The history of virtualization: The rapid development at the turn of the millennia
Our past material on the history of the development of virtualization technologies received a certain response among the audience of “Habra” - in the comments we were pointed out that we omitted some important events and did not talk about companies that have done a lot in this area. It would be impossible to fit everyone into one material, so today we want to talk separately about the “golden age” of virtualization technologies - the 90s of the last century and the beginning of this century.
Emulation and Virtualization
In the nineties of the twentieth century, there was a rapid development of technology, while creating not only the means for virtualization, but also a variety of emulators. In short, with the help of the latter, users were able to reproduce the work of software designed for a specific OS on another (for example, running Windows software on a Mac or Windows itself inside a Mac).
')
At the same time, using virtualization, you can “split” one system into two (or more) virtual servers , with its own software and hardware - each of them will function as a real machine, which is a more productive option.
Emulators - the first half of the 90s (DOSEMU, Wine and Bochs)
One of the first emulators was the DOSEMU project, which allowed to run DOS clone systems (FreeDOS, DR-DOS) and DOS software on IBM PC x86 computers running Linux. Released in 1992, DOSEMU simultaneously used the virtualization and emulation approach, which made it possible to achieve a fairly high speed of operation (it almost corresponded to the speed of the microprocessor 8086 ).

In July 1993, Alexandre Julliard released the first version of Wine he created - tools for running Windows programs on computers with installed Unix family of OS (hence the name of the project - Wi ndows E mulator).
Wine is not an emulator in the generally accepted meaning of the word, because it does not emulate the execution of the processor code. A survey of 38,500 users of desktop computers under Linux conducted in 2007 by desktoplinux, com showed that 31.5% of respondents use Wine to run Windows applications.
Currently, there is also a special library, Winelib , with which developers can compile their Windows software so that it can be easily ported to Unix systems.
A prominent representative of the family of emulators was the product of Bochs, released in 1994 by Kevin Lawton. Using Bochs, users could emulate the environment needed to run the guest operating system (including hard and floppy disks, sound and video cards, etc.) on the x86 architecture, which was new at the time.
The performance of the system left much to be desired, since virtualization was not used, however, Bochs liked the developers, who with its help could create and test programs for different operating systems.
Initially, Bochs was sold for $ 25, and to connect the possibility of emulating additional software, it was necessary to discuss a separate license with the developer. In 2000, the product was purchased by Mandriva (then Mandrakesoft) and released under the free GNU Lesser General Public License for use on Linux.
The second half of the 90s - the launch of Virtual PC and the birth of VMWare
In 1997, Apple created the Virtual PC virtualization software package (sold through a subsidiary of Connectix). With the help of this product, Mac users could run Windows OS - at that time there were many more programs under this operating system, so the launch of Virtual PC helped to smooth out the lack of Mac software.
The product, which includes the desktop and server virtualization programs of Virtual PC and Virtual Server, was demanded by companies that developed software for various platforms. In 2003, the company Connectix was bought by Microsoft, in 2006 it was decided to abandon the development version for Mac.
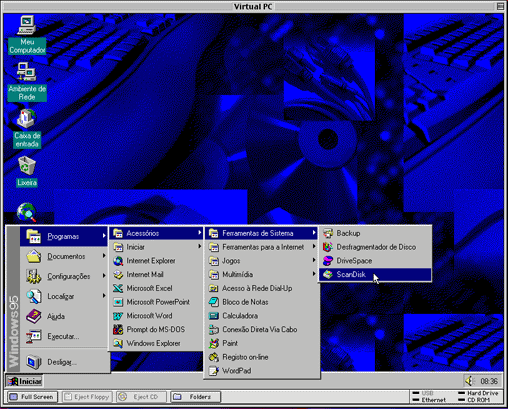
Connectix Virtual PC on Mac OS 9 running Windows 95
In 1998, VMware was founded, and in 1999 it launched a similar product called VMware Workstation. Initially, it was designed to work on Windows, but later the developers added support for other operating systems. In the same year, the company released the first virtualization tool for the x86 platform called the VMware Virtual Platform. By 2001, the first server products were developed (VMware GSX Server, VMware ESX Server, which could be installed directly on hardware without the need for an operating system on it).
2000s: Parallels and DOSbox
In 1997, Russian entrepreneur Sergey Belousov launched SWSoft, while its main office was located in Singapore. In 2004, this company acquired the American startup Parallels, which was engaged in desktop and server virtualization.
According to Maxim Tsyplyaev, who together with Sergey Belousov founded another IT company Acronis, Parallels had only technology, without a finished product. Business development has been helped by Apple’s actions.
In one of the interviews, another SWSoft co-founder, Oleg Melnikov, described the situation this way:
After Apple released the new MacBook on an Intel chipset, which we knew very well, Parallels Desktop for Mac was born, which allowed Windows to run on a Mac without rebooting. It became so popular that soon this brand became more recognizable than the brand of the main SWsoft company, and we decided to rebrand.
Another significant product at the beginning of the two thousandth year was the DOSBox emulator - it was released in 2002. With it, users could run "old" programs for DOS on modern operating systems. DOSBox is a free software product and is distributed under the GNU General Public License. Not long ago, the creators of Wine began the process of integrating their product with DOSBox.
Oracle and Sun: the history of VirtualBox
Cross-platform virtualization package for x86 and AMD64 / Intel64 Virtual Box has a rich history. The first version of the program was released by the German company innotek GmbH from the German Weinstadt in 2007. With its help, users could run as guest operating systems Windows, Linux, BSD, OS / 2, Solaris, Haiku and some others.

In February 2008, Sun Microsystems bought innotek to "create their own virtualization products." In 2010, Sun Microsystems has been absorbed by Oracle (negotiations have been going on since 2009), and the virtualization package has been re-branded and given the name Oracle VM VirtualBox.
Conclusion
The nineties of the last century and the first decade of the twenty-first century were marked by the creation of a large number of products for emulation and virtualization, which allowed. At the moment, the server virtualization segment is the most actively developing (mainly we told about it in the last article) and VMWare is holding it.
The CEO of 1cloud.ru, Vitaly Gritsay, believes that VMWare solutions have gained the largest market share due to their reliability and functionality.
Virtualization in our time has already firmly entered the production processes of many companies (not only from the IT sector) and has established itself as an excellent solution that allows you to expand the company's capabilities and at the same time save money. It seems to us that VMWare products cope well with these tasks, so we offer them to customers .
In the desktop virtualization market, VMWare and Citrix are among the leaders - according to various data , up to 75% of companies that need virtualization are selected from the products of these companies. However, other players are also creating innovative products (for example, an application from Parallels that allows you to access the desktop of your computer from an iPhone) that can help them win back a piece of cake in the future.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/241636/
All Articles