Encryption of cloud services in companies and organizations
 Imagine that you are the head of a company - you have a dynamic project and you prefer to keep up with the times. Every year your organization grows, its staff expands. In this case, one of the main issues that you constantly have to solve is the provision of your organization with modern computing technologies, the purchase of new software and licenses.
Imagine that you are the head of a company - you have a dynamic project and you prefer to keep up with the times. Every year your organization grows, its staff expands. In this case, one of the main issues that you constantly have to solve is the provision of your organization with modern computing technologies, the purchase of new software and licenses.However, this is not at all necessary. Why do not you use the services of cloud services? All you need to do is to connect to the provider’s application of this service, after which your company will receive remote access to its computing resources.
Then, based on the specifics of the tasks and the volume of information being processed, you will need to choose one of the three service models that exist today:
')
SaaS - software as a service. In this case, you use the software, applications and operating systems of the provider, which fully controls the operation of the cloud infrastructure. By and large, you only manage your account (group of accounts) with the ability to make minor changes to some of the application settings. An example of this service can serve as YahooMail, Google Disk, Office Online, etc.
PaaS - platform as a service. Here you get the opportunity to install your own software and build applications of the Saas level. However, control of operating systems, servers, data warehouses is still left to the provider. The simplest example here is hosting, where you install your CMS, modules and plugins to it, as well as get access to MySQL, PHPMyAdmin, etc.
IaaS - infrastructure as a service. Here you have even more freedom - the provider provides only the physical foundation of computing power (virtual machines), on the basis of which you can deploy your cloud infrastructure and implement your own PaaS and Saas solutions, controlling the installed operating systems and applications.
Benefits of Cloud Services
Minimum primary costs . Initially, to build a proprietary information system, a company needs to purchase expensive equipment and software, as well as pay for debugging its efficiency, which translates into not only significant financial but also time costs.
When using cloud technologies, you just have to sign a contract with the provider, after which you almost immediately get all the services necessary for the development of your business on the terms of the agreed monthly payment.
Availability You and your company's employees get access to corporate information placed on the cloud, at any time, from any devices (smartphones, tablets, laptops) and from any place where there is an Internet connection.
Flexibility and adaptability . In that case, if you need to use additional computing resources and connect new services, the provider is able to provide them to you within a few hours. Similarly, at any time you can refuse to use these or other services if they are no longer necessary.
No operational costs . When using cloud services, you are not affected by the costs associated with maintaining the components of the IC and supporting its operation - all this falls on the shoulders of the provider.
Mobility and independence . Standard server infrastructure is tied to the company's office and in case of its relocation, you will have quite a lot of problems associated with the transportation of equipment, laying of cable communications, renewal of contracts with Internet providers, etc. When using cloud services, you are not tied to your office.
Protection of information on cloud resources
Despite all the advantages of cloud technologies, many company executives are wary of using them, because they do not want to trust the processing and storage of their corporate information to third parties, worrying about its safety. In addition, if the data is stored on the cloud, then to whom do they belong - to you or to the provider of this service, on whose servers are they located? And can the provider at some point deny you access to the files placed?
Another important question - how secure is your information after it is placed on the cloud? Cloud service providers argue that there is no cause for concern, because the protection of customer information is of paramount importance to them.
However, even if the provider manages to protect your data from an outside attack, can you be sure that the employees of the cloud service itself will not exceed official authority and will not have access to your information? Even if encryption is provided on the cloud, encryption keys are also stored on the cloud server, which means that anyone who has access to them can access your encrypted data.
Therefore, the only solution in this case is the encryption of information on the user's side and sending it to the cloud already in encrypted form. In this case, encryption keys are stored only for you and the possibility that intruders from your outside will get access to your data or employees of the cloud service itself will be excluded.
Encrypting Cloud Services with CyberSafe
When working with CyberSafe, all data sent to the cloud is pre-encrypted and gets to the remote server already in encrypted form. The encryption keys will be saved either on the user's local computer or on removable media. The security administrator gets the opportunity to assign the keys of certain users to each encrypted folder and thus delimit access to various categories of information.
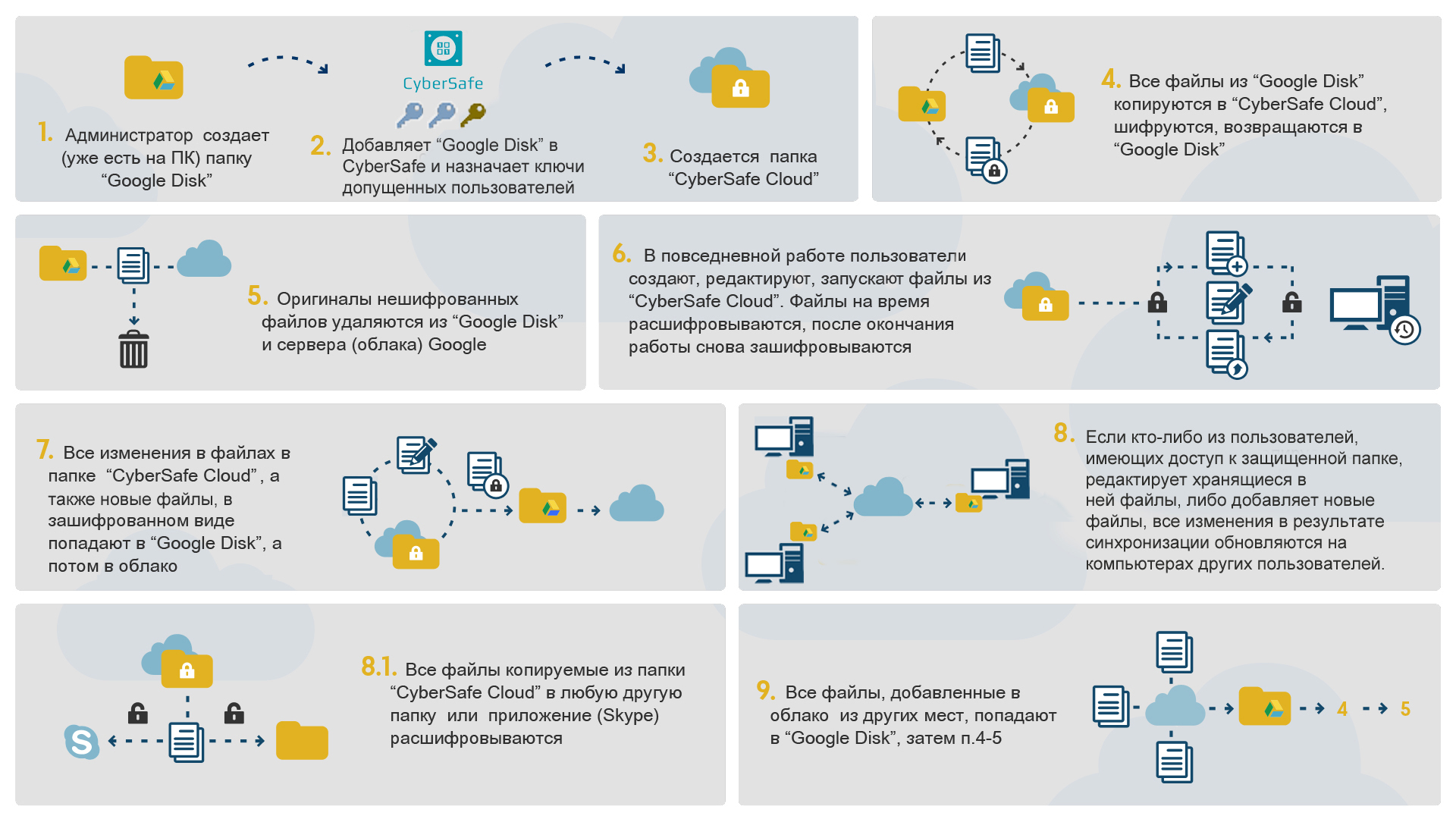
Encrypting data on a remote cloud resource (in this example, it is Google Drive) in CyberSafe follows the following scenario.
1. In a corporate account for a folder with encrypted documents (in this example, Group1), the security administrator sets up sharing for those employees who will work with them in the future. This is done by means of Google Drive - invitations are sent to the email addresses of user data assigned to their accounts with access to this folder. Also, the admin sends the invitation to his email address:

Here, users are given access rights, such as Edit and Read .
2. After that, the administrator logs into his personal Google account, accepts the sent invitation and adds the Group1 folder to his Disk. Both on the administrator’s computer and on the computers of other employees, Google Drive applications that are configured to work with the corresponding accounts must already be installed.
3. After synchronization has occurred and the Group1 folder has been copied to the administrator’s computer, it adds it to CyberSafe in the Cloud Encryption section and assigns keys to this folder to users who can later work with it:
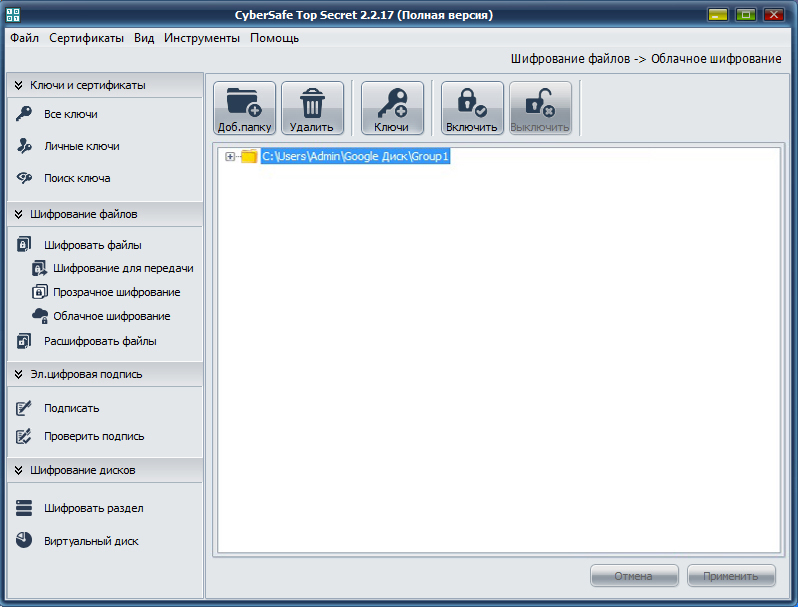
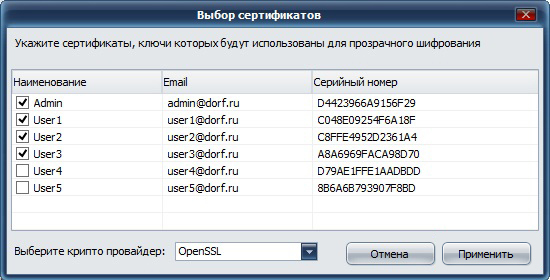
In the future, the security administrator can always reassign keys by removing a user from the group or adding a new key.
4. After adding keys, CyberSafe will create a sync folder (a mirror copy of the Group1 folder). Further, all actions with encrypted files are performed only from the synchronization folder:
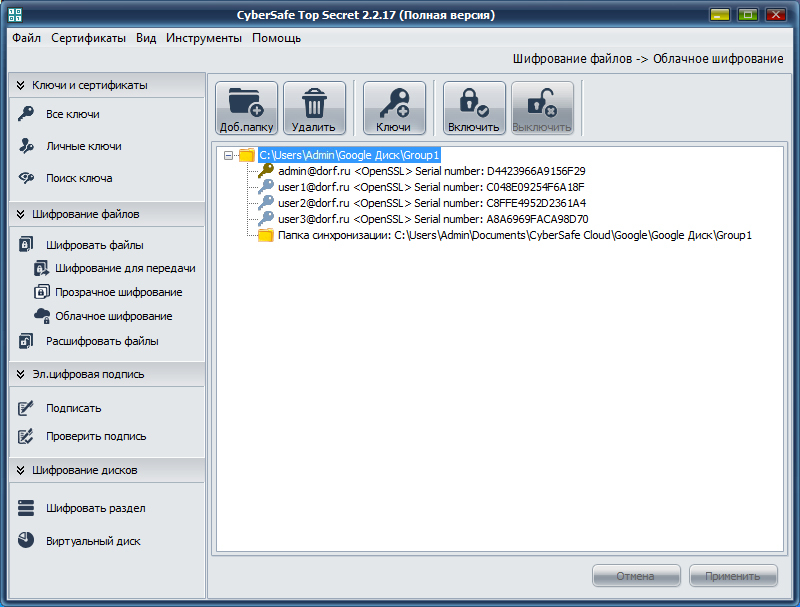
5. Similarly, the administrator adds to CyberSafe other folders with files that must be encrypted and assign keys for them to other employees.
In order to start working with these folders, they must be Enabled :
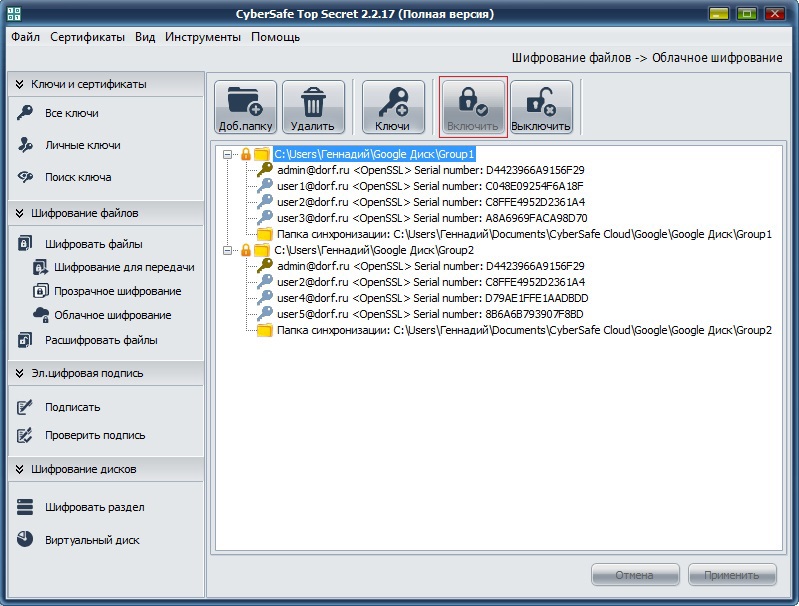
After the folder is included, all files in it are available to work in transparent encryption mode.
6. CyberSafe will create encrypted copies of existing files, after which all unencrypted originals will be deleted both from users' computers and from a cloud resource. All new files added to these folders are automatically encrypted.
7. On the cloud in each of the folders CyberSafe will create a cybersafe.cloud.conf file, which contains the public keys of authorized users. To prevent users from making changes to it or deleting this file, the administrator only permits reading it.
8. Similarly, users add encrypted folders to CyberSafe on their computers. After that, they are able to work with documents in the folders they are allowed to, and the changes made by each of them, as a result of synchronization, are updated on the computers of the entire group. At the same time, copies of files placed on the cloud are always in encrypted form.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/229719/
All Articles