Philae / Rosetta landing probe: what will happen when the probe lands on Churyumov-Gerasimenko comet?

November 11, the date the Philae probe landed on the surface of the comet Churyumov-Gerasimenko ( landing pad J ) is getting closer. But how will the landing take place, and what will the probe do during the various phases of its mission?
Recently, the European Space Agency ESA announced a detailed plan, which, I think, will be of interest to many. By the way, in the continuation of the video model of the landing of the probe on the comet.
')
So, the scientists divided the main mission of the probe into three phases: separation from Rosetta, approaching the comet, landing on the surface of the comet. Philae is equipped with a number of scientific tools, and during all these phases the following tasks are envisaged.

Separation from the parent station and approaching the comet:
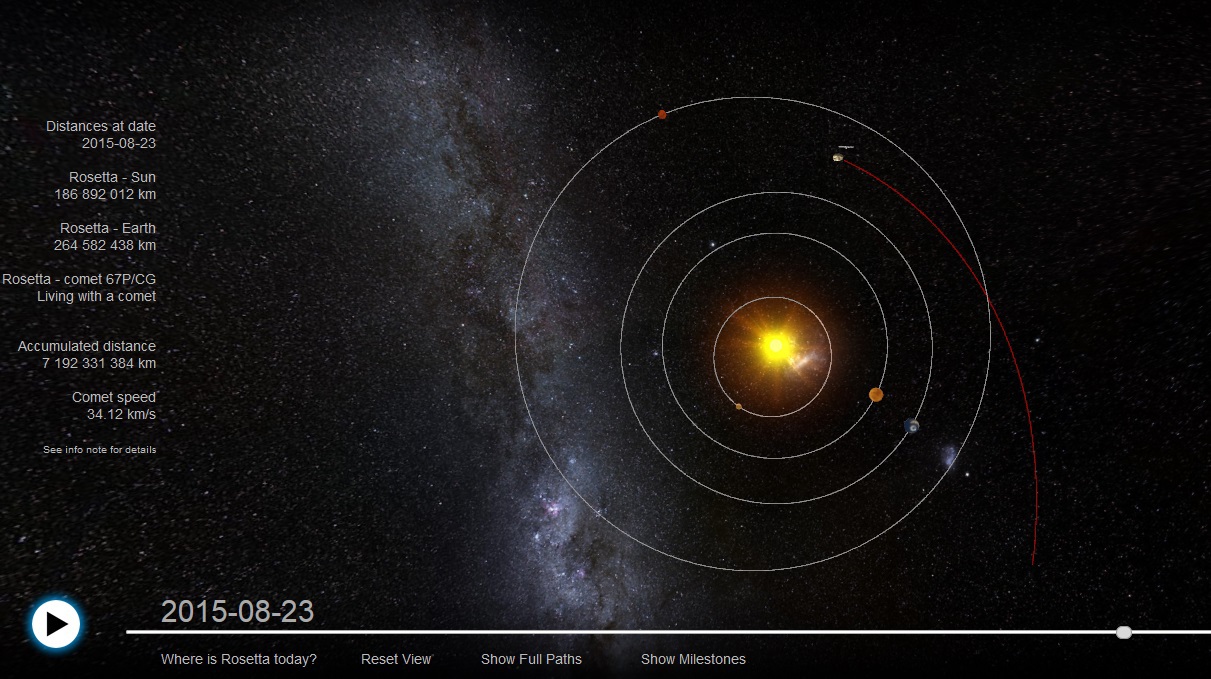
- CIVA will make a “farewell” photograph of the Rosetta station (by the way, on August 23, 2015, Rosetta will pass from Earth at a minimum distance of 264 million kilometers, you can track the trajectory here ).
- ROLIS will take photos during the decline;
- COSAC and PTOLEMY will take samples of the "atmosphere" of the comet during landing;
- ROMAP will measure the level of interaction of the solar wind with cometary matter, “plasma”;
- SESAME / DIM and SESAME / PP will take additional measurements, dust and plasma;
- CONSERT, together with other instruments, will measure the vertical velocity and will also study the upper layers of the cometary nucleus.
Landing:
- CIVA will take a panoramic snapshot of the landing site, this snapshot will allow you to evaluate the module landing;
- MUPUS will measure the deceleration of the harpoons, which serve to attach the probe to the surface of the comet;
- SESAME / CASSE will measure the physical parameters of the surface.
Separation, reduction and landing will take about 10-11 hours. The execution time of this task will depend on the specific landing site and, accordingly, the probe's trajectory.
In case of a successful landing and performing the first three tasks already on the comet, Philae will begin work on the implementation of the next stage, which will take about 54 hours. The task is to carry out all the most important scientific work, after which you can begin to perform tasks that may be called less important (although with regard to the study of the comet, all tasks are extremely important for science).
- ROLIS will take pictures of the surface with micron resolution;
- ROMAP measures the properties of the magnetic field and plasma;
- MUPUS will measure the physical parameters of the surface and the temperature of the surface layers in the landing zone;
- CONSERT will take a sample of the substance of the nucleus of the comet.
At the same time, the probe will study its own location and orientation in space, to find the optimal position in which the solar panels will receive the maximum amount of solar energy.
The next stage of research is the study of the subsurface layers of the comet, with drilling, conducted by the SD2 tool. COSAC and PTOLEMY will estimate the level of gaseous substances while drilling. SD2 will be drilled twice during this stage, the selected samples will be heated in a furnace, to release related chemical compounds that will be in a solid aggregate state without heating.
When analyzing the first sample, the concentration of carbon, oxygen, hydrogen and nitrogen will be measured, with the determination of the isotope content. The second sample will be used to determine the presence and concentration of chemical compounds. Dust studies in the ambient probe environment will be conducted using SESAME.
Among other things, the surface of the comet will be studied. MUPUS “hammer” will immerse itself in the ground to measure the temperature of various surface layers. Acoustic signals and vibrations from the hammer will be analyzed by acoustic sensors, and the data will serve to clarify the properties of the deeper layers of the cometary nucleus. APXS will study the elemental composition of the substance of the comet's surface. With the help of SESAME / DIM, scientists will be able to study the effect of dust particles, and SESAME / PP will help to obtain data on the dielectric properties of the soil, which, in turn, will allow us to understand whether there is frozen water / ice under the surface of the comet.
A little later, SD2 will again drill the comet's surface to obtain samples that will be photographed by CIVA-M with a high magnification in the visible and infrared spectra. The same samples will be studied with the COSAC tool.
Philae probe scientific operations will be performed around March 2015. After this, the temperature of the comet's core will rise to a level when the operation of the probe will no longer be possible, and the mission for a period of ten years will receive its logical conclusion.
Via esa
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/237239/
All Articles