How and why to protect Internet access in the enterprise - part 1
Today we will cynically talk about the good old task - protecting employees and their workstations when accessing Internet resources. In this article, we will look at common myths, modern threats, and typical requirements of organizations for the protection of web traffic.
If you remember only one fact from the whole article, then you should know that on adult websites there is a tenfold less chance of picking up a malicious program than on ordinary Internet resources.

Today, most Russian companies already provide employees with access to the Internet from work computers. In this regard, state organizations, law enforcement agencies and companies that process a large amount of personal data usually lag behind. But even in such organizations there are always separate network segments or workstations connected to the Internet.
')
Not giving employees access to the Internet has long been considered a bad form. About a third of the candidates simply will not come to you to work, having learned that you do not have access to the Internet or that the Internet is severely limited, as they consider it to be as necessary as clean water and ventilation. This is especially true for today's generation of 20-25 year olds, who from school are used to that any information can be quickly found in a search engine, and updates in social networks should be checked in no less than half an hour.
Enough introductions, go to the myths.
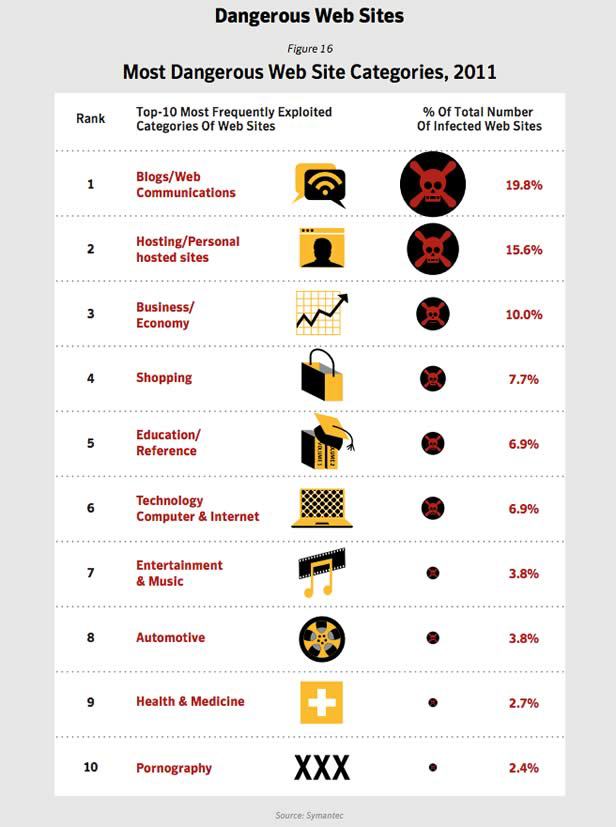
As if not so. According to Symantec's Internet Security Threat Report, only 2.4% of adult sites spread malware, which is several times less than blogs, news portals and online stores.
Suffice it to recall the hacking examples of the New York Times, NBC, Russian Railways, Vedomosti portal, Georgian government sites, TechCrunch Europe and others, from which pages spread viruses and phishing attacks.
On the other hand, as a responsible employee, you can make a strong-willed decision not to visit sites with slippery topics, but can your colleagues be able to resist? Do they tempt with the temptation to click on the link in the "Nigerian letter" or click on the banner with the message about winning 100,500 thousand dollars?
There is a chance, but it is very small. Before being published, the creators of malware check that their creations are not detected by current versions of antiviruses. After the detection of the first versions of the malware by antivirus analysts, it takes from 6 to 24 hours for its research and signature development. The speed of propagation of signatures and patches for vulnerable software depends solely on your infrastructure, but as a rule, it goes on days and weeks. All this time, users are vulnerable.
Please note that the anti-virus vendors themselves offer dedicated specialized solutions for the protection of web traffic. Host solutions are possible and have basic functionality for filtering web sites by categories and risks, but they cannot afford to store the malicious database locally and dynamically update it without sacrificing performance. The host approach to solving the problem is also not applicable for companies in which not all workstations are included in the domain and / or are not managed centrally.
Modern malware is indeed more humane compared to its counterparts from the 90s - most often they try to minimally influence the victim, systematically receiving commands from the master, sending spam, attacking websites and stealing your passwords from bank clients. In addition to them, there are more aggressive types - cryptococci, encrypting the entire contents of the hard disk and demanding ransom, “porno-banners”, showing lewdness and requiring sending very expensive SMS, network worms that disable the network, not to mention targeted attacks.
Imagine that all this can happen to any computer or server in your organization. Agree, it is unpleasant to lose or allow leakage of all data from the computer of a lawyer, chief accountant or director. Even the failure of individual components of your infrastructure at the time of treating or refilling a workstation can be detrimental to your business.
I hope that the colors have thickened enough and it's time to go to the description of typical tasks and requirements for an ideal solution to protect web traffic. While I deliberately do not use the names of products or devices as the task can be solved in various ways.
The solution should provide the ability to block access to known malicious websites or their individual sections. At the same time, information about the level of risk is pulled from the cloud analytics center and is dynamically updated every few minutes. If the site has recently appeared, the solution should be able to independently analyze the content and decide on the degree of danger.
The administrator can only determine the acceptable level of risk and, for example, block all sites with a reputation of less than six on a scale from -10 to +10.
By category and reputation should be divided not only sites, but also their subsections and individual elements of the pages. For example, on the most popular website with weather forecasts, there are links to dubious resources offering to lose weight, if you stop eating just one product, or find out how Pugacheva gave birth to twins. In this case, employees should leave access to the main site and block the display of doubtful parts of the web page.
It should be possible to block access to certain categories of sites, for example, to file hosting services, online casinos and hacker forums. Category information should also be pulled from the cloud analytics center. The more categories the device understands and the more accurately they are defined, the better.
You should also pay attention to the speed of response of the analytics center to your requests for changing categories of websites. Sites that your employees use for business purposes may be incorrectly assigned to a blocked category. It is possible and the opposite situation, when the site is not assigned to a blocked category. These difficulties can be solved manually by adding individual resources to the white list or black list, but this approach is inapplicable if you have to do it every day, and even on several devices.
Special attention is given to the topic of Cyrillic support and the correct classification of Russian-language sites. As a rule, Western vendors do not pay them enough attention. Fortunately, Ironport's divisions, which developed solutions for protecting web traffic and acquired Cisco, are located in / in Ukraine, so there are no problems mentioned above.
It should be possible to scan potentially dangerous files with antivirus engines before giving them to end users. If there are several such engines, this somewhat increases the chances of detecting malware. Also, you implement the principle of echeloned defense and reduce the chances of infection if antivirus is disabled, not updated or simply missing on the final host.
Riding excellence in analyzing potential malware is the use of the Advanced Malware Protection engine (AMP) or its counterparts to protect against targeted attacks. In such attacks, malicious files are designed specifically for several organizations, are not common on the Internet, and, as a rule, have not yet fallen into the traps of anti-virus vendors. VRT Sourcefire and Cisco SIO analytics centers check if this particular file was previously encountered during an attack in another organization, and if not, it tests it in a sandbox, analyzing the actions performed. Earlier we wrote about AMP on Habré
It will also be useful to be able to filter files by extensions and headers, banning executable files, encrypted archives, audio and video files, .torrent files, magnet links, etc.
Traditional access control lists on firewalls almost do not save. For ten years or more, one could be relatively certain that TCP ports 80 and 443 were used only for accessing the Internet through a web browser, and TCP 25 for sending e-mail. Today, over HTTP and port 80, Skype, Dropbox, TeamViewer, torrent clients and thousands of other applications work. English-speaking colleagues call this situation “HTTP is new TCP”. Many of these applications can be used to transfer sensitive files, video streams, and even remote control of workstations. Naturally, these are not the types of activity that we are glad to see in the corporate network.
Here we can be helped by a solution that restricts the use of applications and their individual components. For example, allow Skype and Facebook, but prohibit file transfer and video calls. It will also be useful to ban as a class all p2p file sharing applications, anonymizers and utilities for remote control.
Application definition is based on application signatures, which are automatically updated from the manufacturer’s website. The great advantage is the ability to create "application signatures" independently or load them in clear form from the community website. Many manufacturers are developing "application signatures" only on their own and often do not have time to follow the updates of Russian applications, or simply they are not engaged. Of course, they are unlikely to undertake the development of signatures for industry-specific applications or applications of their own design.
As practice shows, many computers can be members of botnets for several years. The arms race has reached such a level that malware not only tightens updates of its versions from the control center, but also patches holes in the OS and applications through which they hit the computer in order to prevent competitors from appearing. Not all antivirus solutions are able to establish the fact of infection, given that such malware works at a very low level, hiding its processes, connections and existence in general from the antivirus.
Here, solutions that analyze traffic from workstations to botnet control centers on the Internet come to our aid. The main detection method is monitoring connections to servers in “blacklists” - already known to control centers of botnets, “dark” areas of the Internet, etc.
If this is a targeted attack or an unknown botnet so far, then detection is performed using behavioral analysis. For example, the session “phone home” between the zombie and the master can be distinguished by the encryption of the content, the small amount of data transferred and the long connection time.
Virtually all modern security tools have the ability to assign policies not only based on IP addresses, but also based on user accounts in AD and their membership in AD groups. Consider an example of the simplest policy:
As practice shows, in many companies there are organizational difficulties that do not allow immediately begin to restrict access to Internet resources. A formalized policy is either absent or in practice there are too many exceptions for it in the form of privileged employees and their friends. In such cases, you should act on the 80/20 principle and start with minimal restrictions, for example, block sites with the highest level of risk, certain categories and sites that are not specifically related to work duties. It also helps to install the solution in the monitoring mode and provide reports on the use of Internet resources to company management.
Even today, many email services and social networks encrypt their traffic by default, which does not allow analyzing the transmitted information. According to research data, SSL encrypted traffic in 2013 accounted for 25-35% of the total amount of transmitted data, and its share will only increase.
Fortunately, SSL traffic from a user to Internet resources can be decrypted. To do this, we replace the server certificate with the device certificate and terminate the connection on it. After the user's requests have been analyzed and recognized as legitimate - the device establishes a new encrypted connection to the web server on its behalf.
Traffic decoding can be carried out both on the same node that performs the analysis and filtering, and on a dedicated specialized device. When all tasks on a single node are performed, performance goes down by itself, sometimes by times.
In order for the project to protect web traffic to take place, it is extremely useful to show management and benefits that are not directly related to security:
It is also extremely important to understand whether the solution in question is appropriate for your organization; here you should pay attention to:
It is naturally impossible to tell about everything in one article and here are some topics that were not covered:
The next article is planned to tell with what Cisco solutions and how you can solve the above tasks.
I hope that the article was useful for you, I will be glad to hear additions and suggestions about new topics in the comments.
Stay tuned;)
Link to the continuation of the article
If you remember only one fact from the whole article, then you should know that on adult websites there is a tenfold less chance of picking up a malicious program than on ordinary Internet resources.

Today, most Russian companies already provide employees with access to the Internet from work computers. In this regard, state organizations, law enforcement agencies and companies that process a large amount of personal data usually lag behind. But even in such organizations there are always separate network segments or workstations connected to the Internet.
')
Not giving employees access to the Internet has long been considered a bad form. About a third of the candidates simply will not come to you to work, having learned that you do not have access to the Internet or that the Internet is severely limited, as they consider it to be as necessary as clean water and ventilation. This is especially true for today's generation of 20-25 year olds, who from school are used to that any information can be quickly found in a search engine, and updates in social networks should be checked in no less than half an hour.
Enough introductions, go to the myths.
Myth # 1 If you don’t go through adult sites, then everything will be fine
As if not so. According to Symantec's Internet Security Threat Report, only 2.4% of adult sites spread malware, which is several times less than blogs, news portals and online stores.

Suffice it to recall the hacking examples of the New York Times, NBC, Russian Railways, Vedomosti portal, Georgian government sites, TechCrunch Europe and others, from which pages spread viruses and phishing attacks.
On the other hand, as a responsible employee, you can make a strong-willed decision not to visit sites with slippery topics, but can your colleagues be able to resist? Do they tempt with the temptation to click on the link in the "Nigerian letter" or click on the banner with the message about winning 100,500 thousand dollars?
Myth # 2 Even if I get on the infected site, the antivirus will save me
There is a chance, but it is very small. Before being published, the creators of malware check that their creations are not detected by current versions of antiviruses. After the detection of the first versions of the malware by antivirus analysts, it takes from 6 to 24 hours for its research and signature development. The speed of propagation of signatures and patches for vulnerable software depends solely on your infrastructure, but as a rule, it goes on days and weeks. All this time, users are vulnerable.
Myth # 3 The host security solution can filter site categories by risk, and that’s enough.
Please note that the anti-virus vendors themselves offer dedicated specialized solutions for the protection of web traffic. Host solutions are possible and have basic functionality for filtering web sites by categories and risks, but they cannot afford to store the malicious database locally and dynamically update it without sacrificing performance. The host approach to solving the problem is also not applicable for companies in which not all workstations are included in the domain and / or are not managed centrally.
Myth # 4 If you pick up a virus, then nothing terrible will happen.
Modern malware is indeed more humane compared to its counterparts from the 90s - most often they try to minimally influence the victim, systematically receiving commands from the master, sending spam, attacking websites and stealing your passwords from bank clients. In addition to them, there are more aggressive types - cryptococci, encrypting the entire contents of the hard disk and demanding ransom, “porno-banners”, showing lewdness and requiring sending very expensive SMS, network worms that disable the network, not to mention targeted attacks.
Imagine that all this can happen to any computer or server in your organization. Agree, it is unpleasant to lose or allow leakage of all data from the computer of a lawyer, chief accountant or director. Even the failure of individual components of your infrastructure at the time of treating or refilling a workstation can be detrimental to your business.
I hope that the colors have thickened enough and it's time to go to the description of typical tasks and requirements for an ideal solution to protect web traffic. While I deliberately do not use the names of products or devices as the task can be solved in various ways.
Requirements for technical solutions
Filtering Internet resources by reputation
The solution should provide the ability to block access to known malicious websites or their individual sections. At the same time, information about the level of risk is pulled from the cloud analytics center and is dynamically updated every few minutes. If the site has recently appeared, the solution should be able to independently analyze the content and decide on the degree of danger.
The administrator can only determine the acceptable level of risk and, for example, block all sites with a reputation of less than six on a scale from -10 to +10.
By category and reputation should be divided not only sites, but also their subsections and individual elements of the pages. For example, on the most popular website with weather forecasts, there are links to dubious resources offering to lose weight, if you stop eating just one product, or find out how Pugacheva gave birth to twins. In this case, employees should leave access to the main site and block the display of doubtful parts of the web page.
Filtering Internet resources by category (URL filtering)
It should be possible to block access to certain categories of sites, for example, to file hosting services, online casinos and hacker forums. Category information should also be pulled from the cloud analytics center. The more categories the device understands and the more accurately they are defined, the better.
You should also pay attention to the speed of response of the analytics center to your requests for changing categories of websites. Sites that your employees use for business purposes may be incorrectly assigned to a blocked category. It is possible and the opposite situation, when the site is not assigned to a blocked category. These difficulties can be solved manually by adding individual resources to the white list or black list, but this approach is inapplicable if you have to do it every day, and even on several devices.
Special attention is given to the topic of Cyrillic support and the correct classification of Russian-language sites. As a rule, Western vendors do not pay them enough attention. Fortunately, Ironport's divisions, which developed solutions for protecting web traffic and acquired Cisco, are located in / in Ukraine, so there are no problems mentioned above.
Scan downloads
It should be possible to scan potentially dangerous files with antivirus engines before giving them to end users. If there are several such engines, this somewhat increases the chances of detecting malware. Also, you implement the principle of echeloned defense and reduce the chances of infection if antivirus is disabled, not updated or simply missing on the final host.
Riding excellence in analyzing potential malware is the use of the Advanced Malware Protection engine (AMP) or its counterparts to protect against targeted attacks. In such attacks, malicious files are designed specifically for several organizations, are not common on the Internet, and, as a rule, have not yet fallen into the traps of anti-virus vendors. VRT Sourcefire and Cisco SIO analytics centers check if this particular file was previously encountered during an attack in another organization, and if not, it tests it in a sandbox, analyzing the actions performed. Earlier we wrote about AMP on Habré
It will also be useful to be able to filter files by extensions and headers, banning executable files, encrypted archives, audio and video files, .torrent files, magnet links, etc.
Understanding applications and their components
Traditional access control lists on firewalls almost do not save. For ten years or more, one could be relatively certain that TCP ports 80 and 443 were used only for accessing the Internet through a web browser, and TCP 25 for sending e-mail. Today, over HTTP and port 80, Skype, Dropbox, TeamViewer, torrent clients and thousands of other applications work. English-speaking colleagues call this situation “HTTP is new TCP”. Many of these applications can be used to transfer sensitive files, video streams, and even remote control of workstations. Naturally, these are not the types of activity that we are glad to see in the corporate network.
Here we can be helped by a solution that restricts the use of applications and their individual components. For example, allow Skype and Facebook, but prohibit file transfer and video calls. It will also be useful to ban as a class all p2p file sharing applications, anonymizers and utilities for remote control.
Application definition is based on application signatures, which are automatically updated from the manufacturer’s website. The great advantage is the ability to create "application signatures" independently or load them in clear form from the community website. Many manufacturers are developing "application signatures" only on their own and often do not have time to follow the updates of Russian applications, or simply they are not engaged. Of course, they are unlikely to undertake the development of signatures for industry-specific applications or applications of their own design.
Detection of infected hosts based on connections
As practice shows, many computers can be members of botnets for several years. The arms race has reached such a level that malware not only tightens updates of its versions from the control center, but also patches holes in the OS and applications through which they hit the computer in order to prevent competitors from appearing. Not all antivirus solutions are able to establish the fact of infection, given that such malware works at a very low level, hiding its processes, connections and existence in general from the antivirus.
Here, solutions that analyze traffic from workstations to botnet control centers on the Internet come to our aid. The main detection method is monitoring connections to servers in “blacklists” - already known to control centers of botnets, “dark” areas of the Internet, etc.
If this is a targeted attack or an unknown botnet so far, then detection is performed using behavioral analysis. For example, the session “phone home” between the zombie and the master can be distinguished by the encryption of the content, the small amount of data transferred and the long connection time.
Flexible access control policies
Virtually all modern security tools have the ability to assign policies not only based on IP addresses, but also based on user accounts in AD and their membership in AD groups. Consider an example of the simplest policy:
- Internet access is obtained by all domain users from computers included in the domain and corporate tablets.
- With the exception of users included in the domain groups "Call Center Operators" and "Without Internet Access"
- With a speed of no more than 512 Kbps per employee
- All employees are denied access to the Online Casino, Job Search, and Adult Sites categories.
- With the exception of the group "Guide"
- All employees are denied access to sites with a reputation of less than six
- The use of social networks and video streaming services is prohibited for all employees, except for the group “marketing and public relations department”
- Video viewing is limited in speed to 128Kbps
- It is forbidden to use all gaming applications, except for the game created by the company.
- It is forbidden to use torrent-clients, instant messengers and utilities for remote administration
- Scan downloaded files from two of the three anti-virus engines, with the exception of .AVI files
- Prevent downloading of .mp3 files and encrypted archives
As practice shows, in many companies there are organizational difficulties that do not allow immediately begin to restrict access to Internet resources. A formalized policy is either absent or in practice there are too many exceptions for it in the form of privileged employees and their friends. In such cases, you should act on the 80/20 principle and start with minimal restrictions, for example, block sites with the highest level of risk, certain categories and sites that are not specifically related to work duties. It also helps to install the solution in the monitoring mode and provide reports on the use of Internet resources to company management.
Interception and verification of SSL traffic
Even today, many email services and social networks encrypt their traffic by default, which does not allow analyzing the transmitted information. According to research data, SSL encrypted traffic in 2013 accounted for 25-35% of the total amount of transmitted data, and its share will only increase.
Fortunately, SSL traffic from a user to Internet resources can be decrypted. To do this, we replace the server certificate with the device certificate and terminate the connection on it. After the user's requests have been analyzed and recognized as legitimate - the device establishes a new encrypted connection to the web server on its behalf.
Traffic decoding can be carried out both on the same node that performs the analysis and filtering, and on a dedicated specialized device. When all tasks on a single node are performed, performance goes down by itself, sometimes by times.
Additional requirements
In order for the project to protect web traffic to take place, it is extremely useful to show management and benefits that are not directly related to security:
- Quoting traffic by time and user, for example, no more than 1 GB of traffic per month or no more than two hours on the Internet per day
- Limit the bandwidth for individual sites, their parts or applications, for example, a limit of 100 Kbps when downloading streaming video or audio
- Web traffic caching - allows both to speed up the download speed of popular sites and to save traffic when downloading the same files multiple times
- Channel shaping - equal bandwidth allocation and prioritization among all users
It is also extremely important to understand whether the solution in question is appropriate for your organization; here you should pay attention to:
- Single sign on - transparent user authorization without additional login / password input, including for smartphones and tablets
- Supporting multiple ways to integrate into your existing infrastructure
- The ability to install solutions in the form of specialized hardware devices and virtual machines
- Centralized management of both the devices themselves and their policies
- Centralized reporting for all devices with the ability to create custom reports
- The ability to delegate the administration of specific regions, functions, or policies to other administrators
- Solution performance
- Presence of regular functionality for connection logging and leak prevention (DLP) or the ability to integrate with external DLP solutions
- Ability to integrate with SIEM systems
- Licensing model - by users or devices or by IP addresses or bandwidth
- Cost of renewal of annual subscriptions
It is naturally impossible to tell about everything in one article and here are some topics that were not covered:
- Verify domain membership, antivirus, and OS updates before providing Internet access
- How to protect employees who are more likely to travel than to the office
- What difficulties arise when protecting web traffic of workstations with removable employees, virtual workstations (VDI), tablets and smartphones
- When it is cheaper and more convenient to use the cloud service to filter web traffic
- Is it worth trying to implement similar functionality based on Squid and other open source solutions?
The next article is planned to tell with what Cisco solutions and how you can solve the above tasks.
I hope that the article was useful for you, I will be glad to hear additions and suggestions about new topics in the comments.
Stay tuned;)
Link to the continuation of the article
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/230515/
All Articles