How does the chosen network affect the Internet speed of the phone, or the problems of LTE networks in the CIS region?

For the wired internet, the speed promised by the provider is the channel bandwidth on the “last mile”. Typically, the real speed of the providers of wired internet is close to the stated. As applied to mobile networks, the “last mile” is a radio channel, and the speed does not always correspond to that stated in the 3GPP standard (100 - 150 Mbit / s). Below is information about the factors affecting the speed of the mobile Internet in the LTE network.
1.Category of mobile device.
| Category | Dl speed | The number of antennas | UL speed |
|---|---|---|---|
| Category 1 | 10.3 Mbit / s | one | 5.2 Mbit / s |
| Category 2 | 51.0 Mbit / s | 2 | 25.5 Mbit / s |
| Category 3 | 102.0 Mbit / s | 2 | 51.0 Mbit / s |
| Category 4 | 150.8 Mbit / s | 2 | 51.0 Mbit / s |
| Category 5 | 299.6 Mbit / s | four | 75.4 Mbit / s |
| Category 6 | 301.5 Mbit / s | 2 or 4 | 51.0 Mbit / s |
2. Bandwidth. Each of the antennas of a mobile device can receive a signal with a frequency band width of 20 Mhz. The tower can allocate 1.4 MHz, 3 MHz, 5 MHz, 10 MHz, 15 MHz and 20 MHz frequency bands. In order to divide the bands among themselves, 10% of the bandwidth (except for the 1.4 MHz wide band) act as a border zone, information is not transmitted over them. Thus, the maximum width of the frequency channel of a mobile device is 2 * (20Mhz * 90%) = 36 Mhz.
')
3.Resource block ( RB ) - a unit of transmission resource in the LTE channel, consisting of 12 sub-frequency intervals occupied during the time interval ( TS - 0.5 ms). The total RB frequency band is 180 kHz. Therefore, the number of RBs in the maximum frequency range is 36Mhz / 180kHz = 200.
4. Resource element ( RE ) - the smallest unit of data transmission in DL and UL mode. The required frequency band is 15 kHz. During TS - 0.5 ms, the antenna can transmit 7 RE in the range of 15 kHz (in case of poor conditions, this number is 6). 1 RB = 12 * 7 = 84 RE . With a maximum channel width, you can send 200RB * 84RE = 16800RE in a TS time of 0.5 ms.
5. Modulation. Depending on the type of modulation, different amounts of information can be transmitted in one RE . With QPSK modulation type - 2bit; 16QAM - 4bit; 64QAM - 6 bit. The choice of modulation depends on the level of signal coverage. With 64QAM speed: 16800RE * 6 * 2000TS = 201600000 bit / s = 201.6 Mbit / s. 25% of all transmitted information is used to control the physical layer and the level of data transfer. Therefore, the resulting speed 201.6Mbit / s * 75% ~ 150Mbit / s
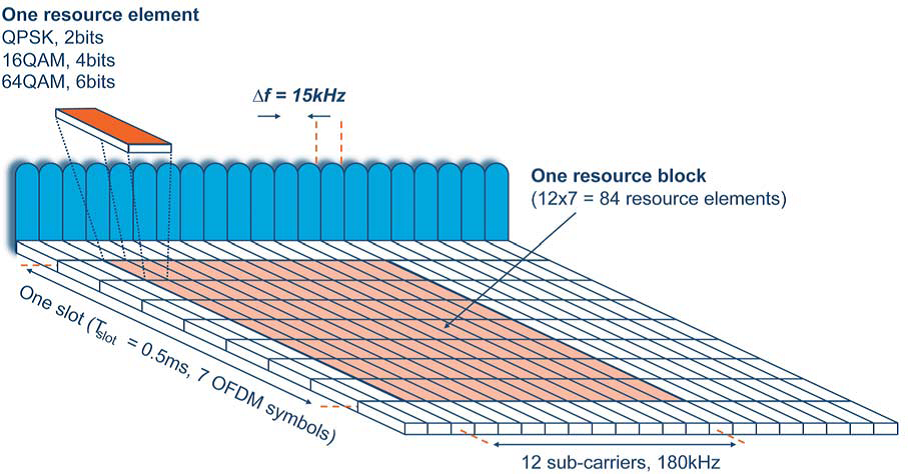
BUT , there is no operator in the CIS that can allocate 2 bands at 20 MHz at the same time and the signal quality leaves much to be desired. Additional overhead from IP packets, temporary interference in the radio channel, the influence of other subscribers in the vicinity only worsens the speed stated in the standard. If the operator has a range of 15 MHz, then only three people can simultaneously download (be in RRC_CONNECTED ) at a speed of 18.3Mbit / s within the same tower, and this is at the ideal signal.
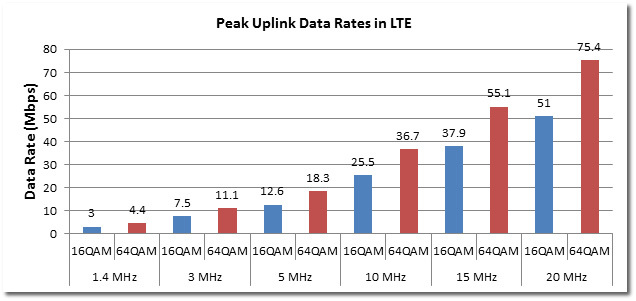
(the graph shows the data transmission rate of one antenna depending on the selected range and type of modulation).
Technologies such as carrier aggregation ( CA ) allow the subscriber to allocate several separated frequency bands from the operator’s possession, while (the amount of information) / Hz remains constant. The features of economic trends and rules in the post-Soviet space are forcing LTE network owners to increase the number of subscribers by expanding coverage. In developed countries, operators have similar frequency bands, but when planning, they use microcell, picocell, femtocell to improve signal quality. Now in the CIS countries, existing LTE networks do not have much better indicators than HSDPA networks. The only mechanism to increase the speed of the Internet - improving coverage and optimizing the use of radio resources.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/238979/
All Articles