Cybercortex. Extended Perception and Thinking System
Good day!
Cybercortex.org - open source project. It is at the start stage and is seen as an opportunity to concentrate and coordinate the efforts of companies and developers to solve problems in the development of human intelligence. To introduce into life new forms of enhancing thinking and accelerating productive communication. Therefore, all those who are somehow interested in the issue are invited to cooperate.
Below is a description of the first module of the Cybermean algorithm, the “core” of Cybercortex. If the logic described below seems adequate to habravchanam, it would be possible to continue the description and discussion of the modules Cybermean and Cybercortex as a whole. Also, at the end of the post, in addition to the logic of the first module, there is an image of the interface communication within Cybercortex, as an additional illustrative material characterizing the subject of the project.
')


Our task is to obtain as complete a selection of synonyms as possible and definitions of the relevant * words in the compared texts.
So, we make a selection of synonyms and definitions for text 1. Then we do the same for text 2 (hereinafter, both texts, since there can be any number of them, are denoted as text N).
Then we can compare the received samples.
The more matches there are (source words, synonyms, and keywords; see below) in these samples, the closer the texts are in their meaning. Not in terms of statements for or against something, but in terms of subject matter, in terms of its subject matter.
Sampling
We can perform a search for synonyms for each relevant source word of the text N first in the dictionaries of the synonyms of the same language (performing the corresponding text normalization operations; first of all, stemming; in diagram 2, this is a separate column of blocks with the same ending L_number). We can also perform a search for definitions for each word of the text N. And then perform a search for synonyms for definition keywords (keywords are extracted using frequency [for example, similar LSA], morphological and lexical analysis of the maximum possible number of definitions presented in dictionaries ; keywords and synonyms of keywords are presented in Schemes 3.1 and 3.2).
At the same time, we can translate each relevant word into a foreign language (from language 1 to 2 (N)) and only then consistently perform the same operations, and we can also translate into a foreign language (into 2 (N) language) words, which will appear in the process of operations with language 1. Complementing operations on language 2 (N) by itself. That is, to translate keywords and their synonyms from language 1 into a foreign language (language 2 (N)) and then, if some words were not there without this operation, build activities taking into account these words (this logic is presented in diagram 4) .
As a result, for each relevant word of the text N we get a set of samples, the number of which for each word is equal to the number of languages included in the system.
- * prepositions and similar formations can be considered irrelevant; “Words” further in the meaning of “relevant words”


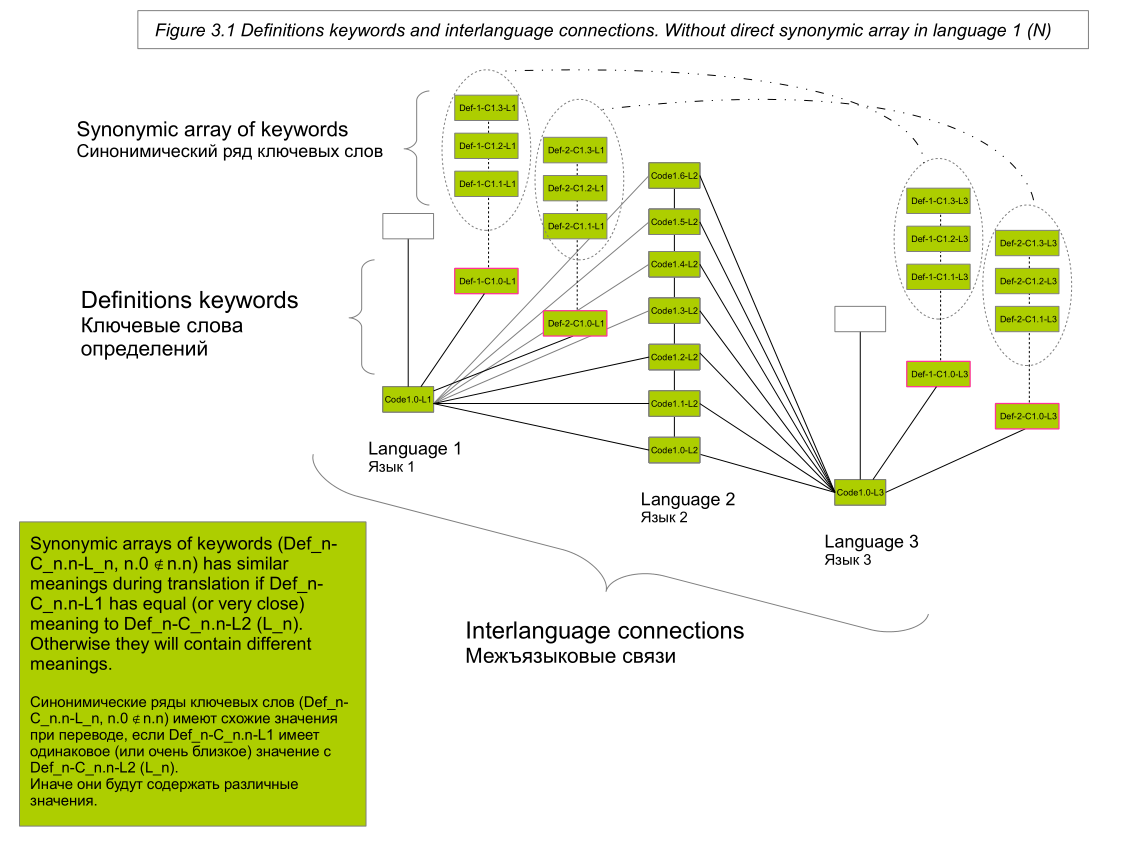
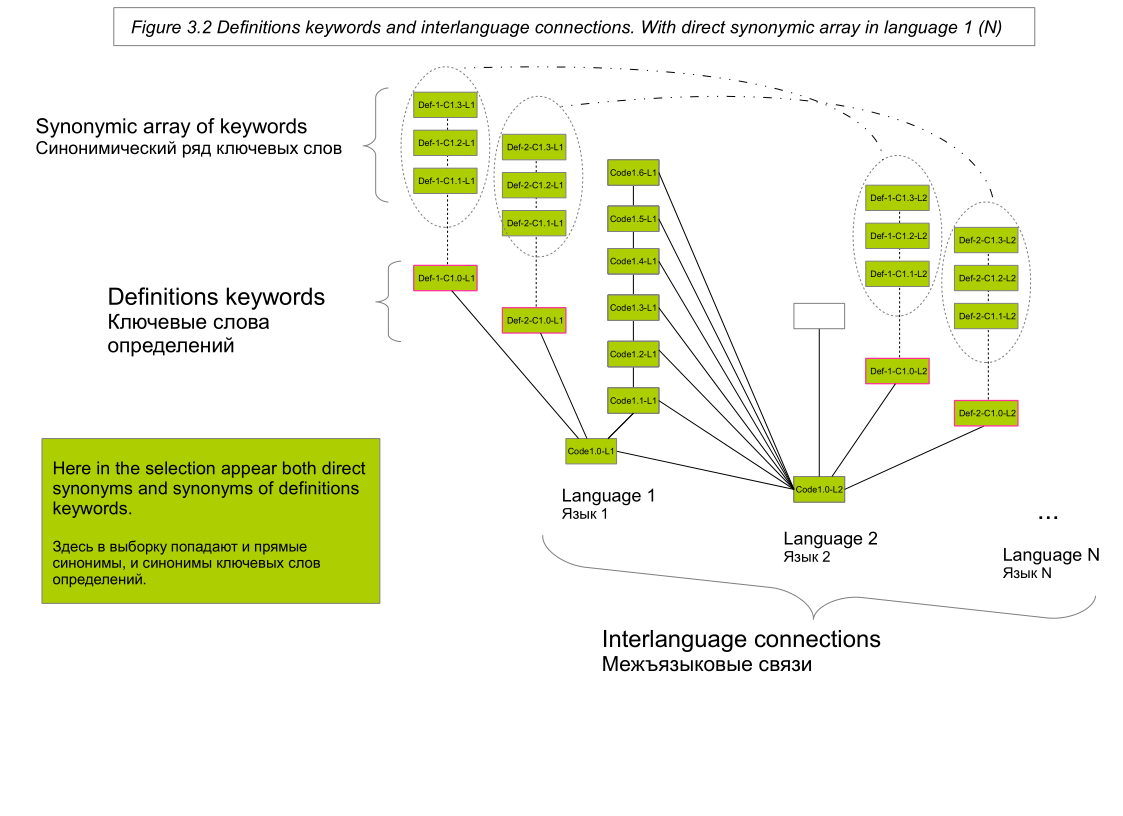
So, when we encounter a word in the text, then the given word and all the words that are associated with it through a vertical link (direct synonyms, definition keywords, synonyms of key words) and through a horizontal interlanguage link, fall into the resulting sample.
Thus, the sample contains relevant related words from the dictionaries of the whole world (from among those that are integrated into the system), and not just the dictionaries of the country of the language in which the text is formulated.
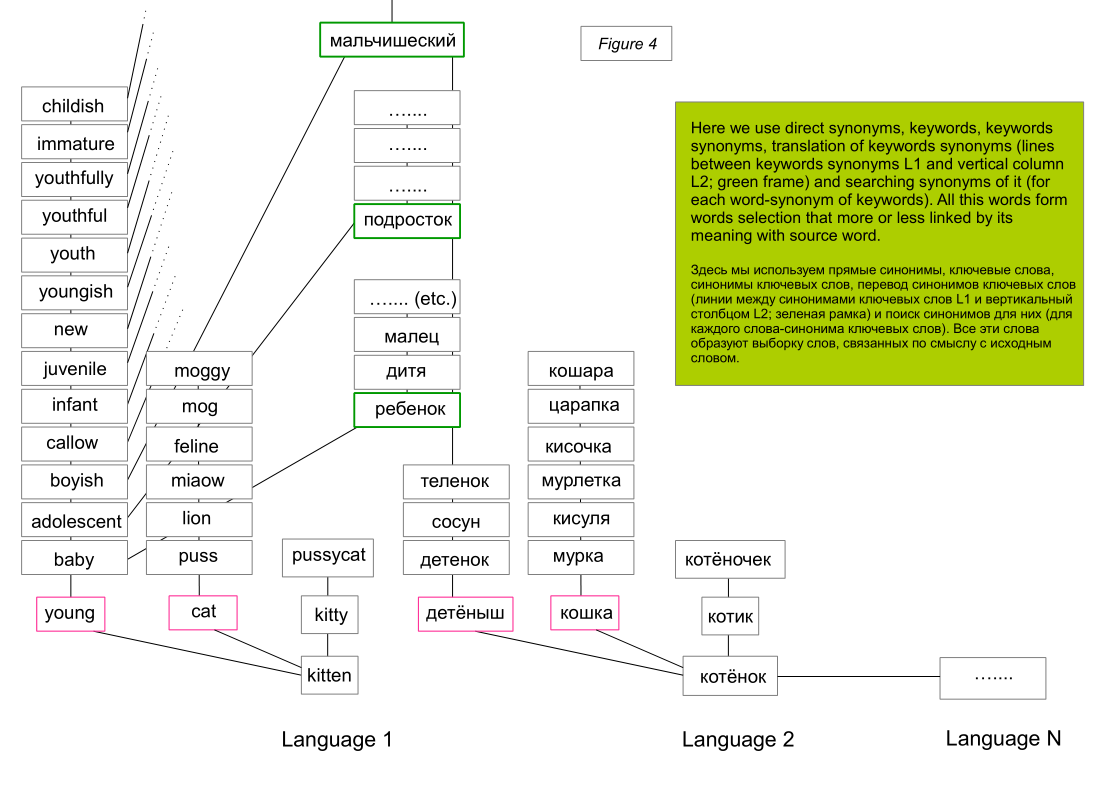
It can be assumed that if a word is found in different languages in the list of synonyms, then it is more synonymous with the original word, rather than if the synonym is found only in one language.
The operations above allow us to refer to the entire spectrum of synonyms that are close in meaning, contained in dictionaries, but placed in them incorrectly. That is, the situation is neutralized when a person sees a synonym, but there is no typical national dictionary.
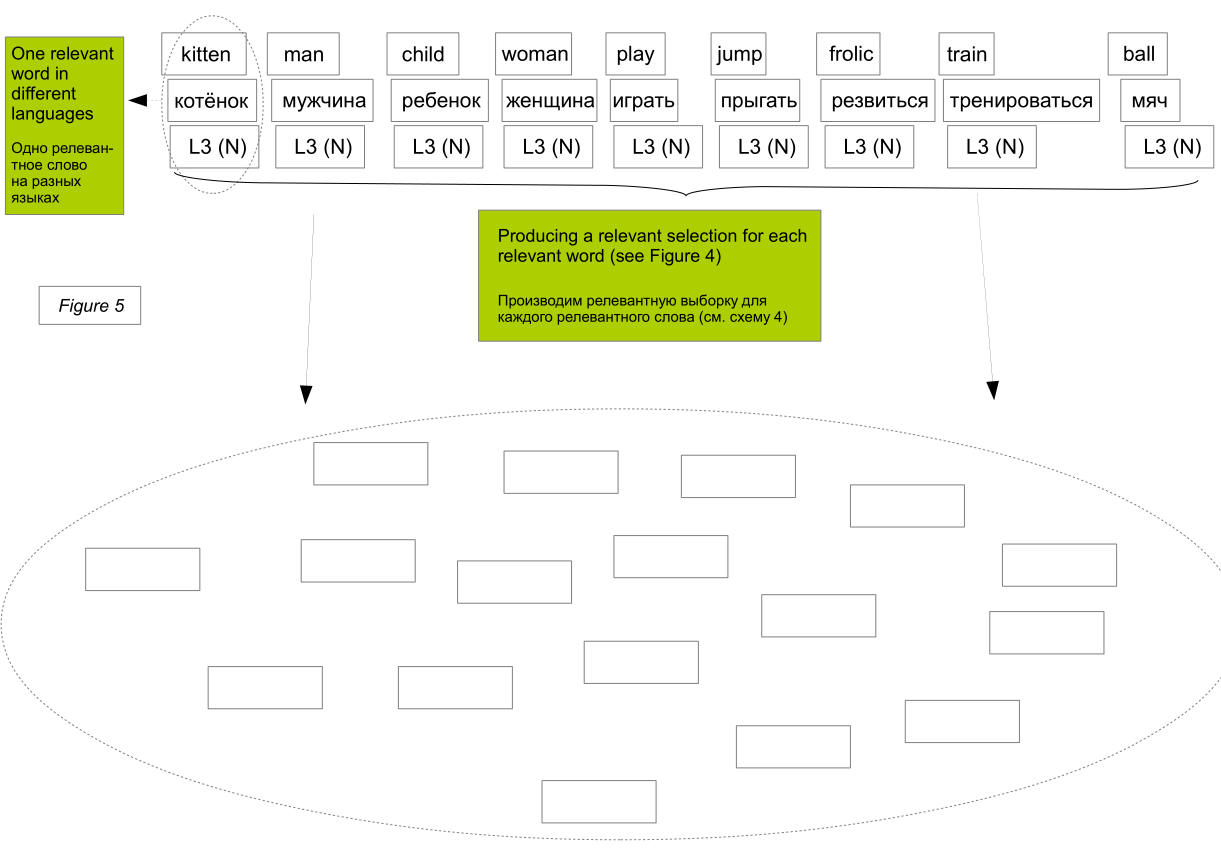
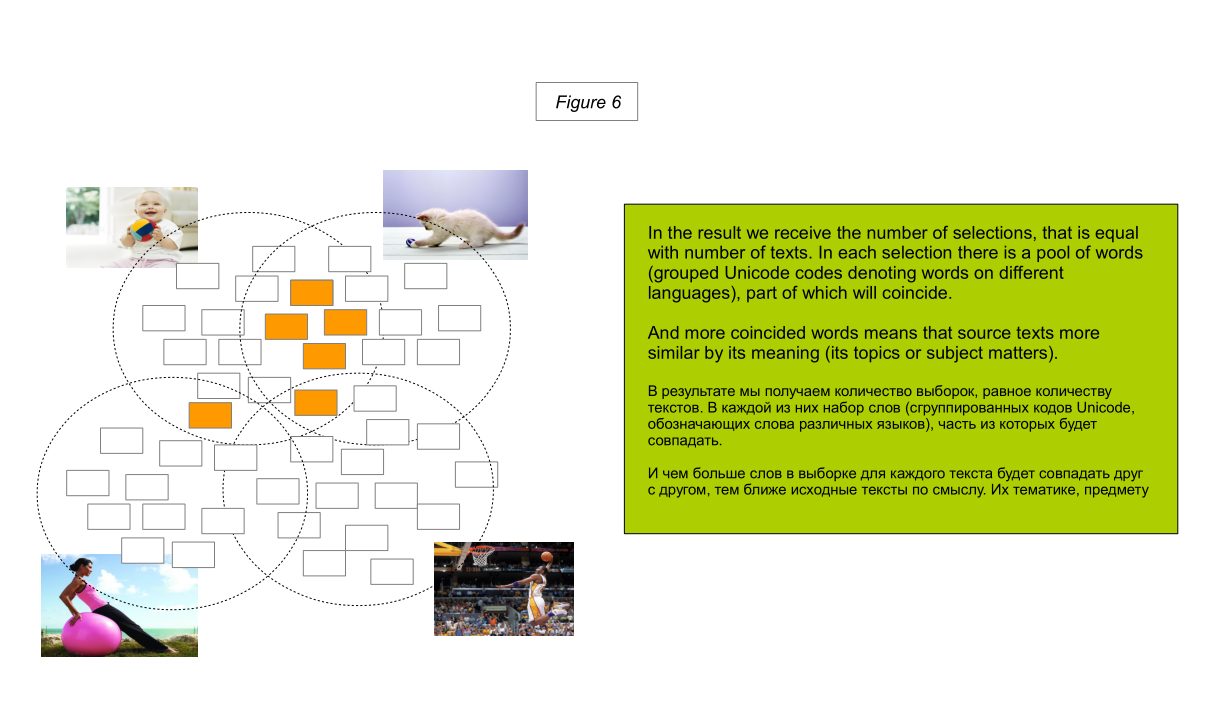
However, "a man jumps with a ball" can be read as "a man plays with a ball." In the algorithm, this is reflected in the fact that in samples of direct and indirect synonyms (synonyms of keywords, translated synonyms of keywords) of the words “jump”, “frolic” and “play” we will find a certain number of identical words.

However, in this case, it is decisive that the words “child” and “kitten” have more coincidences in indirect synonyms than the man, woman - child or man, woman - kitten.
At the same time, if we applied the operation of finding keywords to synonyms of keywords (that is, as an iteration of a new level), then we would see that the child, the man and the woman are people. And the kitten is an animal.
That is, in samples of a new level, a child, a man and a woman, would have more coincidences than each of them with a kitten sample.
This would be the next criterion for the separation of statements according to their meaning, but less so by its influence, since it was revealed at this additional level of iterations.
Conclusion
This simple example demonstrates the principle of text analysis, which allows to determine the semantic proximity of texts. The more signs (words) in the text, the easier it is to differentiate texts that are similar to him in meaning. Since the more unique will be a selection of related words.
This principle is the first module of the Cybermean algorithm. On the basis of this principle, the work of the second and third modules of Cybermean is possible.
***
Image from interface material:
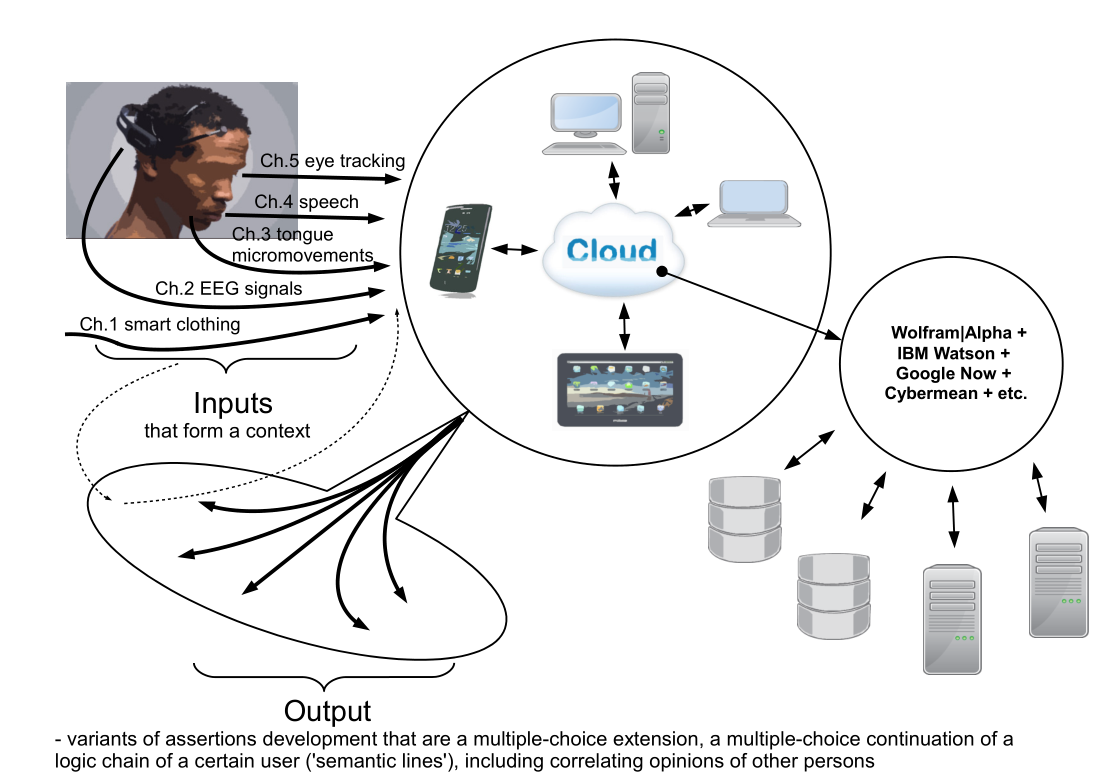
Website: www.cybercortex.org
Cybercortex.org - open source project. It is at the start stage and is seen as an opportunity to concentrate and coordinate the efforts of companies and developers to solve problems in the development of human intelligence. To introduce into life new forms of enhancing thinking and accelerating productive communication. Therefore, all those who are somehow interested in the issue are invited to cooperate.
Below is a description of the first module of the Cybermean algorithm, the “core” of Cybercortex. If the logic described below seems adequate to habravchanam, it would be possible to continue the description and discussion of the modules Cybermean and Cybercortex as a whole. Also, at the end of the post, in addition to the logic of the first module, there is an image of the interface communication within Cybercortex, as an additional illustrative material characterizing the subject of the project.
')
Our task is to obtain as complete a selection of synonyms as possible and definitions of the relevant * words in the compared texts.
So, we make a selection of synonyms and definitions for text 1. Then we do the same for text 2 (hereinafter, both texts, since there can be any number of them, are denoted as text N).
Then we can compare the received samples.
The more matches there are (source words, synonyms, and keywords; see below) in these samples, the closer the texts are in their meaning. Not in terms of statements for or against something, but in terms of subject matter, in terms of its subject matter.
Sampling
We can perform a search for synonyms for each relevant source word of the text N first in the dictionaries of the synonyms of the same language (performing the corresponding text normalization operations; first of all, stemming; in diagram 2, this is a separate column of blocks with the same ending L_number). We can also perform a search for definitions for each word of the text N. And then perform a search for synonyms for definition keywords (keywords are extracted using frequency [for example, similar LSA], morphological and lexical analysis of the maximum possible number of definitions presented in dictionaries ; keywords and synonyms of keywords are presented in Schemes 3.1 and 3.2).
At the same time, we can translate each relevant word into a foreign language (from language 1 to 2 (N)) and only then consistently perform the same operations, and we can also translate into a foreign language (into 2 (N) language) words, which will appear in the process of operations with language 1. Complementing operations on language 2 (N) by itself. That is, to translate keywords and their synonyms from language 1 into a foreign language (language 2 (N)) and then, if some words were not there without this operation, build activities taking into account these words (this logic is presented in diagram 4) .
As a result, for each relevant word of the text N we get a set of samples, the number of which for each word is equal to the number of languages included in the system.
- * prepositions and similar formations can be considered irrelevant; “Words” further in the meaning of “relevant words”
So, when we encounter a word in the text, then the given word and all the words that are associated with it through a vertical link (direct synonyms, definition keywords, synonyms of key words) and through a horizontal interlanguage link, fall into the resulting sample.
Thus, the sample contains relevant related words from the dictionaries of the whole world (from among those that are integrated into the system), and not just the dictionaries of the country of the language in which the text is formulated.
It can be assumed that if a word is found in different languages in the list of synonyms, then it is more synonymous with the original word, rather than if the synonym is found only in one language.
The operations above allow us to refer to the entire spectrum of synonyms that are close in meaning, contained in dictionaries, but placed in them incorrectly. That is, the situation is neutralized when a person sees a synonym, but there is no typical national dictionary.
However, "a man jumps with a ball" can be read as "a man plays with a ball." In the algorithm, this is reflected in the fact that in samples of direct and indirect synonyms (synonyms of keywords, translated synonyms of keywords) of the words “jump”, “frolic” and “play” we will find a certain number of identical words.

However, in this case, it is decisive that the words “child” and “kitten” have more coincidences in indirect synonyms than the man, woman - child or man, woman - kitten.
At the same time, if we applied the operation of finding keywords to synonyms of keywords (that is, as an iteration of a new level), then we would see that the child, the man and the woman are people. And the kitten is an animal.
That is, in samples of a new level, a child, a man and a woman, would have more coincidences than each of them with a kitten sample.
This would be the next criterion for the separation of statements according to their meaning, but less so by its influence, since it was revealed at this additional level of iterations.
Conclusion
This simple example demonstrates the principle of text analysis, which allows to determine the semantic proximity of texts. The more signs (words) in the text, the easier it is to differentiate texts that are similar to him in meaning. Since the more unique will be a selection of related words.
This principle is the first module of the Cybermean algorithm. On the basis of this principle, the work of the second and third modules of Cybermean is possible.
***
Image from interface material:
Website: www.cybercortex.org
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/238249/
All Articles