Black lists of the RuNet in action. How to reduce the risk for your site
 The bill №89417-6, adopted on July 10, 2012 by the State Duma of the Russian Federation, marked a new era in the development of Runet. The authorities finally have a mechanism that allows blocking objectionable sites with the hands of Internet access providers. Unfortunately, like most laws adopted in the last 4 years, the implementation of the implementation was thought out a little less than completely, which led to the blocking of completely innocent sites. Today, after a little over two years, according to rublacklist.net, access to 58,940 domain names that do not contain any illegal content is illegally blocked. The question of why this happens, and how to avoid such a situation, we consider in this article.
The bill №89417-6, adopted on July 10, 2012 by the State Duma of the Russian Federation, marked a new era in the development of Runet. The authorities finally have a mechanism that allows blocking objectionable sites with the hands of Internet access providers. Unfortunately, like most laws adopted in the last 4 years, the implementation of the implementation was thought out a little less than completely, which led to the blocking of completely innocent sites. Today, after a little over two years, according to rublacklist.net, access to 58,940 domain names that do not contain any illegal content is illegally blocked. The question of why this happens, and how to avoid such a situation, we consider in this article.Your site is blocked - who is to blame?
Initial information about which site should be blocked, providers get from several sources at once:
- Unified Register of Prohibited Information eais.rkn.gov.ru
- Register of copyright infringers nap.rkn.gov.ru
- Register of information prohibited by law 398- 398-fz.rkn.gov.ru
- Federal list of extremist materials minjust.ru/ru/extremist-materials
- Court decisions regarding individual providers (once rospravosudie.com/court-proletarskij-rajonnyj-sud-g-rostova-na-donu-rostovskaya-oblast-s/act-101271803 two rospravosudie.com/court-novgorodskij-rajonnyj-sud- novgorodskaya-oblast-s / act-107327437 )
- Prosecution regulations for individual providers forum.nag.ru/forum/index.php?showtopic=95062
Your site does not contain prohibited information and, nevertheless, turned out to be blocked? Welcome to the company of illegally blocked sites. Most likely the reason for this is blocking by IP-address. The fact is that this is the only way for the provider to implement the lock without high costs. But hosting theory involves placing multiple sites on a single IP address. And not only hosting - well-known “cloud” services have already suffered from such locks (they give out an IP address for temporary use) and CDN networks (use geo-distribution to one or several IP addresses).

')
Is your website's IP address missing in the registry? It does not matter - the prosecutor's office may well find the prohibited material on one of the sites that are with you on a shared IP, and write down the prescription to a separate transit provider.
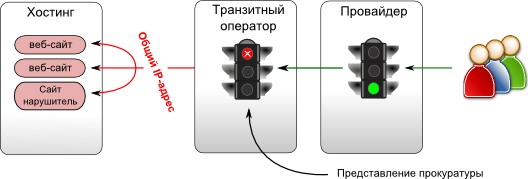
Moreover, even the formal absence of hosting sites that do not contain prohibited content does not guarantee against blocking. The fact is that, in accordance with the recommendations of the RKN, eais.rkn.gov.ru/docs/Recomendation.pdf, in order to combat the frequent change of IP addresses of offenders' sites, providers themselves must resolve the domain name from the registry to an IP address. And this allows the owner of such a domain name to block any server. The RKN looks at this possibility through its fingers ( www.dropbox.com/s/l4lk0uafordlvsi/%D0%98%D1%81%D1%85%D0BB%D0%B4%D1%8EB % D0% B9% 2030.08.2013.pdf ).
As you can see, there are many sources. And if the three registries and the list of materials of the Ministry of Justice can still independently determine whether your site got into them, then it is not technically possible to track the decisions of the courts and the local orders of the prosecutor's office.
How it happens at the provider level
In order to understand how to effectively maneuver in the turbulent flow of prohibitions, it is necessary to understand what the provider and the regulator are doing, and why. Provider anyway. The provider always follows the path of least resistance. The regulator, on the contrary, wants to create the appearance of a hectic activity, and, perhaps, not from evil, is playing solitaire games from standards. Dependence on irresponsible, uncontrollable, constantly changing standards is the main risk in terms of accessibility of sites.
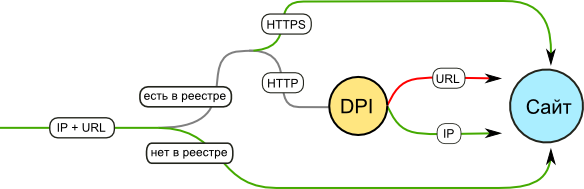
In general, the established blocking method at the provider level is as follows:
- The provider generates lists of IP addresses, access to which should be restricted.
- If the registries do not contain the IP address of the site, the provider receives it, allowing the domain name. Individual providers follow the recommendations of the RKN and always resolve the domain name to an IP address, even if it is explicitly listed in the registry.
- The traffic to this IP is sent to a separate server in the provider's network.
- If the provider has DPI in its network, the traffic is analyzed, only requests for forbidden URLs are blocked. If there is no DPI, all traffic is blocked.
- For the HTTPS protocol - if the URL with HTTPS is explicitly specified in the registry, try to block only traffic to this IP on port 443 (since it is impossible to separate the URL from the encrypted traffic). If the registry contains a URL with HTTP - HTTPS traffic is not blocked.
How to protect against all this?
Moderate your sites and follow them
While the practice of “bases” is not very common, however, it is quite possible to block your website for material of illegal content left on the forum or published using the vulnerability of your website.
In the case of material of extremist content, your hosting provider will not even receive prior notice - the site will be entered in the registry and you will receive a notification after the fact.
If possible, place sites at Russian hosting providers.
This statement only looks "advertising". Russian hosters are aware of the realities of the legislation and make certain efforts to protect their customers - they respond promptly to requests from the RKN, have access to the registries and monitor their changes. After the very first blockings, we smashed user sites by hundreds of different IP addresses, trying to minimize the number of clients that could “fly in” under the blocking along with one of the illegal sites. Most likely, none of the foreign hosting providers will not make such efforts.
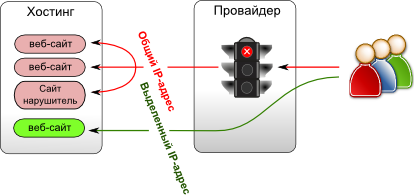
Dedicated IPv4 address.
Try to bring your website to a separate IP address. This will protect you from blocking "for the company." Many hosting providers offer a dedicated IP address for a fee. Unfortunately, the shortage of IPv4 addresses has affected its size, but the loss from blocking can be much greater.
Separate IPv6 address
Hostings that have deployed an IPv6 stack on their network today give out a dedicated IPv6 address for each site. Unfortunately, their number is still small, but due to the shortage of IPv4 addresses, the number of such providers is increasing. And this means that the chance to get under blocking an innocent site is reduced. Separately, it is worth mentioning that most of the inspection bodies have not yet mastered access to sites by IPv6 addresses.

Using encryption and SSL certificates
Unlike the normal HTTP, HTTPS protocol, it is carried out via a secure SSL channel and cannot be viewed, and therefore, a specific URL can be extracted from the encrypted traffic. Because of the lack of understanding of the work of the protocols, the complicated question of the secure channel is still being tried to bypass. In most cases, if there is no direct indication, providers try to ignore HTTPS protocol blocking. This will continue until the use of HTTPS becomes widespread.
It seems something went wrong ...
Special attention deserves the story of blocking the blog Alexei Navalny.
Surely many of you have heard that Alexey Navalny’s blog on the LiveJournal platform is in the registry (despite the fact that so far the agency has not decided on the reasons for blocking). Aleksey's supporters did not put up with the blocking and created a whole system of dynamic domain names and IP addresses to organize free access to the blog. For weeks, the employees of the ILV did nothing but block these domains. And at one moment the blocked domains began to point to the IP addresses of the registry itself. The providers, which followed the recommendations of the RKN on the independent resolution of domain names, automatically blocked access to the registry. And then they could not turn to him. After that, the RKN recommended still not to resolve domain names on their own, but to block the IP addresses specified in the registry.
How was the struggle between supporters of Alexey and Roskomnadzor, you can read Ruslan Leviev’s blog: ruslanleviev.livejournal.com/34401.html
By the way, the result of this struggle was the emergence of its own registry - the registry of subnets of state bodies: github.com/AntiZapret/AntiZapret
We had another similar case. The owner of a domain name in the list of extremist materials of the Justice Ministry decided to transfer its website to us and changed the A-record of its domain to the IP address of our server. As a result, access to this server during the day was cut off by one of the transit operators. And only one, so that access to the server was lost only for a certain number of users. We could only identify the problem by escalating the application through a chain of operators.
What are the prospects?
Unfortunately, the prospects are rather bleak. Having obtained the desired mechanism of censorship, the leaders of lawmaking do not want to stop and put forward new ideas of prohibitions almost daily. In the near future, we will be banned from accessing sites that store personal data outside the territory of the Russian Federation, banning access to major blogs (over 3000 visitors) that are not registered with the Ministry of Communications and Communications, and the ability to block not individual IP addresses, but immediately subnets ( habrahabr.ru / post / 229431 ). The situation is aggravated by the fact that Internet access providers have their own problems, and they will not fight with censorship - they will take the easiest path - the path of non-resistance to “innovation”. We will write in the next article about how hosting providers will deal with this scourge.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/231615/
All Articles