RDP vs RemoteFX
In the group of enterprises "X" use terminal servers.
The new season began and in one of the offices cpu loading started to reach 100 percent, which is bad, especially after users started complaining about the speed of work.
The cause of the problem was not clear, the number of employees did not change, the software did not change ... All offices in the same conditions.
I assembled a test stand and started looking for a solution ...
For a long time I went through different settings of the server and client sites, this is a separate topic.
In a creative search compared the RDP and RemoteFX protocols, I decided to publish the results.
The processor load was compared in three applications: IE11, Adobe PDF Reader 11, 1c8.
I made 8-10 measurements, at the time of measurements only the experimental user and the administrator user worked on the server.
I used two laptops with Windows XP and Windows 7 SP1 as client sites, and the HP t510 thin client with the installed HP Smart Zero 4.4 OS.
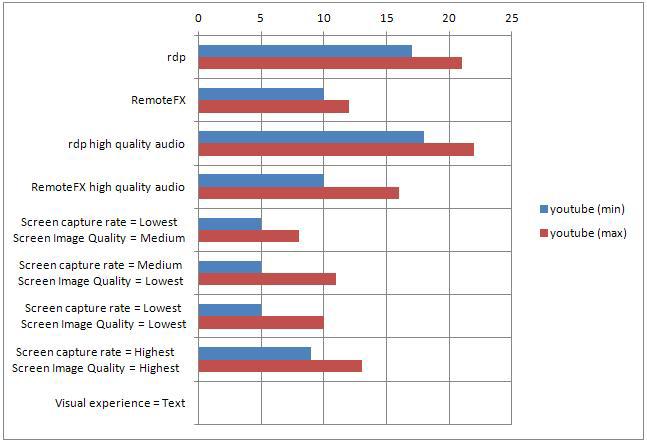
IE11, a test video was launched that was on youtube.
RDP - CPU load 21-23%
RemoteFX - CPU load 11-18%
')
After replacing laptops with HP thin client.
RDP - CPU load 17-21%
RemoteFX - CPU load 10-12%
In laboratory conditions, the difference was 5-10% of the CPU time in favor of RemoteFX.
I’ll add that RDP doesn’t come close to RemoteFX when the video is played smoothly, with RemoteFX turned on, at first glance, there’s no difference in comparison with a regular PC.
I decided to carry out all further measurements on the HP thin client.
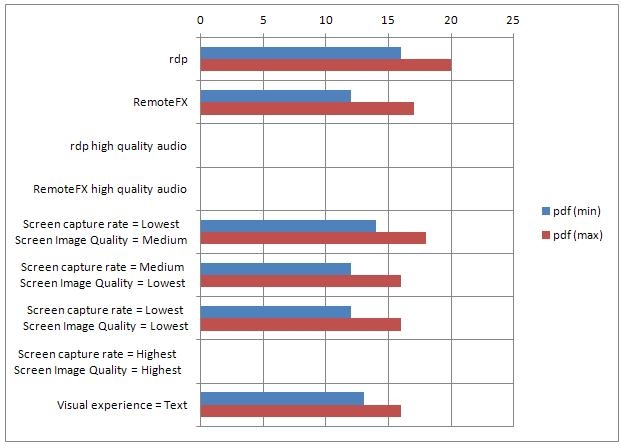
Go to the PDF document and scrolling.
RDP - CPU load 16-20%
RemoteFX - CPU load 12-17%
The difference in favor of RemoteFX was 3-4%.
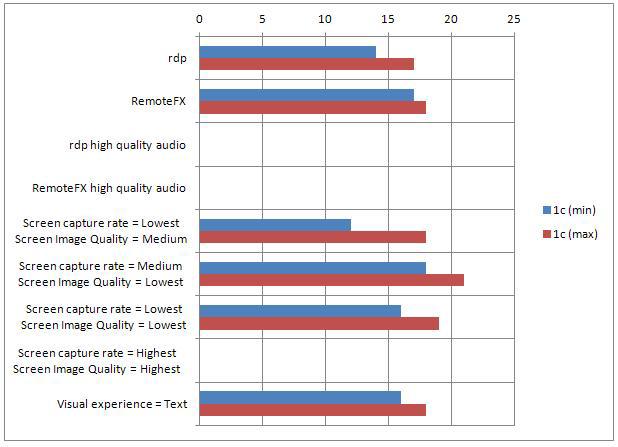
It is the turn of 1c8, again we will be engaged in scrolling the list of documents.
RDP - CPU load 14-17%
RemoteFX - CPU load 17-18%
The difference in favor of RDP was 1-3%.
Honestly, I did not like the result of 1c8. I decided to check everything and make additional measurements.
Re-measured the results, like everything is OK, fit into an error in the measurements, about 1-2%.
The results of 1c can be attributed to the measurement error, in the end it turns out that 1c doesn’t care how the user connects via RDP or RemoteFX.
I think that video is best suited to assess the quality of the codec, I decided to conduct the rest of the tests, since working with 1c and documents should take up most of the users' working time.
I used to try to look at PCoIP, I did not like the result, maybe I need to look again, but it’s not cool, and RemoteFX will cost less than PCoIP, and I like the concept of VDI less than terminal servers.
In the case of enterprise “X”, 18-24 users work on a single Xeon5620 processor with a load of 40-80%, and a domain controller, and some smaller vm, work in parallel with the terminal server.
As I see it, the implementation of RemoteFX will reduce the server processor load by 20-30%, or add about 5-7 users.
First we will compare how the increase in the quality of the transmitted sound affects.
In standard settings, the sound quality is selected dynamically, when a sufficient number of users work on the server - this is audible.
We look at the YouTube video (RDP), the processor load is 18-22%, with standard settings the result is 17-21%.
We are watching a video on YouTube (RemoteFX), the processor load is 10-16%, with standard settings the result is 10-12%.
I conclude that the difference is minimal and, if desired, you can safely set the high quality.
However, please pay attention to the network traffic, I do not measure it, all users and servers are at a distance of the switch; if you work on a narrow channel, you will have to consider network traffic.
YouTube clip:
CPU load 5-8%
PDF and scrolling:
CPU load 14-18%
1c8 and scrolling:
The load on the processor is 12-18%.
In the case of media, we get a win, but it is immediately noticeable that the video does not play so smoothly and jerks are visible, similar to those in RDP.
If you think about it, there is nothing wrong with that, it all depends on the tasks that users must perform.
Although in the case of office work, the meaning is lost, working with documents consumes twice as much CPU time.
Video on youtube
CPU load 5-11%
PDF and scrolling
CPU load 12-16%
1c8 and scrolling
The load on the processor is 18-21%.
We get the result where there is no gain for office tasks, and for the media it will be possible to see the result on network traffic.
Video on youtube
CPU load 5-10%
PDF and scrolling
CPU load 12-16%
1c8 and scrolling
The load on the processor is 16-19%.
No comments.
YouTube clip:
CPU load 9-13%.
For results for 1c and PDF, as it turned out, I did not have enough patience.
I expected a different result from the Highest (best quality) settings, and the result can be attributed to a measurement error.
The default setting of the Rich Multimedia codec.
PDF and scrolling:
CPU load 13-16%
1c8 and scrolling:
CPU load 16-19%

On all terminal servers, I turned on RemoteFX, it won't be any worse.
It became interesting how the result will change if you add a hardware video card.
The new season began and in one of the offices cpu loading started to reach 100 percent, which is bad, especially after users started complaining about the speed of work.
The cause of the problem was not clear, the number of employees did not change, the software did not change ... All offices in the same conditions.
I assembled a test stand and started looking for a solution ...
For a long time I went through different settings of the server and client sites, this is a separate topic.
In a creative search compared the RDP and RemoteFX protocols, I decided to publish the results.
Server:
HP ML350 G6, 1 * Xeon5620, 42gb RAM.
DirectX hardware video card is missing.
Storage:
HP MSA P2000 G3 SAS, array of R5 is assembled from 4 SAS disks.
BY:
ESXi 5.1 is installed on the server.
Terminal servers are VM, 4 vcpu (8000 MHz) and 20gb RAM are allocated, Windows Server 2008R2 SP1 is used as the guest OS.
The processor load was compared in three applications: IE11, Adobe PDF Reader 11, 1c8.
I made 8-10 measurements, at the time of measurements only the experimental user and the administrator user worked on the server.
I used two laptops with Windows XP and Windows 7 SP1 as client sites, and the HP t510 thin client with the installed HP Smart Zero 4.4 OS.
results
IE11, a test video was launched that was on youtube.
RDP - CPU load 21-23%
RemoteFX - CPU load 11-18%
')
After replacing laptops with HP thin client.
RDP - CPU load 17-21%
RemoteFX - CPU load 10-12%
In laboratory conditions, the difference was 5-10% of the CPU time in favor of RemoteFX.
I’ll add that RDP doesn’t come close to RemoteFX when the video is played smoothly, with RemoteFX turned on, at first glance, there’s no difference in comparison with a regular PC.
I decided to carry out all further measurements on the HP thin client.
Go to the PDF document and scrolling.
RDP - CPU load 16-20%
RemoteFX - CPU load 12-17%
The difference in favor of RemoteFX was 3-4%.
It is the turn of 1c8, again we will be engaged in scrolling the list of documents.
RDP - CPU load 14-17%
RemoteFX - CPU load 17-18%
The difference in favor of RDP was 1-3%.
Honestly, I did not like the result of 1c8. I decided to check everything and make additional measurements.
Re-measured the results, like everything is OK, fit into an error in the measurements, about 1-2%.
The results of 1c can be attributed to the measurement error, in the end it turns out that 1c doesn’t care how the user connects via RDP or RemoteFX.
If we sum up the preliminary results
I think that video is best suited to assess the quality of the codec, I decided to conduct the rest of the tests, since working with 1c and documents should take up most of the users' working time.
I used to try to look at PCoIP, I did not like the result, maybe I need to look again, but it’s not cool, and RemoteFX will cost less than PCoIP, and I like the concept of VDI less than terminal servers.
In the case of enterprise “X”, 18-24 users work on a single Xeon5620 processor with a load of 40-80%, and a domain controller, and some smaller vm, work in parallel with the terminal server.
As I see it, the implementation of RemoteFX will reduce the server processor load by 20-30%, or add about 5-7 users.
Interest in RemoteFX began to grow, and decided to continue measurements
First we will compare how the increase in the quality of the transmitted sound affects.
In standard settings, the sound quality is selected dynamically, when a sufficient number of users work on the server - this is audible.
We look at the YouTube video (RDP), the processor load is 18-22%, with standard settings the result is 17-21%.
We are watching a video on YouTube (RemoteFX), the processor load is 10-16%, with standard settings the result is 10-12%.
I conclude that the difference is minimal and, if desired, you can safely set the high quality.
However, please pay attention to the network traffic, I do not measure it, all users and servers are at a distance of the switch; if you work on a narrow channel, you will have to consider network traffic.
Further, how RemoteFX will work when changing settings, frame rate, picture quality, codec optimization
Screen capture rate = Lowest
Screen Image Quality = Medium (default)
YouTube clip:
CPU load 5-8%
PDF and scrolling:
CPU load 14-18%
1c8 and scrolling:
The load on the processor is 12-18%.
In the case of media, we get a win, but it is immediately noticeable that the video does not play so smoothly and jerks are visible, similar to those in RDP.
If you think about it, there is nothing wrong with that, it all depends on the tasks that users must perform.
Although in the case of office work, the meaning is lost, working with documents consumes twice as much CPU time.
Screen capture rate = Medium (default)
Screen Image Quality = Lowest
Video on youtube
CPU load 5-11%
PDF and scrolling
CPU load 12-16%
1c8 and scrolling
The load on the processor is 18-21%.
We get the result where there is no gain for office tasks, and for the media it will be possible to see the result on network traffic.
Screen capture rate = Lowest
Screen Image Quality = Lowest
Video on youtube
CPU load 5-10%
PDF and scrolling
CPU load 12-16%
1c8 and scrolling
The load on the processor is 16-19%.
No comments.
Screen capture rate = Highest (best quality)
Screen Image Quality = Highest (best quality)
YouTube clip:
CPU load 9-13%.
For results for 1c and PDF, as it turned out, I did not have enough patience.
I expected a different result from the Highest (best quality) settings, and the result can be attributed to a measurement error.
Next in line is the codec optimization, Text vs Rich Multimedia
The default setting of the Rich Multimedia codec.
PDF and scrolling:
CPU load 13-16%
1c8 and scrolling:
CPU load 16-19%
Summary table
Total
On all terminal servers, I turned on RemoteFX, it won't be any worse.
It became interesting how the result will change if you add a hardware video card.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/234235/
All Articles