Who are Google, Mozilla and Microsoft friends with? Or is SHA-1 a thing of the past?
As early as September 5, 2014, Chromium browser developers in their blog announced that by January 1, 2017, their browser will no longer support the SHA-1 hashing algorithm. This algorithm is used (and used) to issue SSL certificates. All Chromium based browsers (including Google Chrome) will no longer support SHA-1. This initiative of Google was also supported by Mozilla and Microsoft. The starting point can be considered the release of Chrome browser version 39 at the end of November 2014.

Why did you decide to abandon SHA-1?
Almost all sites that use SSL to encrypt transmitted traffic have SSL certificates based on the SHA-1 hashing algorithm.
This algorithm was created in 2005 and has become morally obsolete in 9 years of use.
Wikipedia has a description of this hashing algorithm and calculations with hacking options. A security expert Bruce Schneier published in his blog calculations and the cost of finding a coliseum (when the same hash amount can correspond to two different messages), the cost of these resources drops sharply every year. Thus, by 2018, conducting an attack will be relatively cheap and will be possible not only by government organizations / research centers, but also by some gangster groups.
Therefore, the replacement of SHA-1 offer to use SHA-2.
What is the reaction of browser developers?
Google
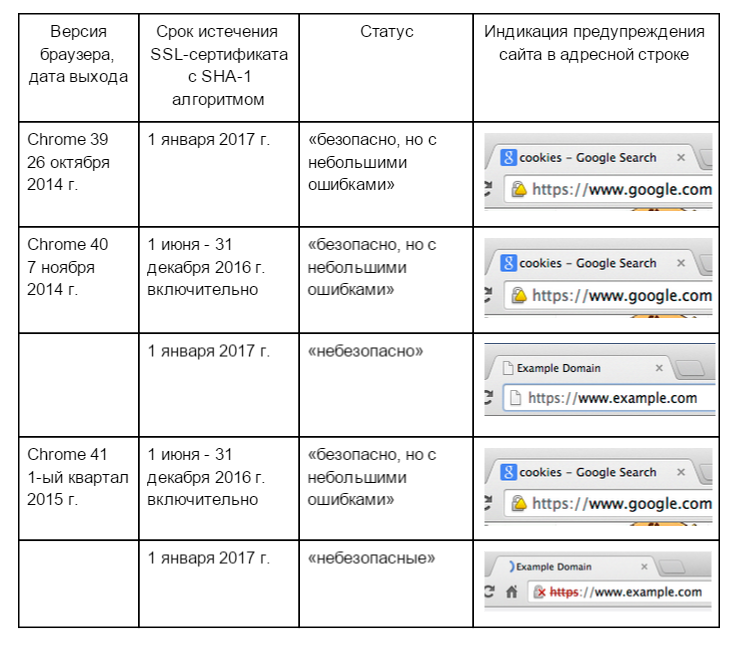
Each version of the Google Chrome browser will display the SSL connection security indicator if the site uses the certificate with the SHA-1 algorithm in the appropriate form.
')
Chronology of the release of new versions of Chrome browsers and the corresponding indicators:
Mozilla
Mozilla supported the Google initiative and also wrote down information on the refusal of working with certificates signed with SHA-1 in the Firefox browser.
Like Chrome, this will be phased in.
Beginning with Firefox 35, it is planned to add warning messages to the Web Console (Menu -> Development -> Web Console) in the Security category. It will be implemented in the next few weeks, and will appear in Firefox versions closer to the beginning of 2015.
Graphic indicators are planned to be added later. For certificates whose validity will expire after January 1, 2016 (inclusive), certificates with SHA-1 will display the “Untrusted Connection” status. From January 1, 2017, when SHA-1 is detected, only this status will be displayed for all sites.

Certificates signed with SHA-1 valid after January 1, 2017 will be rejected from January 1, 2017.
Microsoft
Regarding the refusal of support in Internet Explorer for certificate connections signed using the SHA-1 algorithm , information appeared in the technical blogs of employees back in November 2013. From this point on, Microsoft made policy changes with respect to certificates created using the SHA-1 hashing algorithm and certificate authorities themselves. This applies to Windows versions starting with Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008.
According to the changes, certification authorities should stop issuing SSL certificates or signing them with the SHA-1 algorithm from January 1, 2016.
Windows will no longer accept SSL certificates from January 1, 2017, implying that by this time SHA-1 will be replaced by SHA-2.
Certificates signed by SHA-1 will not be accepted from January 1, 2016, and those issued after January 1, 2016 will have unauthenticated status.
For Windows users themselves, no additional action is required.
You can test your browser at this address: https://ssltest39.ssl.symclab.com/

Why did you decide to abandon SHA-1?
Almost all sites that use SSL to encrypt transmitted traffic have SSL certificates based on the SHA-1 hashing algorithm.
This algorithm was created in 2005 and has become morally obsolete in 9 years of use.
Wikipedia has a description of this hashing algorithm and calculations with hacking options. A security expert Bruce Schneier published in his blog calculations and the cost of finding a coliseum (when the same hash amount can correspond to two different messages), the cost of these resources drops sharply every year. Thus, by 2018, conducting an attack will be relatively cheap and will be possible not only by government organizations / research centers, but also by some gangster groups.
Therefore, the replacement of SHA-1 offer to use SHA-2.
What is the reaction of browser developers?
Each version of the Google Chrome browser will display the SSL connection security indicator if the site uses the certificate with the SHA-1 algorithm in the appropriate form.
')
Chronology of the release of new versions of Chrome browsers and the corresponding indicators:

Mozilla
Mozilla supported the Google initiative and also wrote down information on the refusal of working with certificates signed with SHA-1 in the Firefox browser.
Like Chrome, this will be phased in.
Beginning with Firefox 35, it is planned to add warning messages to the Web Console (Menu -> Development -> Web Console) in the Security category. It will be implemented in the next few weeks, and will appear in Firefox versions closer to the beginning of 2015.
Graphic indicators are planned to be added later. For certificates whose validity will expire after January 1, 2016 (inclusive), certificates with SHA-1 will display the “Untrusted Connection” status. From January 1, 2017, when SHA-1 is detected, only this status will be displayed for all sites.

Certificates signed with SHA-1 valid after January 1, 2017 will be rejected from January 1, 2017.
Microsoft
Regarding the refusal of support in Internet Explorer for certificate connections signed using the SHA-1 algorithm , information appeared in the technical blogs of employees back in November 2013. From this point on, Microsoft made policy changes with respect to certificates created using the SHA-1 hashing algorithm and certificate authorities themselves. This applies to Windows versions starting with Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008.
According to the changes, certification authorities should stop issuing SSL certificates or signing them with the SHA-1 algorithm from January 1, 2016.
Windows will no longer accept SSL certificates from January 1, 2017, implying that by this time SHA-1 will be replaced by SHA-2.
Certificates signed by SHA-1 will not be accepted from January 1, 2016, and those issued after January 1, 2016 will have unauthenticated status.
For Windows users themselves, no additional action is required.
You can test your browser at this address: https://ssltest39.ssl.symclab.com/
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/241603/
All Articles