Traffic from social networks: the most modern methods of attraction, return and analysis
Traffic from social networks: not much happens!
The share of social traffic in top news sites of the Russian Internet averages from 3% to 10% . There are rare exceptions to this pattern, for example, on the Dozhdya website - 25% of social traffic; approximately at the same level, the indicators of youth media Look At Me, etc. under.). *
If we analyze the first page of the issue of Yandex on the microwave request "plastic windows", here the share of social traffic is barely non-zero. And this is typical of many of the resources of competitive commercial topics. **
')
Or, for example, to analyze the issue of “men's swimming trunks” ( HF request) and “Men's swimming trunks- 2014 ” at requests ( MF-LF request). Upon first request, mostly large online stores (sometimes international) fall out. At the second request, major brands are interspersed with small businesses. In the second case, it is surprising that the small business “fights desperately” for positions with unequal opponents, and at the same time makes almost no attempt to use at least 25-30% social traffic. Only in a couple of cases, small shops receive 3-9% of traffic from social networks, although even the topic of men's underwear is almost ideal for working with social networks.
The picture on the Western Internet is completely different. Here, commercial sites and services work much more closely with social sources, so the percentage of social visitors even on commercial resources is higher than in runet. Judging by the long-term tendency of alignment to the west, we should also strive for this.
How to attract social traffic?
Basic options:
- create and develop a group from scratch;
- buy a ready-made group with an already formed audience;
- create a group and promote it in the PS ( much faster and cheaper than promoting the site );
- work more actively with content marketing.
If we talk about specific recommendations on the time and frequency of posting, on the influence of one or another type of content, on the influence of pictures in posts, on the form of surveys and on the mass of other factors, then we’ll get a topic for a separate article. More precisely, for dozens of articles, because the behavior of users from social networks with different topics will differ significantly. It is impossible to give the same recommendations to the gynecological clinic and IT-service, gift shop and auto parts store. It is much more expedient to experiment and display your own formulas.
How and why to analyze traffic on the subject of social behavior?
Suppose the site managed to attract a powerful, stable stream of users from social networks. What's next? How to work with him? Answer: first of all, it is necessary to analyze this traffic.
We will analyze on concrete examples what statistics can be obtained about attracting from social networks, and also consider the picture of the social actions of users on sites in general.

This is a site statistics for slimming women, taken from the counter UpToLike . In a month, about 3,000 social activities attracted more than 1,000 new users. This is a good example of the fact that sharing information in social networks directly works to attract new, loyal users.

This screenshot shows the page activity of the attracted users, as well as a breakdown by social networks where they came from. Obviously, various kinds of calorie analyzers, recipes, and calorie calculators attract the most attention of the female audience. These are useful functions that women want to share with each other, add pages to bookmarks.
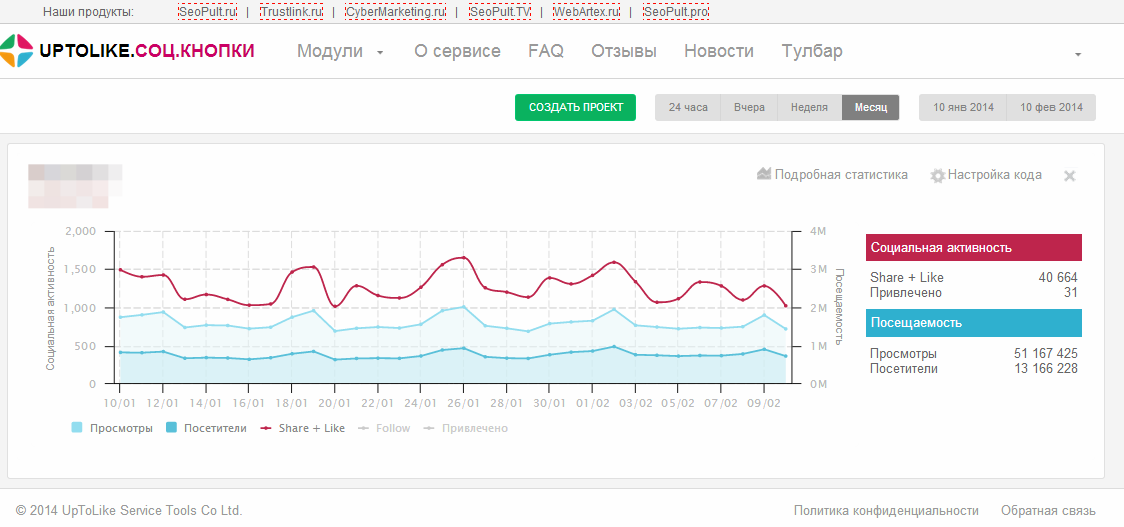
This is an example from another site where a huge stream of social traffic is not active at all. Perhaps in this case it is worth checking all sources of attraction.
If you compare UpToLike statistics with statistics, for example, Metrics or Analytic s, you can see that users attracted from social networks through likes and sheirs are more active and loyal to users attracted from other sources. They linger longer on the site, browse more pages, more often "like" the materials they get from social networking pages. Moreover, a person who has switched to a page from a social network approximately in every fifth case returns to the site directly from the browser or from bookmarks, that is, there is a sound reinforcement of the audience.
Western colleagues share interesting experiences about social statistics. They describe an experiment with a new metrics "attention minutes" . Attention minutes is more than just a fix for how much time a person has spent on a site. This is an indicator of content dedication (does the user launch a video on a page, does the mouse cursor move, etc.). It turns out that a user who is passionate about content at 25% attention minutes, puts a sheer rather than a user who is 100% enthusiastic. Sharing is also highly likely for users with 125% enthusiasm: such users make the most thoughtful sheirs, study the content entirely.

Perhaps, from this experiment, we can conclude that virality is influenced not so much by the quality of the text, but by the design and content of the entire page: the person sheirit the page, not so much studying the text, as sympathizing partly with the format, partly with the layout and other elements of formatting and usability.
In Runet, such studies can be performed using a Webvisor in Yandex.Metrica and compare them with UpToLike data.
Does social traffic affect website ranking?
Suppose we analyzed the social traffic of the site, and, in general, the social behavior of users on the site. What to do with this data?
The most obvious answer is to expand the scope of influence of content marketing. The UpToLike statistics in itself clearly shows which social networks your users have most of all, what content attracts them, what content they most often cheat, etc. If you combine UpToLike data with analysis from Yandex and Google counters, you can get even more subtle statistics (non-obvious dependencies) and use them already for content marketing of aerobatics.
A less obvious answer is to use this data in order to achieve growth in search traffic along with non-search social.
For example, an experiment is described here in which they investigated the influence of various social signals on the ranking of sites in the PS and revealed the enormous influence of social networks on the growth of positions on the low-demand page.
- 100 followers on Google+ gave a 14.63% growth in positions
- 300 likes on Google+ gave 9.44% growth in positions
- 70 sheirs and 50 likes on Facebook gave a 6.9% growth in positions
- 50 tweets yielded 2.88% growth positions
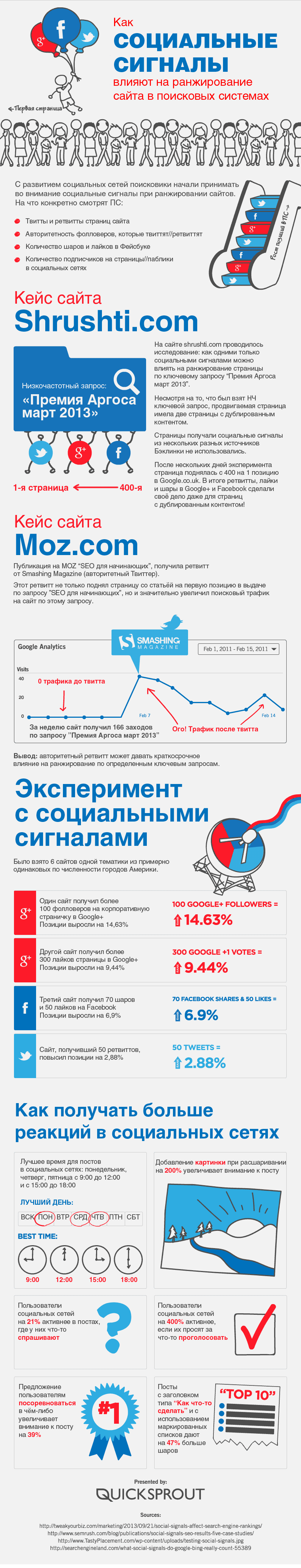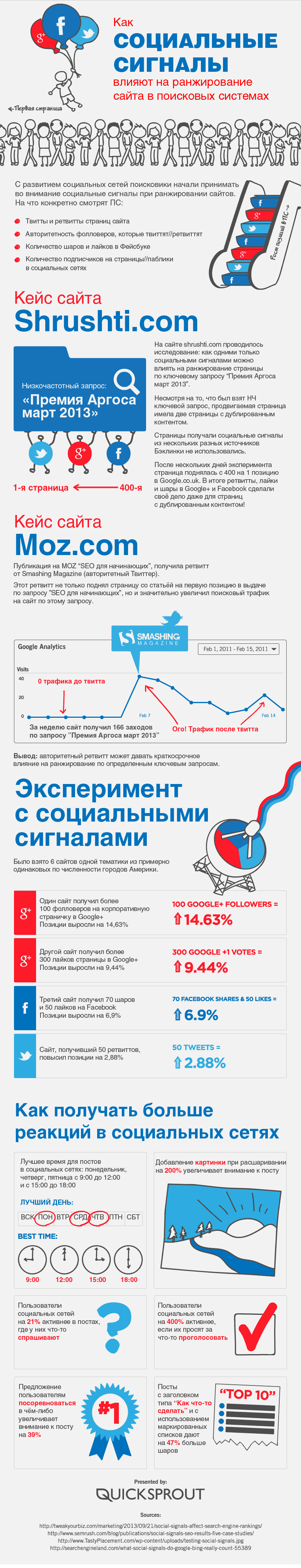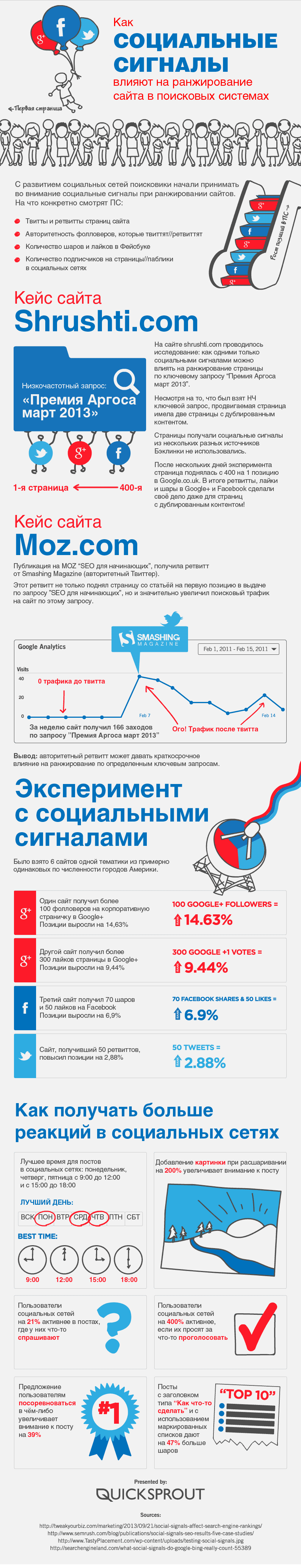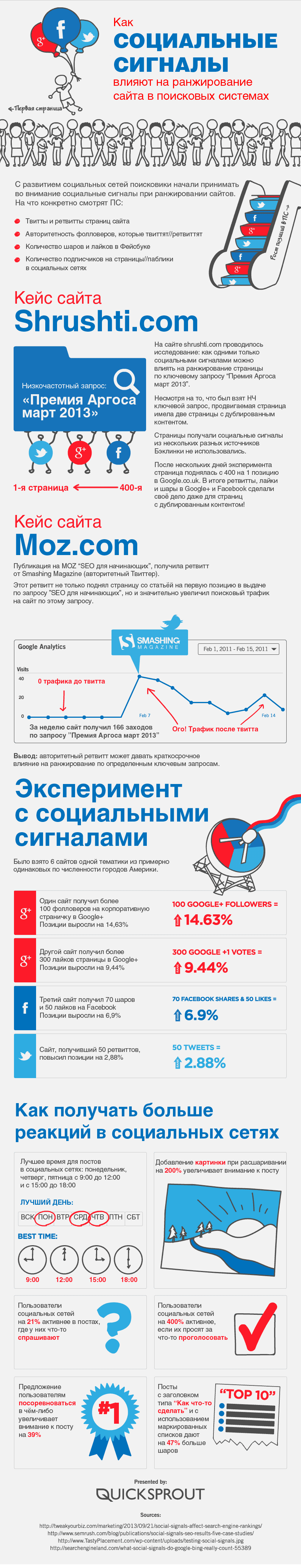
Likes, sheirs, comments, tweets, subscriptions, and so on. Active user actions are working to strengthen the site’s behavioral and social metrics, the importance of which today’s not just lazy. Due to the lively behavior of users from social networks, search engines understand that the resource gives people useful experience, which means that the site should be ranked higher.
This is the perfect scheme of website promotion, absolutely honest with respect to search engines and users. The only problem is that users in social networks are concerned about not all topics, especially commercial ones. Question: how else can you attract non-search traffic, whose behavior will be comparable to the hyperactivity of users who come from social networks? Answer: to attract the maximum target audience from other non-exploratory sources. Actually, this is how classic RTB mechanisms work today.
- This material actually describes all the parties and all the possibilities of social traffic, as well as presents the statistics of social behavior of users on the site. If you still do not use at least one of the aspects described above, you undoubtedly do not receive any part of the traffic, not only from social networks, but also from search results. The situation will be quickly corrected and significantly improved by working with analytics ( UpToLike , Metric, Analytics) and content marketing.
* Data from similarweb
** Data from similarweb
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/237129/
All Articles