Microsoft CloudOS Network - what is it?
Hello,
Let's talk a bit today about IaaS, hybrid history, service providers, hosting and Microsoft. In the new year we will pay more attention to this interesting topic, and we begin by telling you what we have and what CloudOS is and why the COSN network (which includes representative companies like Softline and Parking.ru ) is important.
All posts from the series "Hybrid history" are marked with the corresponding tag hybridstory .
')
So, as we all know, the virtual dedicated server service appeared on the Russian market more than 7 years ago, and was immediately picked up by the largest players in the hosting arena. The evolution of this service is infrastructure as a service (the same IaaS - Infrastracture-As-A-Service).
VPS (Virtual Private Server), also known as VDS (Virtual Dedicated Service), is a virtual machine rental service operating in a data center hosting provider. The service takes up space between virtual hosting (traditionally hosting websites and databases, when services from different users run on the same physical server within the same OS) and a dedicated physical server (you are the king and god of your physical server, and do not share it with by whom).
VPS is used in cases when you want to have full control over the services inside the virtual machine, fine-tune the OS, and also in cases when you want to be able to install any software inside the OS - from game servers to 1C services. At the same time, VPS is traditionally cheaper than renting a dedicated physical server, plus there is no need to bother with failed fans and incompatible drivers.
During these 7 years, the server virtualization market has grown significantly, respectively, and the rental market for dedicated physical servers has also decreased significantly. Many companies want to remove some of the servers from their server to a large data center hosting provider, but they also want to retain all the flexibility that the server-side virtualization system already provides for them. They are faced with the fact that the set of virtual machines that they can buy as part of the VPS service is not an equivalent replacement for what they receive from the internal virtualization environment. And here IaaS is just entering the scene.
In the Microsoft view, IaaS consists of the following main elements:
What is a virtual machine, most likely, is clear to everyone. :)
Virtual storage is the disk space available to the client for use. The client does not know how the storage network is built, which storage systems are used, on which disks and on which types of RAID arrays the storage is collected. The client simply receives the required Nbytes of space and can choose which type of storage he buys - fast, but expensive (for example, on SSD disks), or cheap and roomy, but slow (for example, on SATA disks).
But virtual networks are exactly what allows on IaaS to implement such scenarios that were impossible using VPS. Virtual networks are isolated networks that a client can create with the necessary IP addresses and DHCP settings. And also, in our case, it can configure the Site-to-Site VPN connection between the data center of the hosting provider and its own offices. At the same time, virtual machines of several customers can work on the same host, but they cannot see each other at all. They can even use the same IP address type 192.168.1.1 - not scary, the networks are isolated from each other and do not look directly into the Internet.
It turns out that in the case of IaaS, the client can independently create an isolated network between its virtual machines running at the hosting provider (on different hosts or even in different data centers), and then connect this virtual network with its physical network using Site-to- Site VPN. It can use the usual address space, add virtual machines to an existing domain, while virtual machines will not have direct access to the Internet. You can even get them to go online through an existing proxy server, which is located in one of the offices.
Although, if you wish, of course, virtual machines can be allocated as a full-fledged external IP-address (as in the case of VPS) or released to the Internet through a single NAT gateway hosting provider. But the client at the same time will be able to configure the rules of NAT and publish only the services he needs on the Internet.
The concept of IaaS implies that all routine actions are automated (both by the hosting provider and the client), services are customizable as much as possible, and you need to call for technical support and ask for something to set up or change much less often.
The concept of IaaS also implies a transition from payment for a virtual machine to payment for consumed resources (as was done in Microsoft Azure). That is, you buy from a hosting provider 20 virtual cores, 48 gigabytes of RAM and 1 terabyte of fast disk storage. You can use these resources at your discretion — at least deploy one large virtual machine, at least a dozen small ones.
The monetization model of different hosting providers may differ (for example, Azure counts everything — IOPS, disk space, and traffic), someone may traditionally take money for each virtual machine, and not for consumed resources. We can only give recommendations to our partners and provide tools for measuring consumption, but the decision about what and how to count, each of them takes on their own.
In 2013, Microsoft presented its vision of an operating system that is uniform for use on customer’s servers, in public cloud services and in data centers hosting providers. This vision was called CloudOS.
According to CloudOS ideology, you can easily transfer virtual machines and physical servers running Windows Server to the Microsoft Azure cloud or to a hosting provider. Or back. All 3 scenarios use the same format of virtual machines and virtual disks Hyper-V, which gives us such freedom of choice and mobility.
But hosting providers in the global market are many, and not all of them could quickly remake their infrastructure under the CloudOS ideology and can provide hybrid cloud services. To differentiate hosting providers that are compatible with the ideologies of CloudOS, we are introducing a new affiliate program - CloudOS Network.
CloudOS Network (COSN) is a closed network of hosting providers around the world who provide IaaS service according to the ideology of CloudOS. In essence, this means that the hosting provider uses Hyper-V 2012 R2 as the hypervisor, System Center 2012 R2 as the management environment, and the Windows Azure Pack as a self-service portal for users (or only its API, which is used by hosting companies). provider service control panel can integrate with the infrastructure of Hyper-V and System Center).
Each of our partners participating in the program undergoes regular checks for compliance with the quality of customer service and the reliability of the service infrastructure. We must be confident in those whom we call the CloudOS Network-partner, so that our customers are sure that they choose high-quality and reliable service.
You can get a list of hosting providers in your region participating in the CloudOS Network program on the official website of the program .
The program was launched globally only a few months ago, so there are not so many hosting providers on the Russian market yet. But we are actively working on adding new partners to the catalog, and by the end of next year there will be many times more.
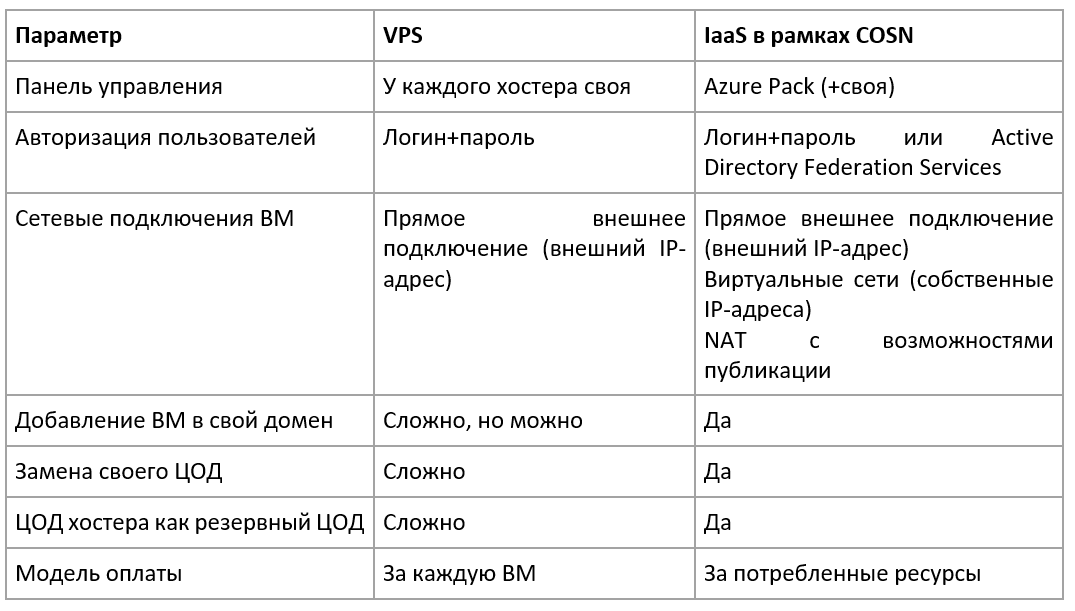
At first glance, IaaS under the CloudOS Network and VPS programs are quite similar - both there and there you get a set of virtual machines to which you have access. But IaaS allows you to implement more usage scenarios due to its distinctive features.
In most cases, VPS did not allow to transfer all servers from your server to a hosting provider. Usually, everything was limited to several servers that were running services for external consumers - websites, b2b-systems, etc.
In the case of IaaS, your virtual network in the data center hosting provider is an extension of your own network - with the same addressing and settings.
For example, you have a main office in Moscow, where you have a large server. And there are a dozen regional offices, in which there are 2-5 servers each. Most likely, you already use virtualization in the branches. Hyper-V is very often used as a hypervisor in branches in Russia, which greatly facilitates the migration process.
What you can do: transfer the files of your virtual machines to the cloud of the service provider, create your own virtual networks there, and then push the Site-to-Site VPS connection between each office and the data center of the service provider. Your virtual machines are transferred to the data center of the service provider and work there, but consumers in offices will not even notice the difference - the IP addresses are the same, and if suddenly the bandwidth of the Internet channel in the remote office is not enough to work correctly with the server located at the hoster, then the hoster will be able to conduct you a fast L2 channel to your data center.
You can also use the service provider data center as a backup for the data center at the head office - virtual machines and servers will simply be replicated from your servers to the service provider’s cloud, and in the case of, for example, if you have disconnected electricity from the server and important services have stopped, You can run the necessary servers in the service provider cloud, and with the same IP addresses.
So, we have solutions for building a private cloud on your servers. Plus, we have CloudOS Network - a community of service providers offering IaaS services with technologies you already know. And we have our own Microsoft Azure cloud.
When you think about hosting servers, you can choose flexibly, deploy them in your home office, in a service provider data center in Russia, or in the Microsoft Azure cloud. For example, you leave heavy SAP servers. Services related to personal data, transfer to the data center service provider in Russia. And public services, and services that can be placed abroad, for which maximum reliability is needed, are transferred to Microsoft Azure. Users get a reliable service that can work on servers in the next room (Private Cloud), in your city (CloudOS Network) or abroad (Microsoft Azure). With the use of virtual networks for you all this turns into one large internal network.
If you want to move the server to the cloud to reduce the cost of ownership, but Microsoft Azure for some reason does not suit you - the cloud hoster, a member of the CloudOS Network, will be the best choice.
Visit the CloudOS Network site and select the service provider: http://aka.ms/cosnru
Let's talk a bit today about IaaS, hybrid history, service providers, hosting and Microsoft. In the new year we will pay more attention to this interesting topic, and we begin by telling you what we have and what CloudOS is and why the COSN network (which includes representative companies like Softline and Parking.ru ) is important.
All posts from the series "Hybrid history" are marked with the corresponding tag hybridstory .

')
So, as we all know, the virtual dedicated server service appeared on the Russian market more than 7 years ago, and was immediately picked up by the largest players in the hosting arena. The evolution of this service is infrastructure as a service (the same IaaS - Infrastracture-As-A-Service).
VPS (Virtual Private Server), also known as VDS (Virtual Dedicated Service), is a virtual machine rental service operating in a data center hosting provider. The service takes up space between virtual hosting (traditionally hosting websites and databases, when services from different users run on the same physical server within the same OS) and a dedicated physical server (you are the king and god of your physical server, and do not share it with by whom).
VPS is used in cases when you want to have full control over the services inside the virtual machine, fine-tune the OS, and also in cases when you want to be able to install any software inside the OS - from game servers to 1C services. At the same time, VPS is traditionally cheaper than renting a dedicated physical server, plus there is no need to bother with failed fans and incompatible drivers.
During these 7 years, the server virtualization market has grown significantly, respectively, and the rental market for dedicated physical servers has also decreased significantly. Many companies want to remove some of the servers from their server to a large data center hosting provider, but they also want to retain all the flexibility that the server-side virtualization system already provides for them. They are faced with the fact that the set of virtual machines that they can buy as part of the VPS service is not an equivalent replacement for what they receive from the internal virtualization environment. And here IaaS is just entering the scene.
Microsoft IaaS and technology
In the Microsoft view, IaaS consists of the following main elements:
- Virtual machines
- Virtual storage
- Virtual networks
What is a virtual machine, most likely, is clear to everyone. :)
Virtual storage is the disk space available to the client for use. The client does not know how the storage network is built, which storage systems are used, on which disks and on which types of RAID arrays the storage is collected. The client simply receives the required Nbytes of space and can choose which type of storage he buys - fast, but expensive (for example, on SSD disks), or cheap and roomy, but slow (for example, on SATA disks).
But virtual networks are exactly what allows on IaaS to implement such scenarios that were impossible using VPS. Virtual networks are isolated networks that a client can create with the necessary IP addresses and DHCP settings. And also, in our case, it can configure the Site-to-Site VPN connection between the data center of the hosting provider and its own offices. At the same time, virtual machines of several customers can work on the same host, but they cannot see each other at all. They can even use the same IP address type 192.168.1.1 - not scary, the networks are isolated from each other and do not look directly into the Internet.
It turns out that in the case of IaaS, the client can independently create an isolated network between its virtual machines running at the hosting provider (on different hosts or even in different data centers), and then connect this virtual network with its physical network using Site-to- Site VPN. It can use the usual address space, add virtual machines to an existing domain, while virtual machines will not have direct access to the Internet. You can even get them to go online through an existing proxy server, which is located in one of the offices.
Although, if you wish, of course, virtual machines can be allocated as a full-fledged external IP-address (as in the case of VPS) or released to the Internet through a single NAT gateway hosting provider. But the client at the same time will be able to configure the rules of NAT and publish only the services he needs on the Internet.
The concept of IaaS implies that all routine actions are automated (both by the hosting provider and the client), services are customizable as much as possible, and you need to call for technical support and ask for something to set up or change much less often.
The concept of IaaS also implies a transition from payment for a virtual machine to payment for consumed resources (as was done in Microsoft Azure). That is, you buy from a hosting provider 20 virtual cores, 48 gigabytes of RAM and 1 terabyte of fast disk storage. You can use these resources at your discretion — at least deploy one large virtual machine, at least a dozen small ones.
The monetization model of different hosting providers may differ (for example, Azure counts everything — IOPS, disk space, and traffic), someone may traditionally take money for each virtual machine, and not for consumed resources. We can only give recommendations to our partners and provide tools for measuring consumption, but the decision about what and how to count, each of them takes on their own.
CloudOS Network
In 2013, Microsoft presented its vision of an operating system that is uniform for use on customer’s servers, in public cloud services and in data centers hosting providers. This vision was called CloudOS.
According to CloudOS ideology, you can easily transfer virtual machines and physical servers running Windows Server to the Microsoft Azure cloud or to a hosting provider. Or back. All 3 scenarios use the same format of virtual machines and virtual disks Hyper-V, which gives us such freedom of choice and mobility.
But hosting providers in the global market are many, and not all of them could quickly remake their infrastructure under the CloudOS ideology and can provide hybrid cloud services. To differentiate hosting providers that are compatible with the ideologies of CloudOS, we are introducing a new affiliate program - CloudOS Network.
CloudOS Network (COSN) is a closed network of hosting providers around the world who provide IaaS service according to the ideology of CloudOS. In essence, this means that the hosting provider uses Hyper-V 2012 R2 as the hypervisor, System Center 2012 R2 as the management environment, and the Windows Azure Pack as a self-service portal for users (or only its API, which is used by hosting companies). provider service control panel can integrate with the infrastructure of Hyper-V and System Center).
Each of our partners participating in the program undergoes regular checks for compliance with the quality of customer service and the reliability of the service infrastructure. We must be confident in those whom we call the CloudOS Network-partner, so that our customers are sure that they choose high-quality and reliable service.
You can get a list of hosting providers in your region participating in the CloudOS Network program on the official website of the program .
The program was launched globally only a few months ago, so there are not so many hosting providers on the Russian market yet. But we are actively working on adding new partners to the catalog, and by the end of next year there will be many times more.
IaaS vs VPS
At first glance, IaaS under the CloudOS Network and VPS programs are quite similar - both there and there you get a set of virtual machines to which you have access. But IaaS allows you to implement more usage scenarios due to its distinctive features.

Empty server
In most cases, VPS did not allow to transfer all servers from your server to a hosting provider. Usually, everything was limited to several servers that were running services for external consumers - websites, b2b-systems, etc.
In the case of IaaS, your virtual network in the data center hosting provider is an extension of your own network - with the same addressing and settings.
For example, you have a main office in Moscow, where you have a large server. And there are a dozen regional offices, in which there are 2-5 servers each. Most likely, you already use virtualization in the branches. Hyper-V is very often used as a hypervisor in branches in Russia, which greatly facilitates the migration process.
What you can do: transfer the files of your virtual machines to the cloud of the service provider, create your own virtual networks there, and then push the Site-to-Site VPS connection between each office and the data center of the service provider. Your virtual machines are transferred to the data center of the service provider and work there, but consumers in offices will not even notice the difference - the IP addresses are the same, and if suddenly the bandwidth of the Internet channel in the remote office is not enough to work correctly with the server located at the hoster, then the hoster will be able to conduct you a fast L2 channel to your data center.
You can also use the service provider data center as a backup for the data center at the head office - virtual machines and servers will simply be replicated from your servers to the service provider’s cloud, and in the case of, for example, if you have disconnected electricity from the server and important services have stopped, You can run the necessary servers in the service provider cloud, and with the same IP addresses.
Hybrid cloud
So, we have solutions for building a private cloud on your servers. Plus, we have CloudOS Network - a community of service providers offering IaaS services with technologies you already know. And we have our own Microsoft Azure cloud.
When you think about hosting servers, you can choose flexibly, deploy them in your home office, in a service provider data center in Russia, or in the Microsoft Azure cloud. For example, you leave heavy SAP servers. Services related to personal data, transfer to the data center service provider in Russia. And public services, and services that can be placed abroad, for which maximum reliability is needed, are transferred to Microsoft Azure. Users get a reliable service that can work on servers in the next room (Private Cloud), in your city (CloudOS Network) or abroad (Microsoft Azure). With the use of virtual networks for you all this turns into one large internal network.
If you want to move the server to the cloud to reduce the cost of ownership, but Microsoft Azure for some reason does not suit you - the cloud hoster, a member of the CloudOS Network, will be the best choice.
Visit the CloudOS Network site and select the service provider: http://aka.ms/cosnru
useful links
- Registration in the BizSpark program
- Try Azure for free for 30 days!
- Microsoft Azure Development Center (azurehub.ru) - scripts, tutorials, examples, design recommendations
- Twitter.com/windowsazure_ru - the latest Microsoft Azure news
- Microsoft Azure Community on Facebook - experts, questions
- Explore Microsoft Virtual Academy courses on cloud and other technologies
- Business and the cloud: best practices solutions
- Windows 8.1 Update for large organizations. Beginning of work
- Microsoft Hybrid Cloud: Typical Solutions Guide
- Toolkit for preparing users for Windows 8.1
- Introduction to the Win2D Graphic Library
- Download free or trial Visual Studio
- Become a universal Windows application developer
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/247085/
All Articles