Summer review of space affairs
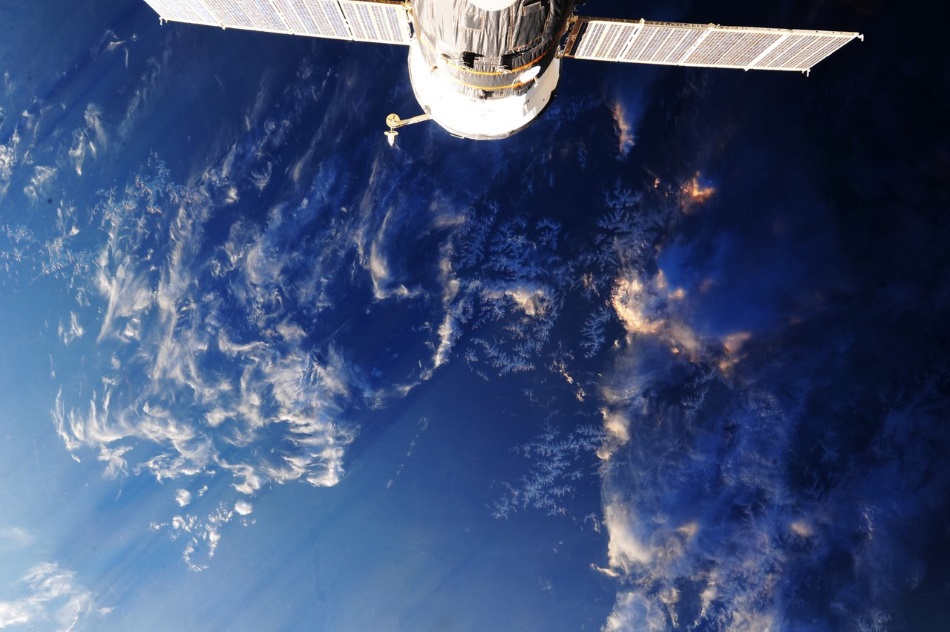

A year ago, I wrote a review post about what is happening in the global and domestic space program, and what are the achievements of various countries in this area. It so happened by chance that the next morning the Proton epically fell live with three GLONASS satellites, so that post was widely sold. Now, a year later, I thought - why not write a new review with a story about the affairs of space for the second half of 2013 - the first half of 2014. Such reviews are usually written for the New Year, the more interesting will be the view from July.
Introduction
The post is structurally divided into the same as in the previous time section - manned cosmonautics, applied unmanned cosmonautics, scientific unmanned cosmonautics, launch vehicles.
Piloted astronautics
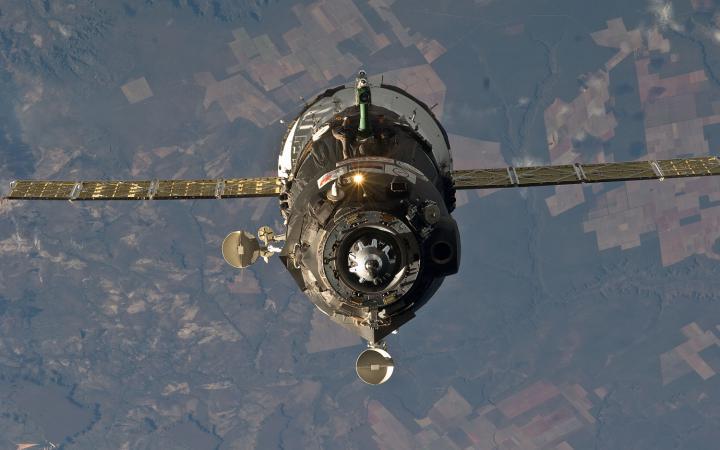

Piloted ships
2014 will certainly be the year in which only Russia will launch manned ships. The fact is that China, which usually launched one “Shenzhou” one in 2012 and 2013, does not plan manned flights this year, and ships of other countries are still being tested.
Russia : “Unions TMA-M” fly, in parallel, new equipment is being tested. For example, the new “Kurs-NA” docking system, which will be installed on the “Soyuz TMA-MS”, is now running around the “Progress”. At the same time, a new PPTS ship, aka PTK NP, is being developed, the first launch is expected in 2017-2018. The model of the ship was shown at MAKS-2013. Separate components are being developed and tested - windows, a control knob, etc. If you are interested in the news of the development of this ship, I recommend to follow the topic on the forum "News of Cosmonautics" and the blog of test-cosmonaut Mark Serov, who participates in the development.
USA : Actively working on the development of several ships. The development of the cargo ship Dragon - manned DragonRider was renamed Dragon V2 , and its layout was shown on May 29, 2014. In terms of the depth of development, the layout was conceded by the PTK NP - there was nothing except stylish racing seats and a large dashboard with touch screens, and the layout sparkled with bare walls of the cockpit. The mini-shuttle DreamChaser has started throwing tests - the prototype was dropped from a helicopter on October 26, 2013. Unfortunately, the tests ended in an accident, the landing gear did not come out, and the prototype was damaged. The ship CST-100 tested the parachute system in 2012, and in August 2013 conducted tests of the cabin ergonomics and communications. The development of the Orion spacecraft is under way, repeated tests of the parachute system, the rescue system were conducted, a test subarbital unmanned flight was expected in December 2014 .
Europe : In 2012, ESA decided to join the Orion program, the ACTS / CSTS project is closed.
China : the Shenzhou ship is operated, the next flight, the Shenzhou-11, is expected in 2015-2016. The uncertainty is due to the fact that this flight is planned to be carried out to a new modular Chinese orbital station, which is not yet launched.
India : In February 2014, it suddenly became clear that the ISRO OV project received funding and a fairly high priority. In March, tests of the parachute system were conducted , and the first unmanned suborbital test flight is expected, no less, in the second half of 2014, I recommend to follow the news.
Japan : No news on the development of any manned ships.
')
Orbital stations
The operation of the ISS continues. Due to some cooling of relations between Russia and the United States, clouds began to thicken over the future of the station - it is not known whether its operation will last after 2020. Russia is the only country that planned to expand the ISS with new modules, and the “Science” module was supposed to go on a flight in the spring of 2013. But the module had technical problems on tests, and its start was postponed. Initially, the dates were called in 2014, but in autumn 2013 the module was returned for revision, and can fly as much in 2016-18. Given the political problems of international cooperation and the aging of the ISS, there is some probability that the block will become the basis for a new Russian or Russian-Chinese orbital station - Nauka was developed on the basis of the FGB, which became the first block of the ISS.
China plans to move from a single-module Tyangun-1 station to a multi-module station in the Mira style or the ISS. Specific dates are still unknown, the launch of the first module is approximately 2015-2016 year.
Bigelow does not cancel its plans to launch a private orbital station , and, according to the news, acquired launch services for one launch of the Falcon 9 rocket, but the payload of this launch is still unknown.
Supply Cargo Ships
Russia : Progresses continue, 2.3 tons of payload, 4 launches per year.
USA : Dragon - 3.3 tons into orbit, 2.5 - back, in 2013 one launch, in 2014 they want to launch 4 launches, but they are unlikely to have more than two launches - the timing of the launches gradually goes right, the second launch in 2014 the year was supposed to be in June. The ship Cygnus made the first flight to the ISS in 2013, can deliver 2 tons of cargo.
Europe : ATV program ends, the ship "Georges Lemaitre" will be the last ship of the series. Starting July 26, 2014. Payload 7.6 tons. After the project is closed, the mastered technologies will work in the service module of the Orion ship.
Japan : HTV - 6 tons per orbit, one launch per year. In 2014, the fifth ship of the series will fly, the launch date has not yet been announced. At least three more ships of the series are expected.
Applied unmanned space program
Applied unmanned spacecraft is, in fact, the bread of astronautics. The commercial benefits of communications, meteorology, government benefits of navigation, government communications, missile attack warning systems all mean that most of the launched vehicles will fall into this category.
Satellite navigation systems
Global navigation systems still have only two countries - Russia and the United States. Several countries also have or are developing regional navigation systems.
Russia : The GLONASS system is in operation, 24 satellites are in operation, 1 is on trial (GLONASS-K on a new unpressurized platform), 2 are under study, 2 are in reserve, 1 is in the system entry phase, a total of 30 satellites. The system is deployed steadily and with a margin, last year’s loss of 3 satellites during a PH accident did not affect the signal availability. The last satellite was put into orbit in June 2014.
USA : GPS , 31 satellites in orbit, last launched in May 2014.
Europe : Galileo , in orbit 4 satellites, last launch in 2012, the system is under testing.
China : Beidou system , deployed as regional in 2012, 14 satellites in orbit. It is planned to develop into the global system by 2020.
India : The IRNSS system is actively developing, over the last year two satellites have already been launched, in 2014 it is planned to launch two more. In total, it is planned to launch seven satellites for full system deployment.
Japan : The QZSS system, which the plans were supposed to put into operation in 2013, is still listed as inactive. Three satellites are in orbit, in 2013 it was announced that another satellite would be launched.
Other
Over the past year, Russia launched the following application satellites:
| date | Title | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| September 12, 2013 | 3 "Gontsa-M" | Low-orbit communication |
| November 12, 2013 | "Rainbow-1M" | Geostationary military connection |
| December 25, 2013 | "Cosmos-2488" / "Strela-3M" | Low-orbit military connection |
| December 26, 2013 | Express-AM5 | Geostationary Telecommunications |
| March 16, 2014 | 2 Express-AT | Geostationary Commercial Telecommunications |
| March 24, 2014 | "Cosmos-2491" / "GLONASS-M" | Navigation |
| April 28, 2014 | "Luch-5V" | Geostationary connection |
| May 6, 2014 | "Cosmos-2495" / "Cobalt-M" | Low-Orbital Species Intelligence |
| May 23, 2014 | 3 "Arrows-3M" | Low-orbit military connection |
| June 14, 2014 | "Cosmos-2500" / "GLONASS-M" | Navigation |
| July 3, 2014 | 3 "Gontsa-M" | Low-orbit communication |
July 8 is expected to launch meteorological "Meteor-M number 2", also worth noting the expected launch of "Electro-L number 2" at the end of the year.
Of the losses of satellites of this year, the most noticeable is “Electro-L No. 1”, which has problems with the orientation system. Despite the dramatic history of the device’s flashing in orbit and its return to service on May 25, problems have resumed, and now the satellite is at least partially inoperable. Also in April, the Kosmos-2479 / Oko-1 satellite of the missile attack warning satellite was removed from combat duty; the missile attack warning tasks now lie on ground stations.
Scientific unmanned cosmonautics

In Asia, the "lunar race" and the "Martian race" are in full force - China landed a lunar rover on the moon, and India launched a probe to Mars.
Automatic interplanetary stations
Russia : There are no interplanetary missions, thanks to international cooperation, some devices stand on foreign AMC. The closest mission is Luna-25 , the launch is expected in 2016.
USA : On September 7, 2013, the mission to study the lunar atmosphere and near-moon dust LADEE was launched. In November, the probe MAVEN went to Mars - to study the Martian atmosphere.
Europe : Rosetta's mission, launched in 2004 to comet Churyumov-Gerasimenko, will reach its destination this year. In November, the study of the comet and landing of the descent vehicle is expected.
China : The Chang'e-3 mission won the Asian “lunar race” stage, landing on the moon for the first time after the USSR and the USA and landing the moon rover on the moon for the first time after the USSR.
India : A great success for India was the launch of the first AMC to Mars - the Mangalyaan probe, despite the problems with the accelerating unit and the dramatic multipulse acceleration, went to Mars. Approaching Mars is expected on September 24th.
Japan : There is no AMS this year, the closest mission is Hayabusa-2 to the asteroid (162173) 1999 JU 3 , the launch is expected at the end of 2014.
Scientific devices
Russia : The Spektr-R radio telescope continues to operate, Chibis-M explores lightning in the atmosphere, two STORTS are examining micrometeorites and space debris. Last year, the Bion-M No. 1 biosatellite successfully flew, the Foton-M4 physical and biological satellite was being prepared - the launch is scheduled for July 18.
USA : On July 2, the OCO-2 satellite was launched to study carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. On June 27, 2013, the IRIS solar observatory started. There were also launches of micro- and nanosatellites - technological, simple scientific, student. From the expected launches - climatological DISCOVR .
Europe : The most notable event is the Gaia telescope, which should map the position and motion of stars in our galaxy, as well as search for exoplanets, asteroids and comets.
China : There are no visible scientific devices for the year.
India : There are no noticeable scientific devices for the year; in 2015, the launch of an astronomical satellite Astrosat is expected.
Japan : Hisaki ultraviolet telescope launched on September 14, 2013.
Removal vehicles
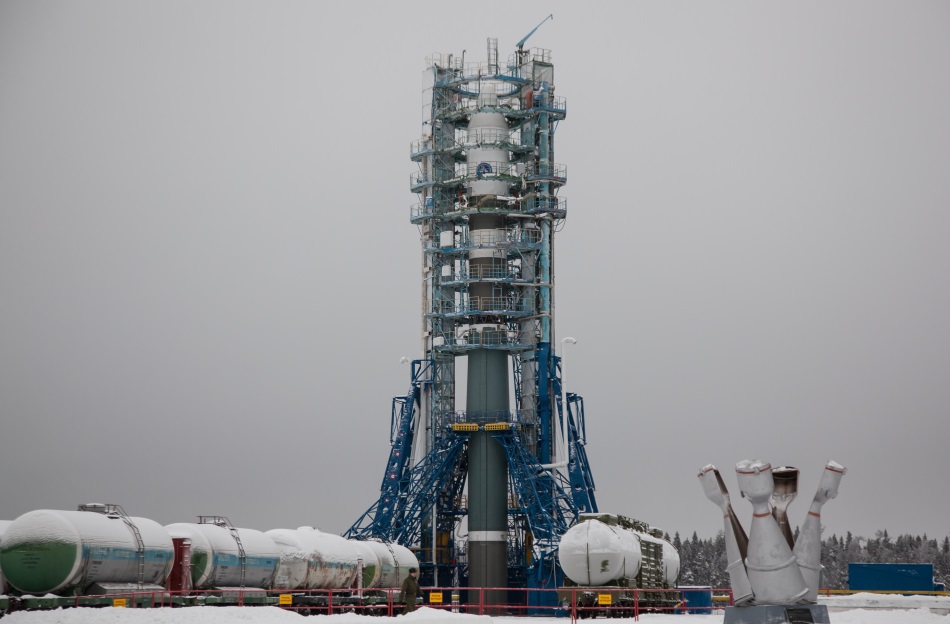

Russia is still "ahead of the rest" by the number of launches. For 2013, Russia has 32 start-ups, second place is the United States with 19 starts, third place is China with 15.
Russia : A gradual renewal of the rocket fleet is taking place - in the segment of light rockets, conversion Dnipro and Rokot , which we inherited from the USSR, are beginning to descend from the stage, they are replaced by a light modification of the Soyuz-2.1v and the Angara -1.2 " (start rescheduled for July 9). The heavy Angara-A5 is expected to appear in the heavy missile segment - the first launch is expected at the end of 2014. In the segment of medium-sized missiles, Soyuz-2.1b should go from experimental to commercial operation, so far only state satellites have been launched on this rocket - they have accumulated statistics.
USA : The first launch was made by an improved version of the Falcon-9 rocket - the Falcon-9 v 1.1 . Also, the first flight made the most severe modification of the Minotaur light rocket - Minotaur V. Dependence on Russian engines under conditions of cooling relations superimposed on the economic rivalry between ULA and SpaceX, giving rise to a series of high-profile statements, scandals and lawsuits - ULA was sued, then forbidden to buy Russian engines, then allowed again.
Europe : The development of the new Ariane-6 rocket is underway , the first launch is not soon - in 2020-2021.
China : Kuaizhou solid propellant launch vehicle made the first flight.
India : The development of a heavy rocket GSLV Mk III , the first test launch is scheduled for August 2014.
Japan : Made the first flight of Epsilon light class rocket.
Conclusion
In my last year post, in my estimation, Russia was in the top three leading space powers. Since then, little has changed; we are still in a good position in this high-tech industry. If we talk about where we are lagging behind - I would highlight our problems with the element base, the lifetime of the satellites and the issues of reliability. Last year's accident occurred for a tragicomic reason (a collector error, not caught by quality control), since then Proton managed to start flying again and fell again, for another reason. If we talk about the areas where we are ahead - this is certainly the mass production of excellent launch vehicles, the development of manned space flight and the great experience in medical support for long flights, active advance, for example, the development of fundamentally new orbital tugs with a nuclear power plant .
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/228803/
All Articles