About trying to evaluate search queries
Today I wondered about the search query evaluation for seo promotion and I was sure that I could easily find the right answer.
A little about what it is for. Naturally, in order to create a semantic core, providing the maximum possible number of target audiences for this site, at the moment, with a certain budget . Moreover, this assessment should be as formalized as possible . I understood and understand that in some situations an individual approach can give the best result, but I would like to have an algorithm for obtaining initial / indicative results. I do not mean the principles: “The more popular, the better” or “We take advantage of the recommendations of SeoPult”, we are talking about more reasonable estimates.
I do not know whether it is worth it, but I warn you that below will be graphic images (graphs).
So, as we well know, search queries can be assessed / classified according to different parameters: geo-dependent / geone-dependent, commercial / non-commercial, one-two-three-word, etc. Obviously, the parameters of popularity / frequency and competitiveness deserve close attention, because the higher the frequency and the lower the competitiveness, the better the query .
')
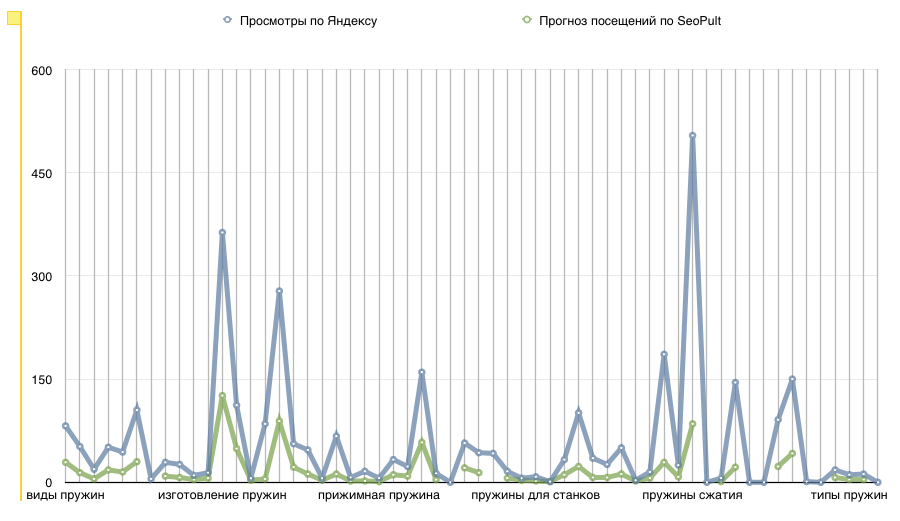
The graphs “browsing by Yandex” and “SeoPult Visiting Forecast” coincide
With popularity, everything is relatively simple - there is, for example, Wordstat. With competition is getting harder! This parameter can be defined in different ways: as the number of pages participating in the ranking by request; or as (approximate) cost of one visitor. If we talk about the first definition, then we come to the KEI (Keyword Effectiveness Index), which in itself has many possible calculation formulas that correlate weakly (or not at all) with each other. If we talk about competitiveness , how about estimating the cost of one visitor, then there also arises the question of which / whose data to take (SeoPult? Direct? Evaluation of the average reference budget? Or something else ...).
In fact, depending on the definition, the parameter should express competitiveness in a single aspect: either it is just a quantitative aspect (classical KEI); or it is a quantitative and qualitative aspect (KEI with additional parameters); or it is a financial aspect; or is it a comprehensive assessment.
Therefore, it can be assumed that by analyzing various expressions of competitiveness , we should get a wide range of information about the search query: do many sites “exploit” the given query; what is the level of their internal optimization; what is the level of their external optimization; and so on. It would seem that this is a good, flexible and fairly easily formalized method: we calculate the competitiveness; we determine the best requests in relation to the frequency; and evaluate the expediency of promotion (for each of the requests) , based on the known levels of competition in various expressions and parameters of the website being promoted and the allocated budget!
But there is one "but" ...
It can be assumed that different expressions of competitiveness should still correlate with each other . Let it be weak, a little, at least somehow. Especially, if we are talking about its integrated assessment.
However, in the first analysis performed, various expressions of competitiveness have no general tendency , which raises at least three questions: what is the reason for the lack of correlation; do these estimates really express competitiveness; validity of the described method.
Below are graphs and analysis data.

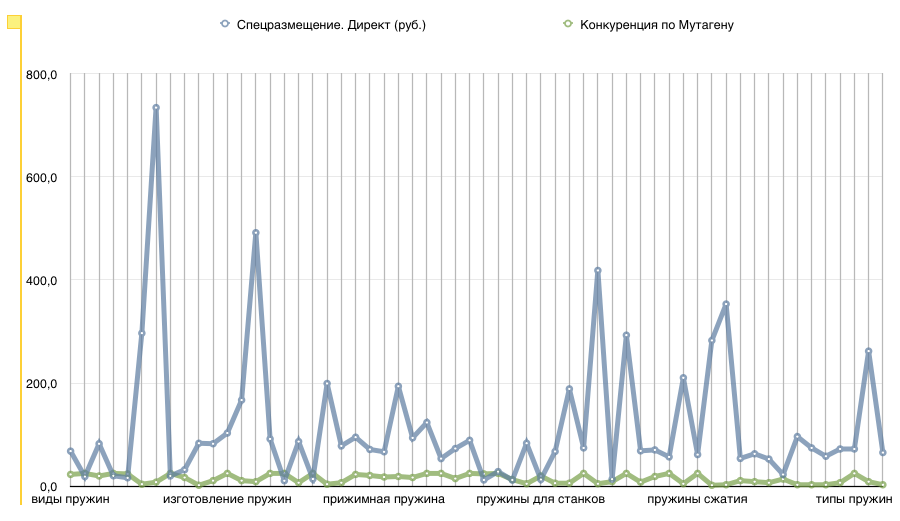
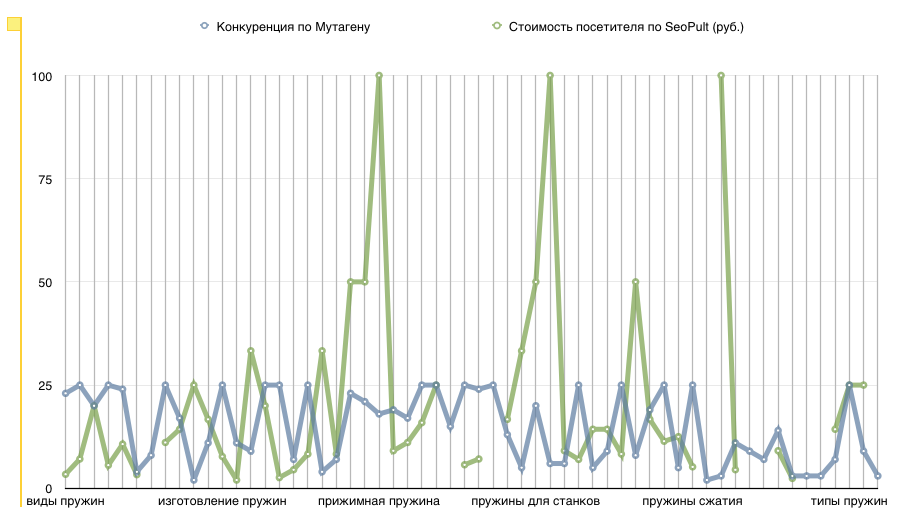
The lack of a relationship between the three expressions of competitiveness: “Mutagen competition”, “Special Placement. Direct (RUB) "," Visitor Cost by SeoPult (RUB) "
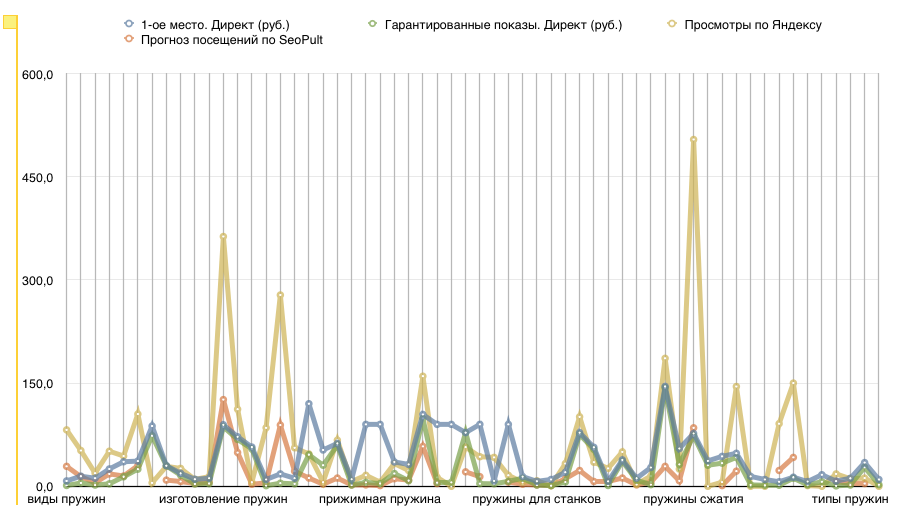
Revealed correlations among expressions of competitiveness: “1st place. Direct (rub.) ”And“ Guaranteed impressions. Direct (RUB) ", as well as their relationship with frequency indicators:" Yandex views "," SeoPult Visits Forecast "

A little about what it is for. Naturally, in order to create a semantic core, providing the maximum possible number of target audiences for this site, at the moment, with a certain budget . Moreover, this assessment should be as formalized as possible . I understood and understand that in some situations an individual approach can give the best result, but I would like to have an algorithm for obtaining initial / indicative results. I do not mean the principles: “The more popular, the better” or “We take advantage of the recommendations of SeoPult”, we are talking about more reasonable estimates.
I do not know whether it is worth it, but I warn you that below will be graphic images (graphs).
So, as we well know, search queries can be assessed / classified according to different parameters: geo-dependent / geone-dependent, commercial / non-commercial, one-two-three-word, etc. Obviously, the parameters of popularity / frequency and competitiveness deserve close attention, because the higher the frequency and the lower the competitiveness, the better the query .
')

The graphs “browsing by Yandex” and “SeoPult Visiting Forecast” coincide
With popularity, everything is relatively simple - there is, for example, Wordstat. With competition is getting harder! This parameter can be defined in different ways: as the number of pages participating in the ranking by request; or as (approximate) cost of one visitor. If we talk about the first definition, then we come to the KEI (Keyword Effectiveness Index), which in itself has many possible calculation formulas that correlate weakly (or not at all) with each other. If we talk about competitiveness , how about estimating the cost of one visitor, then there also arises the question of which / whose data to take (SeoPult? Direct? Evaluation of the average reference budget? Or something else ...).
In fact, depending on the definition, the parameter should express competitiveness in a single aspect: either it is just a quantitative aspect (classical KEI); or it is a quantitative and qualitative aspect (KEI with additional parameters); or it is a financial aspect; or is it a comprehensive assessment.
Therefore, it can be assumed that by analyzing various expressions of competitiveness , we should get a wide range of information about the search query: do many sites “exploit” the given query; what is the level of their internal optimization; what is the level of their external optimization; and so on. It would seem that this is a good, flexible and fairly easily formalized method: we calculate the competitiveness; we determine the best requests in relation to the frequency; and evaluate the expediency of promotion (for each of the requests) , based on the known levels of competition in various expressions and parameters of the website being promoted and the allocated budget!
But there is one "but" ...
It can be assumed that different expressions of competitiveness should still correlate with each other . Let it be weak, a little, at least somehow. Especially, if we are talking about its integrated assessment.
However, in the first analysis performed, various expressions of competitiveness have no general tendency , which raises at least three questions: what is the reason for the lack of correlation; do these estimates really express competitiveness; validity of the described method.
Below are graphs and analysis data.



The lack of a relationship between the three expressions of competitiveness: “Mutagen competition”, “Special Placement. Direct (RUB) "," Visitor Cost by SeoPult (RUB) "
Revealed correlations among expressions of competitiveness: “1st place. Direct (rub.) ”And“ Guaranteed impressions. Direct (RUB) ", as well as their relationship with frequency indicators:" Yandex views "," SeoPult Visits Forecast "


Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/239773/
All Articles