A 19-year-old vulnerability can capture a computer through Internet Explorer.
Researchers from IBM X-Force discovered the dangerous vulnerability CVE-2014-6332 , which, according to their statements, affected all versions of Microsoft Windows, starting with Windows 95. The main potentially vulnerable application with this bug is Internet Explorer, starting with version 3.0. Vulnerability allows unauthorized access to user data or remotely run malware on the attacked computer. In this case, an attacker can bypass such protective mechanisms as the Enhanced Protected Mode sandbox, used in IE 11, and the Enhanced Mitigation Experience Tool Tool (EMET) security system.
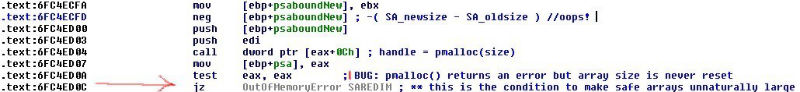
Vulnerability appeared in the code of Windows applications back in 1996 with the release of IE 3.0, where Visual Basic Script (VBScript) was used. Attacks based on this vulnerability belong to the “data manipulation” class, that is, they are a rarer and more dangerous technique than “buffer overflow” and other classic methods of hacking. The vulnerability is related to the incorrect working out of the resizing procedure of the SafeArray arrays, which allows you to quietly knock down the addressing and get access to data at any address, and not only within a given array.
')
A hacker can also use this feature for more complex attacks: for example, run unsafe scripts with arbitrary parameters to bypass control systems. This technology was shown this year at the Black Hat USA conference by Chinese security specialist Yang Yu in his report entitled “ Vital Point Strike ”.
As for the experts from IBM X-Force, they first discovered this vulnerability back in May of this year. Over the past months, they have not yet observed cases of exploitation of this vulnerability in the field. However, the authors of the study emphasize that the vulnerability is not yet closed, and now it is actively being studied not only by security specialists, but also by intruders.
UPD: Media reported that Microsoft has released a patch that fixes several serious security bugs, including the CVE-2014-6332 vulnerability.

Vulnerability appeared in the code of Windows applications back in 1996 with the release of IE 3.0, where Visual Basic Script (VBScript) was used. Attacks based on this vulnerability belong to the “data manipulation” class, that is, they are a rarer and more dangerous technique than “buffer overflow” and other classic methods of hacking. The vulnerability is related to the incorrect working out of the resizing procedure of the SafeArray arrays, which allows you to quietly knock down the addressing and get access to data at any address, and not only within a given array.
')
A hacker can also use this feature for more complex attacks: for example, run unsafe scripts with arbitrary parameters to bypass control systems. This technology was shown this year at the Black Hat USA conference by Chinese security specialist Yang Yu in his report entitled “ Vital Point Strike ”.
As for the experts from IBM X-Force, they first discovered this vulnerability back in May of this year. Over the past months, they have not yet observed cases of exploitation of this vulnerability in the field. However, the authors of the study emphasize that the vulnerability is not yet closed, and now it is actively being studied not only by security specialists, but also by intruders.
UPD: Media reported that Microsoft has released a patch that fixes several serious security bugs, including the CVE-2014-6332 vulnerability.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/243047/
All Articles