Overview of decentralized technology. Part 1
 Bitcoin laid the foundation for creating new types of systems, fundamentally new decentralized services that are designed to solve various problems with the help of the revolutionary Blockchain technology. There are separate articles and notes on this topic on the Runet, but very scatteredly, there were also some publications and references to this topic on Habré, but we decided that it would be useful to create a review series of articles and briefly highlight the most interesting projects from this area.
Bitcoin laid the foundation for creating new types of systems, fundamentally new decentralized services that are designed to solve various problems with the help of the revolutionary Blockchain technology. There are separate articles and notes on this topic on the Runet, but very scatteredly, there were also some publications and references to this topic on Habré, but we decided that it would be useful to create a review series of articles and briefly highlight the most interesting projects from this area.Blockchain
Blockchains are a technology of distributed computing and the general consensus of users, created by the mysterious Satoshi Nakamoto. It lacks central control, and P2P networks, codification, and cryptography are used to verify transactions. Moreover, transactions can be managed using programmable contracts / contracts. In the Bitcoin blockchain, any transactions are not considered legitimate (confirmed) until they are grouped into special structures — blocks. The structure and information in the blocks obeys specified rules and it can be quickly checked. Each block always contains information about one previous block. This allows all existing blocks to be built into one chain, which is a distributed database and contains information about all bitcoin operations ever performed.
Bitcoin is the first and most successful use of blockchain technology, but there are many, many other cryptocurrencies known as altcoins. Moreover, there are many examples of how new blockchains are used not only for cryptocurrency purposes - Ethereum, Ripple and Storj.io, we will talk about them today in the first part of our series of articles about decentralized services. In the light of recent events , the purpose of the article is also to show that
')
Ethereum
 The Ethereum project, launched by a 20-year-old child prodigy from Canada, wants to reorganize the Internet on the principles of Bitcoin and help users acquire a personal cryptocurrency. For a month and a half of the preliminary sale, the “air” on 31.5 thousand bitcoins was sold. At the current rate, this is more than $ 14 million. A cryptocurrency startup is one of the most successful crowdfunding attempts in history.
The Ethereum project, launched by a 20-year-old child prodigy from Canada, wants to reorganize the Internet on the principles of Bitcoin and help users acquire a personal cryptocurrency. For a month and a half of the preliminary sale, the “air” on 31.5 thousand bitcoins was sold. At the current rate, this is more than $ 14 million. A cryptocurrency startup is one of the most successful crowdfunding attempts in history.Zug, a Swiss-based company, is developing a software platform that will use a network of computers that is similar to the Bitcoin network to decentralize any type of economic activity. Developers will be encouraged to create software applications that purposely use such a network and its transparent public register - “blockchain”, in order to get rid of intermediaries and reduce the cost of exchanging funds, assets and information between people or companies.
Among the ideas that have emerged, there is a decentralized, Ethereum-based product similar to Facebook, where users will have complete control over their personal pages, which will allow them to independently receive advertising revenues, instead of sending them to a certain centralized company. Other ideas: securities markets that operate without a stock exchange or a clearing center, contracts for which you do not need legal services or platforms for polls and polls protected from unauthorized access, which carry out impeccable vote count without a sociological center or ballot processing by electoral authorities .
This concept has caused great interest among techies, which may well explain the success of the pre-sale of ether - digital, coin-like title characters from Ethereum, which on its website are characterized as the “fuel” necessary for applications to work on this platform.

The release of these marks, not secured by any rights or gains from ownership, has not yet begun, but the campaign has already passed an unlimited sale of them, in accordance with a sliding tariff scale, where the prices are in Bitcoin. In the end, it sold more than 60 million units of currency. In the first round, which lasted two weeks, the price was set at 2000 ethers for Bitcoin. Then the value decreased by 30 units until the very end of sales. The total amount of sales exceeds almost all such promotions to raise funds on popular crowdfunding sites, such as Kickstarter, and makes more than $ 14 million.
According to information from one of the founders of Ethereum, Joseph Lubin, early orders came from software developers and financial institutions who plan to develop their applications on the basis of Ethereum, as well as from customers who have relied on the demand for signs in the future.
According to Swiss law, pre-sale is not considered a public issue of securities or currency, but is regarded as a product release. That is, ether is considered as a form of software, on the grounds that developers will need title signs to implement their software applications.
Mr Lubin reported that third-party developers are currently creating “hundreds” of promising applications based on the Ethereum platform, including digital currency exchanges, digital wallets, decentralized messaging programs, marketplaces based on reputation and self-regulating “smart legal agreements”.
Ethereum is the embodiment of the idea of Vitalik Buterin, who created a draft version of the technical documentation of the project last year, at the age of 19. Buterin's idea was modeled on the basis of the Bitcoin infrastructure core, the decentralized network of which, together with the blockchain register, eliminates the need to work with commissioning “trusted” third-party intermediaries, such as banks, between individuals.
However, Mr. Buterin thought that the Bitcoin infrastructure was too limited to support the full range of applications that these projects could offer, so he invented Ethereum, which offers a completely new, independent blockchain and its network of miners.
Ethereum is now available in beta. With it, you can create an application or release your own cryptocurrency - according to Buterin, this requires minimal programming skills. A full working version will be released later this year. You can already find videos on YouTube, where the first developers under Ethereum show how to use it to write code for their applications.
Repository - github.com/ethereum
Ripple
 Ripple is a payment system, currency exchange and transfer system developed by Ripple Labs. Her work is based on the use of a distributed open Internet protocol, a registry that works on the principle of universal consent and its own currency, which
Ripple is a payment system, currency exchange and transfer system developed by Ripple Labs. Her work is based on the use of a distributed open Internet protocol, a registry that works on the principle of universal consent and its own currency, whichcalled ripples (xrp). The Ripple network aims to make it possible to conduct “secure, instantaneous and maximum free financial transactions of any amount without revocation worldwide.” It supports working with any fiat currency (dollars, yen, etc.), cryptocurrency (bitcoin, litecoin, etc.). .), goods or other units of value (miles of flights, minutes of cellular communication, etc.).
Ripple is based on a collective and open database - the register. In addition to balance sheet data, the register contains information on offers to buy or sell currencies or assets, thus forming the world's first distributed exchange. Network members agree to changes made to the register through a process called “consensus” (eng. Consensus), which occurs every 2-5 seconds. “Consensus” allows for payments, exchanges and transfers without the need for a single clearing center. Compared to cryptocurrencies, such as Bitcoin, where security is provided by the mining process, maintaining a register based on “consensus” allows the Ripple network to withstand any attacks with firmness and with the effective operation of the system.
In the Ripple system, users make payments among themselves using cryptographically signed transactions expressed either in Ripple's local currency - XRP, or in other arbitrarily chosen assets (including real assets, such as dollars, gold, flight miles, etc.). For transactions expressed in XRP, Ripple can use its internal register. For payments expressed in any other assets, the Ripple register only records the number of units that one user gave to another. Thus, all such assets are presented as debt. This approach requires trust, as Ripple only keeps the registry entries and has no regulatory authority in the real world. Users must determine which participants they believe in and quantify this trust. Such a quantitative expression can be determined for each asset separately.

When two users who trust each other make a non-XRP payment, their mutual credit balance is adjusted. Payments are subject to user-defined limits. In order to send assets between users who have not established trusting relationships with each other, the system tries to find such a path between them, each gap of which would be a pair of trusting each other participants. In the case of such a transaction, all balances are adjusted simultaneously as a whole. This mechanism for making payments through a network of trusted participants is called rippling. It is a digital version of the hawala settlement system existing since ancient times and also received the name “Facebook for Money”.
When processing each transaction in the Ripple network, 0.00001 XRP (approximately one
one hundred thousandth of a cent in dollar terms). This is not a commission charged for anyone; XRP is written off and ceases to exist. Such a commission for the transaction is also set in a very small amount for users. But when the network is under heavy load, for example, when it is attacked, the size of this commission quickly increases. The purpose of such a network device is to quickly bankrupt attackers and ensure the smooth operation of the network. An attack on the Ripple network can be very costly in a very short time, but for ordinary users, it essentially remains “free.”
Ripple Creator is Ripple Labs. Because the Ripple network is based on free and open source code, the software company does not receive revenue from using the network. Ripple Labs hopes to make money on XRP, if the world is convinced that the Ripple network is useful, and the protocol is widely accepted.
Simultaneously with the creation of the Ripple protocol, 100 billion XRPs were released. Over time, Ripple Labs plans to provide 55 billion XRP to charitable organizations, users and strategic partners of the ecosystem. The company will retain part of XRP in the hope of creating a reliable and liquid market in order to monetize its sole asset sometime in the future.
Ruble Gateway Ripple - rippleru.com
Ripple Introductory Course in English - ripple.com/ripple_primer_en.pdf
Repositories - dev.ripple.com
Storj.io
 Storj.io is a distributed, decentralized open-source platform for cloud storage, which is based on the use of the Bitcoin transaction register (blockchain) and its own peer-to-peer protocols. The platform also performs the functions of a payment system using its own cryptocurrency - StorjcoinX (SJCX), working on the Counterparty protocol. In addition, according to the developers, the platform will support the deployment of its own full-fledged web applications.
Storj.io is a distributed, decentralized open-source platform for cloud storage, which is based on the use of the Bitcoin transaction register (blockchain) and its own peer-to-peer protocols. The platform also performs the functions of a payment system using its own cryptocurrency - StorjcoinX (SJCX), working on the Counterparty protocol. In addition, according to the developers, the platform will support the deployment of its own full-fledged web applications.Any interested participant in the system can, for a certain fee, expressed in SJCX, take advantage of the storage and place their data there. Access to this component of the platform is provided through Metadisk - a web client created specifically for user interaction with the repository.
Users can also participate in the work of the system as owners of nodes, giving free space on their disk and bandwidth of the Internet channel using a special DriveShare client, which will be available for Windows, Linux and Mac. In return for this, owners of DriveShare nodes will earn SJCX or other cryptocurrency.
Platform developers are convinced that the emergence of such a system will create competition for centralized cloud storage, such as Amazon S3 or Dropbox. In the project's blog, they provide an analysis of the price policy of Dropbox, concluding that its users pay monthly or annually for the possibility of using a certain fixed amount of storage, while often overpaying for gigabytes of data that they do not actually use. Dropbox pricing is made up of the costs of using third-party servers (Amazon), maintaining infrastructure, renting premises, paying staff salaries, and making money to investors.
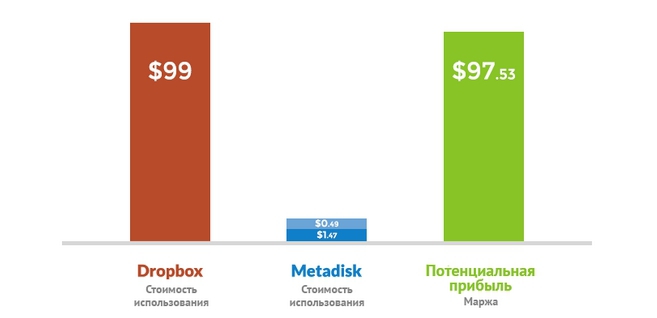
The cost of 100% storage usage of 100 GB for 1 year.
Dark blue shows storage costs, blue shows the cost of retrieving all stored data from Metadisk
The cost of using Storj, on the contrary, is made up of objective factors: it is assumed that the user pays only for the actual space used, the cost of which is determined by the “provider” Storj, which will be the usual owners of nodes that provide the space of their disks for use. But who will set tariffs and how exactly pricing will take place among a huge number of nodes throughout the system, is also unknown at this time.
According to the developers, the cost of the service will fall dozens or even hundreds of times, making it much cheaper compared to the classic centralized competitors. The data shows that the owner of a PC node that has an average Internet access rate of 2.1 Mbit / s and uses the Dropbox pricing policy will be able to earn about $ 150 per month.
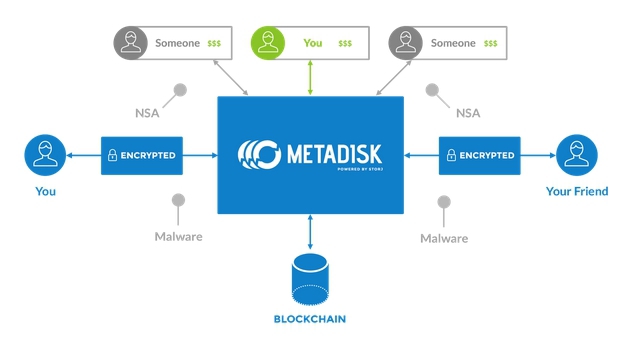
Secure decentralized storage for Storj version
Security and anonymity of the service are guaranteed by eliminating intermediaries (decentralization), as well as the use of encryption to protect data during their transmission over communication channels. At the same time, the authors of the project are categorically opposed to the possibility of taking or copying user data at the request of law enforcement agencies or manual intervention in the work of the system, in case the user violates the user agreement rules. The concept of Storj implies full autonomy and non-interference of any human intermediaries in solving conflict situations.
The developers of Storj argue that in addition to using the public register Bitcoin, the system will inherit its encryption mechanism with public and private keys and the use of cryptographic hash functions.
The project publicly announced itself in March of this year at the Bitcoin Hackaton Conference in Texas, receiving an award winner there. The developers conducted a crowd-ransom of 500 million SJCX, which, however, was not crowned with success: Storj could not even collect 10% of the desired amount of 9800 BTC.
Such a weak result is due to community distrust based on the almost complete absence of any technical information. The Storj team did not provide any specific platform specification. The only currently available technical document looks more like a Metadisk advertising presentation and contains general information, criticism of traditional cloud services, the theoretical concept of Metadisk, but does not answer questions about how the system works at the level of program code and does not provide details about the algorithms. work and technologies used.
A team of 16 people works on Storj, whose names and photographs, along with information about their role in the project, are published on the special page of the official website. The source code for the various Metadisk and Storj modules is available in the Storj github repository . In fact, the work on Storj is at the concept development stage: the written software components are not ready even for full-fledged testing, not to mention the launch of the service. All that is available to study now is an idea supported by the outline of the code.
In order to achieve a successful project, the Storj team will have to answer a lot of questions. How to protect against malicious attacks (for example, Sybil-attacks) or the exploitation of a large number of system nodes by one person? How to meet the growing demand for storage volumes in the event of its success, without referring to the centralized providers? How to deal with the proliferation of prohibited content, using the service for terrorist purposes or for money laundering, taking into account the policy of complete anonymity and non-interference?
Storj is not the first project aimed at implementing the idea of a decentralized, secure and anonymous cloud storage, allowing you to run full-fledged web applications on your base. He is to some extent a competitor to Ethereum, Maidsafe, Permacoin and some other projects that are also working on this promising idea, but have not yet achieved its full implementation.
Repository - github.com/Storj
Conclusion
In this article we covered only a small part of interesting decentralized services, which are now very actively developing, in the next part we will look at other equally interesting new services and technologies that are so poorly covered in the Russian-language Internet.
The second part - geektimes.ru/post/241426
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/237765/
All Articles