Sun Service
For a long time I noticed that on the Hub there is not a single article about the observatory. There are articles about telescopes, satellites, asteroids. But articles about how astronomers' habitats are arranged are not. Why are there! Once there were a lot of articles about the offices of large IT-companies, which boiled down to where they feed what kind of candy, where it is more convenient to select chairs, where they use which computers. But in these articles are not mentioned observatories. But, in my opinion, it is much more interesting to look at a bunch of monstrous works of human genius than to compare the dinner programmer Google and Apple.

Periodically, I go on business trips to various observatories. I wanted to eliminate the misunderstanding described above and write a short story on this topic. The article is devoted to the Ussuri Astrophysical Observatory ( UAFO of the Far East Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences ), which is the largest observatory in the Far East. Residents of Primorsky Territory, she is most likely familiar with, but I think that for the rest it will be curious to read.
')
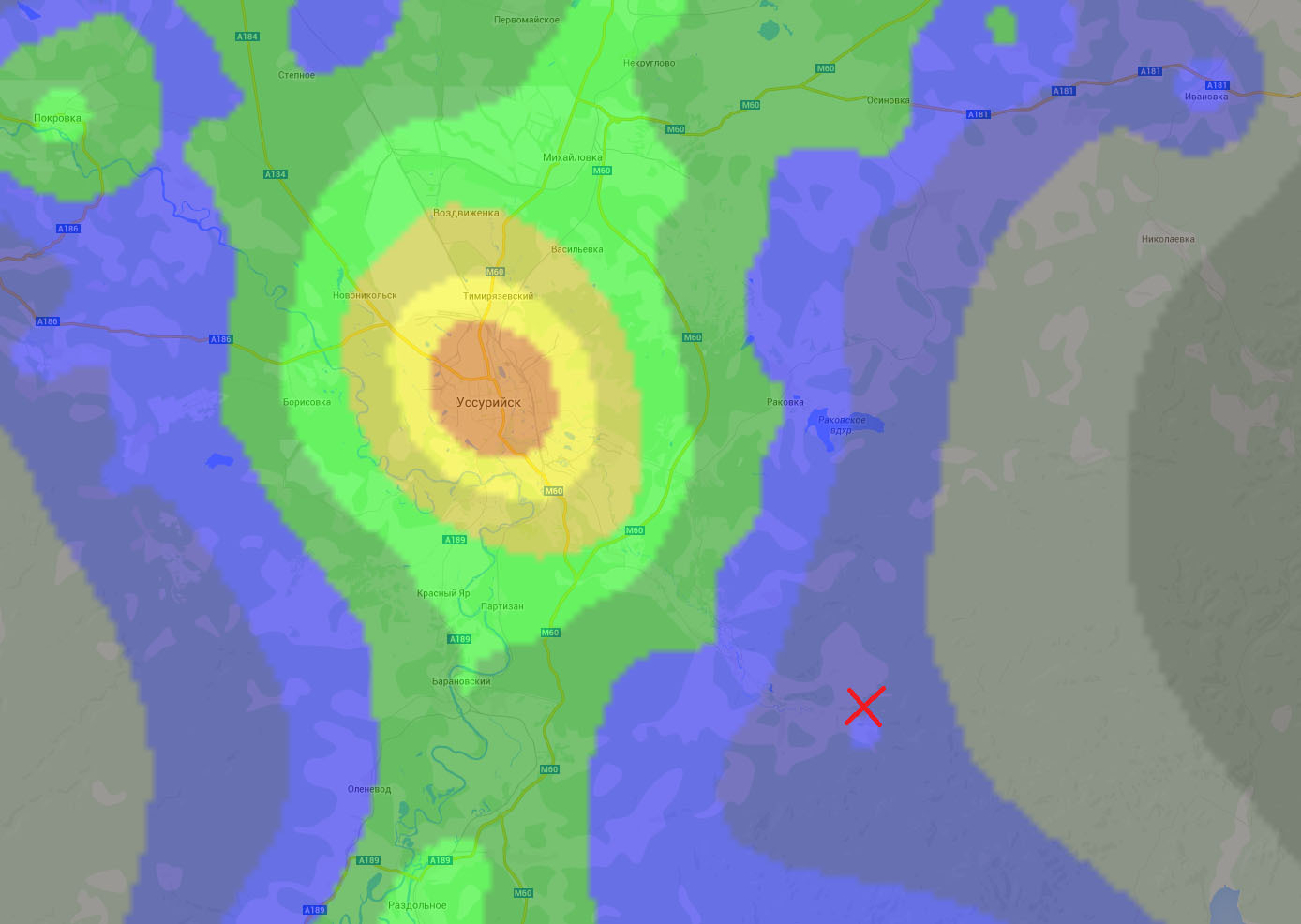
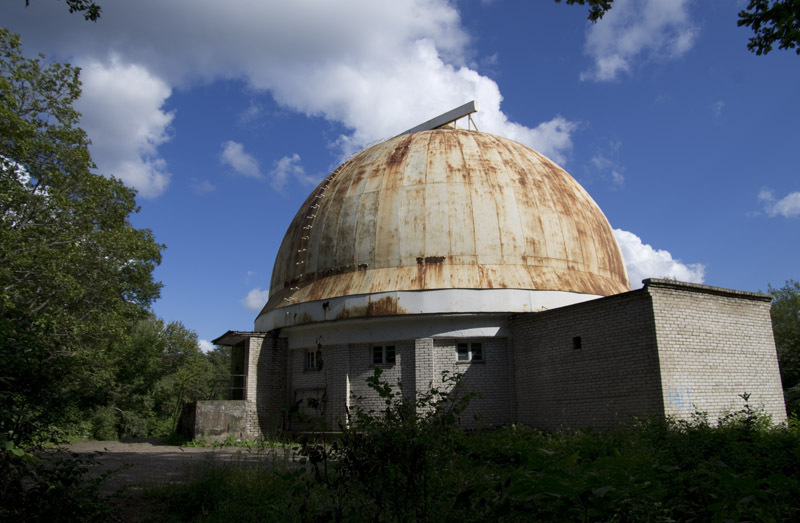
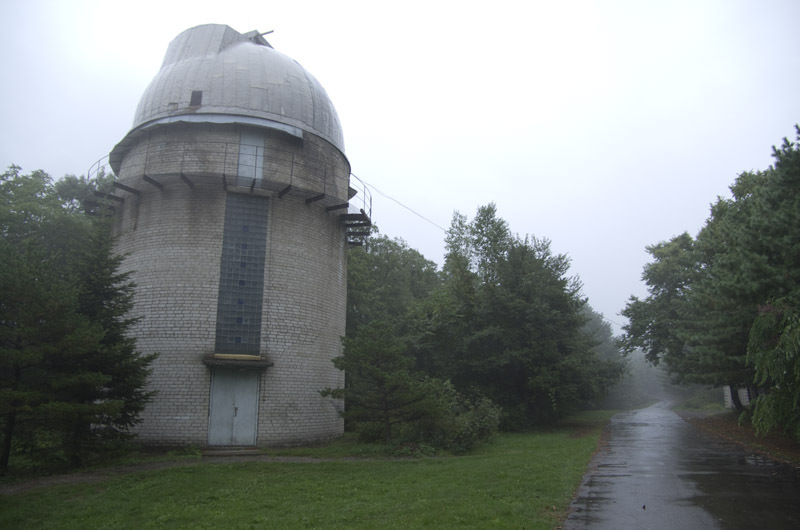
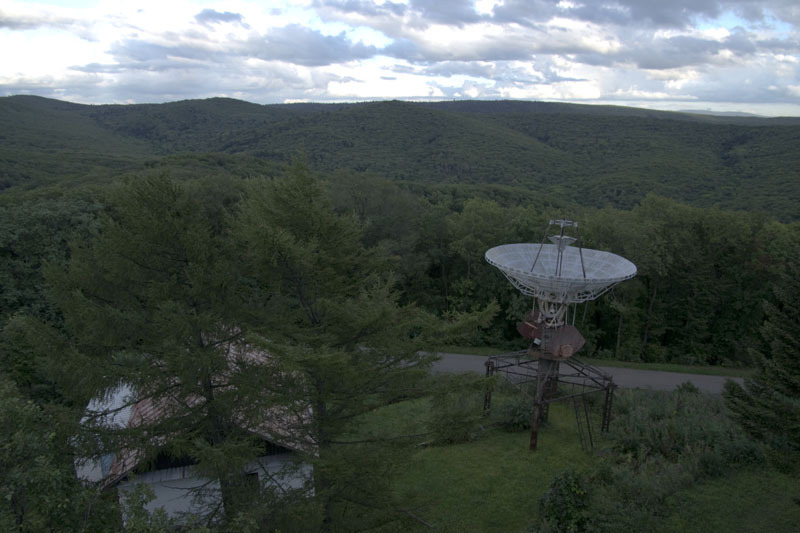
The observatory is located near Ussuriysk (20 km), but at the same time it has a good astroclimate: the illumination from the nearby city is minimal. Taiga is located very close to the observatory. They say, sometimes even tigers wander.
The observatory was created in 1953 for regular observations of the Sun and solar activity. Then the USSR had a unique advantage, which no one else had in the world - it could follow the sun from the moment of its rise in the Far East and the sunset in Kaliningrad. Now, when the same tasks can be performed by several satellites (SOHO and STEREO), the observatory is more of a base, uniting researchers of the Sun, possessing specialized tools, allowing to receive data in real time.
Recently, the observatory has been upgraded and is now solving the tasks of observing asteroids, satellites and gamma-ray bursts.
There are a dozen instruments in the observatory , of which 2/3 are in active operation.
I myself am not familiar with the physics of the sun, and even more so with the technical tricks on the process of observation and information gathering. So I apologize in advance for inaccuracies and simplifications.
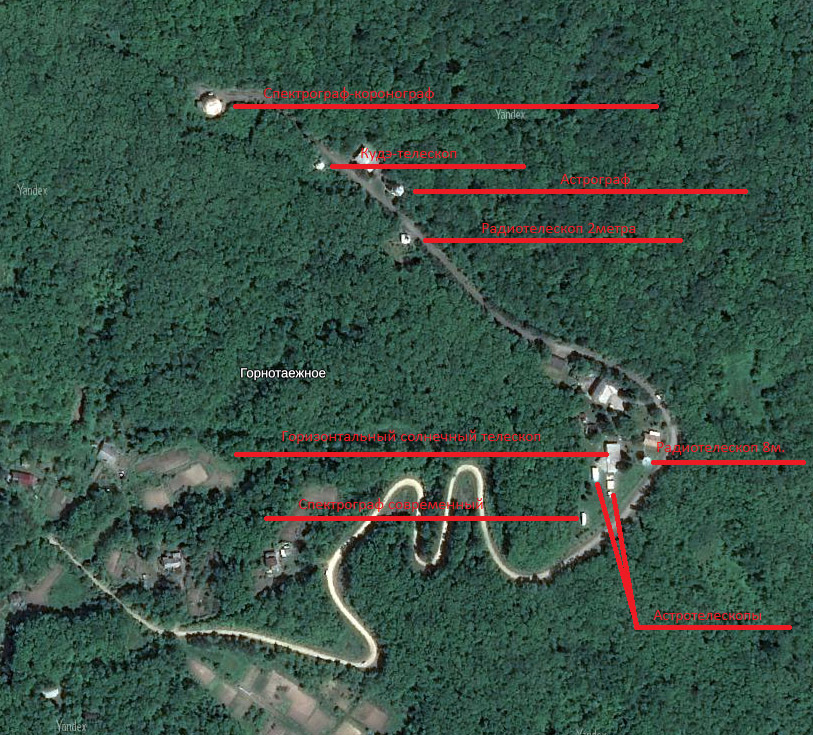
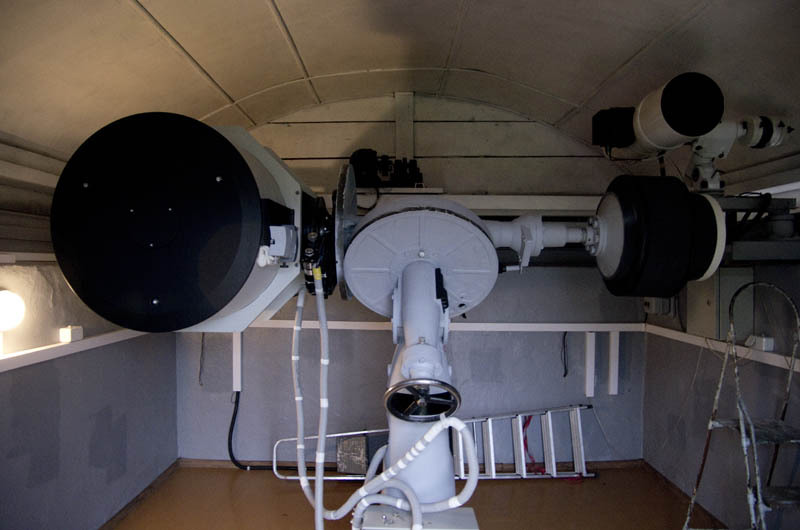
One of the oldest instruments of the observatory is the horizontal solar telescope . His appearance surprises a person not familiar with astronomy. But it should be borne in mind that the Sun moves along a predictable trajectory that is almost identical from day to day. A narrow tool should not have the full breadth of capabilities required from a conventional telescope.
The tool is designed to observe sunspots and analyze their spectrum.
Now it is not used. Both the optics and the analyzing part are already morally and physically obsolete. But this does not make them less interesting!
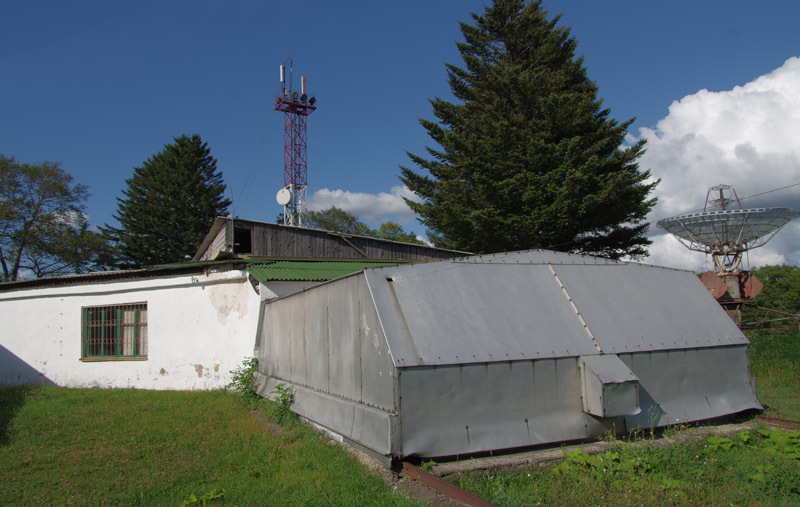

The building looks like anything, even a garage, but not a telescope. The metal part drives off on rails. Under the metal part there are two adjustable mirrors that allow you to follow the movement of the sun. The bottom mirror reflects the sun to the top, and the top one to the hole in the wall.
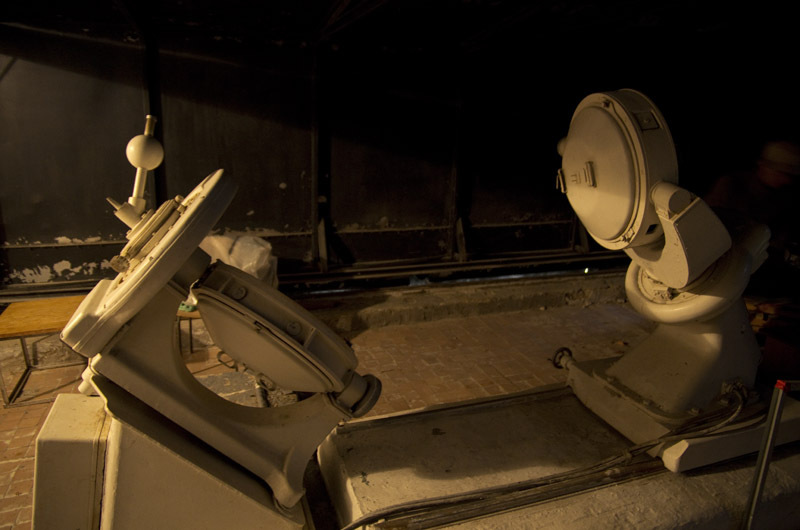


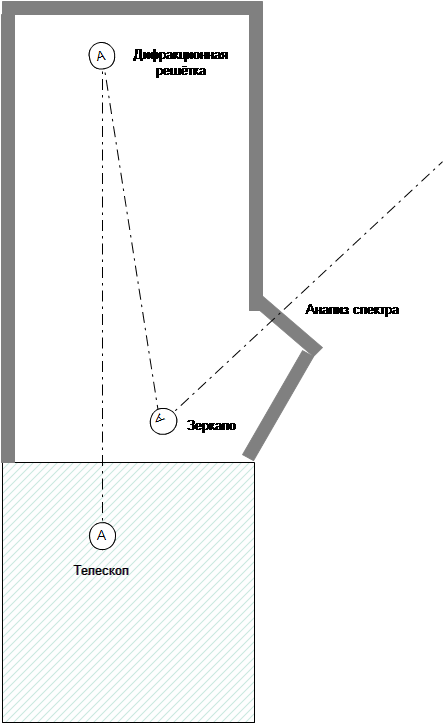
Schematically, the beam goes along the following trajectory:


The image of the sun is redirected to the inside of the building, passing a distance of about 15 meters to the reflecting diffraction grating. after which it returns back to where the reflector stands, which redirects the beam to the adjacent hall, where it is analyzed more accurately.
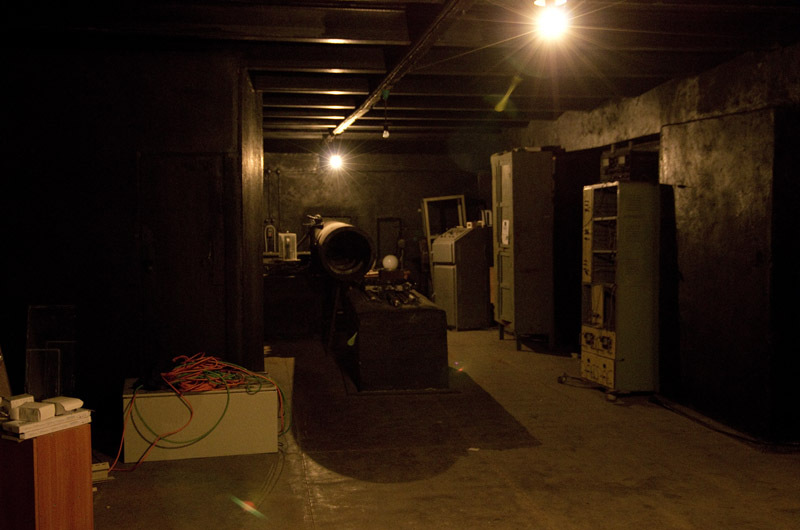

Hole from which comes the image of the sun. Slightly to the left, in the cap you can see the reflector, which redirects the return beam to the hall where the analysis takes place.
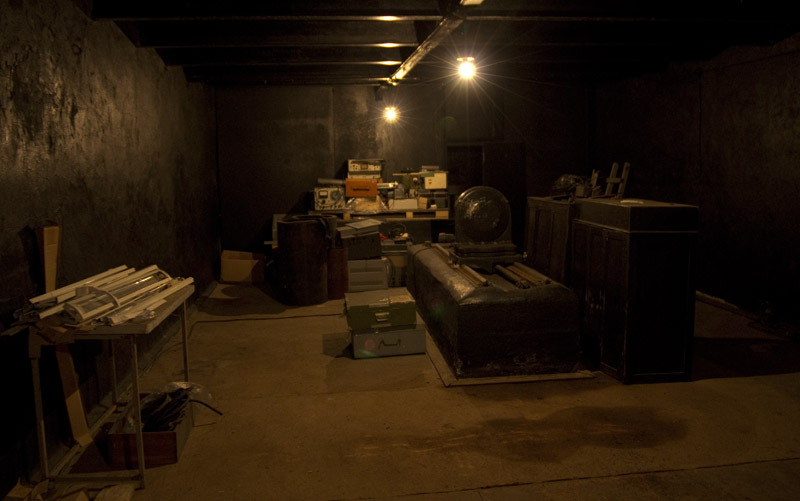

And so is the diffraction grating. By the way, did you notice the color of the walls? Black he specifically - to minimize interference. When the experiment was going on, the whole world was turned off.
The halls of the hall cost a lot of great lamp equipment, whose era is already a little over.
It has a slightly different scheme, more similar to the usual telescope. His main task is to analyze the spectrum of the sun's corona. The equipment is slightly newer, but recently it is also not used.

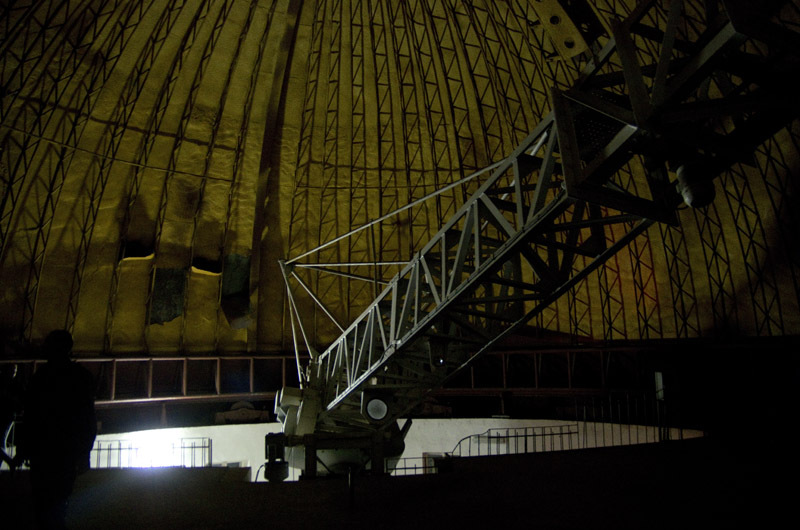
The telescope tube has a truss structure, which allows you to compensate for the deformation of the optical axis and constantly accompany the sun disk, preventing displacements. A lens with a diameter of 50 cm collects the luminous flux from the sun and directs it to the spectral hall using an additional system of mirrors. Further, an artificial moon is placed in the path of the light flux, and this can simulate a solar eclipse when it is convenient and necessary, without waiting for such a rare phenomenon. The solar corona and the chromosphere are the external atmosphere of the Sun, which we do not see because of the greater brightness of the disk itself, and having only eclipsed it, it opens in all its glory for admiring and studying.


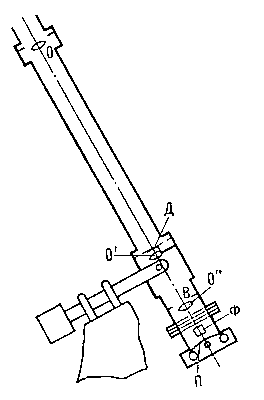
A slightly more detailed description of the action: The extra-dark coronagraph consists of the main lens O, which builds an image of the Sun on a metal disk D, which does not transmit the light of the photosphere and thus creates an artificial eclipse. To eliminate ambient light appearing due to diffraction from the edge of the main lens, a lens O 'is placed behind the metal screen, which builds an image of the main lens on the diaphragm B with an opening small enough not to miss the image of the edges of the main lens. The next lens O "builds the final image of the crown or prominences on the slit of the spectrograph or on the film P.
A reader who has moved through the first two spectrographs asks in surprise “why not modernize these spectrographs, not to fill them with modern equipment, not to bring them to work?”. But ... It is too expensive, difficult and unjustified. Do you know what a modern solar spectrograph looks like? Here he is:
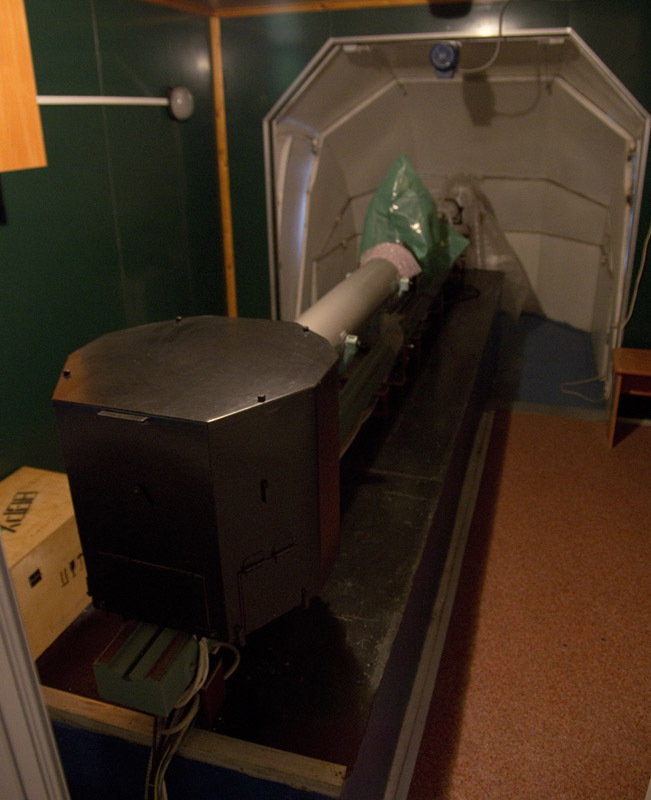


The white part of the booth reclines. A small telescope sends an image to the black box where the spectrum analyzers are located.
At the same time, it is serviced by one operator, gets the result instantly, allows you to quickly analyze it and transfer to the consumer. By the way, the spectrograph belongs to RosHydroMetu and is currently being commissioned.
I could not find out the exact characteristics of all spectrographs, but as it seems to me, according to some experience, they are not much worse for modern ones. On the other hand, a modern one allows to obtain a magnetogram of the entire solar disk in 10 minutes and to make a very operational forecast of space weather.
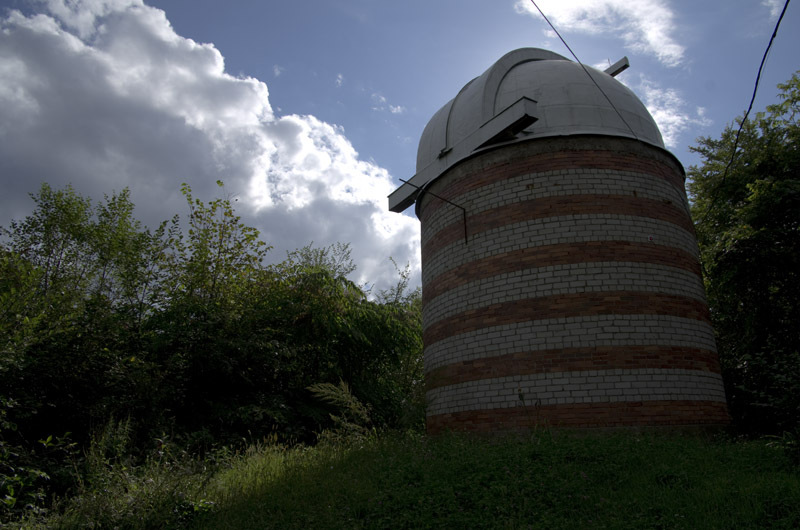

But spectral telescopes are not the only telescopes that are installed in the observatory. The observatory has a number of telescopes for ordinary optical observation of the sun. First of all, this is this telescope:
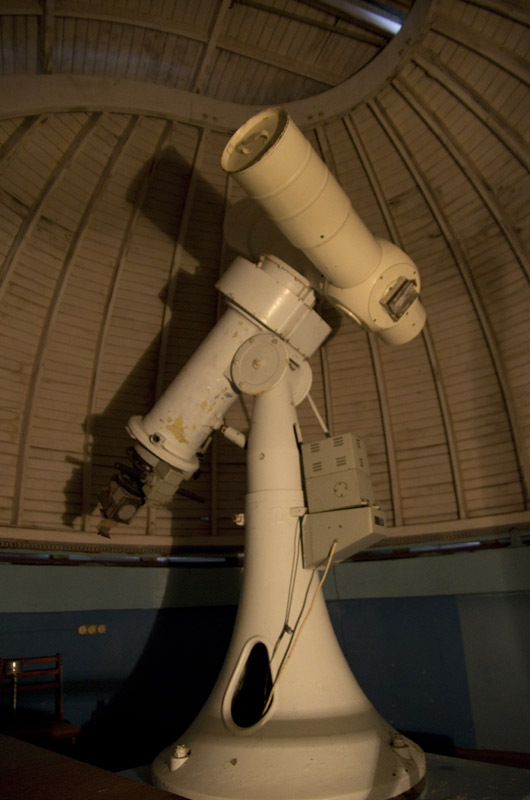

The telescope is an example of the fact that a fairly old telescope can be used with quite modern matrices. By the way, pay attention to an interesting scheme: the image enters the part of the pipe that is located on the top, and is fixed on the bottom left.

In addition, the observatory has a telescope that performs constant observations of the sun through a hydrogen filter. This method allows you to observe the chromosphere of the sun, eliminating the influence of the photosphere. With this filter, you can look protuberances and the dynamics of the upper layers of the sun. And get such awesome pictures .

Let's return to the old technique. Who lives in this house?

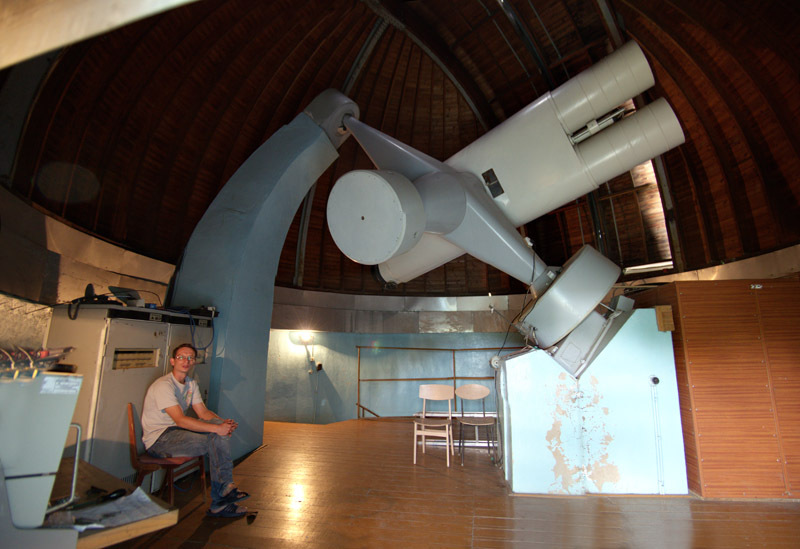
An astrograph lives in this house. Unfortunately, a little late with his era. Bought before the restructuring, he was very modern at the time. But soon perestroika began, there was no money, there were no photographic plates for it. And when the money appeared he was morally outdated: the era of numbers had begun.

The first question that broke out was “why should he have two pipes?”. The solution turned out to be unusual for me, a man of the digital camera era. It turns out that when exposing photographic plates, there is a chance to get a “knocked out pixel”, a point with local overexposure or under-exposure. In order to level such artifacts, systems are used that allow exposing two identical photographic plates to identical areas of the sky simultaneously. But where the photographic plates were placed:

The second miracle of this telescope is located in these drums and in this setup:
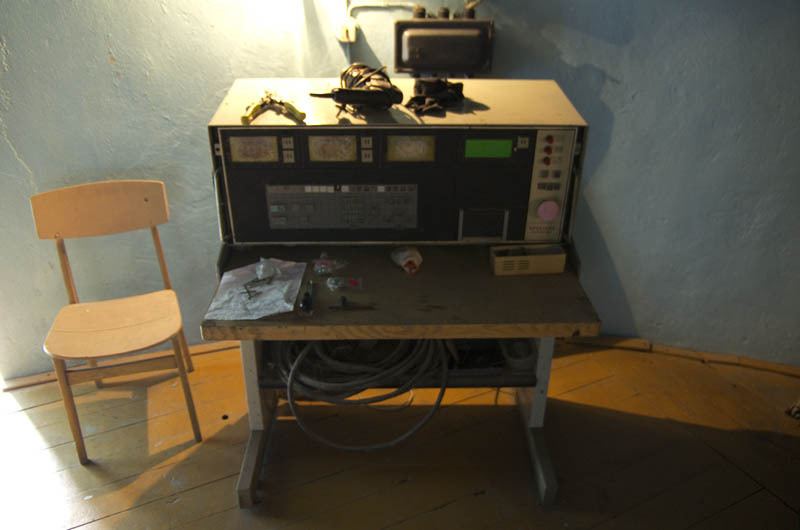


This is an automatic guidance system, quite modern at the time. The drums are encoders on the gray code , and the box is the control computer.
Gray code is a number system in which two adjacent values differ only in one digit. Originally intended to protect against the false triggering of electromechanical switches. The telescope uses the optical code of Gray in the drums. The sensor reads the current position and allows you to automatically point to the starry sky with an accuracy of an angular second.

Unfortunately, the telescope is morally obsolete. No one needs now neither a photographic plate, nor a narrow field of a telescope, nor a large resolvable field in the plane of focus. Today's telescopes look like this:
All three of these telescopes are much smaller, simpler, more compact and more efficient than the monstrous astrograph from the pictures above. Today they are used to observe gamma-ray bursts, asteroids, comets and high-altitude satellites. Two large give not only a larger field, but also the best photosensitivity.

50 centimeter telescope.

60-cm telescope + 20 cm telescope.
On these telescopes, the tasks of the ISON project, as well as warnings about asteroid and comet hazard, are very effectively solved. Discovered a series of asteroids .
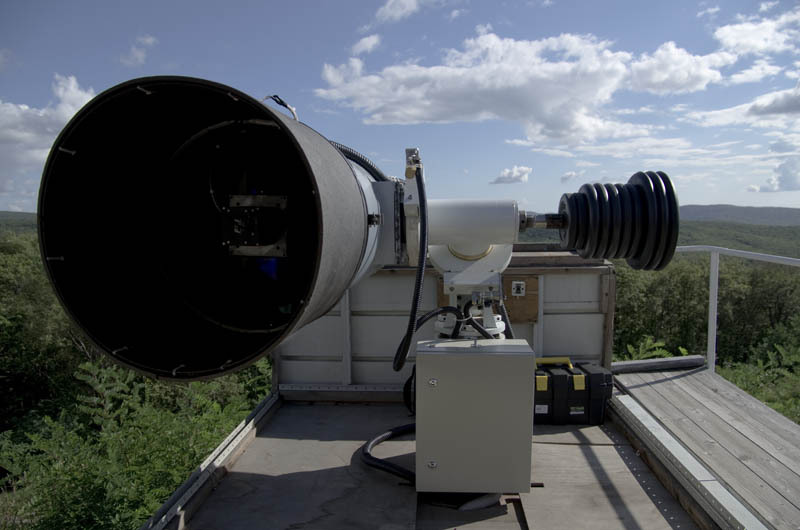
There are two radio telescopes in the observatory. One, sunny, working:
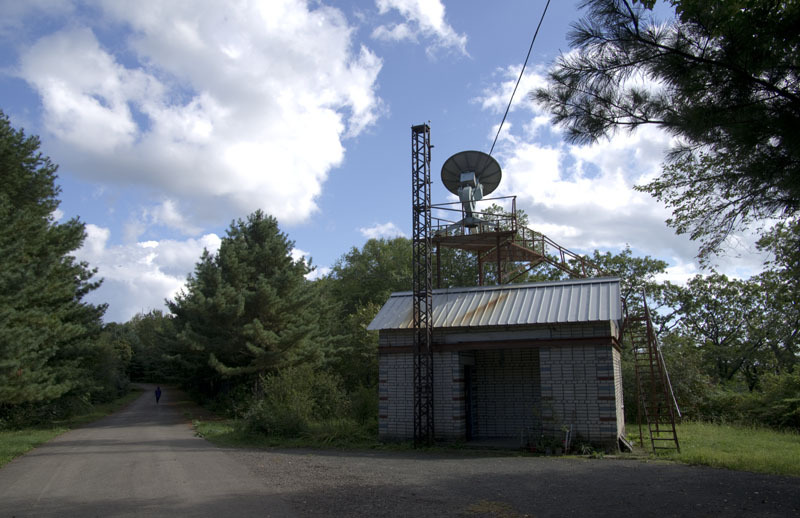

And the second, a gift from the military, which has not yet been launched, but they really want it.

It must be said that in the component of life, the observatory significantly loses both Google and Yandex :) It is difficult to conduct stable water, Internet and electricity to a remote mountain. Everything is there, but unstable. Do not defeat the observatory and in the competition more delicious cookies.
But here it is beautiful. Around the taiga, cedar pines entwined with grapes and actinidia (younger brother of kiwi). At night you can hear boars and other animals. Sometimes, they say, tigers pass nearby. The end of the working day marks the dawn and fog covering the hills. The kilometer from the observatory is the largest arboretum in the Far East.
Why do we need coolers with Coca-Cola and tables with cookies, when, in between work, you can go for a walk in the taiga ?!

Z.Y. Thank you so much Alexey for the tour!

Periodically, I go on business trips to various observatories. I wanted to eliminate the misunderstanding described above and write a short story on this topic. The article is devoted to the Ussuri Astrophysical Observatory ( UAFO of the Far East Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences ), which is the largest observatory in the Far East. Residents of Primorsky Territory, she is most likely familiar with, but I think that for the rest it will be curious to read.

')
The observatory is located near Ussuriysk (20 km), but at the same time it has a good astroclimate: the illumination from the nearby city is minimal. Taiga is located very close to the observatory. They say, sometimes even tigers wander.
The observatory was created in 1953 for regular observations of the Sun and solar activity. Then the USSR had a unique advantage, which no one else had in the world - it could follow the sun from the moment of its rise in the Far East and the sunset in Kaliningrad. Now, when the same tasks can be performed by several satellites (SOHO and STEREO), the observatory is more of a base, uniting researchers of the Sun, possessing specialized tools, allowing to receive data in real time.
Recently, the observatory has been upgraded and is now solving the tasks of observing asteroids, satellites and gamma-ray bursts.
There are a dozen instruments in the observatory , of which 2/3 are in active operation.
I myself am not familiar with the physics of the sun, and even more so with the technical tricks on the process of observation and information gathering. So I apologize in advance for inaccuracies and simplifications.

Horizontal solar telescope
One of the oldest instruments of the observatory is the horizontal solar telescope . His appearance surprises a person not familiar with astronomy. But it should be borne in mind that the Sun moves along a predictable trajectory that is almost identical from day to day. A narrow tool should not have the full breadth of capabilities required from a conventional telescope.
The tool is designed to observe sunspots and analyze their spectrum.
Now it is not used. Both the optics and the analyzing part are already morally and physically obsolete. But this does not make them less interesting!

The building looks like anything, even a garage, but not a telescope. The metal part drives off on rails. Under the metal part there are two adjustable mirrors that allow you to follow the movement of the sun. The bottom mirror reflects the sun to the top, and the top one to the hole in the wall.


Schematically, the beam goes along the following trajectory:


The image of the sun is redirected to the inside of the building, passing a distance of about 15 meters to the reflecting diffraction grating. after which it returns back to where the reflector stands, which redirects the beam to the adjacent hall, where it is analyzed more accurately.

Hole from which comes the image of the sun. Slightly to the left, in the cap you can see the reflector, which redirects the return beam to the hall where the analysis takes place.

And so is the diffraction grating. By the way, did you notice the color of the walls? Black he specifically - to minimize interference. When the experiment was going on, the whole world was turned off.

The halls of the hall cost a lot of great lamp equipment, whose era is already a little over.
Spectrograph-coronagraph (Off-Korongraf).
It has a slightly different scheme, more similar to the usual telescope. His main task is to analyze the spectrum of the sun's corona. The equipment is slightly newer, but recently it is also not used.

The telescope tube has a truss structure, which allows you to compensate for the deformation of the optical axis and constantly accompany the sun disk, preventing displacements. A lens with a diameter of 50 cm collects the luminous flux from the sun and directs it to the spectral hall using an additional system of mirrors. Further, an artificial moon is placed in the path of the light flux, and this can simulate a solar eclipse when it is convenient and necessary, without waiting for such a rare phenomenon. The solar corona and the chromosphere are the external atmosphere of the Sun, which we do not see because of the greater brightness of the disk itself, and having only eclipsed it, it opens in all its glory for admiring and studying.



A slightly more detailed description of the action: The extra-dark coronagraph consists of the main lens O, which builds an image of the Sun on a metal disk D, which does not transmit the light of the photosphere and thus creates an artificial eclipse. To eliminate ambient light appearing due to diffraction from the edge of the main lens, a lens O 'is placed behind the metal screen, which builds an image of the main lens on the diaphragm B with an opening small enough not to miss the image of the edges of the main lens. The next lens O "builds the final image of the crown or prominences on the slit of the spectrograph or on the film P.
Another spectrograph
A reader who has moved through the first two spectrographs asks in surprise “why not modernize these spectrographs, not to fill them with modern equipment, not to bring them to work?”. But ... It is too expensive, difficult and unjustified. Do you know what a modern solar spectrograph looks like? Here he is:


The white part of the booth reclines. A small telescope sends an image to the black box where the spectrum analyzers are located.
At the same time, it is serviced by one operator, gets the result instantly, allows you to quickly analyze it and transfer to the consumer. By the way, the spectrograph belongs to RosHydroMetu and is currently being commissioned.
I could not find out the exact characteristics of all spectrographs, but as it seems to me, according to some experience, they are not much worse for modern ones. On the other hand, a modern one allows to obtain a magnetogram of the entire solar disk in 10 minutes and to make a very operational forecast of space weather.
Solar telescope (coude refractor)

But spectral telescopes are not the only telescopes that are installed in the observatory. The observatory has a number of telescopes for ordinary optical observation of the sun. First of all, this is this telescope:

The telescope is an example of the fact that a fairly old telescope can be used with quite modern matrices. By the way, pay attention to an interesting scheme: the image enters the part of the pipe that is located on the top, and is fixed on the bottom left.
Solar telescope (with H-filter)

In addition, the observatory has a telescope that performs constant observations of the sun through a hydrogen filter. This method allows you to observe the chromosphere of the sun, eliminating the influence of the photosphere. With this filter, you can look protuberances and the dynamics of the upper layers of the sun. And get such awesome pictures .

Astrograph
Let's return to the old technique. Who lives in this house?

An astrograph lives in this house. Unfortunately, a little late with his era. Bought before the restructuring, he was very modern at the time. But soon perestroika began, there was no money, there were no photographic plates for it. And when the money appeared he was morally outdated: the era of numbers had begun.

The first question that broke out was “why should he have two pipes?”. The solution turned out to be unusual for me, a man of the digital camera era. It turns out that when exposing photographic plates, there is a chance to get a “knocked out pixel”, a point with local overexposure or under-exposure. In order to level such artifacts, systems are used that allow exposing two identical photographic plates to identical areas of the sky simultaneously. But where the photographic plates were placed:

The second miracle of this telescope is located in these drums and in this setup:


This is an automatic guidance system, quite modern at the time. The drums are encoders on the gray code , and the box is the control computer.
Gray code is a number system in which two adjacent values differ only in one digit. Originally intended to protect against the false triggering of electromechanical switches. The telescope uses the optical code of Gray in the drums. The sensor reads the current position and allows you to automatically point to the starry sky with an accuracy of an angular second.

Unfortunately, the telescope is morally obsolete. No one needs now neither a photographic plate, nor a narrow field of a telescope, nor a large resolvable field in the plane of focus. Today's telescopes look like this:
Modern telescopes
All three of these telescopes are much smaller, simpler, more compact and more efficient than the monstrous astrograph from the pictures above. Today they are used to observe gamma-ray bursts, asteroids, comets and high-altitude satellites. Two large give not only a larger field, but also the best photosensitivity.

50 centimeter telescope.

60-cm telescope + 20 cm telescope.
On these telescopes, the tasks of the ISON project, as well as warnings about asteroid and comet hazard, are very effectively solved. Discovered a series of asteroids .
Radio telescopes
There are two radio telescopes in the observatory. One, sunny, working:

And the second, a gift from the military, which has not yet been launched, but they really want it.

Other little things in life
It must be said that in the component of life, the observatory significantly loses both Google and Yandex :) It is difficult to conduct stable water, Internet and electricity to a remote mountain. Everything is there, but unstable. Do not defeat the observatory and in the competition more delicious cookies.
But here it is beautiful. Around the taiga, cedar pines entwined with grapes and actinidia (younger brother of kiwi). At night you can hear boars and other animals. Sometimes, they say, tigers pass nearby. The end of the working day marks the dawn and fog covering the hills. The kilometer from the observatory is the largest arboretum in the Far East.
Why do we need coolers with Coca-Cola and tables with cookies, when, in between work, you can go for a walk in the taiga ?!

Z.Y. Thank you so much Alexey for the tour!
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/236773/
All Articles