A brief excursion into the cooling server
At a certain moment, some enterprises grow to the state when their internal information systems no longer fit in a single server cabinet. Then the head of the IT department will have to weigh the pros and cons and decide whether to build or not to build a server. There can be several options: from completely getting rid of our own capacities and taking them to the clouds or collocation in a large data center, to building your own mini (or not very mini) data center with blackjack.
The process of calculating, planning and building a server is very responsible and expensive. It will be necessary to invest at the project stage, here, by the way, you can save if all the procedures in the server room, from design to construction, will be done by one contractor. The natural desire of the head of the enterprise in such a situation is to meet the minimum possible amount. And hostility is perceived any appreciation of the project. In such skirmishes, it is often forgotten that, in addition to the construction of the facility, its content will follow, which, if not properly designed, can deplete the enterprise’s budget for another non-existent server after two to three years.
The second largest consumer of resources (in this case, electricity and consumables) in the server is the cooling system. It’s not news to anyone that the “power” of the server’s cooling system should at least match, and at best, exceed by a couple of tens of percent the peak power of all the equipment installed in the server room. We will talk about what cooling systems are and how to save on the operation of such systems in this article.
The most common for operation and understanding are compressor air conditioners. In them, the refrigerant (in most cases - freon) transfers heat from the radiator of the indoor unit to the external one, where it dissipates energy into the environment. Read more about the principle of the air conditioner can be found here . Then there are liquid and combined systems, water or ethylene glycol are used as the main refrigerant, and the choice of coolant depends not only on the operating conditions, but also on the cooling method. And the most effective solution, under certain conditions, of course, are free-cooling systems. These are exclusively precision devices developed from almost nothing in each particular case.
')
Also pay attention to the classification by "form factor". Here it is conditionally possible to divide the system into two types. Household systems to which we are all accustomed, usually installed in offices and apartments, hanging on the walls or ceiling, but may well serve as cooling systems for specialized rooms. And precision systems, which include specialized air-conditioning systems, and, of course, all free-cooling and fluid systems.
Inside the precision systems, there is systematization according to the principle of operation and the method of delivery of the “cold” to “consumers”. And if with fundamental differences everything is more or less clear, then there are a great many ways to cool devices directly.
Among the classic common cases, you can distinguish a cold room with installed racks, here come home air conditioners. The classic versions of precision solutions are devices with in-line ducts, with cold and hot corridors, where racks stand in rows in such a way as to take in cold air coming in, for example, from under the raised floor. They give heated air to the corridors, from where it is forcibly removed. There are also options with air ducts to each rack, where air is fed into each individual rack from the top or bottom and then as actively withdrawn.
Non-classical solutions are slightly more than a lot. Needless to say that they are all precision. Most solutions are combinations of the above systems to increase efficiency and reduce costs. The variation here is from individual air conditioners for each server cabinet to liquid cooling of each individual server or even a processor. And it is also worth noting the system with direct contact of the consumer with the liquid. In this case, the server is completely immersed in a special oil. Oil is odorless and does not conduct electricity at all. The fluid is constantly circulating inside the equipment pools, and passes through cooling radiators.
Not once should think about the need to build a server. There is an opinion that a dedicated server room is not needed for capacities less than 5 kW. Usually, all the equipment is completely “stuffed” in a 42-47-unit rack cabinet, and the most that is needed is a separate one-frame rack for the cross. All this can be fenced off from the "admin" or some other room (most importantly not from the accounting department) with a glass or plasterboard partition with a sealed door, put a paired household air conditioner and go drink beer.
But we are building a server. First of all, we need to decide what kind of cooling system we will use, and it's not just the price. The choice of cooling method depends on many factors: the power of the equipment, the location of the server room in the building, the geographic location of the building itself and even the bias towards certain types of cooling devices and the blunt foresight of the authorities.
There is a widespread opinion that a household air conditioner will be enough for systems up to 10kW. It is understandable, because domestic split-systems of greater power, firstly, are quite problematic to buy, and secondly, their cost is approaching, or it exceeds the cost of similar precision precision air conditioners.
The ability to install a cooling system, the ability to connect communications, air ducts for specialized systems, arrange a raised floor or install turbines depends on the location of the server room in the building. With an insufficient ceiling height it is impossible to arrange a raised floor of the required depth, for installing air ducts there for blowing and for taking in air of a precision system. The situation in the middle of the building will create problems when laying air ducts, one of the options for a free cooling system, and the neighborhood with the economic department will generally put an end to the construction of a server room due to "we have a lot of noise."
The geographical factor plays one of the primary roles and often puts an end to the possibility of free cooling, if you are, for example, in the tropical belt. That is why TSODo builders are so fond of the northern regions of our planet, because you can not use air conditioners at all.
On top of that, some technicians have their own very strong belief in the applicability of one system and the absolute unacceptability of other cooling options. They will calmly and confidently prove their case, finding arguments “for” and looking for the flaws of other sentences, from real to mythical.
As a result, based on the chosen strategy, we will design the device of the server itself.
You are the owner of a small fleet of servers, 2-3 racks with which will stand in a separate room. You have no prospects for a smooth increase in capacity and you either do not want to bother, or (most likely) do not have a budget for more energy-efficient and environmentally friendly solutions.
First of all, decide how the racks with the equipment relative to the air conditioners will be located in your server room. The best option in your case would be to install the internal modules of the split-system opposite a row of racks, one above one, aimed at the "front" side of an open rack or cabinet with a mesh door. The equipment inside the rack makes sense to install the side with which it takes the air to cool the internal components. Some devices that are installed in racks can be rebuilt or even produced in the design, when they either take in or emit air from the front side, or into one of the side walls. Think about it when buying.
Even if the growth of total power is not expected, air conditioners should be taken with a margin of power, for example, taking the peak consumption-dispersion of the “hottest” rack itself and multiplying them, racks, quantity.
The minimum fault tolerance in this strategy is N + 1. In practice, it looks like two or more air conditioners of the same power, where "N" air conditioners are able to maintain the operating temperature in the server while "+1" is repaired or serviced. Most often in small server two units are used. To extend the life of both air conditioners it is necessary to use a device for rotating air conditioners. The device in certain periods of time switches from one air conditioner to another, monitors their starts and monitors performance. If one of the air conditioners fails, it should automatically switch on the “sleeping one” and notify the person in charge about the problem. It should be noted that not all models of household air conditioners support this function.
All server split systems installed in the latitudes of our country should have a so-called “winter set”. It is a board unit, some improvement in the radiator of the external unit of the air conditioner and the heating system for the pump crankcase. Works automatically.
Fig.1. Cooling household air conditioners.
Precision ( high-precision ) air conditioner (or other cooler) - created precisely so as to work most effectively in the infrastructure with the given final parameters. In other words, when we say “precision air conditioning”, we mean that both the room and the server equipment, and the “refrigeration unit” itself are developed in the project as a set of technologies that make it possible to ensure the performance, safety and durability of expensive equipment.
Needless to say that custom design devices are expensive. Sacred wars are between supporters of different camps. Some argue that for an ordinary server room there is a sufficiently paired industrial version of a domestic air conditioner, such as Daikin (FT series and FAQ) or Mitsubishi (Heavy series) have such. When choosing this option, it is important to take into account such disadvantages as local hot air stasis in the corners or in the units of racks that are not occupied by active equipment. No less dangerous factor - low humidity, because, as you know, air conditioning, dries the air. Dry air contributes to the accumulation of static electricity, the presence of static potential in thin electronics adversely affects the operation of chips, and increases the risk of their destruction by discharge. Of course, most of the factors are disposable, but in most cases it is a production crunch. Additional fans, air humidifiers are all multiplying points of failure, the cost of electricity and maintenance. The service, by the way, of the same humidifier, is not so much costly in its means as in time. Need regular cleaning and daily topping up with water.
Precisionists, too, not everything is smooth. First of all, they are very large: freon air conditioners have dimensions of two or three full-size racks. Since humidity control is one of the main functions of a specialized air conditioner, it is required to bring water to the indoor units, which is completely unacceptable for some IT workers. Cold air from such units is supplied to the racks through ducts, which are held either under the raised floor, the most frequent and most expensive option, or under the ceiling, which implies high ceilings and imposes additional restrictions on the installation of cable communications. Condensers-coolers of such air conditioners have decent dimensions, and immediately the question arises with their placement and connection of the pipe system from the indoor unit.
With the minuses done, let's move on to the pluses. These include: high performance, redundancy of only the active components of the air conditioner (for example, air ducts, I think, there is no sense to reserve), precise control over temperature and humidity, the possibility of detailed monitoring. The advantages from here are relative savings, guaranteed delivery of cold air to the consumer, support for high density of consumers per rack (this is more likely the rule, if the rack is empty, it will work inefficiently and affect the entire “ecosystem”). Between the increase in the cost of air conditioning and the subsequent energy efficiency can be traced quite understandable relationship.
As I said before, the most common precision air conditioning is the corridor system, where the racks are arranged in rows and installed so as to take air from the cold corridors (where air is supplied by the air conditioner) and return to the hot (where air is taken from the ventilation system). The air duct of such a system often serves as a raised floor. The panels of the floor itself are mostly solid, all cable communication is transferred from the ceiling to the ceiling whenever possible, under the floor, in front of the rows of racks in the floor are lattice panels from where the cooled air enters the front side of the rack. The doors of server cabinets with such a device do mesh at both ends, or they do not do it at all. Then the air heated by the servers is blown into the hot corridor from where it is sucked out by the forced ventilation system. Ideally, following the principles of thermodynamics, the hood should be placed at the top of the hot corridor, but often it is done in a raised floor to save space above the racks for laying cable communications. Recently, cold and hot corridors have become airtight from the common server room. This was able to achieve substantial savings on the dispersion of valuable cold. It is obligatory to install plugs in the free unit spaces of cabinets, because the hot air still tries to mix with the cooled one. This can increase the efficiency of cooling and a half to two times.
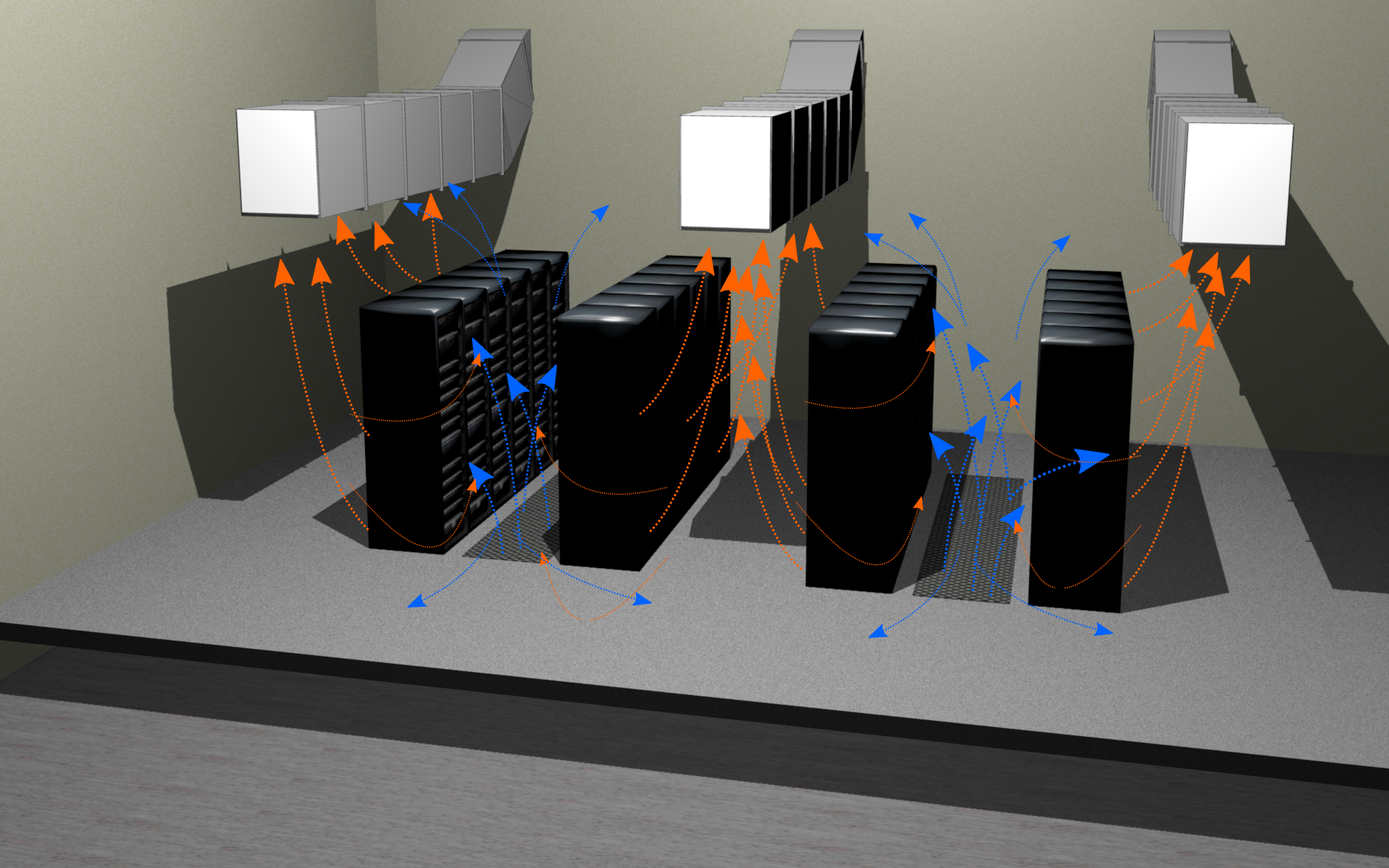

Fig. 2. The system with open corridors, the loss of precious cold air is obvious.

Fig. 3. More efficient, system with isolated corridors.
Intel, for example, pursuing the idea of cooling equipment as simply and efficiently as possible, went ahead and even patented a rack with an exhaust hood . The rack is an ordinary 19 "cabinet, but deeper than its counterparts and has an air duct in the upper lid that opens into a false ceiling, from where hot air is sucked out by air conditioners. The entire system, except air conditioners, is completely passive. But at the same time, according to Intel, it can cool 32 kW equipment on the rack.
Taking into account the climate of our country, precision air conditioners have another big plus: their scheme can be quite painlessly modified by adding a full or partial liquid circuit. Using ethylene glycol as a refrigerant, another liquid-cooled circuit is built parallel to the circuit of the air conditioner, thereby reducing the cost of electricity, air conditioning maintenance and extending the service life of the refrigerant. The effectiveness of the glycol contour begins already at a temperature below +20 C, which even in the summer at night in Russia is not uncommon.
An additional liquid circuit duplicates that of freon, and in principle can work around the clock, during the daytime “hot” time, cool the air conditioner compressor and the condenser, and when the street temperature drops, it switches to partial and full cooling of the internal heat exchanger.
Leaders among manufacturers of precision cooling systems are Schneider Electric, STULZ, Emerson Network Power, RC Group. Among their solutions are ready-made combined systems.
The fundamental difference between liquid cooling and freon cooling is only that in the circuit the liquid most often does not change the phase state, therefore, with the same power of the system, water and glycol systems will lose to freon in efficiency. However, fluid systems have undeniable advantages, such as capacity and versatility. In systems with liquid cooling, the cooler can be either fancoil on the roof or in the courtyard of the building, or the heating system of the building itself. The liquid can cool the air in the server, and can be used as a refrigerant for a single processor . The indisputable advantage of liquid conditioning is almost unlimited length of the tras, due to the low price of the refrigerant, for the system itself is only a plus. The most dangerous thing in this situation is a leakage of a conductive agent, but, apparently, this does not frighten anyone. IBM in this situation distinguished itself by the construction of SuperMUC, where it achieved 40% energy savings due to the lack of chillers in the cooling system. And Google in most of its data centers and does use a system of its own design, which uses a system of hot and cold corridors.
Another system with liquid involves immersing the server in a special mineral oil. Oil - dielectric, so that the circuit will not. With regard to energy efficiency, then, according to experts of the same Intel, the cooling system in this case spends 90% less energy, and also reduces the power consumption of the servers themselves. Racks for immersion liquid cooling are already being produced, for example, by CarnotJet . The racks are suitable for hosting any servers, only you first need to pull out all the fans from them.

Fig. 4. The most liquid cooling
Another factor of versatility is the huge number of ways to cool the refrigerant. For example, the technology SeaWater Air Conditioning (SWAC), this technology is built Google data center in Finland. From the name it is clear that to cool the water entering the data center, a heat exchanger is used on cold water withdrawn from the depths of the sea.
The classic liquid cooling system acts as an intermediary between the relatively high temperature inside the server room and the cooler, usually a dry cooling tower and a chiller, outside.
A dry cooling tower is a closed cooling circuit where the liquid enters the radiator, which is forcibly blown by air. There are still wet cooling towers in which water is sprayed and blown at the same time. In the ranges, or fancoils, the liquid refrigerant is usually only prepared, cooled to air temperature, the very same cooling takes place in the chiller heat exchanger.
A chiller is a refrigerator, it acts on freon, cooling the liquid passing through its cooler to the required temperature.
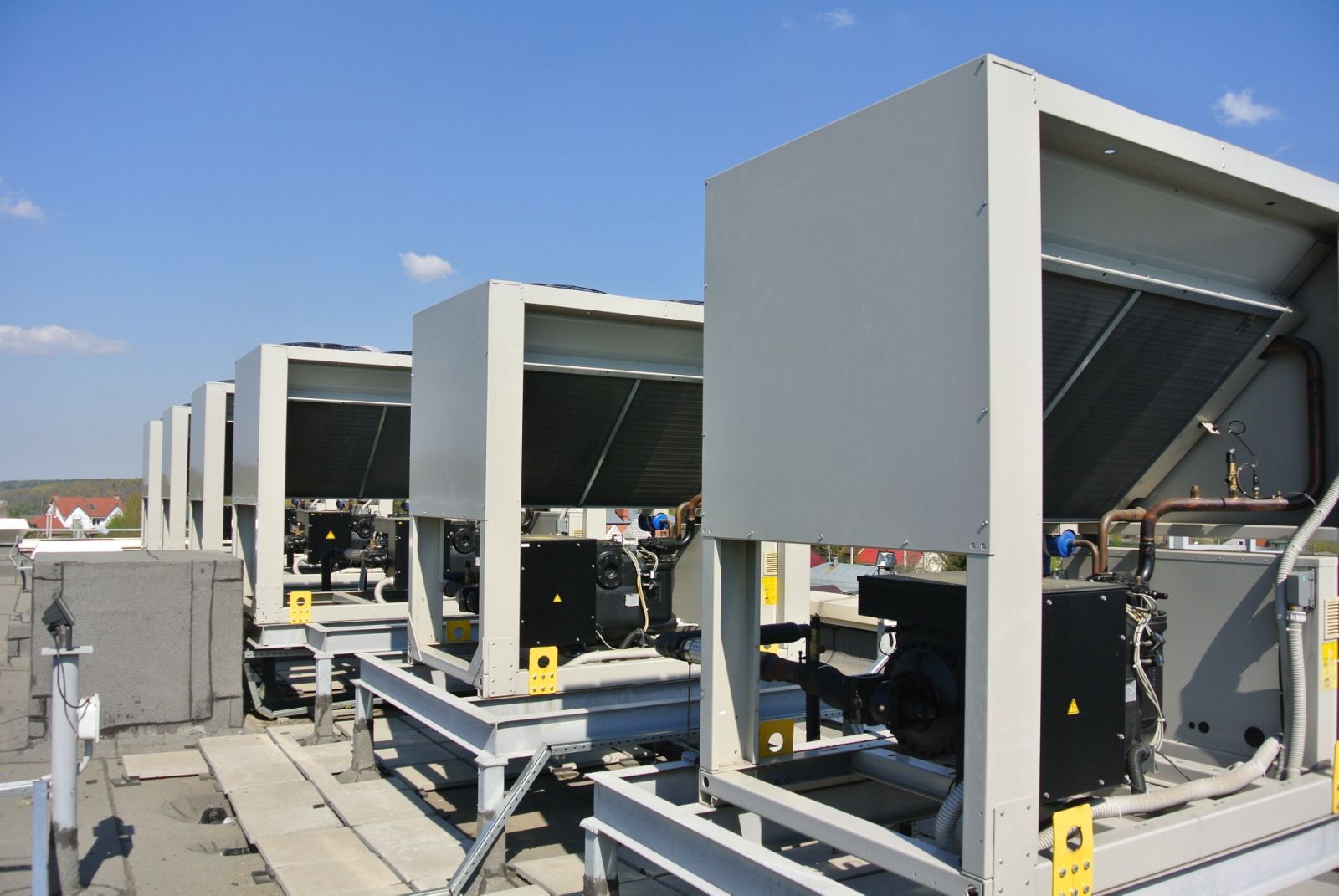

Fig. 5. Chillers installed on the roof (source www.quantum-v.ru )
For classic liquid conditioning, the same rules are true as for systems on freon. The air cooled in the evaporator passes through the consumers and is taken from the server by the cooling system itself. Despite the fact that fluid systems are more versatile and generally cheaper to use than freon ones, their efficiency is lower due to a larger number of air-chiller-liquid-air intermediaries. Agree, not the most successful scheme.
Direct freecooling is the most energy efficient way of server cooling. Of course, its efficiency depends entirely on air temperature “overboard”, but some changes in standardization and various green technologies are gradually moving the server’s cooling systems in this direction.
To begin with, the largest standardizer of engineering systems, and in particular cooling and heating systems, ASHRAE (eng. American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers) is the American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air Conditioning Engineers since 2004. twice increased the recommended air temperature for cooling server from +22 to +27 degrees C. And in 2011, the standard was amended to stratify two new equipment classes for server A3 and A4, where the temperature range was increased to +40 and +45 degrees . Server manufacturers are already producing such models. Although they are not yet widespread, more and more TsODO builders tend to use green technologies in cooling.
For server servers in our latitudes, free cooling can become, if not a complete replacement for the classical model of cooling, then a serious help in cooling in the cold season, and also will reduce the capacity of air conditioners.
The biggest problem with direct free cooling is general air pollution in cities. It may happen that the number, consumption of filters and the power of the fans for blowing them can negate all the savings in electricity and power. This problem is solved by the separation of the circuits and the introduction between them of a heat exchanger based on a rotor heat exchanger . In this case, filters will also be needed, but cheaper and with minimal air resistance.
Another big problem is that, with the auxiliary function of our free-cooler, it will be badly combined with home systems and best of all with precision ones.
Of the benefits: with direct free cooling, there is no risk of overdrying the air in the server room, because There is a constant exchange of air with the external environment. On the other hand, the humidity of the air on the street can absolutely not meet the accepted standards of humidity for server rooms, and here one of the main trump cards of free cooling systems - adiabatic cooling - comes to the rescue.
It has long been observed that humid air in water bodies is always cooler than on the plains in the distance from them, to recall at least the sea breeze. For adiabatic air cooling, neither backup systems nor complex technical solutions are needed. They are arranged according to the principle of wet cooling towers, water is sprayed into the heated outside air in the chambers by the nozzles, which evaporates and cools the air. This system not only effectively lowers the temperature of the outside air, but also creates the necessary humidity. The truth is, in such systems a new expendable material appears - water. Therefore, along with PUE ( Power usage effectiveness ), ASHRAE introduced the new term WUE ( Water usage effectiveness (PDF)) . For what these parameters are responsible, I think everyone understands.
As a striking example of the introduction of such systems, we can mention the eBay Mercury data center in Phoenix (USA) and Facebook in Prineville (USA).
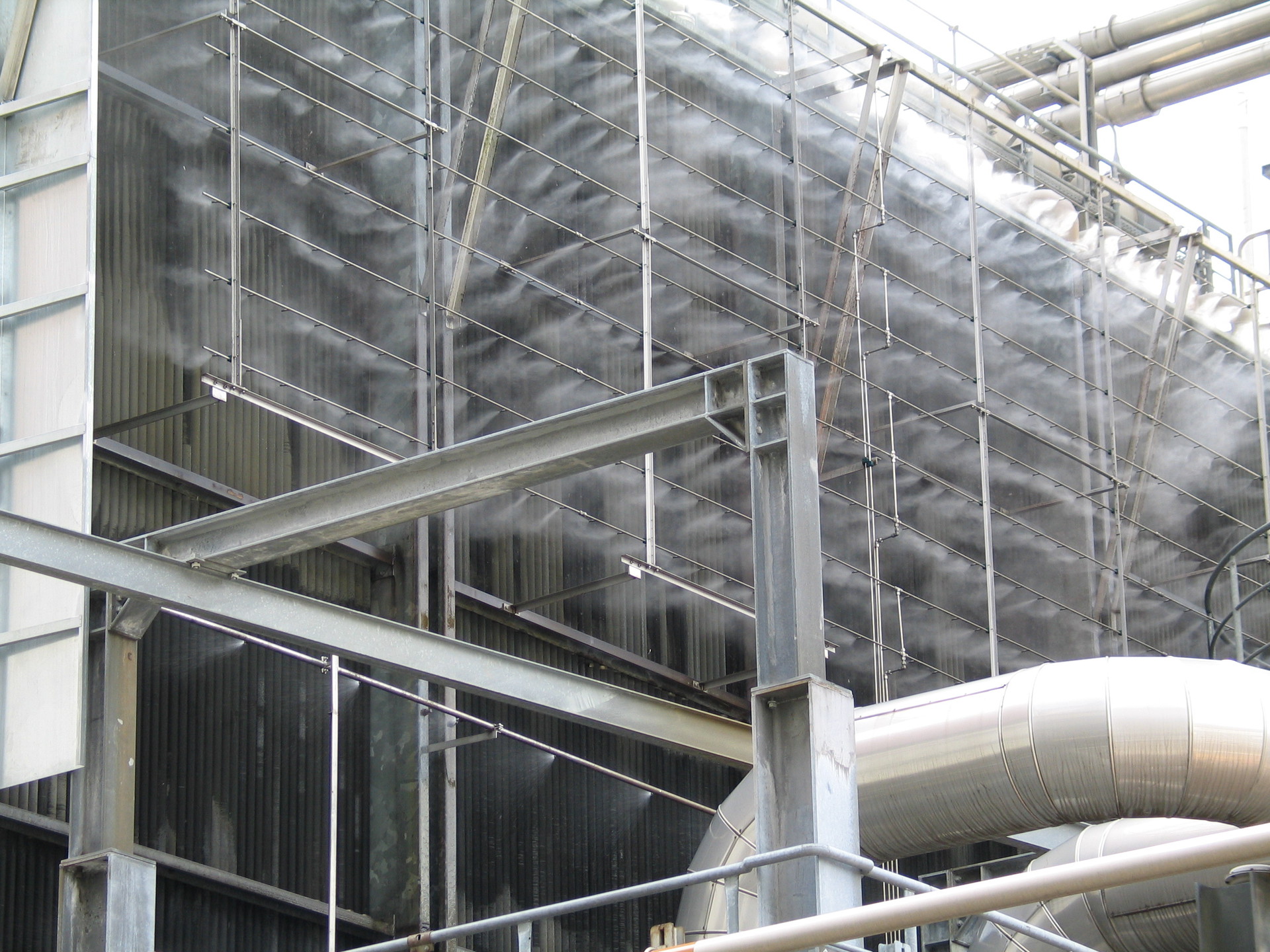

Fig. 6. Adiabatic cooling in action (source www.es-engineering.ru ).
"So how, all the same, cool the small server for a couple of dozen kilowatts?" - you ask.
The answer is ambiguous. Most readers will find a solution of two normal household air conditioners. Those who can convince their own leadership in the need to save and introduce green innovation will get a lot of headaches and then endless enjoyment of the final result.
As I have already said, a particular solution strongly depends on the climatic conditions of a particular region. For the perception of the climate pattern, it is best to take a historical reference to the maximums and minimums of temperature and humidity in the entire history of instrumental observations in your region or city, as well as to analyze detailed data on the hottest temperatures in the last 10-20 years. This is more than enough to develop a clear strategy.
Despite all the advantages of free cooling, in the middle band, in 80 cases out of 100 it is most likely that you will not be able to do without a compressor or liquid conditioner. In this regard, the general idea of building a “large” energy-efficient server is:
, . , , .
, . , , , . , Ethernet Wifi. , 19" . , netping GSM SMS-, , .
, , , Zabbix , , . , , - .
.
, . , , — , , . , . , , , .
, .
The process of calculating, planning and building a server is very responsible and expensive. It will be necessary to invest at the project stage, here, by the way, you can save if all the procedures in the server room, from design to construction, will be done by one contractor. The natural desire of the head of the enterprise in such a situation is to meet the minimum possible amount. And hostility is perceived any appreciation of the project. In such skirmishes, it is often forgotten that, in addition to the construction of the facility, its content will follow, which, if not properly designed, can deplete the enterprise’s budget for another non-existent server after two to three years.
The second largest consumer of resources (in this case, electricity and consumables) in the server is the cooling system. It’s not news to anyone that the “power” of the server’s cooling system should at least match, and at best, exceed by a couple of tens of percent the peak power of all the equipment installed in the server room. We will talk about what cooling systems are and how to save on the operation of such systems in this article.
Classification of cooling systems
The most common for operation and understanding are compressor air conditioners. In them, the refrigerant (in most cases - freon) transfers heat from the radiator of the indoor unit to the external one, where it dissipates energy into the environment. Read more about the principle of the air conditioner can be found here . Then there are liquid and combined systems, water or ethylene glycol are used as the main refrigerant, and the choice of coolant depends not only on the operating conditions, but also on the cooling method. And the most effective solution, under certain conditions, of course, are free-cooling systems. These are exclusively precision devices developed from almost nothing in each particular case.
')
Also pay attention to the classification by "form factor". Here it is conditionally possible to divide the system into two types. Household systems to which we are all accustomed, usually installed in offices and apartments, hanging on the walls or ceiling, but may well serve as cooling systems for specialized rooms. And precision systems, which include specialized air-conditioning systems, and, of course, all free-cooling and fluid systems.
Inside the precision systems, there is systematization according to the principle of operation and the method of delivery of the “cold” to “consumers”. And if with fundamental differences everything is more or less clear, then there are a great many ways to cool devices directly.
Among the classic common cases, you can distinguish a cold room with installed racks, here come home air conditioners. The classic versions of precision solutions are devices with in-line ducts, with cold and hot corridors, where racks stand in rows in such a way as to take in cold air coming in, for example, from under the raised floor. They give heated air to the corridors, from where it is forcibly removed. There are also options with air ducts to each rack, where air is fed into each individual rack from the top or bottom and then as actively withdrawn.
Non-classical solutions are slightly more than a lot. Needless to say that they are all precision. Most solutions are combinations of the above systems to increase efficiency and reduce costs. The variation here is from individual air conditioners for each server cabinet to liquid cooling of each individual server or even a processor. And it is also worth noting the system with direct contact of the consumer with the liquid. In this case, the server is completely immersed in a special oil. Oil is odorless and does not conduct electricity at all. The fluid is constantly circulating inside the equipment pools, and passes through cooling radiators.
Strategy
Not once should think about the need to build a server. There is an opinion that a dedicated server room is not needed for capacities less than 5 kW. Usually, all the equipment is completely “stuffed” in a 42-47-unit rack cabinet, and the most that is needed is a separate one-frame rack for the cross. All this can be fenced off from the "admin" or some other room (most importantly not from the accounting department) with a glass or plasterboard partition with a sealed door, put a paired household air conditioner and go drink beer.
But we are building a server. First of all, we need to decide what kind of cooling system we will use, and it's not just the price. The choice of cooling method depends on many factors: the power of the equipment, the location of the server room in the building, the geographic location of the building itself and even the bias towards certain types of cooling devices and the blunt foresight of the authorities.
There is a widespread opinion that a household air conditioner will be enough for systems up to 10kW. It is understandable, because domestic split-systems of greater power, firstly, are quite problematic to buy, and secondly, their cost is approaching, or it exceeds the cost of similar precision precision air conditioners.
The ability to install a cooling system, the ability to connect communications, air ducts for specialized systems, arrange a raised floor or install turbines depends on the location of the server room in the building. With an insufficient ceiling height it is impossible to arrange a raised floor of the required depth, for installing air ducts there for blowing and for taking in air of a precision system. The situation in the middle of the building will create problems when laying air ducts, one of the options for a free cooling system, and the neighborhood with the economic department will generally put an end to the construction of a server room due to "we have a lot of noise."
The geographical factor plays one of the primary roles and often puts an end to the possibility of free cooling, if you are, for example, in the tropical belt. That is why TSODo builders are so fond of the northern regions of our planet, because you can not use air conditioners at all.
On top of that, some technicians have their own very strong belief in the applicability of one system and the absolute unacceptability of other cooling options. They will calmly and confidently prove their case, finding arguments “for” and looking for the flaws of other sentences, from real to mythical.
As a result, based on the chosen strategy, we will design the device of the server itself.
The strategy of cooling household air conditioners
You are the owner of a small fleet of servers, 2-3 racks with which will stand in a separate room. You have no prospects for a smooth increase in capacity and you either do not want to bother, or (most likely) do not have a budget for more energy-efficient and environmentally friendly solutions.
First of all, decide how the racks with the equipment relative to the air conditioners will be located in your server room. The best option in your case would be to install the internal modules of the split-system opposite a row of racks, one above one, aimed at the "front" side of an open rack or cabinet with a mesh door. The equipment inside the rack makes sense to install the side with which it takes the air to cool the internal components. Some devices that are installed in racks can be rebuilt or even produced in the design, when they either take in or emit air from the front side, or into one of the side walls. Think about it when buying.
Even if the growth of total power is not expected, air conditioners should be taken with a margin of power, for example, taking the peak consumption-dispersion of the “hottest” rack itself and multiplying them, racks, quantity.
The minimum fault tolerance in this strategy is N + 1. In practice, it looks like two or more air conditioners of the same power, where "N" air conditioners are able to maintain the operating temperature in the server while "+1" is repaired or serviced. Most often in small server two units are used. To extend the life of both air conditioners it is necessary to use a device for rotating air conditioners. The device in certain periods of time switches from one air conditioner to another, monitors their starts and monitors performance. If one of the air conditioners fails, it should automatically switch on the “sleeping one” and notify the person in charge about the problem. It should be noted that not all models of household air conditioners support this function.
All server split systems installed in the latitudes of our country should have a so-called “winter set”. It is a board unit, some improvement in the radiator of the external unit of the air conditioner and the heating system for the pump crankcase. Works automatically.

Fig.1. Cooling household air conditioners.
Precision room cooling systems
Precision ( high-precision ) air conditioner (or other cooler) - created precisely so as to work most effectively in the infrastructure with the given final parameters. In other words, when we say “precision air conditioning”, we mean that both the room and the server equipment, and the “refrigeration unit” itself are developed in the project as a set of technologies that make it possible to ensure the performance, safety and durability of expensive equipment.
Needless to say that custom design devices are expensive. Sacred wars are between supporters of different camps. Some argue that for an ordinary server room there is a sufficiently paired industrial version of a domestic air conditioner, such as Daikin (FT series and FAQ) or Mitsubishi (Heavy series) have such. When choosing this option, it is important to take into account such disadvantages as local hot air stasis in the corners or in the units of racks that are not occupied by active equipment. No less dangerous factor - low humidity, because, as you know, air conditioning, dries the air. Dry air contributes to the accumulation of static electricity, the presence of static potential in thin electronics adversely affects the operation of chips, and increases the risk of their destruction by discharge. Of course, most of the factors are disposable, but in most cases it is a production crunch. Additional fans, air humidifiers are all multiplying points of failure, the cost of electricity and maintenance. The service, by the way, of the same humidifier, is not so much costly in its means as in time. Need regular cleaning and daily topping up with water.
Precisionists, too, not everything is smooth. First of all, they are very large: freon air conditioners have dimensions of two or three full-size racks. Since humidity control is one of the main functions of a specialized air conditioner, it is required to bring water to the indoor units, which is completely unacceptable for some IT workers. Cold air from such units is supplied to the racks through ducts, which are held either under the raised floor, the most frequent and most expensive option, or under the ceiling, which implies high ceilings and imposes additional restrictions on the installation of cable communications. Condensers-coolers of such air conditioners have decent dimensions, and immediately the question arises with their placement and connection of the pipe system from the indoor unit.
With the minuses done, let's move on to the pluses. These include: high performance, redundancy of only the active components of the air conditioner (for example, air ducts, I think, there is no sense to reserve), precise control over temperature and humidity, the possibility of detailed monitoring. The advantages from here are relative savings, guaranteed delivery of cold air to the consumer, support for high density of consumers per rack (this is more likely the rule, if the rack is empty, it will work inefficiently and affect the entire “ecosystem”). Between the increase in the cost of air conditioning and the subsequent energy efficiency can be traced quite understandable relationship.
As I said before, the most common precision air conditioning is the corridor system, where the racks are arranged in rows and installed so as to take air from the cold corridors (where air is supplied by the air conditioner) and return to the hot (where air is taken from the ventilation system). The air duct of such a system often serves as a raised floor. The panels of the floor itself are mostly solid, all cable communication is transferred from the ceiling to the ceiling whenever possible, under the floor, in front of the rows of racks in the floor are lattice panels from where the cooled air enters the front side of the rack. The doors of server cabinets with such a device do mesh at both ends, or they do not do it at all. Then the air heated by the servers is blown into the hot corridor from where it is sucked out by the forced ventilation system. Ideally, following the principles of thermodynamics, the hood should be placed at the top of the hot corridor, but often it is done in a raised floor to save space above the racks for laying cable communications. Recently, cold and hot corridors have become airtight from the common server room. This was able to achieve substantial savings on the dispersion of valuable cold. It is obligatory to install plugs in the free unit spaces of cabinets, because the hot air still tries to mix with the cooled one. This can increase the efficiency of cooling and a half to two times.

Fig. 2. The system with open corridors, the loss of precious cold air is obvious.

Fig. 3. More efficient, system with isolated corridors.
Intel, for example, pursuing the idea of cooling equipment as simply and efficiently as possible, went ahead and even patented a rack with an exhaust hood . The rack is an ordinary 19 "cabinet, but deeper than its counterparts and has an air duct in the upper lid that opens into a false ceiling, from where hot air is sucked out by air conditioners. The entire system, except air conditioners, is completely passive. But at the same time, according to Intel, it can cool 32 kW equipment on the rack.
Taking into account the climate of our country, precision air conditioners have another big plus: their scheme can be quite painlessly modified by adding a full or partial liquid circuit. Using ethylene glycol as a refrigerant, another liquid-cooled circuit is built parallel to the circuit of the air conditioner, thereby reducing the cost of electricity, air conditioning maintenance and extending the service life of the refrigerant. The effectiveness of the glycol contour begins already at a temperature below +20 C, which even in the summer at night in Russia is not uncommon.
An additional liquid circuit duplicates that of freon, and in principle can work around the clock, during the daytime “hot” time, cool the air conditioner compressor and the condenser, and when the street temperature drops, it switches to partial and full cooling of the internal heat exchanger.
Leaders among manufacturers of precision cooling systems are Schneider Electric, STULZ, Emerson Network Power, RC Group. Among their solutions are ready-made combined systems.
Fluid systems
The fundamental difference between liquid cooling and freon cooling is only that in the circuit the liquid most often does not change the phase state, therefore, with the same power of the system, water and glycol systems will lose to freon in efficiency. However, fluid systems have undeniable advantages, such as capacity and versatility. In systems with liquid cooling, the cooler can be either fancoil on the roof or in the courtyard of the building, or the heating system of the building itself. The liquid can cool the air in the server, and can be used as a refrigerant for a single processor . The indisputable advantage of liquid conditioning is almost unlimited length of the tras, due to the low price of the refrigerant, for the system itself is only a plus. The most dangerous thing in this situation is a leakage of a conductive agent, but, apparently, this does not frighten anyone. IBM in this situation distinguished itself by the construction of SuperMUC, where it achieved 40% energy savings due to the lack of chillers in the cooling system. And Google in most of its data centers and does use a system of its own design, which uses a system of hot and cold corridors.
Another system with liquid involves immersing the server in a special mineral oil. Oil - dielectric, so that the circuit will not. With regard to energy efficiency, then, according to experts of the same Intel, the cooling system in this case spends 90% less energy, and also reduces the power consumption of the servers themselves. Racks for immersion liquid cooling are already being produced, for example, by CarnotJet . The racks are suitable for hosting any servers, only you first need to pull out all the fans from them.

Fig. 4. The most liquid cooling
Another factor of versatility is the huge number of ways to cool the refrigerant. For example, the technology SeaWater Air Conditioning (SWAC), this technology is built Google data center in Finland. From the name it is clear that to cool the water entering the data center, a heat exchanger is used on cold water withdrawn from the depths of the sea.
The classic liquid cooling system acts as an intermediary between the relatively high temperature inside the server room and the cooler, usually a dry cooling tower and a chiller, outside.
A dry cooling tower is a closed cooling circuit where the liquid enters the radiator, which is forcibly blown by air. There are still wet cooling towers in which water is sprayed and blown at the same time. In the ranges, or fancoils, the liquid refrigerant is usually only prepared, cooled to air temperature, the very same cooling takes place in the chiller heat exchanger.
A chiller is a refrigerator, it acts on freon, cooling the liquid passing through its cooler to the required temperature.

Fig. 5. Chillers installed on the roof (source www.quantum-v.ru )
For classic liquid conditioning, the same rules are true as for systems on freon. The air cooled in the evaporator passes through the consumers and is taken from the server by the cooling system itself. Despite the fact that fluid systems are more versatile and generally cheaper to use than freon ones, their efficiency is lower due to a larger number of air-chiller-liquid-air intermediaries. Agree, not the most successful scheme.
We remove intermediaries
Direct freecooling is the most energy efficient way of server cooling. Of course, its efficiency depends entirely on air temperature “overboard”, but some changes in standardization and various green technologies are gradually moving the server’s cooling systems in this direction.
To begin with, the largest standardizer of engineering systems, and in particular cooling and heating systems, ASHRAE (eng. American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers) is the American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air Conditioning Engineers since 2004. twice increased the recommended air temperature for cooling server from +22 to +27 degrees C. And in 2011, the standard was amended to stratify two new equipment classes for server A3 and A4, where the temperature range was increased to +40 and +45 degrees . Server manufacturers are already producing such models. Although they are not yet widespread, more and more TsODO builders tend to use green technologies in cooling.
For server servers in our latitudes, free cooling can become, if not a complete replacement for the classical model of cooling, then a serious help in cooling in the cold season, and also will reduce the capacity of air conditioners.
The biggest problem with direct free cooling is general air pollution in cities. It may happen that the number, consumption of filters and the power of the fans for blowing them can negate all the savings in electricity and power. This problem is solved by the separation of the circuits and the introduction between them of a heat exchanger based on a rotor heat exchanger . In this case, filters will also be needed, but cheaper and with minimal air resistance.
Another big problem is that, with the auxiliary function of our free-cooler, it will be badly combined with home systems and best of all with precision ones.
Of the benefits: with direct free cooling, there is no risk of overdrying the air in the server room, because There is a constant exchange of air with the external environment. On the other hand, the humidity of the air on the street can absolutely not meet the accepted standards of humidity for server rooms, and here one of the main trump cards of free cooling systems - adiabatic cooling - comes to the rescue.
It has long been observed that humid air in water bodies is always cooler than on the plains in the distance from them, to recall at least the sea breeze. For adiabatic air cooling, neither backup systems nor complex technical solutions are needed. They are arranged according to the principle of wet cooling towers, water is sprayed into the heated outside air in the chambers by the nozzles, which evaporates and cools the air. This system not only effectively lowers the temperature of the outside air, but also creates the necessary humidity. The truth is, in such systems a new expendable material appears - water. Therefore, along with PUE ( Power usage effectiveness ), ASHRAE introduced the new term WUE ( Water usage effectiveness (PDF)) . For what these parameters are responsible, I think everyone understands.
As a striking example of the introduction of such systems, we can mention the eBay Mercury data center in Phoenix (USA) and Facebook in Prineville (USA).

Fig. 6. Adiabatic cooling in action (source www.es-engineering.ru ).
Instead of conclusion
"So how, all the same, cool the small server for a couple of dozen kilowatts?" - you ask.
The answer is ambiguous. Most readers will find a solution of two normal household air conditioners. Those who can convince their own leadership in the need to save and introduce green innovation will get a lot of headaches and then endless enjoyment of the final result.
As I have already said, a particular solution strongly depends on the climatic conditions of a particular region. For the perception of the climate pattern, it is best to take a historical reference to the maximums and minimums of temperature and humidity in the entire history of instrumental observations in your region or city, as well as to analyze detailed data on the hottest temperatures in the last 10-20 years. This is more than enough to develop a clear strategy.
Despite all the advantages of free cooling, in the middle band, in 80 cases out of 100 it is most likely that you will not be able to do without a compressor or liquid conditioner. In this regard, the general idea of building a “large” energy-efficient server is:
- This is a room with a precision cooling system. Indoors arranged raised floors for the supply of cold air, with the division into cold and hot corridors, isolated from the common server room to provide a more accurate heat exchange.
- Most of the time, the system works on direct free-cooling; when the outside air temperature rises, the adiabatic cooling system is connected. When the permissible norms of temperature are exceeded, the compressor or liquid cooling system is connected, i.e. air conditioning.
, . , , .
, . , , , . , Ethernet Wifi. , 19" . , netping GSM SMS-, , .
, , , Zabbix , , . , , - .
.
, . , , — , , . , . , , , .
, .
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/241581/
All Articles