How to use psychological principles to increase conversion
Conversion optimization is an increase in the likelihood that a user will perform some targeted action on your page.
Your user needs to make a decision, and you want to influence this process.
Understanding the psychology that drives human behavior can help us with this.

Fear of loss is a powerful conservative force that makes people strive more to save something than to risk in order to achieve something more. The study showed that people get more pleasure from circumventing losses than from making a profit (the same value).
')
Imagine, for example, that you are playing eagle and tails for money, if you throw a coin and tails out, you lose $ 10. How much would you like to get if an eagle fell?
Most people answer $ 20. That is, they want a potential reward of twice the potential loss. In other words, we want to have a lot of money in our pockets without losing anything.
The fear of loss is one of the reasons for the success of the trial strategy, which works very effectively for SAAS. When we get something for free, we eventually get used to it and don’t want to part with it, so we’re ready to pay the money, keeping the status quo.
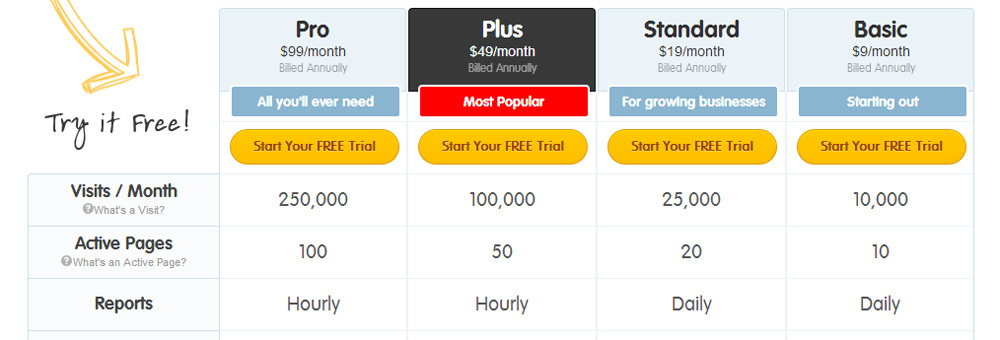
Simply put, we overestimate losses and try to avoid unnecessary costs and high prices. Booking.com benefits from this by using the “Block price” points before prices “can” jump.
Self-efficacy is the power of faith in your own competence — how well, in your opinion, you will cope with the task. Self-efficacy can directly influence your motivation and your desire to complete the task.
I will give an example, self-efficacy directly affects how you follow a diet or exercise regimen. If you do not believe in your capabilities, then chances are high that you will give up everything.
Thus, low self-efficacy can force people to believe that a task is more difficult than it actually is and this can prevent even starting a task.
Self-efficiency grows with success, we can give the user the appearance of this success, occasionally rewarding him for the faithfulness of the action performed, thereby increasing the probability that he will go further and complete the task. Anything can be a reward, even a green check mark indicating the correctness of the action performed.
The reward for the success of the task in the process strengthens the belief that you can complete the task
In a test published by Luke Wroblewski, a built-in form validation on a web page showed a 22 percent increase in success rates and a 31 percent increase in user satisfaction.
People with low self-efficacy may not cope with the task, so breaking the process into several parts can make everything visually easier. As you work on the process, reward them for each step in order to maintain self-efficacy as you progress.
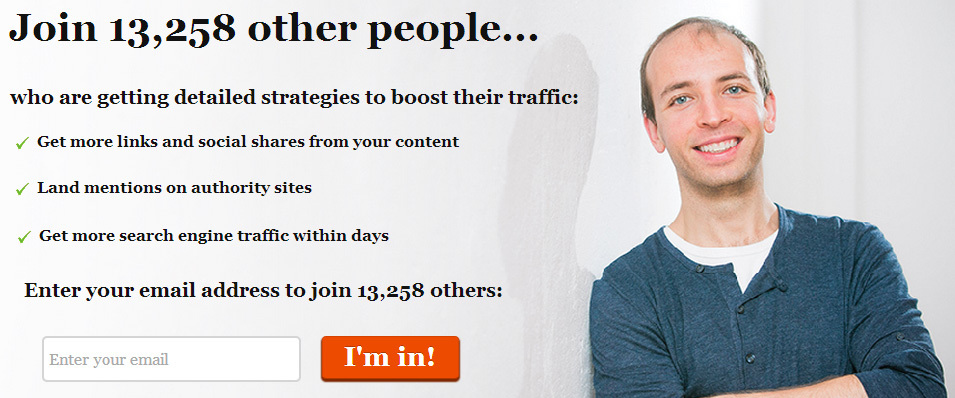
Self-efficacy can also increase due to the activity of other users. If we see how others successfully perform the task, we also begin to believe that we can cope with the task. You can use this to show existing customers who have already made a purchase:

Or the number of people already subscribed:
We can also benefit greatly by knowing how our brain processes information in the decision-making process.
One of the most popular theories about thought is the “dual process theory,” which says that our brain forms thoughts using two separate processes. One of the processes is conscious, and the other is subconscious.
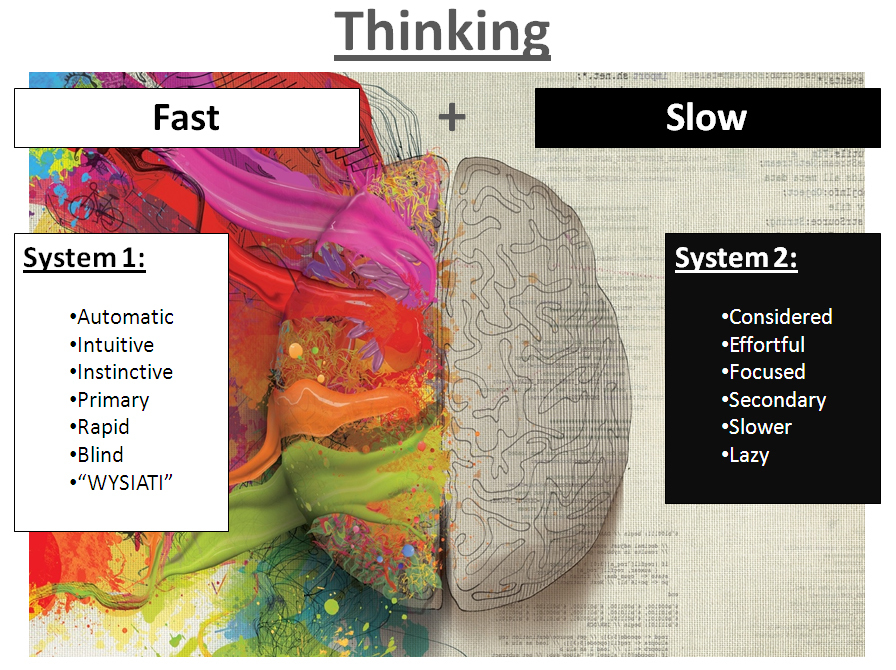
In his book Thinking: Fast and Slow, Daniel Kahneman describes two systems as follows:
System 1: Fast, automatic, frequent, emotional, stereotypical, subconscious
System 2: Slow, Effortless, Infrequent, Logical, Prudent, Conscious
Both systems are constantly involved and some of them make decisions for us every time. Simply put, we either make hasty decisions or digest thoughts very scrupulously.
“Systems 1 and 2 are always active when we are awake. System 1 starts automatically, and System 2 is only partially used in standard mode. If System 1 has problems, System 2 is connected, providing more detailed information to solve the problem at the moment. Thus, an experienced driver can comfortably control most aspects of driving without thinking, using System 1. Quick decisions such as changing gears or choosing a course can be made automatically, even if you talk to a passenger or listen to music.
When he approaches a complex intersection, system 2 is turned on, since at this moment more concentration and rationality of reasoning is required.
According to Harvard University professor Gerald Zaltman, up to 95% of purchases we make using System 1.
And we can effectively use System 1 the main thing is not to force the user to think.
Visual targeting
Use visual cues to literally direct attention where it’s needed. Our attention is very easily influenced, so that even imperceptible signals can be effective.
Optimizely it does "attracting" the view to the motivation for action:

Evernote does the same, even with more intensity, creating a silhouette of the cursor near the CTA.
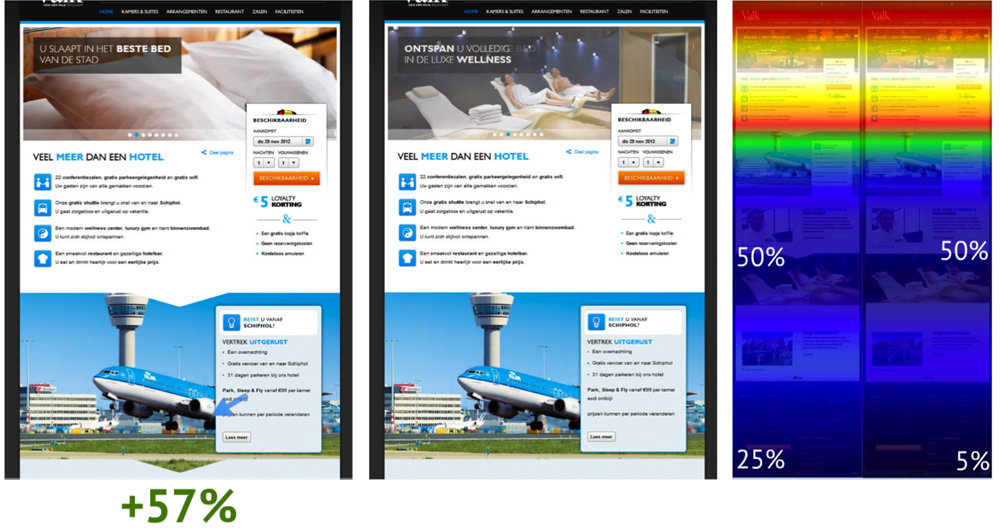
In Wheelofpersuasion published the results of using visual targeting to the page with the reporting form for the client of their hotel Van Der Valka. You can see below that the usual addition to the cursor resulted in a 57 percent conversion increase!
Of course, we don’t have to emphasize visual signs. But this is the current method of attracting the attention of users.

Since System 1 is initially emotional, we can control emotions with the help of images of real people (NOT stock photos!), And this is closely related to facial expression.
Note that in this example, the eye is first attracted to the face of the woman, and only then we pay attention to the registration form - this is another example of visual indication. Kissmetrics has published studies of how to attract the eye and what we can learn from this.
Since we unconsciously first react to a person’s face, with the help of properly selected physiognomy we can help the visitor of our site to form a positive feeling from our product.

System 1 makes quick, automated decisions so that immediate rewards can play into the hands of the effect of cognitive bias. The study, published on ContentVerve, shows a 31 percent increase in visits to the payment page by adding information about the promotion to a key.

The search for psychological principles when creating ideas for testing does not exclude the need for testing itself. We are trying to help the user make a decision by acting on certain points in his mind - but not all buyers are the same.
In addition, no one has not canceled the impact of simple logic and competent description of your product. In any case, by better understanding the decision making process of our customers, we are more likely to convince them to make the decision we need.
Translated by Multi-landing project staff. We will be happy to answer all your questions.
Your user needs to make a decision, and you want to influence this process.
Understanding the psychology that drives human behavior can help us with this.

Fear of loss
Fear of loss is a powerful conservative force that makes people strive more to save something than to risk in order to achieve something more. The study showed that people get more pleasure from circumventing losses than from making a profit (the same value).
')
Imagine, for example, that you are playing eagle and tails for money, if you throw a coin and tails out, you lose $ 10. How much would you like to get if an eagle fell?
Most people answer $ 20. That is, they want a potential reward of twice the potential loss. In other words, we want to have a lot of money in our pockets without losing anything.
Free Trial Versions
The fear of loss is one of the reasons for the success of the trial strategy, which works very effectively for SAAS. When we get something for free, we eventually get used to it and don’t want to part with it, so we’re ready to pay the money, keeping the status quo.

Simply put, we overestimate losses and try to avoid unnecessary costs and high prices. Booking.com benefits from this by using the “Block price” points before prices “can” jump.
Self-efficacy
Self-efficacy is the power of faith in your own competence — how well, in your opinion, you will cope with the task. Self-efficacy can directly influence your motivation and your desire to complete the task.
I will give an example, self-efficacy directly affects how you follow a diet or exercise regimen. If you do not believe in your capabilities, then chances are high that you will give up everything.
Thus, low self-efficacy can force people to believe that a task is more difficult than it actually is and this can prevent even starting a task.
Reward for success
Self-efficiency grows with success, we can give the user the appearance of this success, occasionally rewarding him for the faithfulness of the action performed, thereby increasing the probability that he will go further and complete the task. Anything can be a reward, even a green check mark indicating the correctness of the action performed.

The reward for the success of the task in the process strengthens the belief that you can complete the task
In a test published by Luke Wroblewski, a built-in form validation on a web page showed a 22 percent increase in success rates and a 31 percent increase in user satisfaction.
Let things look simpler
People with low self-efficacy may not cope with the task, so breaking the process into several parts can make everything visually easier. As you work on the process, reward them for each step in order to maintain self-efficacy as you progress.

Demonstrate the success of the rest.
Self-efficacy can also increase due to the activity of other users. If we see how others successfully perform the task, we also begin to believe that we can cope with the task. You can use this to show existing customers who have already made a purchase:

Or the number of people already subscribed:

Dual Process Theory
We can also benefit greatly by knowing how our brain processes information in the decision-making process.
One of the most popular theories about thought is the “dual process theory,” which says that our brain forms thoughts using two separate processes. One of the processes is conscious, and the other is subconscious.
In his book Thinking: Fast and Slow, Daniel Kahneman describes two systems as follows:
System 1: Fast, automatic, frequent, emotional, stereotypical, subconscious
System 2: Slow, Effortless, Infrequent, Logical, Prudent, Conscious
Both systems are constantly involved and some of them make decisions for us every time. Simply put, we either make hasty decisions or digest thoughts very scrupulously.

“Systems 1 and 2 are always active when we are awake. System 1 starts automatically, and System 2 is only partially used in standard mode. If System 1 has problems, System 2 is connected, providing more detailed information to solve the problem at the moment. Thus, an experienced driver can comfortably control most aspects of driving without thinking, using System 1. Quick decisions such as changing gears or choosing a course can be made automatically, even if you talk to a passenger or listen to music.
When he approaches a complex intersection, system 2 is turned on, since at this moment more concentration and rationality of reasoning is required.
Optimization for System 1
According to Harvard University professor Gerald Zaltman, up to 95% of purchases we make using System 1.
And we can effectively use System 1 the main thing is not to force the user to think.
Visual targeting
Use visual cues to literally direct attention where it’s needed. Our attention is very easily influenced, so that even imperceptible signals can be effective.
Optimizely it does "attracting" the view to the motivation for action:

Evernote does the same, even with more intensity, creating a silhouette of the cursor near the CTA.

In Wheelofpersuasion published the results of using visual targeting to the page with the reporting form for the client of their hotel Van Der Valka. You can see below that the usual addition to the cursor resulted in a 57 percent conversion increase!

Of course, we don’t have to emphasize visual signs. But this is the current method of attracting the attention of users.

Communication using images
Since System 1 is initially emotional, we can control emotions with the help of images of real people (NOT stock photos!), And this is closely related to facial expression.

Note that in this example, the eye is first attracted to the face of the woman, and only then we pay attention to the registration form - this is another example of visual indication. Kissmetrics has published studies of how to attract the eye and what we can learn from this.
Since we unconsciously first react to a person’s face, with the help of properly selected physiognomy we can help the visitor of our site to form a positive feeling from our product.

Offer a quick reward
System 1 makes quick, automated decisions so that immediate rewards can play into the hands of the effect of cognitive bias. The study, published on ContentVerve, shows a 31 percent increase in visits to the payment page by adding information about the promotion to a key.

Psychology of Your Customers
The search for psychological principles when creating ideas for testing does not exclude the need for testing itself. We are trying to help the user make a decision by acting on certain points in his mind - but not all buyers are the same.
In addition, no one has not canceled the impact of simple logic and competent description of your product. In any case, by better understanding the decision making process of our customers, we are more likely to convince them to make the decision we need.
Translated by Multi-landing project staff. We will be happy to answer all your questions.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/242469/
All Articles