VDI: pros, cons, pitfalls for big business, NGOs and design bureaus

One of the older engineers decided that he had in his hands an ultramodern secret cluster for 3D calculations. We were cruel and did not say that this is just a thin client.
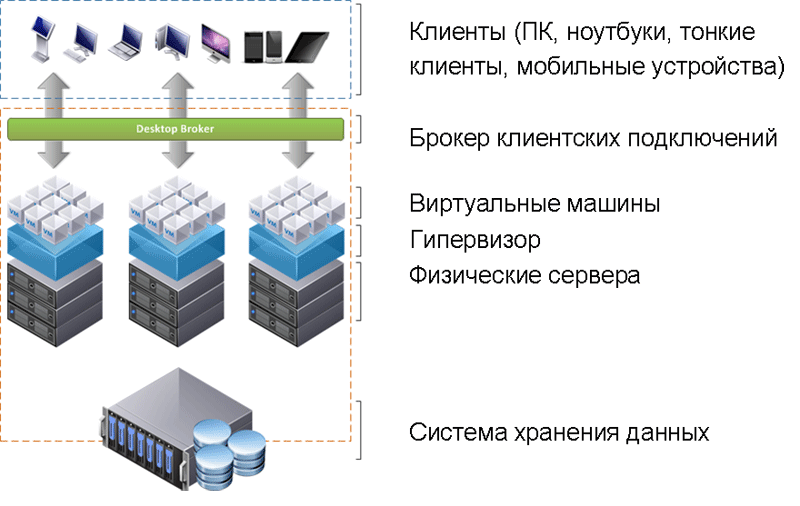
VDI is a virtual desktop infrastructure . Unlike the "normal" terminal access, simplifying, we are not talking about several simultaneous user sessions on a single server with the operating system, but about several virtual machines on a physical server. Each user gets their own virtual PC, which can connect to even from the phone.
There is a myth that VDI is always very expensive. In general, it was true until recent years. In my practice, only last year, VDI began to be used as a solution to save on infrastructure. Prior to this, VDI was most often a necessary expense for the security of corporate data.
')
Not so long ago, an example of reducing the cost of the workplace appeared: there is a design office in Moscow, and there are factories in Russia. Drawings are sent to the plants in 3D-format, it was necessary to make small changes. The factories could not make changes without expensive infrastructure. A very powerful server-level machine was bought, an expensive software was put on it. Then this machine and this software were supported by administrators from the parent organization — in difficult cases it came to a long exit. With the introduction of VDI, everything began to happen in a data center in Moscow.
General moments
Until about 2013, the main problem in implementing VDI was the very high price of infrastructure. Approximately half of the cost was the cost of storage. Due to the reduction in the cost of hybrid technology HDD + Flash in 2014 began a kind of boom VDI-environments.
The first factor that has always been the criterion for choosing VDI is safety. As it is known, if the security officer says “it is necessary”, the business suffers to close its eyes to the account and silently signs. Because they are taught by life. That was the way - with the suffering face of the administrator - the first introductions in Russia, in which I participated, were. Even after the introduction of modern commercial directors (for example, in a call center) they come to try plugging the keyboard into a thin client (it connects to the VDI machine), and then stick a USB flash drive. It does not connect. They stick a second flash drive, a third ... But the security policy prohibits the transfer of data beyond the limits of VDI, so nothing is left. The commercial director leaves the workplace a little more relaxed: he seems to have spent a lot of money, but now there is no problem with the fact that his trade secret will come up from a competitor. Or even worse.
But back to the first serious introductions. So, the administrator's pained face at some point began to smooth out. The fact is that he understood that an incredible elimination of various real hemorrhoids was taking place with the administration of individual machines. The features of a thin client are such that in the event of a breakdown on the user’s side, it is easier to pick up and change it without really understanding it. All custom machines for hardware and OS are exactly the same.
The best example: we had a retail, for which the “last straw” was the moment when they with incredible difficulty updated their application software across the country for a sleepless night on the new version. In the morning when the shops opened, it turned out three important points:
- In the test environment, a unique combination of events was created when this software worked.
- In a combat environment, the software does not start, that is, the stores are left without infrastructure.
- Roll back in minutes does not work - you need to bypass each car and do.
They had to turn off the phones and lock the door while the rollback was being made. Outside, they were literally waiting for a grateful crowd of users. After the restoration in the IT department was cleaned, flew heads. The new leader received the first priority task: “To never again.”
So, VDI is still when a thousand stations can be served by one person from one place. And this was the second factor in choosing VDI solutions for large businesses. And today in some cases (most often, as with the CB), we can talk about savings. Savings are achieved only with the miscalculation of risk reduction, increased stability of the infrastructure and assessment by security personnel. VDI itself has become more complex in structure and has acquired more functions, but the essence remains the same. Generally.
Some years ago, in Russia, it suddenly turned out that VDI is a kind of best practice for typical western-type offices, for typical large call centers, and so on. And this year, prices have become more reasonable, and those who care about long-term savings, have begun to look closely already seriously.
Hardware and software users
In the late 80s, almost everyone thought that the IT infrastructure would look like rather thin, easily replaceable terminals and supercomputers to which connections are made. Everything went slowly towards this (and this was logical), but ultimately the data storage paradigm at the local nodes won. What a great merit Microsoft, by the way. In the pre-virtual infrastructure, everyone has a system unit and a hard disk inside. The data is processed there, and only the results are sent to the server.
The main idea of VDI is to take all the data from users' computers to the central site. A thin client is used, on which there are absolutely no hard drives, physically there is no user data. A terminal is simply a means of communication between a user monitor and a data center. And all user data, all its files are stored in the data center, which, by definition, is much more secure than the employee's local workplace.
Here security guards usually come with the words: “Dear our IT director, our data is poorly protected. We lose a lot of information because it is carried away. Because the data is stored by users. " Then comes the commercial director: “Dear IT director, I want our employees to work 24 hours a day, even in the village of my grandmother. We will increase milk yield! And it is also convenient for me to enter from the phone on a business trip, also screw it there at the same time. ” And already further admin, looking at the system, comes to the conclusion that it will be easier to live with it. Although, of course, it will take a lot to learn, and not everyone is ready to change the world view so quickly and get new data. They are more often afraid of losing their jobs, because their knowledge “will be unclaimed”. At once I will say that the fear is completely justified - with the introduction of VDI, enikeyschikov are most often reduced because they are useless, but the main people of the IT department remain. And get this experience and a level of control that makes them even more valuable for the core business.
In the role of a terminal for accessing VDI, any device with a screen, processor and input-output means can act. Tablet, phone, ordinary PC, laptop and thin client. In fact, such a monoblock is a PAC, which is optimized to the lowest possible cost per unit and ease of replacement.
Here is an example of a Dell Wyse D10DP thin client workstation device:

The price is comparable to a modern good external hard drive. The architecture of iron and software designed to work 24/7 under continuous load "for slaughter." Ordinary workstations gradually litter at the level of software (especially Win-machines), plus are subject to wear. Optimized for this operating mode of the OS are installed here, and the iron is put weak, but reliable. Weak is because years 7..10 nobody will change it, and reliability is more important. In the case of a minimum of moving parts, even the fan is not, only passive cooling radiator (see how many holes in the photo above?). Dust is also not stuffed, by the way (not more than inside the monitor), and if it is stuffed, it doesn’t really hurt the operation.
Usually these boxes are stored in a warehouse with a business executive or support. As soon as something happens in the same retail with a light bulb on the trading floor, the elderly Semenych, who has a very weak relationship with IT, comes out with a new light bulb and changes it, and throws out the old one. When a thin client breaks down, the same Semenych appears from the warehouse in an oily robe, carrying a box, which he was placed there a couple of years ago. Carefully squinting, connects all three connectors and pokes into the power supply. Workplace restored. The user enters his password and continues to work from the place where he stopped - exactly from that, even without rebooting.
Our case - retail has reduced the cost of the workplace by 47%. The task was for cashiers, cash desks - 2000 pieces, it was necessary to simultaneously reduce costs and simplify support. Solution: Citrix XenDesktop + XenServer + Wyse.
But back to the car on the trading floor. If you had to roll a critical security update on it, there would be a lot of problems. Here, everything is solved on the server, and the update occurs in the data center almost instantly and for everyone on the network.
How to choose a thin client? As a rule, under the task. There are specialized sharpened solutions for Citrix, for others, thin Linux clients are important to someone due to the peculiarities of the licensing policy. In general, according to the situation. There are software features, and there are iron ones (for example, the availability of necessary ports, often specific ones). And so on for each level.
Yes, by the way, it is not necessary to purchase a separate iron for a thin client. With him, of course, it is better and simpler, but all the old (often already depreciated according to the documents, but still working) second Pentiums, old Tseleron, remembering even overclocking in the middle lane, and in general all the hardware from the warehouse, go into business. The admin carefully wipes them with a cloth and gives them to work. 3-4 years they will serve. Then, of course, they change to thin clients as they break down, and the system becomes homogeneous, to the greater happiness of the IT department. But the holes for the Order "For Honorable Economy" they all twist in sweaters.
Data center part
Here is a sample table of our practice of working with big business for data center connectivity - the terminal:
VDI Solution Level | Manufacturer (vendor) |
Applications inside a virtual workstation | From the manufacturer of the application; compatible with the OS of the virtual workstation (with Windows 7, for example) |
Operating system (virtual workstation) | Mostly Windows 7, Windows 8, Linux distributions (mostly RedHat), sometimes Windows XP |
User Environment Management | Either built into the VDI broker (see below), or, for example, AppSense |
Print management | Either built into the VDI broker (see below), or, for example, Cortado (ThinPrint) |
Manage user connections and all aspects of VDI | VMware Horizon, Citrix XenDesktop, Dell vWorkspace - leaders; Microsoft RDS, RedHat 2x Software - in some cases |
Virtualization platform | VMware vSphere, Microsoft Hyper-V, Citrix XenServer, in some cases RedHat RHEV, Parallels Virtuozzo Containers |
Data Storage Systems (DSS) | All classic vendors - EMC, HP, Dell, NetApp, maybe Huawei |
Software to optimize VDI interaction with storage | Atlantis, DataCore, Nexenta, etc. |
Some solutions are certified by regulators. This is especially important for the public sector and various research institutions, such as pilot production of compressors, where no compressor has been seen.
In addition to software, it is particularly worthwhile to dwell on data storage. The fact is that for VDI, the bottleneck often becomes storage, and it is expensive. In recent years, storage vendors have discovered that a fairly large percentage of their customers use hardware specifically for office-type VDI, and have made significant optimization in this regard. Almost all software, up to the firmware level of the controllers, is optimized for working with such tasks (in particular, it helps in data deduplication and their protection).
As a rule, today, for a loaded task, a bunch of Flash-DSS for hot data and a disk for normal, or hybrid DSS Flash + HDD is used, or, if a very small budget, recently, cache tools like this .
Previously, everything was built on the fact, on the HDD - these are difficulties with random reading, assembling into large clusters to provide the necessary speed, problems with redundancy and unexpected breakdowns. Today, for the storage system, it’s enough not a cabinet with 150–200 disks, but shelves. Well, in fact - two or three (including UPS) standard units for the enterprise level.
The biggest mistake of inexperienced designers is that they overload the storage system too much. Because storage is a single point of failure for the entire infrastructure. For her fear, and the price tag is growing sharply. On average, up to two times the cost of storage systems due to improper design. Why? Very simple: incorrectly collected data. We did not analyze the workplace. Yes, there are many reasons.
Therefore, the main question is to calculate all the parameters of the infrastructure. Therefore, before the introduction you need a survey to accurately determine the estimated power. The survey is usually carried out at the level of communication on business processes and the installation of users of a special application that profiles the workstation. When all the data for, say, a month of work is collected, it becomes clear what to do and how. Month is enough. Yes, it is clear that accounting has peaks before reporting, development is activated on large releases, marketers love to watch videos when advertising goes out, and so on. But these peaks do not occur at the same time, and 10–15% of the power reserve is quite enough to not rest against the data center.
Channels
When VDI is deployed locally, it's simple. When remotely - as a rule, the minimum requirement today - guaranteed 128 Kbps per user. Please note: guaranteed. Of course, they often talk about 30–40 Kb / s, but this is, let's say, not true. While the user is typing, everything is fine. But when he scrolls through his "VKontakte" tape, the traffic is generated slightly less than when watching a video.
Fortunately, most modern solutions are very well optimized for traffic: the data does not go back and forth from the machine to the application server, but walk in a ring inside the data center, at the OS level, too, everything is good in terms of downloading remote desktops.
Naturally, in Moscow, where the situation with guaranteed 10 Mbit / s to a regular office is more common, there, as a rule, there are no problems at all. At large offices of 200–300 employees (according to the situation and traffic profile), we often put traffic compaction solutions ranging from the transport level to deduplication, for example, from Riverbed (http://habrahabr.ru/company/croc/blog/214693 /).
Here are the user desktops. Please note: OS distributions of workstations are collected for the sake of one goal - optimization of work with VDI, including traffic:
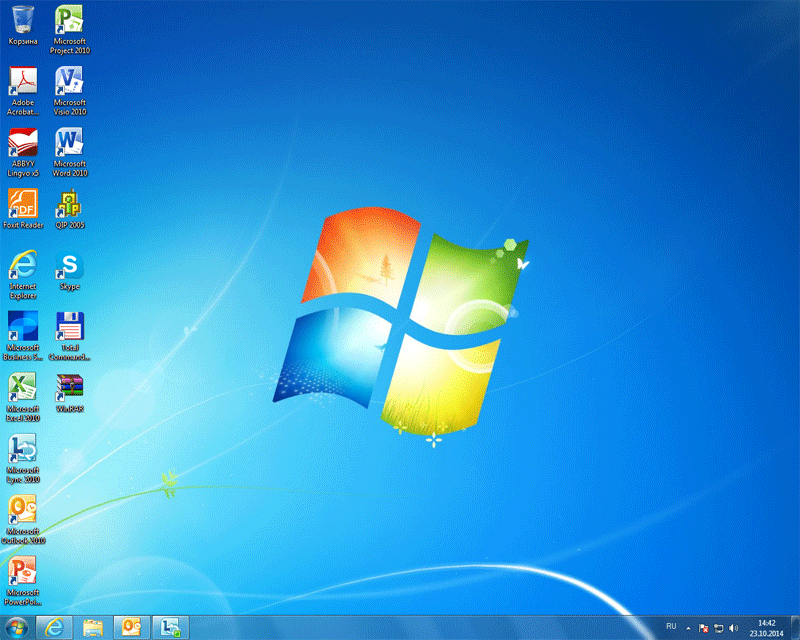
Windows desktop operating on a physical workstation:
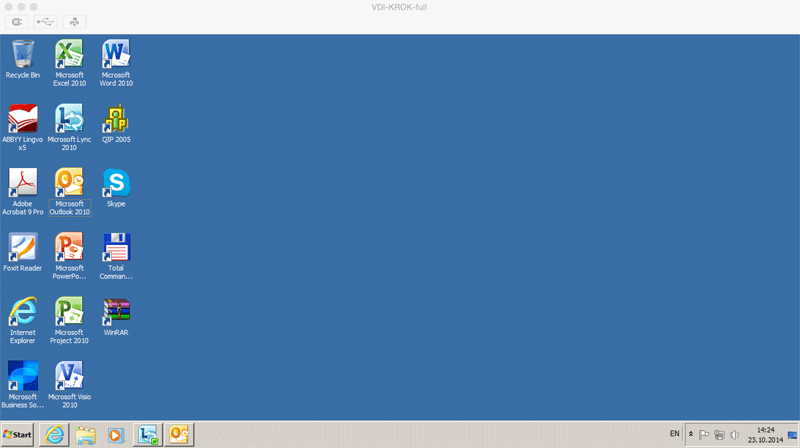
Windows OS, but operating in a virtual machine located in the data center:
Software VDI Client Interface:

Who uses VDI?
The principle is very simple. If you are a small or medium business and it’s relatively simple to administer, your choice is terminal access. Where you spend 500 rubles on it, VDI would have to spend 5 thousand.
But at some point the infrastructure becomes too large, the risks increase, the ratio of smart people from the IT department to the workplace falls, and the technological debt grows. At this point, a sensible decision on the implementation of VDI, calculated under the situation. Sometimes it is too early to implement - it is easier to live for another two years with increasing chaos in the infrastructure and move on later. Sometimes you need to implement a purely business-specific.
For example, in call centers, stability of work and measures against high staff turnover are important. Stability is when there are 60 thousand calls to a CC per day, and there are three shifts without interruptions at the same places. I know thin clients who have been working for 5–6 years without shutting down at such facilities.
Safety and control are important because of the turnover - there are very few permanent employees in line positions in such CC. In banking systems and medicine there is a lot of customer data, here each step to prevent leakage adds a lot of restful sleep to the company - from the admin to the investor.
Big business is very jealous of storage. As a rule, it is backed up with the same active-active, plus an iterative backup system in another data center like Avamar (http://habrahabr.ru/company/croc/blog/149306/). Because in VDI the human risk grows. I know a case in one bank, when they rolled the wrong update on 2000 cars. Work got up. True, only 12 minutes - admins quickly rolled back.
Sometimes they come up with VDI to us: we have 3 of our commercial data centers, they are at different sites, there are solutions of increased reliability (two confirmations by TIER III). For large customers, this is one contractor who takes care of all the services, reservations and all the questions about the routine.
Where to find out more?
We quite often conduct test drives, plus we can just help with the demonstration of such systems. If it is interesting to participate - write to vdi@croc.ru, I will call to the next. There you can also ask questions about a specific infrastructure, with pleasure I will prepare an approximate quick estimate of the cost of the solution. And, of course, here and in the mail, you can ask questions about the nuances of implementation.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/241686/
All Articles