ABAP Development for SAP HANA
Hello, habrasoobschestvo!
In this article, I would like to highlight the new approaches to the development of ABAP, with reference to SAP HANA. We will look at the new elements of the ABAP language, which will make it possible to more effectively use the opportunities offered by SAP HANA.
Suppose we have a report written in the ABAP language, the work time of which does not suit us. We want to optimize the performance of this report. The main idea of changing the logic of the report, is that part of the logic of the report, which intensively uses data from the DBMS (in our case, this is SAP HANA), will be delegated to the DBMS level.
')
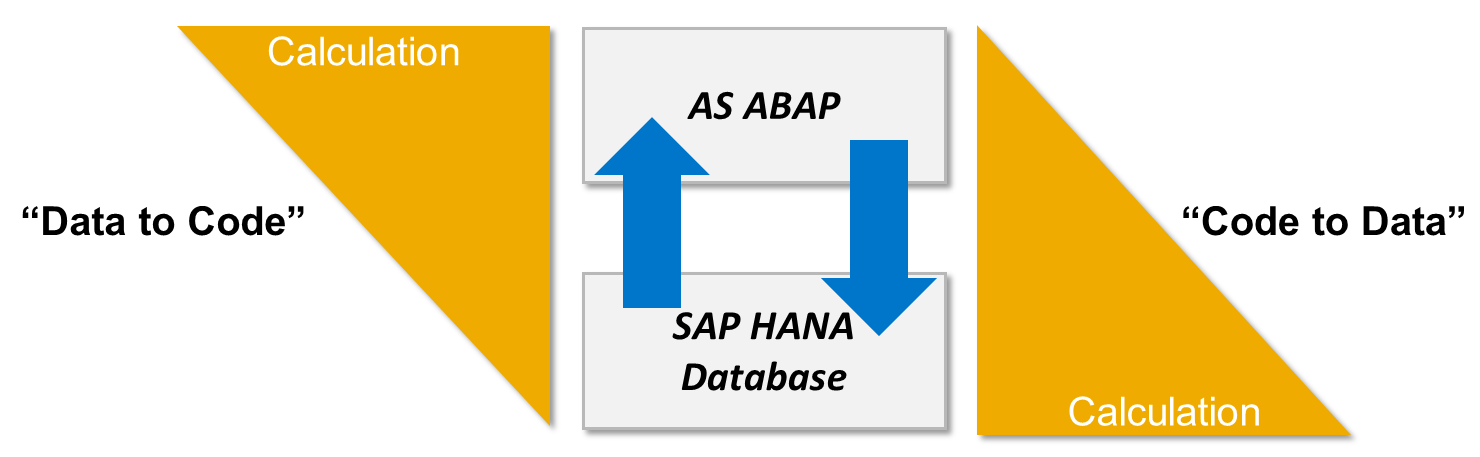
Fig.1. Code to Data pushdown.
To implement this approach, the following constructions can be used:
Starting from the Application Server ABAP 7.4 SP5, the possibilities of the database language built into ABAP for working with databases –– Open SQL have been significantly expanded.

Fig.2. Advanced Open SQL
New Open SQL features:
For more information on extended Open SQL, see the course on Open SAP called “ABAP Development for SAP HANA” ( link ).
New features, as a rule, relate to operating on tables at the DBMS level. But often there are situations when you need to “manipulate” both internal tables and database tables together. For these purposes, you can use the SELECT ... FOR ALL ENTRIES (FAE) construction.
SELECT result FROM table FOR ALL ENTRIES IN itab WHERE ... col op itab_comp ...
This construction of an expression does not have a correspondence in the standard of the SQL language; therefore, the interpreter performs the conversion to a semantically equivalent SELECT expression that can be executed by the database.
You can control the conversion process using ProfileParameters (set in RZ11 operations):
For example, the design:
ABAP
SELECT col1, col2, ..., colM from TAB
FOR ALL ENTRIES IN itab
WHERE col1 op1 itab-a1
op col2 op2 itab-a2
...
op colM opM itab-aM
depending on the settings can be converted in the following ways:
UNION
SELECT col1, col2, ..., colM FROM TAB WHERE col1 op1 i11 op col2 op2 i12 op ... op colM opM i1N
UNION ALL SELECT col1, col2, ..., colM FROM TAB WHERE col1 op1 i21 op col2 op2 i22 op ... op colM opM i2N
...
UNION ALL SELECT col1, col2, ..., colM FROM TAB WHERE col1 op1 iM1 op col2 op2 iM2 op ... op colM opM iMN
OR
SELECT col1 ,, col2, ..., colM FROM TAB WHERE col1 op1 i11 op col2 op2 i12 op ... op colM opM i1N
OR col1 op1 i21 op col2 op2 i22 op ... op colM opM i2N
...
OR col1 op1 iM1 op col2 op2 iM2 op ... op colM opM iMN
IN
SELECT col1, col2, ..., colM FROM TAB WHERE (col1, ..., colM) IN ((i11, ..., i1N),
(i21, ..., i2N),
...
(iM1, ..., iMN))
JOIN
SELECT col1, col2, ..., colM FROM TAB, ABAP_ITAB AS T1 (C_1 datatype, C_2 datatype, ..., C_M datatype)
WHERE TAB.col1 op1 T1.C_1 op
op TAB.col2 op2 T1.C_2
...
op TAB.colM opM T1.C_M
Profile parameters can be overloaded using hints:
SELECT * FROM [..] FOR ALL ENTRIES IN [..] WHERE [..]
% _HINTS HDB '& prefer_join 1'.
For more information on FOR ALL ENTRIES, see SAP Notes 48230, 129385, 1622681.
Not always Open SQL functionality is enough. For example, an open SQL statement can get an input and return only one internal table. To implement a more complex query logic to the DBMS, all in the same version of AS ABAP 7.4 SP5 have the opportunity to create SAP HANA stored procedures directly in ABAP. It looks like the stored procedure “wraps” into a class method. ABAP Development Tools in Eclipse version 2.19 or higher is required for creating and editing AMDP. You can also view the AMDP code in the SAP GUI (for example, through transactions SE24, SE80).

Fig.3. ABAP Managed Database Procedures
AMDP features:
Additional information on AMDP can be found in the same course from “ABAP Development for SAP HANA” ( link ) or in SCN ( link ).
Results
In this article we wanted to show that ABAP has a developed toolkit that allows you to effectively use the capabilities of SAP HANA.
useful links
In this article, I would like to highlight the new approaches to the development of ABAP, with reference to SAP HANA. We will look at the new elements of the ABAP language, which will make it possible to more effectively use the opportunities offered by SAP HANA.
Suppose we have a report written in the ABAP language, the work time of which does not suit us. We want to optimize the performance of this report. The main idea of changing the logic of the report, is that part of the logic of the report, which intensively uses data from the DBMS (in our case, this is SAP HANA), will be delegated to the DBMS level.
')

Fig.1. Code to Data pushdown.
To implement this approach, the following constructions can be used:
- Advanced Open SQL
- FOR ALL ENTRIES
- ABAP Managed Database Procedures
Advanced Open SQL
Starting from the Application Server ABAP 7.4 SP5, the possibilities of the database language built into ABAP for working with databases –– Open SQL have been significantly expanded.

Fig.2. Advanced Open SQL
New Open SQL features:
- Extended JOIN database tables
- Arithmetic expressions
- String expressions
- CASE, COALESCE expressions
For more information on extended Open SQL, see the course on Open SAP called “ABAP Development for SAP HANA” ( link ).
FOR ALL ENTRIES
New features, as a rule, relate to operating on tables at the DBMS level. But often there are situations when you need to “manipulate” both internal tables and database tables together. For these purposes, you can use the SELECT ... FOR ALL ENTRIES (FAE) construction.
SELECT result FROM table FOR ALL ENTRIES IN itab WHERE ... col op itab_comp ...
This construction of an expression does not have a correspondence in the standard of the SQL language; therefore, the interpreter performs the conversion to a semantically equivalent SELECT expression that can be executed by the database.
You can control the conversion process using ProfileParameters (set in RZ11 operations):
- rsdb / prefer_in_itab_opt (convert to IN)
- rsdb / prefer_join (convert to JOIN)
- rsdb / prefer_union_all (convert to UNION ALL)
- rsdb / max_blocking_factor (maximum number of lines transmitted from itab)
- rsdb / max_in_blocking_factor (maximum number of rows sent from itab in the case of IN)
For example, the design:
ABAP
SELECT col1, col2, ..., colM from TAB
FOR ALL ENTRIES IN itab
WHERE col1 op1 itab-a1
op col2 op2 itab-a2
...
op colM opM itab-aM
depending on the settings can be converted in the following ways:
UNION
SELECT col1, col2, ..., colM FROM TAB WHERE col1 op1 i11 op col2 op2 i12 op ... op colM opM i1N
UNION ALL SELECT col1, col2, ..., colM FROM TAB WHERE col1 op1 i21 op col2 op2 i22 op ... op colM opM i2N
...
UNION ALL SELECT col1, col2, ..., colM FROM TAB WHERE col1 op1 iM1 op col2 op2 iM2 op ... op colM opM iMN
OR
SELECT col1 ,, col2, ..., colM FROM TAB WHERE col1 op1 i11 op col2 op2 i12 op ... op colM opM i1N
OR col1 op1 i21 op col2 op2 i22 op ... op colM opM i2N
...
OR col1 op1 iM1 op col2 op2 iM2 op ... op colM opM iMN
IN
SELECT col1, col2, ..., colM FROM TAB WHERE (col1, ..., colM) IN ((i11, ..., i1N),
(i21, ..., i2N),
...
(iM1, ..., iMN))
JOIN
SELECT col1, col2, ..., colM FROM TAB, ABAP_ITAB AS T1 (C_1 datatype, C_2 datatype, ..., C_M datatype)
WHERE TAB.col1 op1 T1.C_1 op
op TAB.col2 op2 T1.C_2
...
op TAB.colM opM T1.C_M
Profile parameters can be overloaded using hints:
SELECT * FROM [..] FOR ALL ENTRIES IN [..] WHERE [..]
% _HINTS HDB '& prefer_join 1'.
For more information on FOR ALL ENTRIES, see SAP Notes 48230, 129385, 1622681.
ABAP Managed Database Procedures (AMDP)
Not always Open SQL functionality is enough. For example, an open SQL statement can get an input and return only one internal table. To implement a more complex query logic to the DBMS, all in the same version of AS ABAP 7.4 SP5 have the opportunity to create SAP HANA stored procedures directly in ABAP. It looks like the stored procedure “wraps” into a class method. ABAP Development Tools in Eclipse version 2.19 or higher is required for creating and editing AMDP. You can also view the AMDP code in the SAP GUI (for example, through transactions SE24, SE80).

Fig.3. ABAP Managed Database Procedures
AMDP features:
- Lifecycle-Management Support
- Using ABAP Dictionary Objects
- Calling other AMDP
- Writing language - SQL Script
- Called as normal ABAP method
Additional information on AMDP can be found in the same course from “ABAP Development for SAP HANA” ( link ) or in SCN ( link ).
Results
In this article we wanted to show that ABAP has a developed toolkit that allows you to effectively use the capabilities of SAP HANA.
useful links
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/245923/
All Articles