - Pandemiya and Kronos (a little technical analysis here ) appeared on the black market, not using the source codes of Zeus and Carberp.

Crusade
At the end of March 2012, Microsoft conducted a set of activities, codenamed Operation b71 , aimed at disabling some elements of the Zeus infrastructure, as well as SpyEye and Ice IX (a project based on the source code of Zeus). As a result, the work of the command servers on two hosting sites was terminated: in the cities of Scranton (Pennsylvania) and Lombard (Illinois). Also, two IP addresses and about 800 domains were removed from the botnet management structure.
This operation has been heavily criticized by the IT security community. In particular, Fox-IT specialists noted that Microsoft in its reporting documents not only disclosed information about suspects, including authors and individual users, but also completely unrelated persons. At the same time, all these data were the property of the IT security community and were not subject to disclosure in connection with the conduct of operational search activities. In addition, some domain names belonged to legal, but hacked resources. Among other things, it was found that, despite the statement by Microsoft that a disconnection simply occurred for the domain names that were withdrawn, this was not the case and the syncholy process went at full speed, that is, during it not only the IP addresses of the victims were saved, but also recorded HTTP requests with all the headers, which, in fact, could include various confidential information, including user names, email addresses, passwords, etc.
In addition, this operation almost did not affect the Zeus Gameover botnet. This is how Microsoft works, a lot of PR plus a lot of its colleagues in the workshop for a minute of glory. The materials feature Slavik and Gribodemon, to whose personalities we will return.
')
Nevertheless, while promoting the chain of links of cybercriminals, the experts also took the Trojan Citadel and its developer AquaBox under the scope. He, clearly noticing close attention to his person, at the end of 2012 lay down and stopped the open sale of his product.
The decisive impact on the infrastructure of Citadel was dealt in May-June 2013 during the Operation b54 event held jointly by Microsoft and the FBI. The essence of the operation was to remove 4,000 domain names that were used by Citadel. In fact, 1462 domain names were withdrawn, redirection to Microsoft servers for synchol was made for them. According to experts of the whole Trojan, Citadel infected about 5 million computers, mainly in the USA, Europe, Hong Kong, Singapore, India and Australia.
But here, Microsoft could not help but fix it. As it turned out , about 1000 domain names belonged to other security companies and were used specifically for monitoring. This circumstance was noticed by the owner of the tracker abuse.ch Roman Hüssi, who simultaneously lost about 300 domain names used for syncholy.
The ultimate goal of management interception is the distribution of specially configured Microsoft configuration files for Citadel, in which antivirus companies' websites were blocked. This feature, redirect for sites from the black list, was distinctive for Citadel, it appeared in version 1.3.5.1 of the Rain Edition, it was not in the original Zeus. And then a natural ethical question arises, and which other commands could potentially be given to Microsoft through “its” config? In general, it is strange that the Citadel developers have not implemented a digital signature mechanism for the configuration file.
Meanwhile, Citadel developers continued closed sales. In June 2013, Trend Micro experts discovered Citadel version 3.1.0.0, which had the function of distributing via USB devices. And in July, there were reports in the press that the banking systems of Japan were attacked with just this version. Nine command servers were identified and accessed from about 20,000 unique IP addresses, with 96% of the infected systems located in Japan.
Hype and confusion
While the security men were struggling with numerous variations of Zeus version 2 (a small digression - information about the x64 version of Zeus 2 with C & C on the TOR network from December 2013 here ), KINS - Kasper Internet Non Security appeared on the underground scene. According to Fox-IT, the private version of KINS, based almost entirely on Zeus source codes, has been used since December 2011 to attack the banking systems of Germany and the Netherlands. And then some confusion begins. The fact is that close attention to KINS was paid much later, in 2013.
As already mentioned here, in 2012-2013, a wave of operations against banking Trojans took place. In addition to Operation b71 and Operation b54, in 2012, mass arrests of cyber-group members using Carberp, which ended with the arrest of Carberp developers in Ukraine in March 2013, were made. One way or another, the underground since 2012 has become an urgent need for another tool with appropriate support for bank robberies.
Apparently, the name KINS later began to be used as a kind of brand, that is, in 2013 they released a relatively new product, which the security officers began to call after the old one - KINS. However, it is more correct to call this version a PowerZeus or ZeusVM.
Distinctive features of this version:
- using VMProtect to obstruct its analysis (hence ZeusVM);
- Detection of the execution of your code in the environment of virtual machines and sandboxes;
- use SSL to communicate with the command center;
- deleting your startup key at startup and restoring before rebooting.
In addition, it is noticeable that the base for the dropper served as PowerLoader 2 (hence the PowerZeus). In fact, it uses the source code of the Zeus and SpyEye grabbers as a dll as modules. The French researcher Xylitol conducted his KINS study on the basis of source codes, and came to the conclusion that KINS = Zeus 2.0.8.9 + Power Loader 2.0 + SpyEye Plugins. Interestingly, in the course of his research, Xylitol came out on the KINS developer, he got his Jabber from the hacked KINS test admin. A rather interesting dialogue took place with the developer.
During the dialogue, it turned out that he was hired to develop KINS, but then "something went wrong." All his work was stolen during hacking, and that KINS source code, which was merged into the network, is a very raw alpha of the final product. Anyway, the development and closed sale of KINS is underway, and KINS and ZeusVM have become forks being developed by different teams.
ZeusVM, in particular, was used during the attacks of the Polish RB systems in the summer of 2013. A distinctive feature of the attack was that the config with web injections was not downloaded from the Internet (although the URL to the config URL was), but was entirely contained inside one of the sections of the PE file.
During the development of ZeusVM, additional features such as the use of steganography (November 2013) were implemented, when the config after processing xor, rc4 and base64 was introduced into the jpg image, as well as the change of the hook installation mechanism (May 2014) borrowed from Carberp. The last change, many rushed to announce, as another super cool Zeus and Carberp hybrid called Zberp , but in reality this is just another buggy.
The current state of affairs shows that, for the most part, cybercriminals have switched from using Citadel to ZeusVM.
End of the game?
As you can see, several Zeus forks are developed in parallel by several teams of intruders. Let's go back to the “main” Zeus branch called GameOver (aka Murofet). In total, there are three versions of it:
- Version 1, distributed since September 2011, first implemented P2P functionality, using DGA as a backup channel;
- version 2, discovered in February 2012, in this version both the DGA algorithm and the P2P mechanism were improved;
- version 3, began to spread in July 2014, its distinctive feature is the use of the Fast Flux algorithm for working with a command server, while the P2P functionality has been completely removed.
Version 3 appeared after another operation called “Tovar”, conducted from April to June 2014 jointly by the FBI, Europol and a number of companies working in the field of information security, such as CrowdStrike, Dell SecureWorks, Symantec, Trend Micro and McAfee. In the course of the investigation, it was established that Zeus GameOver was managed with the help of more than ten servers, which were located on the bulletproof site of one of the hosting providers in Odessa. Thus, the main control center was deactivated.
As a result of the disclosure of the hacker grouping Zeus GameOver, one of the alleged organizers was named - 30-year-old resident of Russia Yevgeny Bogachyov, he was put on the wanted list by the FBI. He was charged in absentia on the basis of intercepted negotiations in one of the chats. In them, Bogachev, writing under the nicknames Lucky12345 and Slavik, confesses to the interlocutor that he is the creator of the Zeus Trojan.
By the way, in 2013, the US authorities announced the arrest of a Russian citizen Alexander Panin, who was detained on June 28 by Interpol officers and extradited from the Dominican Republic to the United States. January 28, 2014 at the trial in Atlanta Panin admitted that he was one of the SpyEye developers and his pseudonym - Gribodemon. How to know if it was not through Panin that the law enforcement agencies came to Bogachev?
According to Interpol, more than 1 million computers worldwide have been infected with Zeus GameOver, the cumulative financial damage from theft from RBS systems is estimated at 75 million euros. In addition, through Zeus GameOver, 234,000 computers were installed with the malicious software CryptoLocker, with which the ransom was collected in the amount of 27 million US dollars. For distribution of Zeus GameOver, the power of the Cutwail botnet and the PonyLoader bootloader were used.
In August 2013, experts at the Dell SecureWorks Counter Threat Unit discovered that in addition to the PonyLoader, cybercriminals use the new Upatre loader to distribute the Zeus GameOver. Its file is small and extremely simple. Upatre uses an SSL connection to download and run the necessary malicious file, whose URL is hard-coded inside the loader code. Like the Pony Loader, Upatre was distributed via the Cutwail spam botnet as an attachment, which is a zip archive.
Since the end of January, the scheme has been slightly improved, the Zeus GameOver executable file has been compressed, encrypted with the xor operation using a 32-bit key, and the resulting file has the extension .enc. When decrypting, the updated version of Upatre reverses this process and gets the original executable file.
Since February 2014, Zeus GameOver has gotten a Necurs rootkit to hide its presence. The dropper contained x86 and x64 versions of the kernel mode driver. To raise the privileges, if there are no administrator rights required to install the driver, use the CVE-2010-4398 exploit. The x64 driver is signed, but since the certificate is not on the list of trusted ones, to bypass PathGuard, the regular bcdedit.exe utility is called to set the TESTSIGNING boot option.
Anyway, after the operation “Tovar” Zeus GameOver has not disappeared anywhere. Its next version , without P2P, Necurs and with Fast Flux support continues to spread by cybercriminals.
New Spiral Coil
In December 2014, Kaspersky Lab employees announced the discovery of a new version of Zeus, called Chthonic . This version is a kind of hybrid bootloader Andromeda and ZeusVM. Chthonic has a modular structure, the following modules have been discovered to date:
- main - the main module (version 4.6.15.0 - v4.7.0.0);
- info - collection of information about the system;
- pony - a module to steal stored passwords;
- klog - keylogger;
- http - webinject and formgrabber module;
- vnc - remote access;
- socks - proxy;
- cam_recorder - webcam video recording.
By the version number you can see that the evolution of Zeus is in full swing. Moreover, in the summer of 2014, new players in the field of banking Trojans - Pandemiya and Kronos (a little technical analysis here ) appeared on the black market, not using the source codes of Zeus and Carberp.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/247265/
All Articles