Assessment of renewable energy potential. Regional experience
 This post is devoted to the presentation of results on the assessment of the potential of renewable energy sources (RES) on the example of the Tomsk region. The results of the monitoring based on actual data on the results of the work of expert groups were taken as the basis for the assessment of potential. The information is summarized into a geographic information system accessible for free review.
This post is devoted to the presentation of results on the assessment of the potential of renewable energy sources (RES) on the example of the Tomsk region. The results of the monitoring based on actual data on the results of the work of expert groups were taken as the basis for the assessment of potential. The information is summarized into a geographic information system accessible for free review.The purpose of creating a geographic information system
Tomsk region has a number of areas not provided with centralized power supply. Diesel, coal or fuel oil stations are used to provide the population with energy. This circumstance leads to a significant increase in tariffs, which in some localities of the Tomsk region reaches 90-110 rubles per kilowatt. At the same time, the social tariff does not exceed 4 rubles per kilowatt, and the difference in the tariff is covered by the regional budget. However, for part of the Tomsk region there are prospects for the introduction of alternative energy sources. The purpose of creating a geographic information system (GIS) is to compile information on the production and consumption of heat and electricity in the Tomsk region, as well as the potential possibility of replacing solid and liquid hydrocarbon fuels (oil, fuel oil, diesel, coal) with regional organic fuel (biogas, waste logging, timber processing, peat) and renewable energy sources (wind, solar stations, geothermal sources).
')
Study area
GIS is built on the example of the Tomsk region. The Tomsk Region is located in the south-eastern part of the West Siberian Plain, and is part of the Siberian Federal District of the Russian Federation. The region borders: in the north - with the Khanty-Mansiysk autonomous region, in the east - with the Krasnoyarsk Territory, in the south - with the Kemerovo and Novosibirsk regions, in the west - with the Omsk region.
The territory of the region - 316.9 thousand square meters. km (1.5% more than the area of Poland)
The population of the Tomsk region as of January 1, 2013 was 1064.2 thousand people (0.74% of the population of the Russian Federation), the average population density is 3.4 people per square meter. km
Features of nature and climate The region consists of 4 urban districts (Tomsk, Strezhevoy, Kedrovy, Seversk ZATO), 16 municipal districts, including 6 urban (Tomsk, Strezhevoy, Kedrovy, Seversk, ZATO, Asino, Kolpashevo) and 116 rural settlements, 1 urban-type settlement (p Belyy Yar) and 579 rural settlements. The regional center is the city of Tomsk. The relief of the area is extremely flat. The highest point of the Tomsk region: +274 m from sea level. Lowest point: +34 m from sea level. Most of the territory is covered by forests, swamps, rivers and lakes. The largest rivers are the Ob, Tom, Chulym, Ket, Vasyugan, Tym. The whole river system belongs to the Ob basin, which crosses the region from the south-east to the north-west at a distance of about 1000 kilometers, dividing the region into two almost equal parts. The number of lakes in the Tomsk region reaches 95 thousand, especially a lot of them in the floodplains of rivers. The largest lake on the territory of the Tomsk Region is the Peace Lake located on a flat interfluve of the Chuzik and Chizhapka rivers. In total, there are 573 rivers in the region. The type of climate is continental. Winter is harsh and long. The average January temperature is from -19 ° C to -21 ° C. Summer is warm, short. The average July temperature is from +17 ° to +19 ° . Rainfall 450-700 mm per year. The vegetation period is about 125 days. Located in the middle and southern taiga and partially mixed forests. The soils are mainly sod-podzolic and peat-marsh, in the southeast gray forest. Forests (main species: birch, pine, cedar, aspen, fir, spruce) occupy about 54% of the territory. The region is rich in minerals such as oil, gas, iron ore, peat, lignite.
The region consists of 4 urban districts (Tomsk, Strezhevoy, Kedrovy, Seversk ZATO), 16 municipal districts, including 6 urban (Tomsk, Strezhevoy, Kedrovy, Seversk, ZATO, Asino, Kolpashevo) and 116 rural settlements, 1 urban-type settlement (p Belyy Yar) and 579 rural settlements. The regional center is the city of Tomsk. The relief of the area is extremely flat. The highest point of the Tomsk region: +274 m from sea level. Lowest point: +34 m from sea level. Most of the territory is covered by forests, swamps, rivers and lakes. The largest rivers are the Ob, Tom, Chulym, Ket, Vasyugan, Tym. The whole river system belongs to the Ob basin, which crosses the region from the south-east to the north-west at a distance of about 1000 kilometers, dividing the region into two almost equal parts. The number of lakes in the Tomsk region reaches 95 thousand, especially a lot of them in the floodplains of rivers. The largest lake on the territory of the Tomsk Region is the Peace Lake located on a flat interfluve of the Chuzik and Chizhapka rivers. In total, there are 573 rivers in the region. The type of climate is continental. Winter is harsh and long. The average January temperature is from -19 ° C to -21 ° C. Summer is warm, short. The average July temperature is from +17 ° to +19 ° . Rainfall 450-700 mm per year. The vegetation period is about 125 days. Located in the middle and southern taiga and partially mixed forests. The soils are mainly sod-podzolic and peat-marsh, in the southeast gray forest. Forests (main species: birch, pine, cedar, aspen, fir, spruce) occupy about 54% of the territory. The region is rich in minerals such as oil, gas, iron ore, peat, lignite.
One of the most valuable natural resources of the Tomsk region is the forest. Wood reserves are 2.8 billion cubic meters. m
The main highways are located in the southern part of the region with access to the neighboring regions. The total length of paved roads is 6,278 km.
 The region consists of 4 urban districts (Tomsk, Strezhevoy, Kedrovy, Seversk ZATO), 16 municipal districts, including 6 urban (Tomsk, Strezhevoy, Kedrovy, Seversk, ZATO, Asino, Kolpashevo) and 116 rural settlements, 1 urban-type settlement (p Belyy Yar) and 579 rural settlements. The regional center is the city of Tomsk. The relief of the area is extremely flat. The highest point of the Tomsk region: +274 m from sea level. Lowest point: +34 m from sea level. Most of the territory is covered by forests, swamps, rivers and lakes. The largest rivers are the Ob, Tom, Chulym, Ket, Vasyugan, Tym. The whole river system belongs to the Ob basin, which crosses the region from the south-east to the north-west at a distance of about 1000 kilometers, dividing the region into two almost equal parts. The number of lakes in the Tomsk region reaches 95 thousand, especially a lot of them in the floodplains of rivers. The largest lake on the territory of the Tomsk Region is the Peace Lake located on a flat interfluve of the Chuzik and Chizhapka rivers. In total, there are 573 rivers in the region. The type of climate is continental. Winter is harsh and long. The average January temperature is from -19 ° C to -21 ° C. Summer is warm, short. The average July temperature is from +17 ° to +19 ° . Rainfall 450-700 mm per year. The vegetation period is about 125 days. Located in the middle and southern taiga and partially mixed forests. The soils are mainly sod-podzolic and peat-marsh, in the southeast gray forest. Forests (main species: birch, pine, cedar, aspen, fir, spruce) occupy about 54% of the territory. The region is rich in minerals such as oil, gas, iron ore, peat, lignite.
The region consists of 4 urban districts (Tomsk, Strezhevoy, Kedrovy, Seversk ZATO), 16 municipal districts, including 6 urban (Tomsk, Strezhevoy, Kedrovy, Seversk, ZATO, Asino, Kolpashevo) and 116 rural settlements, 1 urban-type settlement (p Belyy Yar) and 579 rural settlements. The regional center is the city of Tomsk. The relief of the area is extremely flat. The highest point of the Tomsk region: +274 m from sea level. Lowest point: +34 m from sea level. Most of the territory is covered by forests, swamps, rivers and lakes. The largest rivers are the Ob, Tom, Chulym, Ket, Vasyugan, Tym. The whole river system belongs to the Ob basin, which crosses the region from the south-east to the north-west at a distance of about 1000 kilometers, dividing the region into two almost equal parts. The number of lakes in the Tomsk region reaches 95 thousand, especially a lot of them in the floodplains of rivers. The largest lake on the territory of the Tomsk Region is the Peace Lake located on a flat interfluve of the Chuzik and Chizhapka rivers. In total, there are 573 rivers in the region. The type of climate is continental. Winter is harsh and long. The average January temperature is from -19 ° C to -21 ° C. Summer is warm, short. The average July temperature is from +17 ° to +19 ° . Rainfall 450-700 mm per year. The vegetation period is about 125 days. Located in the middle and southern taiga and partially mixed forests. The soils are mainly sod-podzolic and peat-marsh, in the southeast gray forest. Forests (main species: birch, pine, cedar, aspen, fir, spruce) occupy about 54% of the territory. The region is rich in minerals such as oil, gas, iron ore, peat, lignite.One of the most valuable natural resources of the Tomsk region is the forest. Wood reserves are 2.8 billion cubic meters. m
The main highways are located in the southern part of the region with access to the neighboring regions. The total length of paved roads is 6,278 km.
GIS Objects and Legend
 Geothermal Waters - Geothermal waters are waters with temperatures above 20 ° C located in the bowels of the Earth. In most cases, they have a temperature of 40 - 100 ° C and higher. They relate to energy sources that are used as renewable energy resources for the generation of heat and / or electrical energy.
Geothermal Waters - Geothermal waters are waters with temperatures above 20 ° C located in the bowels of the Earth. In most cases, they have a temperature of 40 - 100 ° C and higher. They relate to energy sources that are used as renewable energy resources for the generation of heat and / or electrical energy. Hybrid Wind Station - Systems including wind generators, solar panels, and redundant power supplies
Hybrid Wind Station - Systems including wind generators, solar panels, and redundant power supplies DES - Diesel power station (diesel generator set, diesel generator) is a stationary or mobile power installation equipped with one or several electric generators driven by a diesel internal combustion engine.
DES - Diesel power station (diesel generator set, diesel generator) is a stationary or mobile power installation equipped with one or several electric generators driven by a diesel internal combustion engine. Liquid fuel boiler houses - a building or premises with a boiler (heat generator) and auxiliary technological equipment designed to generate heat, the fuel resource of which is: diesel fuel; fuel oil; raw oil.
Liquid fuel boiler houses - a building or premises with a boiler (heat generator) and auxiliary technological equipment designed to generate heat, the fuel resource of which is: diesel fuel; fuel oil; raw oil. Boiler houses for solid fuel - a building or premises with a boiler (heat generator) and auxiliary technological equipment designed to generate heat, the fuel resource of which is: chips; firewood; coal.
Boiler houses for solid fuel - a building or premises with a boiler (heat generator) and auxiliary technological equipment designed to generate heat, the fuel resource of which is: chips; firewood; coal. Livestock facilities are agricultural producers with livestock complexes of cattle (in the geographic information system there are farms with a population of over 500 animals). Production waste is considered as a bioresource for biogas production .
Livestock facilities are agricultural producers with livestock complexes of cattle (in the geographic information system there are farms with a population of over 500 animals). Production waste is considered as a bioresource for biogas production . Treatment facilities - a complex of engineering structures of the settlement, intended for sewage treatment from the pollution contained in them. Waste treatment plants can be considered as a resource for biogas production.
Treatment facilities - a complex of engineering structures of the settlement, intended for sewage treatment from the pollution contained in them. Waste treatment plants can be considered as a resource for biogas production. Breweries and food industry enterprises - enterprises with high food industry waste. Production wastes are considered as raw materials for biogas production.
Breweries and food industry enterprises - enterprises with high food industry waste. Production wastes are considered as raw materials for biogas production. MSW landfills are places of accumulation of solid household waste (objects or goods that have lost consumer properties) of human life. Considered as the location of raw materials for landfill gas (due to the collection of gas resulting from the natural biochemical decomposition of organic waste), as well as for biogas and for recycling and use.
MSW landfills are places of accumulation of solid household waste (objects or goods that have lost consumer properties) of human life. Considered as the location of raw materials for landfill gas (due to the collection of gas resulting from the natural biochemical decomposition of organic waste), as well as for biogas and for recycling and use. Poultry farms - enterprises of the poultry industry of the Tomsk region. Production wastes are considered as raw materials for biogas production.
Poultry farms - enterprises of the poultry industry of the Tomsk region. Production wastes are considered as raw materials for biogas production. Logging areas - areas where logging activities are conducted, consisting of a complex of logging operations and timber hauling.
Logging areas - areas where logging activities are conducted, consisting of a complex of logging operations and timber hauling. Pig farms are enterprises intended for a full technological cycle - from reproduction to slaughter and processing of pig meat. Production wastes are considered as raw materials for biogas production.
Pig farms are enterprises intended for a full technological cycle - from reproduction to slaughter and processing of pig meat. Production wastes are considered as raw materials for biogas production. Thermal power plants are large stations of the Tomsk region that produce electrical energy by converting the chemical energy of fuel into mechanical energy of rotation of the generator shaft with the generation of heat.
Thermal power plants are large stations of the Tomsk region that produce electrical energy by converting the chemical energy of fuel into mechanical energy of rotation of the generator shaft with the generation of heat. Dried peat deposits - a peat deposit from the surface to the mineral bottom or to sapropel deposits usually consists of several types of peat with a set of hydrotechnical measures to create a drainage system and having a different degree of readiness to start producing peat.
Dried peat deposits - a peat deposit from the surface to the mineral bottom or to sapropel deposits usually consists of several types of peat with a set of hydrotechnical measures to create a drainage system and having a different degree of readiness to start producing peat. Peat deposits (promising for development for energy purposes) are peat deposits with a low degree of ash content of up to 15% and large reserves of peat, such deposits may be involved in operation in a short time due to the relative transport accessibility and location near settlements.
Peat deposits (promising for development for energy purposes) are peat deposits with a low degree of ash content of up to 15% and large reserves of peat, such deposits may be involved in operation in a short time due to the relative transport accessibility and location near settlements.GIS includes wind isolines, sun isolines, a map of roads, existing gas pipelines, power lines (if necessary). All objects are geo-referenced and have a detailed description. The description includes public information about the generation facility or expert opinion on the potential of a renewable energy source. View GIS presented in the figure.
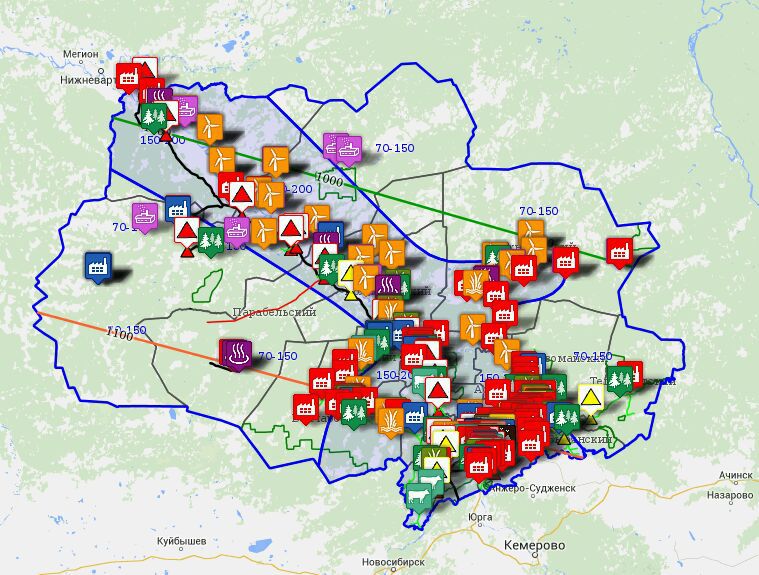
GIS is built in layers. You can temporarily turn off any layers and work with information, for example, on peat deposits.
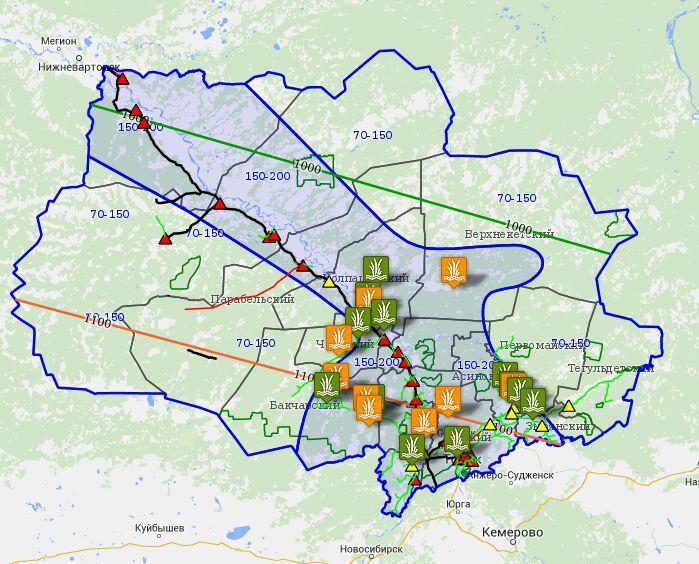
It is possible to combine layers, thereby assessing the logistical possibilities and a convenient location for the potential location of the generation facility on alternative fuel, taking into account the corresponding fuel resource (sawdust, peat, chips, biomass, etc.).
Reasons for entering information into GIS
The main task of this work is to obtain the most reliable data on the potential of renewable energy sources and the most up-to-date information on the generation objects. In this regard, data were used from at least several independent sources, or data of expert opinions directly at the sites. For this purpose, groups of experts were formed, who were seconded to the relevant areas of the Tomsk region. Also in GIS were used
1. Data of regional reports on generation objects
2. Trends of long-term meteorological observations
3. Ecological studies of the territory
4. Scientific data on the publication of independent research teams of research institutes and universities of Tomsk and Russia
5. Laboratory studies of biomass of various origins (manure, beer pellet, wastewater treatment plants)
6. The results of geological exploration of various years for the application of information on peat deposits.
This approach allowed us to obtain a GIS with a high degree of validation. For example, you can see that the data of expert opinions on the potential of wind solar energy fit perfectly in the wind isolines, sustainably formed for many years of meteorological observations (in the figure, the steady wind isolines are marked with blue lines in the center)

An example of an expert opinion
Let us consider in more detail the example of the work of the expert group. To obtain evidence from the enterprises, expert groups of 2-3 people were formed with relevant professional competencies. Also, special laboratory facilities were used for work to conduct additional studies of raw material samples. Since I headed one of the expert groups , I will describe in more detail the methods of work of specialists in our area.
In the work of our expert group were subject to evaluation
1. Agricultural enterprises
2. Poultry farms
3. Pig farms
4. Beer factories
Also, some experts worked on assessing the potential of wastewater treatment plants. The subject of evaluation is biomass and industrial biological waste of the indicated enterprises. All expert groups worked on the basis of relevant written requests to the owners (or top managers) of enterprises, which (surprisingly) actively contributed to the work of specialists.
The work of the expert was regulated by the methods of the work of the experts, including all the necessary actions and manipulations. Each expert group had
1. Samples of documents for filling in the form of questionnaires .
2. A camera configured to automatically display the date and time
3. GPS, voice recorder
4. Capacities for sampling biomass for laboratory research
5. Additional materials (bags, tags, puffs, disposable gloves, sample intakes, markers)
The task of the expert was to clearly fill out the information in the questionnaire, familiarity with the company, the process, waste management system, slaughterhouse, etc. in accordance with the algorithm of action of the expert. All actions are clearly regulated, so there were no significant errors and omissions. The photographing and calculation of the geographical coordinates of the enterprise was carried out. Experts also made selective sampling of biomass samples for further laboratory research. The work of the expert group (depending on the company) took 3-5 hours.
Laboratory research
Biomass samples were sent for laboratory tests. The purpose of the study was to analyze the structure of biomass, the presence of impurities, heavy metals, as well as general chemical indicators such as ash, pH, C: N: P ratio. Analyzes were carried out in an independent accredited laboratory.
Test Report Example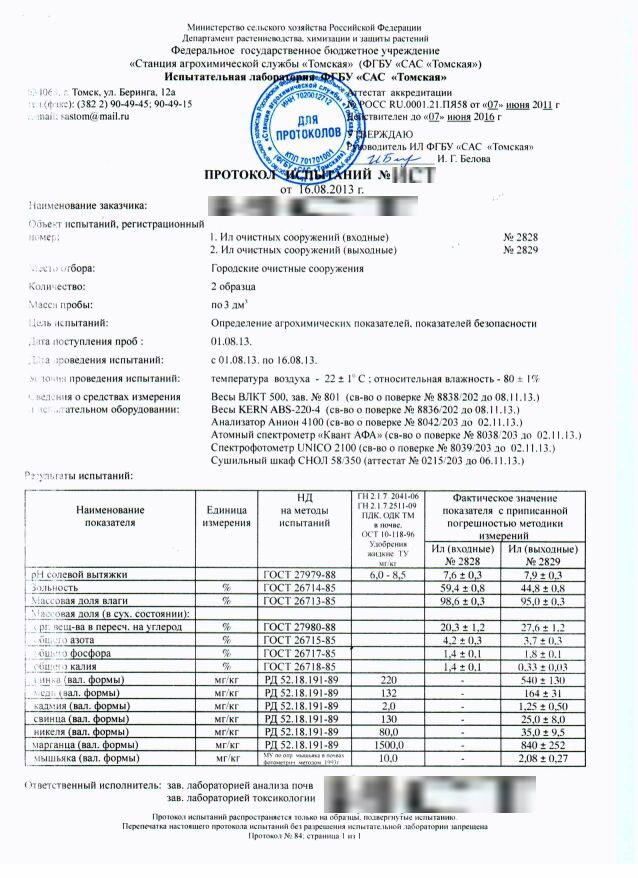

This initial information was necessary to conduct experiments for the fermentation of biomass in laboratory biogas plants, in order to determine the maximum calorific value of raw materials for biogas output. The type and technical characteristics of laboratory installations are presented in the photo.

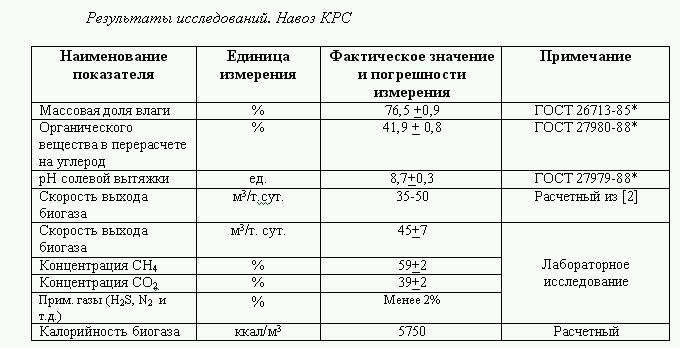
The results of laboratory tests, analysis of information from questionnaires and all the information collected by experts was summarized into a final expert opinion, which was the basis for entering information into the GIS. In this case, only large enterprises of the agricultural sector were taken into account, in particular, with a livestock population of at least 500 heads.
Other expert groups worked in a similar way in analyzing the wind load potential, solar insolation, peat potential, geothermal sources, etc. Of course, other tools and laboratory facilities were used in accordance with the tasks of expert groups.
Analysis and prospects of using GIS
Were compiled and updated large amounts of information. GIS provided a single information resource for analyzing the potential of renewable raw materials for alternative energy sources. Taking into account the development of renewable energy technologies, this will allow in the medium term to form projects for the creation of alternative generation generating facilities. At the same time, the potential of peat and waste wood production is already significant. At the moment, work is underway on the analysis of promising technologies to solve these problems. Approaches to assessing the potential of renewable energy sources and the competence of Tomsk expert groups can be used for similar work in other regions of Russia and we are ready to share our experience in this direction.
Link to GIS here . I cannot evaluate the reaction to the Habr effect. Possible failures.
Thanks
This work was conducted by dozens of people from various organizations, universities, and research institutes of Tomsk. The work took about a year and a half. I thank all my colleagues who worked in this project. GIS was built in the interests of the Tomsk region and is currently supported and developed by the Center for Energy Efficiency and Energy Saving of the Tomsk Region. The head of the Center, Alexander Dmitriev, and his staff actively participated in this work, and I also express my gratitude to them.
Important addition
Many may be extremely skeptical about the prospects for the use of biogas technology in Siberian conditions. This is, indeed, an interesting topic for analysis and discussion. In the coming days, I will publish the appropriate post and I invite everyone to discuss this topic in more detail.
PS - Post published by habrahabr.ru/post/226953
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/229919/
All Articles