Robots in medicine
In the past, my post on telemedicine was mentioning a robot surgeon Da Vinci, which in 2010 was installed around 1000 in the world. But this is not the only achievement of robotics, used in medicine.
In what areas and for what use robots? In surgery, as carers for children and the elderly, in telemedicine and even for drug delivery. More - I ask for habrakat.

')
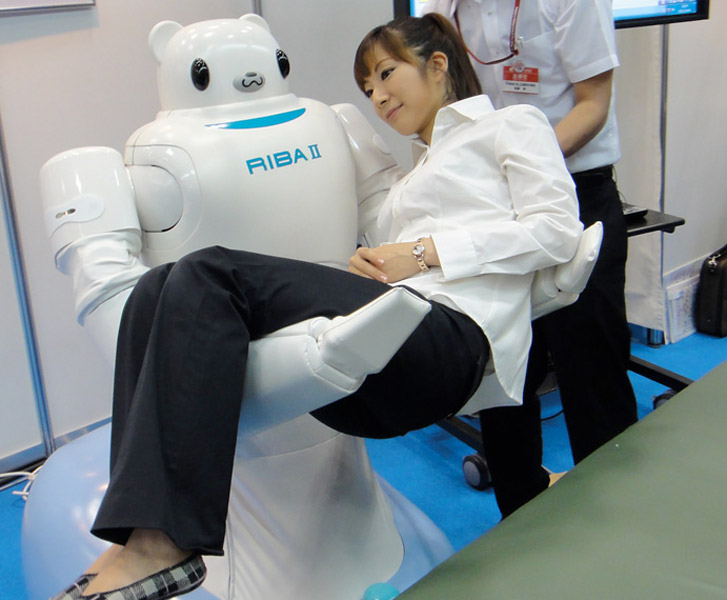
Robot Riba is from Japan. He was introduced in 2009. Its main purpose is to rock the sick and the elderly with the help of its long and strong hands. This is a great helper in clinics, as he can move patients from place to place, or shift them from a wheelchair to a bed.

In 2009 presented RIBA II. This version of the robot can lift patients directly from the floor, whereas the first robot could take them only from the stroller or bed. Also, the payload increased to 176 pounds, or about 80 kg, which is 41 pounds, or 18.5 kg more than in the first version.

Why do the Japanese need such a robot? It's all about longevity. In Japan, by 2015, the number of elderly people who will need care is projected to reach five and a half million people. So imagine how many nurses and orderlies will have to lift daily patients from the futon to the stroller, from the stroller to the bed, back, and so on. Robots are better suited for this, and let the nurses do their work - they just care about the elderly.
And this robot is listed in the Guinness Book of Records as "The most therapeutic robot in the world." It is equipped with a variety of sensors - touch, light, sound, temperature and position. It is necessary for good communication with the patient, helps to calm the patient.
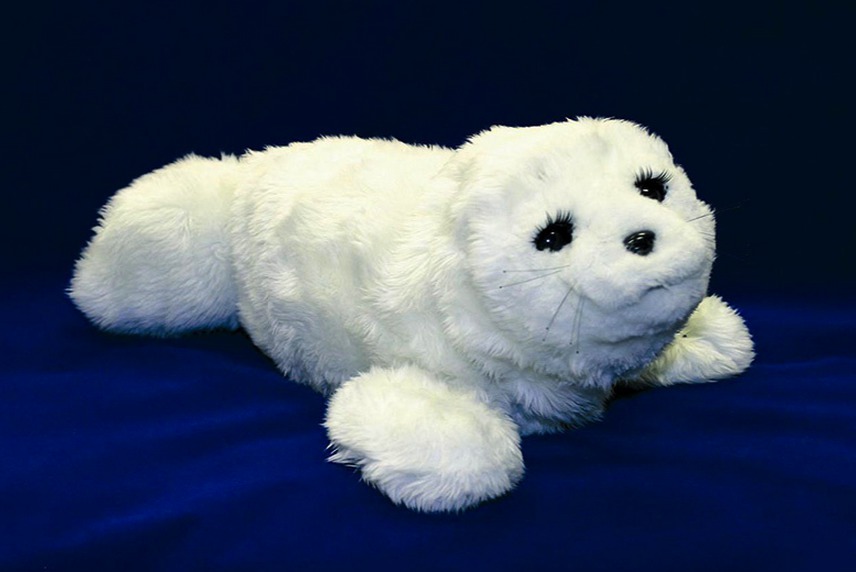

Keepon needed for the same, but he, in my opinion, less cute. He dances and reacts to touch.
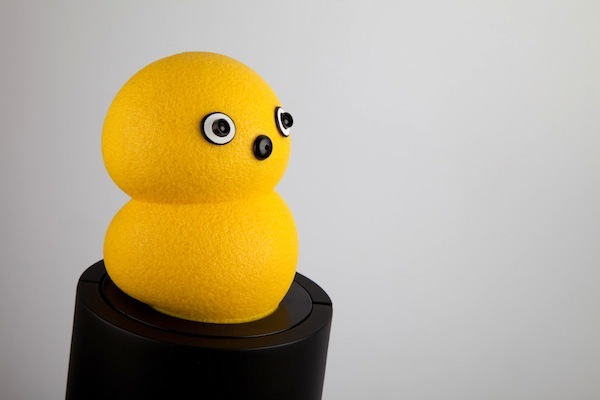

Another way to save nurses from routine work, taking up their time with more useful things, is a robot from Murata Machinery Ltd, designed to dispense medicines.

The robot from Panasonic is also designed to deliver drugs from the pharmacy to the sick. The first version of this robot could already store information about 400 patients, and issue medicines in accordance with the prescription at the request of the patient or nurse.

Returning to the issue of telemedicine (which, according to comments, on Habré is considered to be telecasts from Malysheva), it is worth mentioning telepresence robots. These are complexes capable of independent movement, equipped with cameras, displays, speakers and microphones, and in addition to them - means for carrying out diagnostics and analyzes. Such means can be both the ability to connect to devices, such as ultrasound, and built-in devices — for example, for blood analysis.
In the Russian reality, the use of such robots is almost impossible, because we have problems with ramps everywhere - what is at the entrance to the clinics, what is inside them. So the robot will be able to move only within one floor maximum, and at least - within the room, unable to overcome the hefty threshold.
PR-7

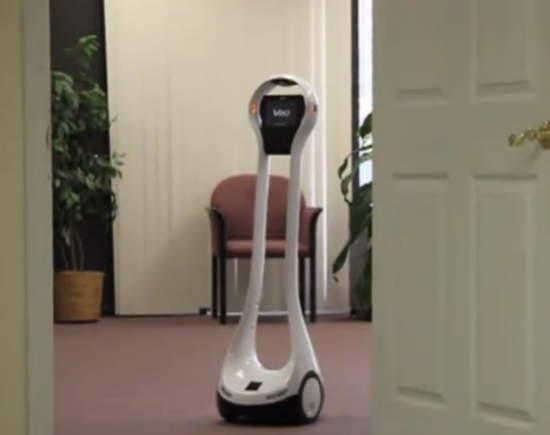
Vgo - is controlled by 4G.

PUMA 560 was the first robot used in neurosurgery. This is a robot assistant, introduced in 1985.

In orthopedics, in 1992, RoboDoc was used in prosthetic joints.

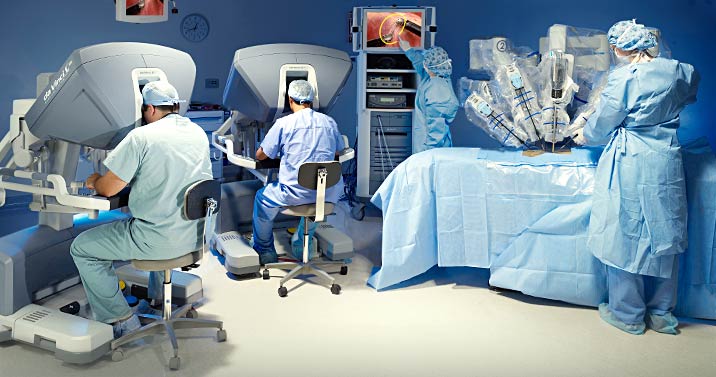
Later, assistants Zeus and Aesop appeared, but the surgeon was still the main actor in the operation. In the late 1990s, this changed with the advent of Da Vinci - a robot for remote operations.
The surgeon at the console sees the area in 3D with a multiple increase and works with joysticks. At this time, the four-armed robot is doing the operation. Initially, the image was not voluminous, of course, but then this problem was solved.
Minute Transformers: ARES from Italian scientists is designed to carry out operations without damaging the skin. Because the patient swallows it in parts, and also he goes out later through the intestines. Inside, the robot assembles itself, after which the surgeon performs the operation.

Sending living patients to newcomers is not very humane. It is much better to practice first on robots that cope with natural needs, who have a heartbeat and that are more or less similar to humans.
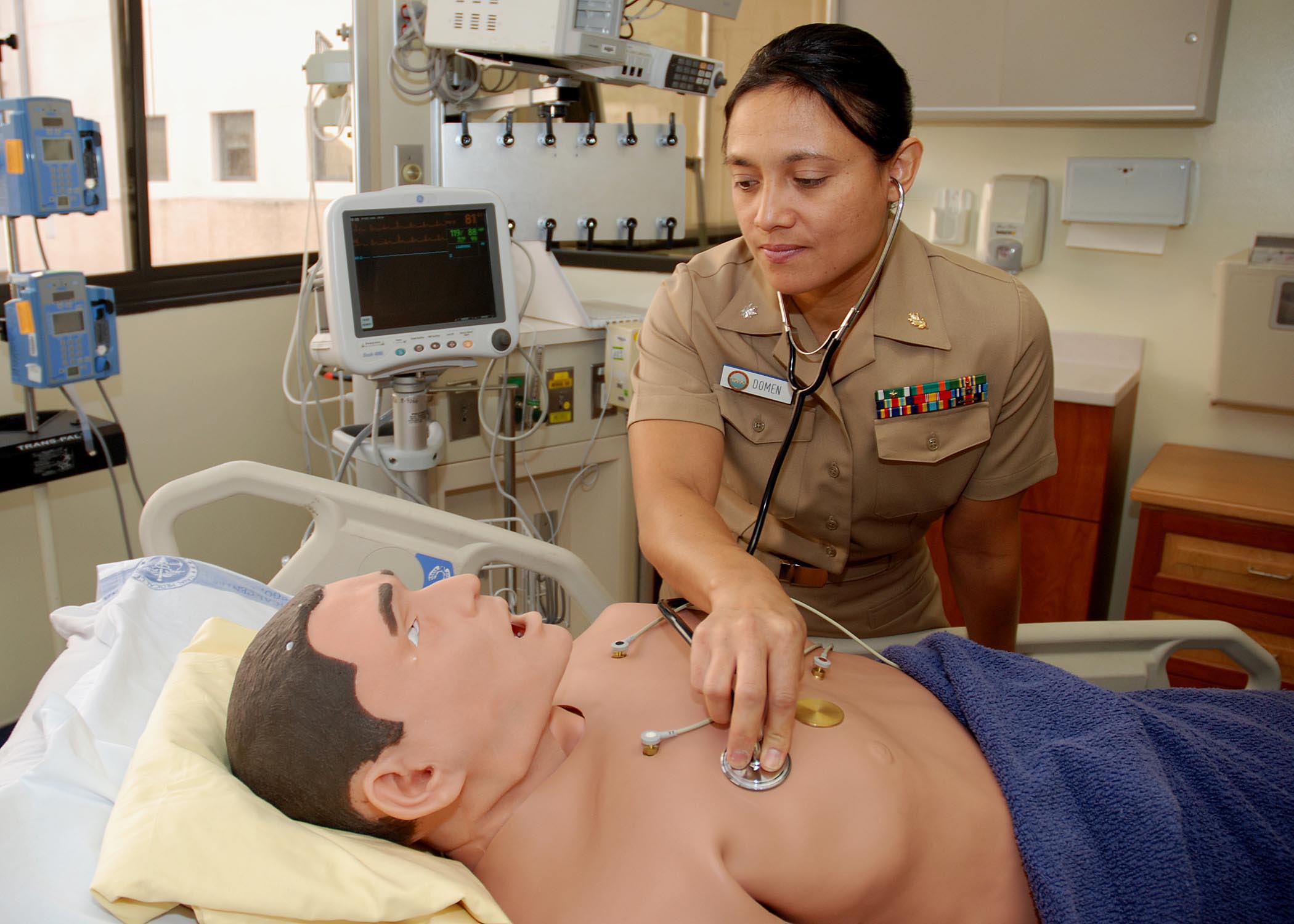
The most functional robot of this type is HPS (Human Patient Simulator). He keeps 30 different patient profiles, differing in physiology and individual reactions to drugs. These may be profiles of a healthy child of a pregnant woman and an elderly alcoholic. The pulse felt on the carotid, shoulder, femoral, radial popliteal arteries varies with pressure, the robot exhales carbon dioxide, which is displayed on the monitors, and its pupils react to light.


With dentists - the same story. Stop shred unhappy people with bad teeth! First, train on cats. In the photo - Hanako 2, originally from Japan, which is immediately apparent.

Please write in the comments what other robots should be in this publication.
In what areas and for what use robots? In surgery, as carers for children and the elderly, in telemedicine and even for drug delivery. More - I ask for habrakat.

')
Riba
Robot Riba is from Japan. He was introduced in 2009. Its main purpose is to rock the sick and the elderly with the help of its long and strong hands. This is a great helper in clinics, as he can move patients from place to place, or shift them from a wheelchair to a bed.

In 2009 presented RIBA II. This version of the robot can lift patients directly from the floor, whereas the first robot could take them only from the stroller or bed. Also, the payload increased to 176 pounds, or about 80 kg, which is 41 pounds, or 18.5 kg more than in the first version.

Why do the Japanese need such a robot? It's all about longevity. In Japan, by 2015, the number of elderly people who will need care is projected to reach five and a half million people. So imagine how many nurses and orderlies will have to lift daily patients from the futon to the stroller, from the stroller to the bed, back, and so on. Robots are better suited for this, and let the nurses do their work - they just care about the elderly.
And this robot is listed in the Guinness Book of Records as "The most therapeutic robot in the world." It is equipped with a variety of sensors - touch, light, sound, temperature and position. It is necessary for good communication with the patient, helps to calm the patient.

Keepon needed for the same, but he, in my opinion, less cute. He dances and reacts to touch.

Distribution Robot
Another way to save nurses from routine work, taking up their time with more useful things, is a robot from Murata Machinery Ltd, designed to dispense medicines.

The robot from Panasonic is also designed to deliver drugs from the pharmacy to the sick. The first version of this robot could already store information about 400 patients, and issue medicines in accordance with the prescription at the request of the patient or nurse.

Telepresence
Returning to the issue of telemedicine (which, according to comments, on Habré is considered to be telecasts from Malysheva), it is worth mentioning telepresence robots. These are complexes capable of independent movement, equipped with cameras, displays, speakers and microphones, and in addition to them - means for carrying out diagnostics and analyzes. Such means can be both the ability to connect to devices, such as ultrasound, and built-in devices — for example, for blood analysis.
In the Russian reality, the use of such robots is almost impossible, because we have problems with ramps everywhere - what is at the entrance to the clinics, what is inside them. So the robot will be able to move only within one floor maximum, and at least - within the room, unable to overcome the hefty threshold.
PR-7

Vgo - is controlled by 4G.

Surgery
PUMA 560 was the first robot used in neurosurgery. This is a robot assistant, introduced in 1985.

In orthopedics, in 1992, RoboDoc was used in prosthetic joints.

Later, assistants Zeus and Aesop appeared, but the surgeon was still the main actor in the operation. In the late 1990s, this changed with the advent of Da Vinci - a robot for remote operations.
The surgeon at the console sees the area in 3D with a multiple increase and works with joysticks. At this time, the four-armed robot is doing the operation. Initially, the image was not voluminous, of course, but then this problem was solved.

Minute Transformers: ARES from Italian scientists is designed to carry out operations without damaging the skin. Because the patient swallows it in parts, and also he goes out later through the intestines. Inside, the robot assembles itself, after which the surgeon performs the operation.

Training: Patient Simulators
Sending living patients to newcomers is not very humane. It is much better to practice first on robots that cope with natural needs, who have a heartbeat and that are more or less similar to humans.
The most functional robot of this type is HPS (Human Patient Simulator). He keeps 30 different patient profiles, differing in physiology and individual reactions to drugs. These may be profiles of a healthy child of a pregnant woman and an elderly alcoholic. The pulse felt on the carotid, shoulder, femoral, radial popliteal arteries varies with pressure, the robot exhales carbon dioxide, which is displayed on the monitors, and its pupils react to light.



With dentists - the same story. Stop shred unhappy people with bad teeth! First, train on cats. In the photo - Hanako 2, originally from Japan, which is immediately apparent.

Please write in the comments what other robots should be in this publication.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/239473/
All Articles