Ranking Factor # 1: User Satisfaction
Yesterday we published a translation of a Yandex report on how behavioral factors are taken into account by the search engine when evaluating the generation of an issue. Cyrus Shefard's MOZ article on behavioral factors continues this topic, revealing it for Google. The author is an employee of MOZ.
You yourself know these numbers: Google takes into account more than 200 ranking signals, updates its algorithms 500 times a year, and thousands of engineers work for it. In this pursuit, in desperate attempts to keep up with the changes of the algorithms, we so often forget that all this is necessary for one single purpose:
')
Satisfy user.
Just do not think now that this will be a post on the topic of emotional experiences about it. “Make great content and visitors will come themselves” or “Surprise your customers and a miracle will happen”.
No miracles. User satisfaction is an up-to-date ranking factor.
Unlike other ranking factors, satisfaction is difficult to measure because it requires the internal data of the search engine itself - and this is what they don’t like to share. We certainly know that search engines measure and encourage satisfaction in various ways. In fact, I’m pretty sure that satisfaction is one of the most important metrics for Google, allowing you to evaluate the success of your own pages of issue. (In this regard, it is appropriate to mention yesterday’s publication of a translation of the Yandex report on this topic - approx. Transl.)
Cling to a keyword is easy enough. It is much more difficult to get users to stop going back to the search from your site if they did not find what they were looking for. "Screw" satisfaction is extremely difficult (in fact, no - approx. SERPClick). Perhaps it is because of the complexity of such cheating search engines pay so much attention to this factor.
How Google measures and predicts satisfaction
User satisfaction with search results
Stephen Levy’s wonderful book In the Plex describes how Google’s engineers came up with a way to improve search results by collecting and processing user behavior data (highlighted by me - the author):
"... Google can track how satisfied users are. ... The best signal of their satisfaction is the" long click "- this happens when someone chooses the result of the issue, ideally if it is first on top and then does not return to the search. This means that Google successfully processed the request. However, unsatisfied users were dissatisfied each for some reason. The most eloquently talked about this "short clicks", when the user followed the link and immediately went back. “If a person typed something and then changed his query, it means that he did not find what he was looking for,” says Patel. - "If they went to the next page of issue, it means that they are not satisfied with what they saw."
This name is often called pogosticking : a designation for users' behavior when they click on the result in the output, and then return (pogostick) back and click again on the results of the issue, trying to find what they need .Search query weight
In 2012, Google announced a short version of its Quality Rating Guidelines for Search Quality Assessment ( Search Rating Guidelines ). A small army of specially trained users are guided by this document when evaluating search results.
One of the highest grades that can be assigned according to this document is “useful” (author’s selection):“Useful pages should be of high quality and well suited to the request. Also, they often have one or all of the following characteristics: satisfying user requests, authoritative, interesting, and / or recently posted (such as the latest news on the topic). Useful pages are usually well organized and inspire user confidence. They contain information from trusted sources. Helpful pages are not recalled. ”
Unfortunately, an appraiser can view only a few thousand web pages in a certain time, while millions of sites are online. Therefore, Google has developed a new system:Panda
Instead of evaluating the results by fact, Panda gives Google the ability to predict user satisfaction based on research using the users themselves. Thus, you can rank all indexed sites.
Less satisfying pages get a lower ranking in the search, and every few weeks the index is updated based on the newly collected data.
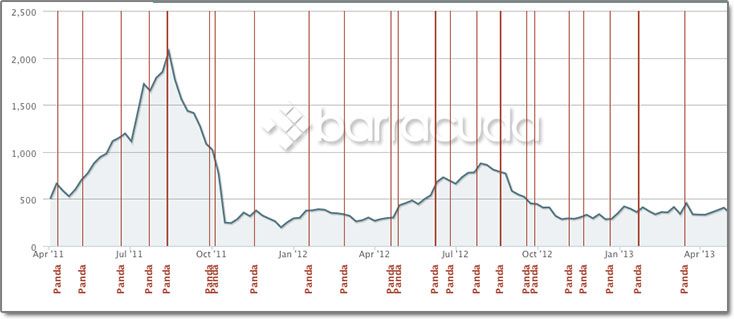
The graph below shows how the Panda consistently lowers the site in the ranking.
Information about visiting sites Panda can be obtained through the Panguin Tool and Google Algorithm Change History.What we can do?
If search engines measure user satisfaction and use it as a ranking factor, then our goal should be as follows:
- Create conditions under which users will not go back to the search and click on another URL.
- Create sites that Panda regards as conforming to quality characteristics.
- Surprise and delight our users so that they come back to us again and again.
5 Ways to improve behavioral factors:
1. Free Google Satisfaction Survey
As if in order to specifically draw attention to the topic of behavioral factors, Google recently released free, embedded surveys to measure user satisfaction for webmasters .
After you add a line of JavaScript to your website, your users will receive the following questions:
- How satisfied are you with this site as a whole?
- Is there anything that disappointed you on this site or is it unattractive?
- What is the purpose of your visit to this site today?
- Did you achieve this goal today?
If you want to customize questions, Google offers to do it at a price of $ 0.01 per question.
Apparently, Google wants to give webmasters the opportunity to feedback, like the one that it itself collects from data on user behavior. Of course, the survey will not give a direct answer to the question “What to do?”, However, they allow any webmaster to collect a lot of useful data on user satisfaction.2. Remove obstacles.
For years, we only do what we say that our site should be made available both for the search robot and for people. But rarely does anyone talk about how these usability factors affect ranking.
Imagine, if you wish, a site that requests registration to view any content, even in order to get search results from this site in return. But we are increasingly seeing this on the net.
What if I had to register on Moz?
It's simple: people click on the issue, see the registration form and go back to the search for another URL. After a couple of hundreds of such returns (or even less), the search engine will take into account that the URL in the search does not satisfy the users.
We at Moz have seen sites that made registration access only for part of their most requested pages. And their rating fell. In fact, it is full of literally anecdotal situations when Panda lowered sites after the introduction of such measures.
3. Accelerate
We know that a faster site is good, but the page has two mechanisms by which you can influence the ranking:
Directly: Google officially announced that page loading speed directly affects the ranking for a certain percentage of requests (only 1% in 2010).
Indirectly: Since the speed of the page affects the usability of the page, it can indirectly affect the degree of user satisfaction. If the user waits too long for the page to load, he may be disappointed and go back to the search.
Google is literally obsessed with page loading speed and Microsoft researchers have shown that users will visit the site less often if it is only 250 milliseconds slower loading than a competitor's site .
Source: The New York Times .
If you need to convince a client or manager of the need to increase download speed, try the speed comparison tool Webpagetest.com , which allows you to export video in slow motion playback.4. Empathy
Empathy - a ranking factor? "Cyrus, - I already hear you say that to me - you talked with Rand along the way!"
You can add this comment at our next seminar. I changed the comments below to highlight the important points:Recently, I have paid a lot of attention to making the web page look like I would like to see it if I was looking for it. I redid it and finished it so that the product line (and this is an e-commerce store) was all that the user might want to see and added a code for the discount to the page.
After that, the user time on the page and page views after visiting this page increased significantly while the percentage of failures was reduced (twice!). For 7 weeks the page went to the top. In order to be sure, I did not post links from other sites to the page. The reference weight leading to the And page to the domain remained unchanged during this period according to the testimony of AHRefs, OSE, Majestic, GWM & LRT.5. Shredding
One of the best articles on promotion, which I read over the last year - AJ Kohn's Time to Long Click (It is time for a long click). AJ explains how the linking (as well as content) can be used to increase user satisfaction (highlighted by the bold author of the article):I always recommend that you link together important sources of information whenever possible in order to fully satisfy a user request . In this way, you create a situation for longer clicks and eventually get more links to yourself. Both of these implications have a positive effect on your ranking.
Stop thinking about how to optimize your page and think about how to optimize search behavior.
- AJ Kohn
Think: it is much more convenient for users to click from your site to another URL rather than go back to the search and search again. If people find something with you, then you are an authoritative source. If they can only find it in Google, then Google is the authority.
Be an authoritative source.How do you personally improve user satisfaction?
There are two types of tactics: try to satisfy the robot or try to satisfy the site visitors.
Centering the strategy on robots leads to the creation of pages filled with the correct keywords and meta tags - this is an attempt to help the search robot to recognize relevance. I said “attempt” because the search engine itself is tracking users. If they are unhappy, the robot too.
A user-driven promotion strategy with the same keywords and meta tags offers users more: come and try the site. And then - you need to do everything to make the user happy.
Have you observed an improvement in the ranking of your site after a set of works to improve user factors? Tell your story in the comments.
From the translator:
The article was prepared by the analytical department of the ALTWeb Group . It reveals the mechanisms, work on which includes strategic planning and step-by-step implementation. This complex set of measures can be enhanced by working with behavioral factors through the SERPClick system, whose work is based on the factors outlined in this article.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/237417/
All Articles




