The role of industrial design in creating a product for the electronics market
More than a year ago we published a short tutorial on industrial design for electronics on Habré: what it is, how to design a case for a device and evaluate the results. This time we want to explore the topic more deeply, both from the point of view of our development team, and from the point of view of the economy / marketing project for the customer.
Under the cut, we will talk about the goals and objectives of industrial design, its role in the development of new products, and also address the issue of the return on investment in industrial design.
The purpose of industrial design in product development
To understand the role of industrial design in creating a product, first of all you need to answer the question: why do manufacturers need design and what tasks can it solve? There are many scientific and "mundane" definitions of the purpose of industrial design, but they all agree that design serves to define the formal qualities of industrial products, such as appearance, structural and functional features, etc. More concisely the purpose of industrial design was formulated by Thomas Maldonado ( Member of the College of Industrial Design USA): to improve the external advantages of objects produced in industry. Despite the prescription of this definition (1969), it is still relevant.
')

Example number 1. Lapka - a set of sensors for the Apple iPhone: nitratomer, radiometer, meters of electromagnetic fields and humidity. In this project, an important role was assigned to the appearance of the device. As a rule, measuring devices do not have an attractive design. Against the background of traditional devices, Lapka was an exception, it was able to attract new customers and successfully entered the consumer electronics market. Today, these mobile gadgets are sold in the United States, Canada and Russia. We dedicated a separate post to this project last year.
The importance of industrial design for the consumer
The commercial success of any product largely depends on their design.
We will single out five tasks that industrial design is intended to solve:
1. Ease of use of the product. First of all, it is connected with the user interface, which should be safe, as simple and intuitive as possible - by its appearance it should inform the user about its purpose.
Practicality of use can be extremely important, both for simple products and for products with a large number of types of interaction - and the more complex the device is in this regard, the more the product depends on industrial design. Moreover, the designer must understand the essence of all possible types of interaction, because each of them may require a separate design approach.
2. Serviceability. This parameter is extremely important for products that need frequent maintenance or repair. Product details should carry information about the procedures required for maintenance, although ideally it is better to strive to completely eliminate the need for maintenance.
3. External product quality. An attractive product is associated with high fashion and image, and, moreover, it is capable of evoking consumers with pride in owning it (this is one of the main goals the designer should strive for in his work). Also, industrial design contributes to the visual differentiation of goods, this is especially important for products with a stable sales market and technology.
4. Work with the brand. Product design should inform the consumer about the company's philosophy and mission. Attitude to the brand, sympathy for the image of the goods of this manufacturer serve as a certain conditional constant for the consumer in choosing a product.
5. Reducing the cost of equipment and production. Functional features, materials used and other factors significantly affect the costs in the manufacture of a product, i.e. at its cost price. Poor product design, redundant functions or the use of exotic materials affect processing, assembly, etc. With the right choice of material, taking into account factors relating to the environment and other industrial design can save you from significant economically unjustified injections when creating a new product.

Example number 2. Already known to you from our list of top-10 digital IPTV-prefix SML-282 Base of the company "Smartlabs". The intelligent design of the housing of this device allowed for the necessary heat exchange parameters (without visible perforation of the upper and side surfaces of the device). Due to this, active cooling is not used in the hardware platform of the console. Thus, with the help of the design, it was possible to optimize the costs of production and maintenance without deteriorating the external qualities of the product.
Industrial design plays an important role in determining the key factors for the success of a new product, because the average buyer will acquire the product that is attractive in appearance, easy to use and has a relatively high quality.
And although domestic producers can fully realize the role of industrial design in product creation, however, a clear understanding of the place of design in the design process, unfortunately, is not always present.
Place and role of industrial design in the product development process
Historically, manufacturers in the post-Soviet space thought about design as a last resort, because their designs were based on technology, without focusing on ergonomics and style. Today, any company due to fierce competition is unlikely to be able to achieve significant competitive advantages only due to technology.
However, even in those domestic companies that have realized the role of industrial design, designers themselves often participate in product development only in the final stages of the process. The work constructed in this way, in most cases does not give the best result, so it is important to choose a conscious approach to the use of design in the development of new devices.
Much depends on the direction of the product. Conventionally, the design approach can be defined as “user focus” and “technology focus”. If in the first case, the main benefit from using the product is, for example, related to the functionality of the interface or to the external aesthetic appeal, then in the second case, the technologies, the ability of a product to perform a specific technical task.
Consider everything in order:
1. For a product with a focus on the user, appearance plays an important role in its differentiation (difference from similar products of competing companies). The product itself may be technically difficult, however, due to a certain technology, the issue of product interaction with the user becomes a priority. As an example of such products, ready-to-use mass consumer electronics can serve.
In this case, the work of the designer is relevant at the beginning of product development, since from the very beginning the designer can help with the solution of a number of issues:
- Marketing: assistance in identifying needs, field verification of concepts, marketing research, etc.
- Ergonomics of the device: the development of a common concept of the device together with the engineers, and not under their dictation.
- Defining the user interface: for example, the designer can provide a justification for the sufficiency of two buttons in the device, instead of five, as suggested by the engineers.

Example number 3 . Portable dosimeter-radiometer "DO-RA" of the company "Eurasia Intersoft". This miniature sensor is connected to various mobile devices, their energy resources are used, and the measurement results are displayed in the interface of a special program for Android or iOS. Designers of the project managed to change the familiar look at the radiation measuring device and create a completely new product aimed at a wide audience of potential consumers. The customer of the development filed an application in the Guinness Book of Records for the recognition of “DO-RA” as the smallest universal dosimeter in the world.
2. For products with a focus on technology, the priority are issues of technical requirements for devices, engineering solutions. Despite the fact that such ergonomic requirements can also be imposed on such products, the need to comply with certain external aesthetic standards, etc., the consumer acquires them according to the criterion of technical parameters. So, for example, it does not really matter what the battery looks like in the player - the main thing is that it allows the user to listen to music for a long time. Examples of such a product are shock absorbers for automobiles, batteries, computer hard drives, etc.
For this type of product, the designer’s work may begin at later stages of development, since here the design issues mainly concern only the external design.

Example number 4 . A portable car recorder (“black box” for cars) was developed by request of an American company as a technology-oriented product. It is installed in the standard OBD-II connector of the car and captures dozens of different parameters (the technical capabilities of the device can be found in our portfolio ). In this case, the team of designers and designers solved an interesting technical problem - developed a mechanism for blocking the device off. The fact is that the design of the OBD-II connector does not involve the use of locks, it is designed so that the user can freely connect and disconnect the necessary devices. To create the locking mechanism, it was decided to use the element of the standard design of the OBD-II connector - a metal strip (see photo + diagrams). The jamming of the locking element (strip) occurs due to the rotation of the special key. This version of the lock is easy to manufacture, because it does not need a mold, the whole mechanism is machined on the machine. Designers connected at a later stage of development, but were able to ensure compliance with the technical requirements for the device.
The manufacturer already at the initial stages of development should determine the expected expectations of the consumer (target audience) and be able to express these expectations in their product. And it is industrial design, first of all, designed to solve this problem.
As practice shows, our manufacturers have mastered these rules, but did not fully understand how to use them - some mixing or even the imposition of old school ideas on new market laws occurs. Let us explain with an example how this happens: the designer is connected to the development process only at the last stage and put before the finished result of the work of engineers: the device should be, for example, rectangular, the interfaces are derived here and here (where it was convenient for designers to bring them out they will be more convenient to use), etc.

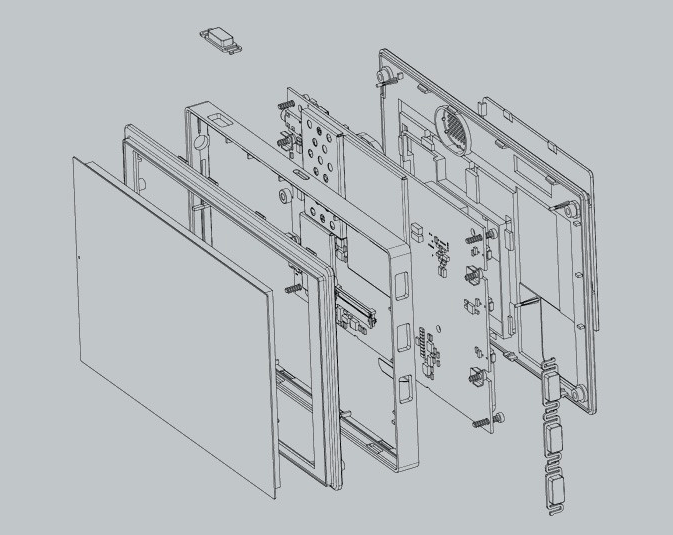
Example number 5. Automobile GPS / GLONASS-navigation-communication device - an example of well-coordinated collaboration of designers and designers ( description of the development ). By coordinating all the stages of the design of the device, a high density of the layout of all electronic components was implemented, which allowed the development of the thinnest body of the navigator with the thoughtful placement of controls and connectors. The strength was provided by the aluminum alloy chassis (see the explosion diagram of this device at the beginning of the article).
The issue of return on investment in industrial design
To answer this question we compare the costs of industrial design and the benefits derived from it. Such costs include:
- directly the cost of services of industrial designers;
- expenses for the implementation of product elements that are the result of the work of designers;
- the costs associated with the possible increase in product development time - for example, designers need to do a lot of additional work to determine the ergonomic qualities of the product, etc.
The result of the successful work of a designer in creating a product is increasing the attractiveness of the product and greater customer satisfaction caused by additional or improved product functions, a pronounced brand personality and product differentiation - all this translates into a premium to the product price and an increase in market share. In practice, this means that industrial design pays for itself as follows:
- investments in design lead to a price premium per unit of product (a simple principle applies here: an attractive product is estimated by the buyer as more expensive and, accordingly, the consumer is willing to pay more) and then it is possible to determine the overall economic effect for a given predicted sales volume;
- investment in design leads to an increase in demand for the product, which allows to calculate the profit at a given price per unit of product.
We hope that with time, the role of industrial design for domestic products will become more relevant for all developers and the products of our manufacturers will be able to fully compete with their foreign counterparts.
* All projects described in the framework of this article were carried out by the Promwad electronics design center team by order of clients from Russia and the USA.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/244067/
All Articles