Professions of the future: 3D printing in medicine
Hi, Habr!
3D printing is penetrating our lives little by little, as it once was with mobile phones and even earlier with computers. Now, however, we are much less surprised by some innovations in the field of IT. You probably have not forgotten the news, which tells about the vertebra printed on a 3D printer, implanted in a living person. The time is coming closer when parts of the bodies and organs can literally be printed.
New opportunities open up new requirements for specialists.
')
"External" prosthetics, I specifically did not touch, as this is a separate and very complex topic.
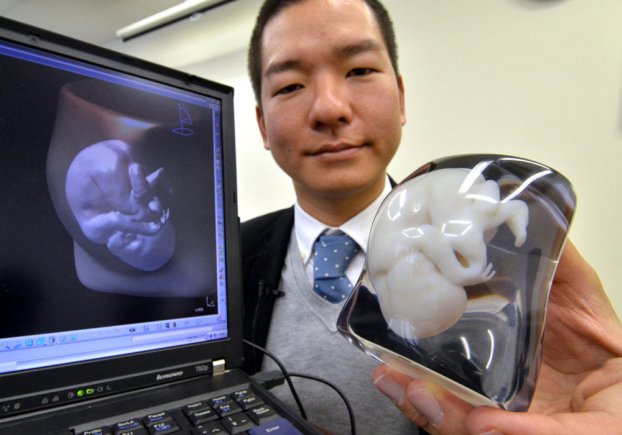
In 2012, the first operation on implantation of a lower jaw implant, printed on a 3D printer, took place. The material is titanium. The artist is a LayerWise company.
This summer, two more "lucky ones" became the owners of the new lower jaws. One of them lost his jaw due to a tumor, and the second broke it. Apparently, very much, so they could not collect.
These are dental surgeons from Kimberley Hospital.
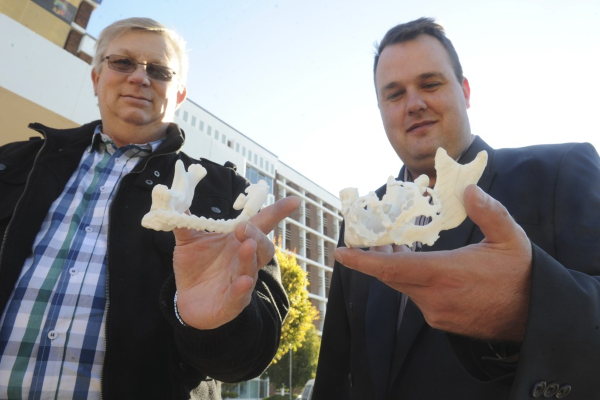

The technology of 3D printing in dentistry has been used since 1999. The pioneer of this field is Align Technology, which started the production and sale of dental caps as an alternative to braces.
Problems with intervertebral discs are quite common. Recently, I ran into it: as the neurologist claims, one of the cervical vertebrae is skewed, that is, it somehow “hesitated” and stands incorrectly. The result of sports. But Plushenko somehow continues to ride with an artificial vertebra - and alive.
The crown of development in this area is the recent operation of Peking scientists on the spinal column of a 12-year-old boy with a malignant tumor of the spinal cord. The material from which the vertebra was made is porous, so scientists do not have to change the vertebra: it will simply acquire bone tissue, that is, become an integral part of the body.
The only negative, except for a heap of pluses: rehabilitation will take place a little longer than using traditional materials.
Using volumetric printing, 75% of the patient's skull was replaced . Not a bad indicator. This operation took place on March 4, 2013 in the USA; it was done after two weeks of work with a scanned model of the patient's skull. The result repeats the smallest details of the form.
According to Oxford Performance Materials, from 300 to 500 people in the US can become monthly patients who need such operations. These include victims of traffic accidents, military personnel and cancer patients with a tumor in the skull.
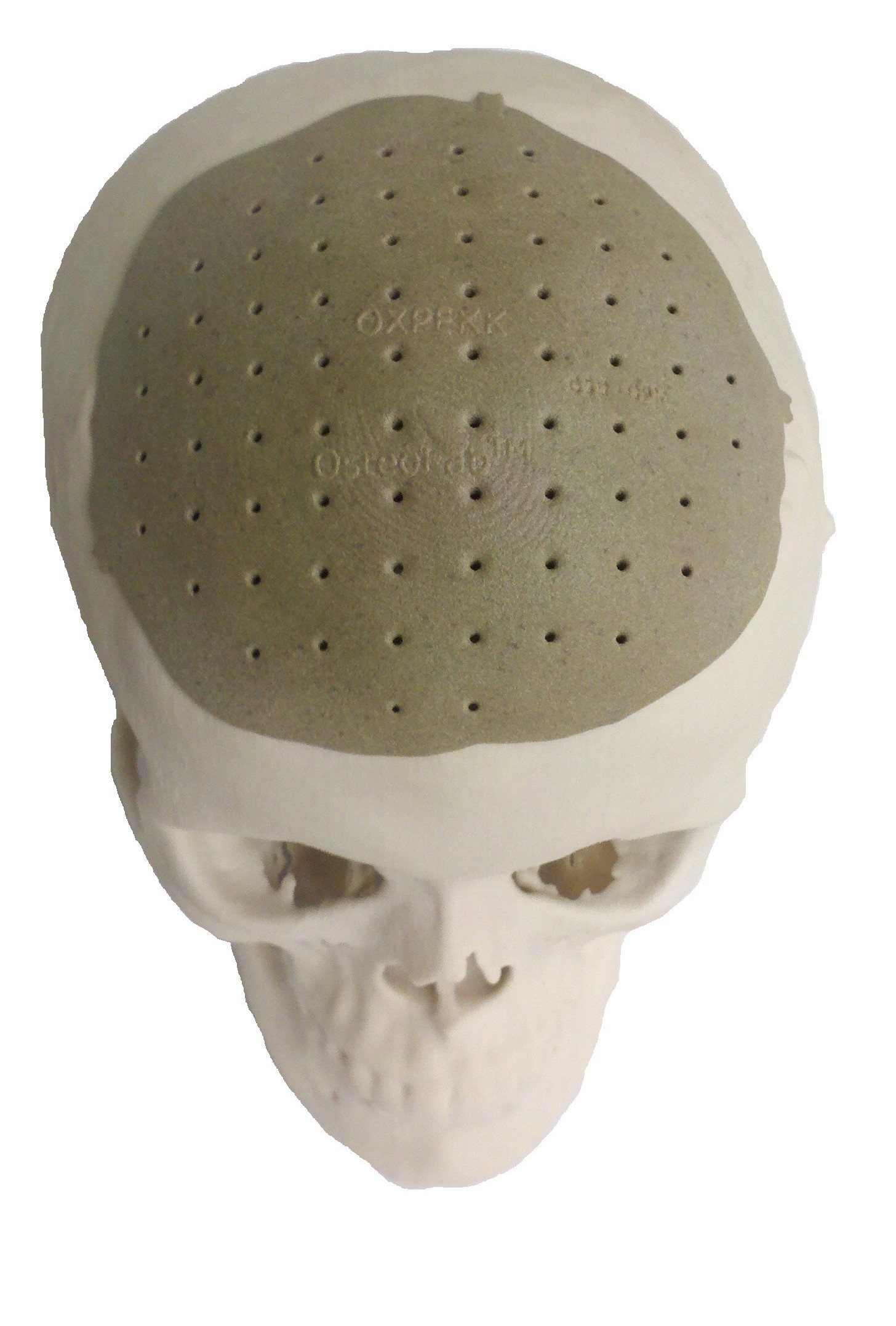
Why 3D printing in terms of bone prosthetics is so effective?
1) Speed. The use of traditional denture casting technology is a long process.
2) Ease. Weight, by the way, can be adjusted by changing the porosity of the titanium prosthesis.
3) Porosity. It is this quality that allows the prosthesis to quickly “overgrow” with living tissues.
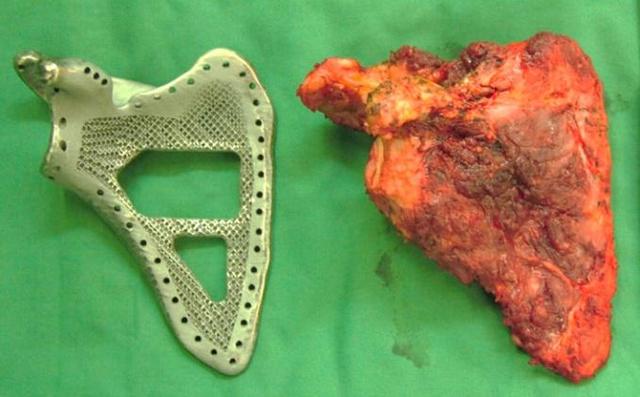
This June, several operations were performed in the same China, in which patients were implanted with the clavicle, scapula, and right iliac pelvis. Indications for surgery - cancer.
This is a prosthetic paddle printed on the printer.
And here in the hands of doctors we see not a prosthesis, but a 3D model of the pelvis. Having such a model before their eyes, the doctors were able to work faster and more efficiently during the operation.
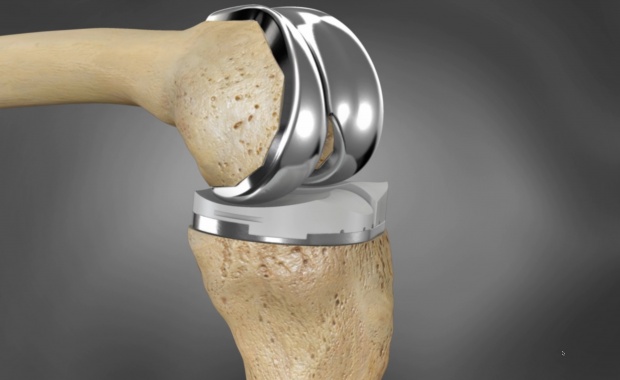
At the beginning of this year, the first person appeared in the USA who was implanted with a knee joint printed on a 3D printer.
What is better than conventional implants? The essence lies in the "little things": usually a prosthesis is selected for prosthetics of the knee joint, after which the bone is ground to approach it. In the case of printing, the developers took the results of computed tomography and made a joint that would fit this patient as naturally as possible.
Engaged in this work of companies Conformis. According to Mike Myers, who now walks normally and even plays golf, and does not stop every quarter, he does not feel a foreign body in the body.
Another important difference of this type of joints from the classic steel and plastic: "Classics" in 10-20 years will have to be changed.

In Britain, an operation to replace the hip joint with a printed one was performed this year. 71-year-old grandmother raised to his feet. The material is titanium powder again.


And this is not just a sink, but a real bionic ear. Only he was not sewn to the man.
This device, made with the participation of human living cells, contains an inductive radio antenna. This is still a concept on which they will still work. It was created to test the use of nanoelectronics in 3D printing.

For drug research in 2013, scientists were able to print liver tissue on a 3D printer. Hepatocytes, stellate cells, and epithelial cells lining blood vessels were used as materials.
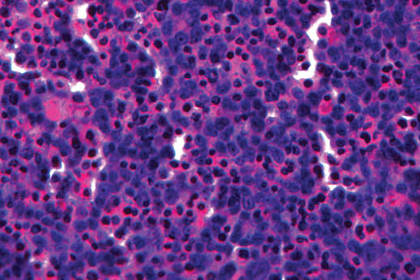
The process of bioprinting.
The main problem at the moment is the use of 3D printing in organ prosthetics - this is the blood supply. After all, every cell in the tissues is located next to the capillaries. So far, scientists have not solved this problem.
Idea on the surface: printing orthopedic insoles on a 3D printer after scanning becomes very easy and fast.

Having a 3D model before your eyes, it will be much easier for surgeons to navigate inside a living person during an operation.
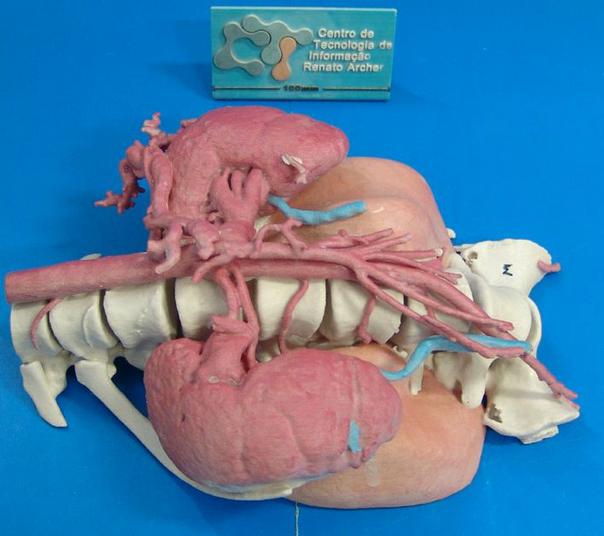
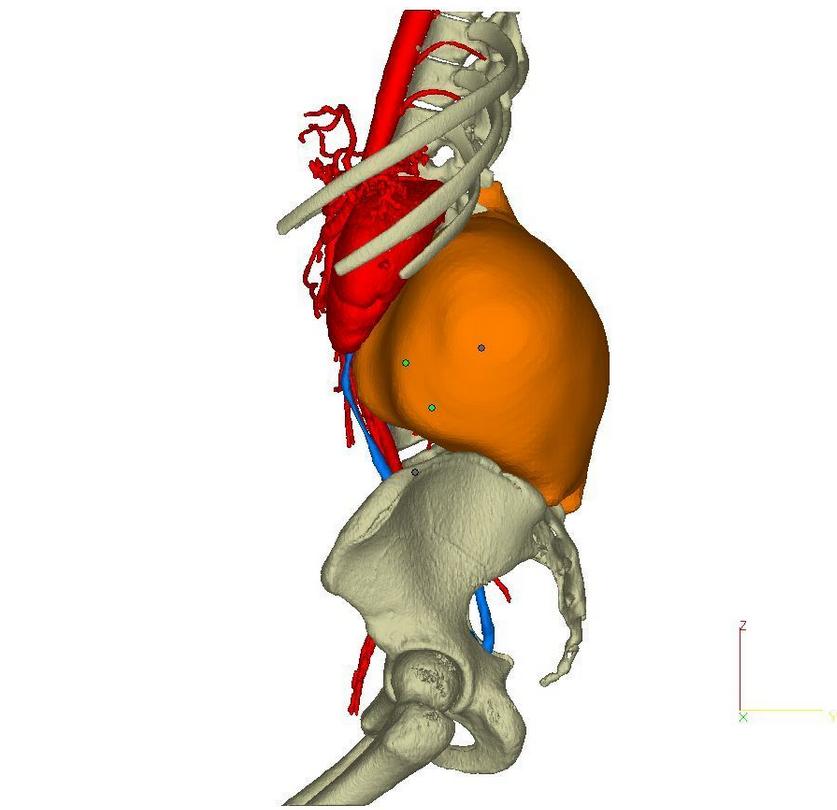
Especially when the operation takes place on a little girl whose cancer is considered inoperable. The tumor of a twelve-year-old girl, whose models we see on these images, was too close to the spine, and was also surrounded by healthy tissues, organs, veins and arteries. This dangerous operation was successful, because the doctors used this printed 3D model and carefully planned the operation with its help.
Also now collect a library of 3D layouts of hearts from around the world. A printed heart also helps doctors plan an operation, because one thing is to see the results of the scan, and the other is to keep them full-size in their hands.

3D printing in the field of medicine has not yet revealed its full potential. Many believe that the printing of organs in real time is on the way. Perhaps this is about 10-12 years left. So the doctors will not wait for the donor to have an accident, leaving behind a heart: the doctors will simply take the necessary tests and print the necessary organ.
The history of bulk printing from the 1980s leads us to this opportunity. And then new jobs and business opportunities are created: companies whose purpose is to assist surgeons in conducting operations, develop and create new types of prostheses and study materials, as well as drug testing and the creation of bio-printing fabrics for this.
New opportunities and trends give rise to new requirements for specialists. So the profession of "bio-architects" in the field of 3D printing.
The organs of each person are far from the same, and injuries during transplantation can be reduced by adjusting the size and unique features of the new organ. If we can print a new body, then we can use all the best features of the old body in it, but at the same time correct the flaws. It turns out we need a specialist who knows medicine, anatomy, knows how to work with 3D models, understands 3D printing and is able to literally modify the new printed organ.
3D printing is penetrating our lives little by little, as it once was with mobile phones and even earlier with computers. Now, however, we are much less surprised by some innovations in the field of IT. You probably have not forgotten the news, which tells about the vertebra printed on a 3D printer, implanted in a living person. The time is coming closer when parts of the bodies and organs can literally be printed.
New opportunities open up new requirements for specialists.
')
"External" prosthetics, I specifically did not touch, as this is a separate and very complex topic.

Dentistry
In 2012, the first operation on implantation of a lower jaw implant, printed on a 3D printer, took place. The material is titanium. The artist is a LayerWise company.
This summer, two more "lucky ones" became the owners of the new lower jaws. One of them lost his jaw due to a tumor, and the second broke it. Apparently, very much, so they could not collect.
These are dental surgeons from Kimberley Hospital.

The technology of 3D printing in dentistry has been used since 1999. The pioneer of this field is Align Technology, which started the production and sale of dental caps as an alternative to braces.
Spine
Problems with intervertebral discs are quite common. Recently, I ran into it: as the neurologist claims, one of the cervical vertebrae is skewed, that is, it somehow “hesitated” and stands incorrectly. The result of sports. But Plushenko somehow continues to ride with an artificial vertebra - and alive.
The crown of development in this area is the recent operation of Peking scientists on the spinal column of a 12-year-old boy with a malignant tumor of the spinal cord. The material from which the vertebra was made is porous, so scientists do not have to change the vertebra: it will simply acquire bone tissue, that is, become an integral part of the body.
The only negative, except for a heap of pluses: rehabilitation will take place a little longer than using traditional materials.
Skull
Using volumetric printing, 75% of the patient's skull was replaced . Not a bad indicator. This operation took place on March 4, 2013 in the USA; it was done after two weeks of work with a scanned model of the patient's skull. The result repeats the smallest details of the form.
According to Oxford Performance Materials, from 300 to 500 people in the US can become monthly patients who need such operations. These include victims of traffic accidents, military personnel and cancer patients with a tumor in the skull.

Other bones
Why 3D printing in terms of bone prosthetics is so effective?
1) Speed. The use of traditional denture casting technology is a long process.
2) Ease. Weight, by the way, can be adjusted by changing the porosity of the titanium prosthesis.
3) Porosity. It is this quality that allows the prosthesis to quickly “overgrow” with living tissues.
This June, several operations were performed in the same China, in which patients were implanted with the clavicle, scapula, and right iliac pelvis. Indications for surgery - cancer.
This is a prosthetic paddle printed on the printer.

And here in the hands of doctors we see not a prosthesis, but a 3D model of the pelvis. Having such a model before their eyes, the doctors were able to work faster and more efficiently during the operation.
Joints
At the beginning of this year, the first person appeared in the USA who was implanted with a knee joint printed on a 3D printer.
What is better than conventional implants? The essence lies in the "little things": usually a prosthesis is selected for prosthetics of the knee joint, after which the bone is ground to approach it. In the case of printing, the developers took the results of computed tomography and made a joint that would fit this patient as naturally as possible.
Engaged in this work of companies Conformis. According to Mike Myers, who now walks normally and even plays golf, and does not stop every quarter, he does not feel a foreign body in the body.
Another important difference of this type of joints from the classic steel and plastic: "Classics" in 10-20 years will have to be changed.


In Britain, an operation to replace the hip joint with a printed one was performed this year. 71-year-old grandmother raised to his feet. The material is titanium powder again.


Auricle
And this is not just a sink, but a real bionic ear. Only he was not sewn to the man.
This device, made with the participation of human living cells, contains an inductive radio antenna. This is still a concept on which they will still work. It was created to test the use of nanoelectronics in 3D printing.

Liver
For drug research in 2013, scientists were able to print liver tissue on a 3D printer. Hepatocytes, stellate cells, and epithelial cells lining blood vessels were used as materials.

The process of bioprinting.
The main problem at the moment is the use of 3D printing in organ prosthetics - this is the blood supply. After all, every cell in the tissues is located next to the capillaries. So far, scientists have not solved this problem.
Orthopedic products
Idea on the surface: printing orthopedic insoles on a 3D printer after scanning becomes very easy and fast.

Assistance during operations
Having a 3D model before your eyes, it will be much easier for surgeons to navigate inside a living person during an operation.
Especially when the operation takes place on a little girl whose cancer is considered inoperable. The tumor of a twelve-year-old girl, whose models we see on these images, was too close to the spine, and was also surrounded by healthy tissues, organs, veins and arteries. This dangerous operation was successful, because the doctors used this printed 3D model and carefully planned the operation with its help.


Also now collect a library of 3D layouts of hearts from around the world. A printed heart also helps doctors plan an operation, because one thing is to see the results of the scan, and the other is to keep them full-size in their hands.

3D printing in the field of medicine has not yet revealed its full potential. Many believe that the printing of organs in real time is on the way. Perhaps this is about 10-12 years left. So the doctors will not wait for the donor to have an accident, leaving behind a heart: the doctors will simply take the necessary tests and print the necessary organ.
The history of bulk printing from the 1980s leads us to this opportunity. And then new jobs and business opportunities are created: companies whose purpose is to assist surgeons in conducting operations, develop and create new types of prostheses and study materials, as well as drug testing and the creation of bio-printing fabrics for this.
New opportunities and trends give rise to new requirements for specialists. So the profession of "bio-architects" in the field of 3D printing.
The organs of each person are far from the same, and injuries during transplantation can be reduced by adjusting the size and unique features of the new organ. If we can print a new body, then we can use all the best features of the old body in it, but at the same time correct the flaws. It turns out we need a specialist who knows medicine, anatomy, knows how to work with 3D models, understands 3D printing and is able to literally modify the new printed organ.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/237699/
All Articles