Theoretical minimum * nix-based-systems for WebDev-padawan

Remember: the power of the Jedi Knight is the power of the universe.
But remember: anger, fear - all this leads to the dark side of the Force.
As soon as you take the first step on the dark path,
you will not be able to roll it ...
Good afternoon, dear galactic senate! Denis Melsky is on the line again, and today the agenda is to define the theoretical minimum of knowledge * nix systems for the young Padawan of web-mastery.
')
I would like to start with the fact that we all know very well: on 67.4% of our favorite webs are spinning on * nix-based-servers, and in the life of the average web developer in a vacuum - and on all 90%.

For lovers of proofs - welcome .
T. h. In our craft without the knowledge of * nix-systems in any way. Let's take an excursion into the world of * nix and understand what knowledge the young Padawan should have.
I propose to consider the three junior degrees of knowledge of Zen controlled by Shaitan-machine aka * nix-server on the example of the beloved ubuntu.
1st junior
Let's start with the basics - forget about the GUI, only the console, only hardcore ^ _ ^!

Several beautiful consoles in xmonad to increase motivation.
We begin our adventure by getting to the console (in the case of an SSH connection, we'll be there right away). By the way, if you are a windows user, the magic putty program will help you.
If you are already in Linux and you have installed it, I believe that you can find a console there and how to get into it. If not, here is a manual on the example of ubuntu with the most popular DWM. There you will find a description of the basic console commands. Consider this list in more detail and group a little.
Let's look at the file system structure.
Yes, do not worry, the usual C: and D: there is no, everything comes from the root (/).
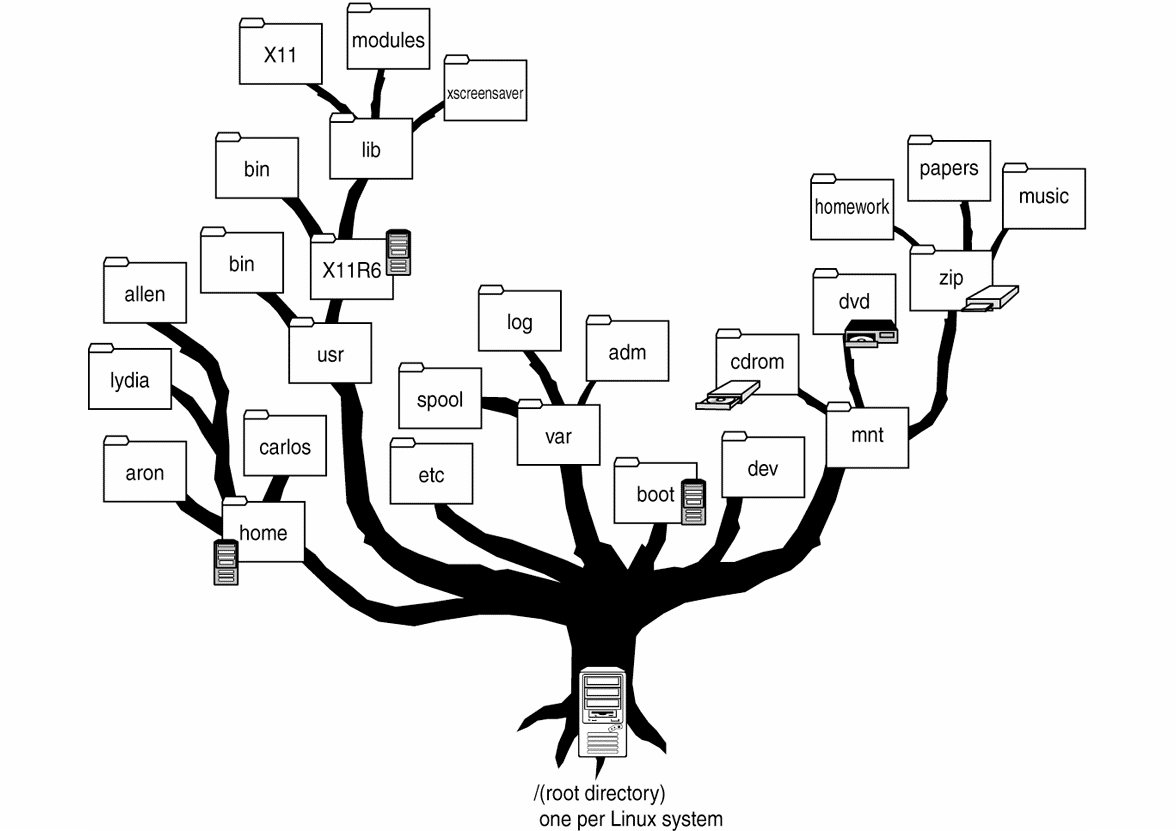
| / | The root directory containing the entire file hierarchy. |
| / bin / | Basic system utilities needed in single user mode and during normal operation for all users (cat, ls, cp). |
| / boot / | Boot files (including loader files, kernel, etc.). Often made in a separate section. |
| / dev / | The main system device files (for example, physical devices: sata hard drives / dev / sda, video cameras or TV tuners / dev / video or pseudo-devices, for example, black holes / dev / null, / dev / zero). |
| / etc / | System-wide configuration files and configuration files of installed programs (the name comes from et cetera). |
| / home / | Contains the home directories of users, which, in turn, contain personal settings and user data. Often placed on a separate section. |
| / lib / | The main libraries needed for running programs from / bin / and / sbin /. |
| / media / | Mount points for removable media (CD-ROM, DVD-ROM, flash-drives). |
| / opt / | Additional software. |
| / proc / | A virtual file system that represents the state of the operating system kernel and running processes in the form of file directories. |
| / root / | Home directory for the root user. |
| / sbin / | The main system programs for administering and configuring the system, for example, init, iptables, ifconfig. |
| / tmp / | Temporary files (see also / var / tmp). |
| / usr / | Secondary hierarchy for user data; contains most user applications and utilities used in multiuser mode. It can be mounted on a read-only network and be shared across multiple machines. |
| / var / | Variable files: log files (temporary log files), temporary mail files, spooler files. |
| / var / cache / | Application cache data. Packages are downloaded here before installation into the system, but here they are stored for some time. |
| / var / lib / | Information about the state. Permanent data changed by programs during work (databases, package manager metadata, etc.). |
| / var / log / | Various log files (log files). |
| / var / www / | The directory of the Apache web server, everything that is inside is transmitted to the Internet (default configuration) |
Now we know what the file system looks like * nix.
Then I recommend learning how to navigate in space ( cd - www.linfo.org/cd.html ), create files ( touch - www.linfo.org/touch.html ) edit and delete too (understand the joke about sudo rm -rf / - I strongly recommend to google those who do not know), to get acquainted with how the console text editor (for example, Nano) works - yes, yes, do not be afraid of newcomers Vim and Emacs. There is also a nice mcedit option.

Nano

MCEdit
Chip and Dale Rescue Rangers! In any confusing situation, enter man% commandName% , and a delightful man utility on * nix-systems will tell you how this or that command (program) works in bash.
If you are lost in the file system, the pwd command will help.
Now let's denote some more features of this OS family.
* nix-systems are case-sensitive, i.e. file.txt and File.txt are different files. Both the / uploads and / uploads directories are also different directories.
A few more important differences:
- Different slashes Win - Backslash “\”; * nix - Slash “/”

- Win line break characters - “\ r \ n - CRLF”; * nix - “\ n - CR”; mac - “\ r - LF” related article: en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Newline
In PHP development, we recommend using PHP_EOL for a new line in the console and DIRECTORY_SEPARATOR for correct slashes to eliminate these cross-platform issues.
In the context of the discussion of the file system and linux features, let's consider an interesting feature - symlinks. If to explain in a simple way - these are shortcuts, as in the well-known windows, only here a shortcut can be to another server, and to a directory, and to a file. The difference from the shortcuts in windows is that shortcuts are used not only on the desktop, but in the entire file system. There is a good wiki article on en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Symbolic_link and a little syntax from the debian wiki after: wiki.debian.org/SymLink .
Why do many developers like * nix-systems? Because they are standardized by the POSIX standard system, which makes them all related and helps to quietly migrate from one standardized OS to another (to both the developer and the user. The topic is disclosed here: en.wikipedia.org/wiki/POSIX .
We continue to meet.
The main difference between * nix-systems is their multi-user approach. From this a logical conclusion follows: if there are many users, it is necessary to distinguish between their spheres of influence. One of the main tools for this is file and directory permissions.
The designations of the rights are in alphabetic or numeric format.
We can see the rights through the ls - l or ls - la commands , and change them via chmod .
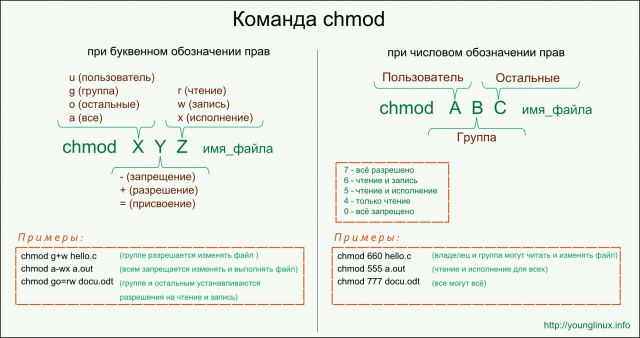
Found an amazing picture that explains the whole essence of what is happening.
I will add that in the life of a web developer, you should always remember about rights in linux, because there is an everyday situation: developed under windows, secured and suddenly (!) Nothing works. In general, nothing terrible in them, no, but keep in mind.
PS I advise you to understand this point well, because putting 777 on the whole project is also not very secure.
For system users, there is a standard rule mode for the files they create — umask. It depends on him, with what rights will the files of this user be created by default.
Read here: ru.wikipedia.org/wiki/Umask .
I casually mentioned the presence of users and groups in * nix-systems, but there is still an administrative user - root.
Root-user helps you to do a lot: install software, mount (https://help.ubuntu.com/community/Mount) sections, resolve the rights to files and folders where your regular user is not enough, and so on.
For this there is the magic command sudo. In more detail I suggest to familiarize here: help.ubuntu.ru/wiki .
Under the root must be very careful. Especially on live servers. Especially deleting something through the console.
Since we remembered the live servers, they have such a property - the memory runs out.
First we check that we have RAM, top / htop is suitable for this.
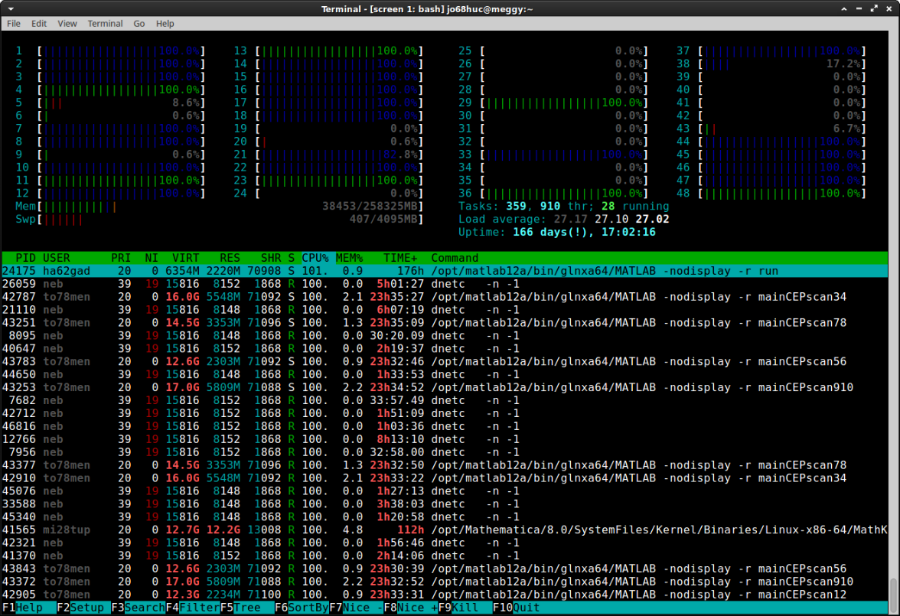
Let's also remember the wonderful tool - ps. It displays a report on running processes. Convenient also with several tricks:
- It is convenient to use the pipeline and the less utility to scroll through the displayed information using the up and down buttons, for example, ps aux | less.
- Using the grep utility, it is convenient to search and display only the necessary processes, for example, ps aux | grep node.
To check how much free space we have on hard, there are commands: df -h and df –k.
If the problem is in RAM, we look at what we consume more than necessary, and kill, or, if these are the necessary processes, we think further :).
If resources of a hard come to an end and there is nothing to delete, archivers come to the rescue. The main archiver in the linux world is tar. Here is a small guide on the subject, which in everyday life you should be enough with your head: help.ubuntu.ru/wiki/tar .
It is worth adding that the console has options for working with several programs at the same time - the GNU Screen utility: help.ubuntu.ru/wiki/screen .
In general, this is the end of the first degree of dedication, but I will gladden a few who are very afraid of the console: there is a console 2-panel classic file manager - Midnight commander.
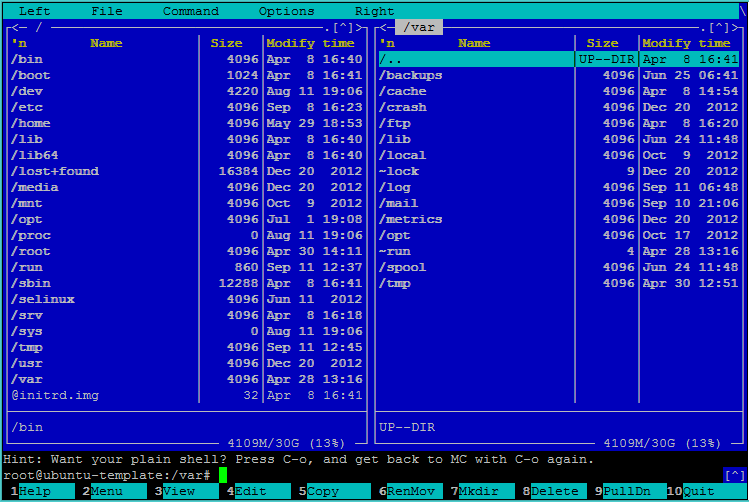
Let's continue with the rubric “What not to do” :).
- You do not know why it and how it works - do not delete!
- I saw a file or folder that starts with a dot - much less do not delete ^ _ ^!
These are dotfiles - hidden files, just by ls they are not visible, you can see through ls –la. Often these are system files or program files (sometimes settings). And here, too, the wiki is a good topic: en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hidden_file_and_hidden_directory .
2nd Junior
The first junior one will help us to do something, but for everyday tasks of the web-developer this is not enough, so let's go ahead to master the level that we have enough for resolving daily tasks.
The first thing to be mentioned at this level is the aptitude package manager (using the example of ubuntu and debian-based systems as a whole).
With it, we can install and remove programs in the system, I recommend reading more details, as they say, on the manufacturer's website: help.ubuntu.ru/wiki/apt .
The next daily task is to install the lamp (linux apache php mysql) server.

You will not believe it, but after installing the server on Windows in Ubuntu, doing this is simple and pleasant, literally in a few commands: help.ubuntu.com/community/ApacheMySQLPHP
Of course, Virtual Hosts will be useful to us. The hosts file is located at / etc / hosts, and the hosts must be edited as root.
It's time to mention the basic Apache commands.
We include modules in apache, including the PHP module (if we put hands) - a2enmod% moduleName%.
Server restart - sudo service apache2 restart.
Let's go back to the hosts. In apache, and in nginx, the host system is not very complicated, but, as practice shows, it is better to tell, in order not to see the huge and terrible httpd.conf / nginx.conf afterwards.
Hosts that are configured and exist (but not the fact that they are included!) Are separate files in the / etc / apache2 / sites-available folder. And the hosts that are currently in use and active are symlinks in the / etc / apache2 / sites-enabled folder.

In real life, everything looks like this: we create a config file for the new host in sites-available, then use the a2ensite% hostName% apache command to create a symlink in the sites-enabled folder, thereby activating the host. Reverse procedure - a2dissite .
When you do it with your hands or just write to the main config file, somewhere one cat is crying, well, or a doggy - who is more sorry for someone :).
Another common task is to raise https. A good manual is here:
help.ubuntu.ru/wiki/apache_%D0%B8_https .

The picture explains the essence of why we need https.
If you are still tormented by the question of why this whole security, I advise you to read a good manual on the subject of security for developers: www.owasp.org/index.php/PHP_Security_Cheat_Sheet - here on the example of PHP, but much is relevant for all Web developers.
Also, when working with lamp, try to close the use of exec (execution of commands in the OS console via php) www.php.net/manual/ru/function.exec.php .
At the php level, this is a potential gap in your protection.
I will add a frequently encountered task - closing the server for non-logged-in users using web server methods, as in this screenshot.

It's very easy to do this through htpasswd, here's an example: doc.norang.ca/apache-basic-auth.html .
It's time to mention databases. In our junior race we will consider MySql. In general, a lot of books have been written on Database Administration and a lot of things appear with experience, but some basic things are simply necessary.
The first is that the config lives at the address /etc/mysql/my.cnf, to go on a visit, as usual, under the root.
You can restart the "pug" with the sudo service mysql restart command.
If you have done something wrong with the rights of your root or simply lost the root password from mysql, you can reset it and set a new one with the command sudo dpkg-reconfigure mysql-server-5.5 (or 5.6), in general, substitute the necessary version :).
Let us turn to the next burning question in the life of a web developer:
Hobbit SQL dumps - back and forth.
To backup the database into a sql file, use the excellent mysqldump command with the following syntax:
mysqldump —opt -u [uname] -p [pass] [dbname]> [backupfile.sql]
[uname] username
[pass] Password (Be careful there is no space between the p parameter and the password)
[dbname] The name of our database
[backupfile.sql] As we call the dump file (you can also specify the path to it if you are not in the folder where you want to create it)
[--opt] Advanced Options
Example: mysqldump -u root -p Tutorials> tut_backup.sql
- add-drop-table - adds to dump DROP TABLE before CREATE TABLE.
- no-data - dumps only tables without content.
- add-locks - adds LOCK TABLES and UNLOCK TABLES to the dump.
And if the base is large and the VPN connection is not the fastest, you can immediately compress our dump into the archive with the following command:
mysqldump -u [uname] -p [pass] [dbname] | gzip -9> [backupfile.sql.gz]
Now let's analyze the knurling of the base (condition: the base does not exist, knurling from scratch).
The basic syntax is:
mysql -u [uname] -p [pass] [db_to_restore] <[backupfile.sql]
Following our example, we get something in the spirit:
mysql -u root -p Tutorials <tut_backup.sql
And if we are packed in the archive, it will be like this:
gunzip <[backupfile.sql.gz] | mysql -u [uname] -p [pass] [dbname]
If we roll the base not from scratch, but it is already created, there is another command:
mysqlimport -u [uname] -p [pass] [dbname] [backupfile.sql]
With the archive by analogy.
This excellent cheat sheet on the dumps took from here: webcheatsheet.com/sql/mysql_backup_restore.php .
The next important point in MySQL is Grants rights. “Pug” we have a multiplayer, if there are many users, it means that they have their own rights - life is cruel :). I advise you to read about them. The most common task is to open the user input not from localhost. It is solved as follows:
Remove the bind-address 127.0.0.1 line from the main config.
Then we execute the following commands:
~ # mysql -u root mysql -p
mysql> GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON database. * TO username @ "%" IDENTIFIED BY 'password' WITH GRANT OPTION;
mysql> exit;
~ # mysqladmin -u root -p flush-privileges
Here database is the database to which we assign rights to the user username with the password password, and% indicates that the user can come not only from the local host, but from anywhere.
These teams on Respect gathered from here: saradmin.ru/?p=792 .
Node JS we can also install in two commands “sudo apt-get install nodejs” “sudo apt-get install npm”.
Node-projects are usually easy to get, something in the spirit of node server.js
I want to share an interesting nodemon tool - it gives us a lot more development opportunities on nodeJS, since it keeps track of changes in project files and restarts the server automatically:
nodemon.io

Further I recommend to get acquainted with the work in the console of the most popular in the world web development VCS - git and svn. Manuals for them are very many different and good, I think, will choose to your taste;).


On the topic of VCS, you may need a manual for generating SSH keys for Git: help.github.com/articles/generating-ssh-keys .
I will share an interesting trick: if you need live output of changing files to the console (often logs) - use the tail –f command, for example, ( tail -f /var/log/apache2/error.log ).
3rd Junior
So we got to the 3rd junior! A pretty good level, after which hardcore is already underway, but there’s nothing wrong either, everything is quite interesting and fun.
The experience of the real upgrade of servers with full stack (lamp + ftp (s) + ssh) on the situation, with the CI-system spin is started, the experience of raising hosting systems like Virtualmin / WebMin is also interesting.
In actual operation it is not recommended to leave a clean ftp server, it is better to use SFTP (ftp over ssh) for security.

help.ubuntu.ru/wiki/webmin
An interesting experience with nginx instead of apache - an excellent manual can be found here: help.ubuntu.ru/wiki/nginx-phpfpm .
I also add a good online tool that transforms rewrite rules from apache to nginx format: winginx.com/ru/htaccess .
Even at this level, you should not be afraid of BASH-scripting and know what sed and grep are. I recommend reading the basics here:
help.ubuntu.com/community/Beginners/BashScripting
A good level is knowing vim or emacs. A very holivar topic, but not to mention.
If at times you really miss some programs from windows, or you have specific software that you still need and cannot find an analog in any way (what is so terrible you need ?!), there is wine - w e mulator.

IE In Ubuntu ("works" even more fun than in the native habitat).
This is really not a windows emulator, but a set of libraries to start Windows programs under the Nix. There is a database, which programs and even games are supported by wine - appdb.winehq.org .
Let's touch the network topic, the first guest of our studio will be netstat ( net work stat istics), welcome! Tulsa will help us see network activity statistics, open ports, our network interfaces, etc.
Basic information:
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Netstat
Examples of use: putty.org.ru/articles/netstat-linux-examples.html .
Thanks, netstat.
Our next guest is iptables, welcome!
IPtables - the standard interface for managing the firewall.
Basic information: en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Iptables
Thanks, iptables!
And in conclusion, the network theme, let's call our headliner - nmap. Poprivetsveem guest nmap !
A very well-known utility in the field of network security, we could see it in dozens of films;).

nmap.org/movies
Basic information: en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nmap#Bibliography .
Examples of use: habrahabr.ru/post/88064 .
Thanks nmap for such an exciting story and a happy childhood.
I propose to switch to a slightly advanced level of MySQL tuning - PIMP MY DB.


In living projects, it is very important to keep MySQL in a combat state, tuned for maximum stability and performance, otherwise we get a very unpleasant bottleneck.
DB Tuning can be divided into two parts:
Optimization of the database structure (normalization / denormalization, foreign keys, indexes, etc.).
Optimize DB server settings.
A lot of guides and manuals have been written about optimizing the database structure, and there is no silver bullet here. Always look at a specific project and individual problems. Explain to help :).
I advise you to read:
ruhighload.com/post habrahabr.ru/post/108418
In the issue of tuning and optimizing DB settings, Percona was very successful - MySQL-fork. I recommend to get to know them better.
From the base set for tuning they have a toolkit and a wizard for setting up your server.
www.percona.com/software/percona-toolkit
tools.percona.com/wizard
Also known tulza - mysqltuner (http://mysqltuner.com/).
To test the load on MySQL there is an interesting sysbench tool. You can read about it here: ruhighload.com/index.php/2010/03/05/sysbench-testiruem-proizvoditelnost-mysql .
Add to our adventure a bit of stylish, fashionable and youth technology - CI.
Wiki: Continuous Integration (eng. Continuous Integration) is a software development practice that consists of performing frequent automated project builds to identify and solve integration problems as soon as possible.
In practice, this is a very convenient software that allows you to build builds, run all kinds of tests, do js / css minification, monitor the quality of the code, deploy, and so on.
Most popular - Jenkins, Travis, TeamCity.
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Jenkins_ (software)
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Travis_CI
ru.wikipedia.org/wiki/TeamCity
PS Cool Guake Tulza — leaving quank in quake style.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/243563/
All Articles