Banking Trojan Zeus Gameover returns in new modification
A few days ago, researchers from Malcovery Security announced the discovery of a new modification of the most famous banking Trojan Zeus. This is a new modification of the so-called. Zeus Gameover (the latest version of this banking malware). In addition to the new Zeus executable files with a modified botnet algorithm, a spam email was recorded, the attachment to the letters of which contain a Zeus dropper. The new modification is detected by ESET as Win32 / Spy.ZBot.AAU .

Domains for communication with the management server, which are generated by the DGA algorithm of the Trojan program, confirm that it is a new version. Earlier we wrote about the operation of disabling the botnet Zeus Gameover, which was conducted by FBI and Europol in collaboration with security companies. As part of that operation, the security services also seized control over the domains that were used by Zeus, taking possession of them and making it impossible for the bots to receive new instructions from intruders.
')
A distinctive feature of the new version is the use of the Fast flux algorithm for working with a command server, instead of the previously used P2P. In the P2P scheme, there is no centralization in receiving commands from a single server; instead, there are many so-called peers (other infected computers) in the botnet that can transmit instructions to the bot for execution. Fast flux offers a different work scheme. In it, the domain for communication with C & C can constantly change its assignment in the form of a computer’s IP address (domain association with IP), while the computer’s IP address over which attackers have control can be used as a system to register a DNS record. As a rule, this is a set of computers whose IP addresses are used by attackers to quickly reassign the required C & C domain for them. The bot receives a list of such C & C domains through the updated DGA algorithm.
The story with Zeus stretches for quite some time. The first versions of the bot were born in 2007 or even earlier. Zeus was distinguished from other malicious programs by the fact that it became a kind of first crimeware toolkit or a full-featured tool for stealing online banking data from various banks and transmitting this information to the attacker's server. To carry out such operations, he had in its composition a configuration file, which allowed attackers to quickly redirect it to the goals they needed (banking sites). Since then, several generations or versions of Zeus have appeared, the cumulative financial damage from which is estimated at more than half a billion dollars. The number of different families or modifications of this malicious program and botnets based on it already amounts to several dozen.
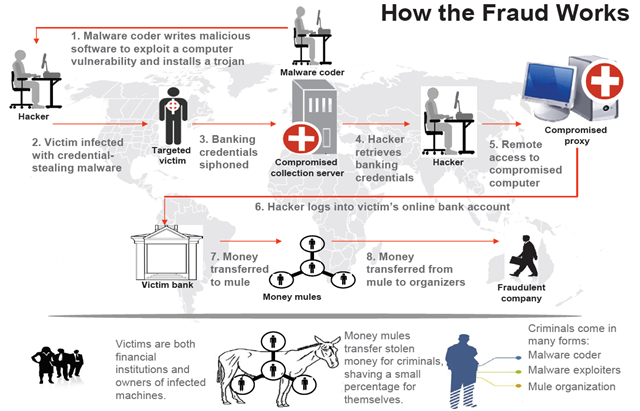
Fig. Cybercriminals who use crimeware toolkit to steal funds from bank accounts.


Fig. FBI press release issued in the context of the case of arresting “money mules”, the so-called United States v. “Zeus money mules” in 2010. More than two dozen students from the former USSR were arrested, many of whom came to the United States using forged documents and cashing “dirty money” that had been stolen from bank customers using Zeus. According to the investigation, within the framework of this case, more than $ 70 million was stolen.

Domains for communication with the management server, which are generated by the DGA algorithm of the Trojan program, confirm that it is a new version. Earlier we wrote about the operation of disabling the botnet Zeus Gameover, which was conducted by FBI and Europol in collaboration with security companies. As part of that operation, the security services also seized control over the domains that were used by Zeus, taking possession of them and making it impossible for the bots to receive new instructions from intruders.
')
A distinctive feature of the new version is the use of the Fast flux algorithm for working with a command server, instead of the previously used P2P. In the P2P scheme, there is no centralization in receiving commands from a single server; instead, there are many so-called peers (other infected computers) in the botnet that can transmit instructions to the bot for execution. Fast flux offers a different work scheme. In it, the domain for communication with C & C can constantly change its assignment in the form of a computer’s IP address (domain association with IP), while the computer’s IP address over which attackers have control can be used as a system to register a DNS record. As a rule, this is a set of computers whose IP addresses are used by attackers to quickly reassign the required C & C domain for them. The bot receives a list of such C & C domains through the updated DGA algorithm.
The story with Zeus stretches for quite some time. The first versions of the bot were born in 2007 or even earlier. Zeus was distinguished from other malicious programs by the fact that it became a kind of first crimeware toolkit or a full-featured tool for stealing online banking data from various banks and transmitting this information to the attacker's server. To carry out such operations, he had in its composition a configuration file, which allowed attackers to quickly redirect it to the goals they needed (banking sites). Since then, several generations or versions of Zeus have appeared, the cumulative financial damage from which is estimated at more than half a billion dollars. The number of different families or modifications of this malicious program and botnets based on it already amounts to several dozen.

Fig. Cybercriminals who use crimeware toolkit to steal funds from bank accounts.
- The author of the Trojan is developing the necessary functionality of the bot.
- The operator (hacker) is responsible for distributing the compiled executable files of the Trojan program. He can use the services of spammers to organize spam mailings, “iframes” to redirect legitimate users of hacked sites to a Trojan or other methods known in the cybercrime world.
- The user is infected with a banking trojan, after which he uses a browser (in the process of which the malicious code is located) to work with online banking. The confidential data specified when working with the online banking system is sent to the attacker's server.
- The operator (hacker) receives the data sent by the bot in the previous step.
- The operator may use another compromised computer (proxy) to conduct fraudulent operations with the victim’s account, thus hiding the source of the attack.
- Using the proxy specified in the previous paragraph, the operator logs on to the user's online banking account using the login / password pairs stolen in step 4.
- Funds from the victim’s account are transferred to several dummy bank accounts in small portions, and then cashed at ATMs by various persons participating in the criminal scheme (mules).
- The organizer (coordinator) of the entire criminal scheme receives funds from the “mules”, and each of them “mules” receives its share.


Fig. FBI press release issued in the context of the case of arresting “money mules”, the so-called United States v. “Zeus money mules” in 2010. More than two dozen students from the former USSR were arrested, many of whom came to the United States using forged documents and cashing “dirty money” that had been stolen from bank customers using Zeus. According to the investigation, within the framework of this case, more than $ 70 million was stolen.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/229657/
All Articles