How does international roaming work?
In this article, I will talk about how the international roaming service works and how the call and SMS travels while in roaming. Abbreviations can be read in this article.
Roaming is a service that allows subscribers to make calls, use data transfer service, use other services provided by the operator, being in the networks of other operators, including foreign ones, with which the subscriber operator has a roaming agreement. In this case, the phone number of the subscriber remains unchanged.
National roaming r - is the ability to use the services of a "foreign" network within the same country.
International roaming is an opportunity to use the services of a mobile network of a foreign operator with which there is an agreement. The article will describe this type of roaming.
The first action that occurs when trying to register on the network of a foreign partner is to check the subscriber for “validity”. This is done by the VLR / MSC, in which the MS is located. After the guest VLR / MSC receives the “Location Update” command from MS, knowing the subscriber’s IMSI, sends the message “Send Authentication Info” to the HLR via MAP; he in turn checks that the MS and the received IMSI are valid. If the verification is successful and the subscriber is “valid”, the HLR sends the IMSI to the AUC. AUC generates a triplet (SRES, RAND, Kc) and sends it to the HLR, then the HLR sends this data to the VLR / MSC that serves the MS. After the VLR / MSC has received this data, the VLR / MSC sends the RAND to the MS. Upon receiving the RAND request, MS substitutes the received RAND and Ki (recorded on the SIM card) and calculates SRES, which is sent to the VLR / MSC. If the SRES received from the MS is the same as the SRES received from the AUC, then the MS is considered authorized.
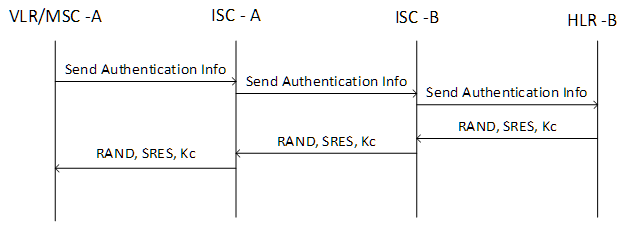
')
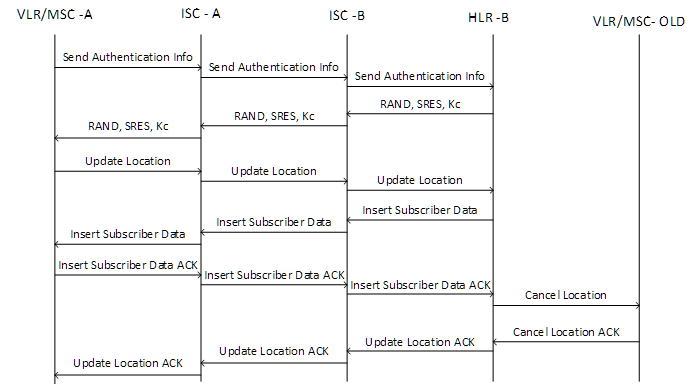
After VLC / MSC has authorized MS, it sends an Update Location message to the home HLR. This message is sent so that the HRL knows which VLR / MSC is in range of the subscriber. The message “Update Location” contains the subscriber's IMSI and the GT VLR / MSC. The HLR, after receiving the data, will check if the roaming service is connected. If the subscriber does not have a ban, the HLR will delete the subscriber profile from the VLR / MSC where the subscriber was registered prior to this procedure, by sending the message “Cancel Location”. The HLR also sends the subscriber profile to the VLC / MSC requesting this information using the “Insert Subscriber Data” message. After the VLR / MSC receives this information, the “Update location” will be completed, and the HLR will keep the VLR / MSC address that requested the Update location in the subscriber profile. At this stage, the “Update Location” is finished. When a call or SMS arrives, the HLR knows which VLR / MSC to send it to.
After these procedures, the subscriber is considered to be registered in the network, i.e. he can make and receive calls, SMS, use other available services. Let us consider in more detail the procedures of incoming and outgoing call.
From subscriber A, a call is received to subscriber B who is in roaming. Subscriber A dials the number of subscriber A (MSISDN). If it is a call from the city network, the ISUP IAM message will go to the GMSC, then the GMSC will determine the HLR address based on the received MSISDN and send the message “sendRoutingInfo” using the MAP protocol to the HLR. The HLR, having received MSISND, determines the IMSI of subscriber B, as well as which VLR / MSC the subscriber is in. The HLR then sends the ProvideRoamingNumber message via the MAP protocol to the VLR / MSC which contains the IMSI of the subscriber B. The ProvideRoamingNumber message is used to request a temporary MSRN number from the pool of numbers registered on the VLR / MSC. MSRN has the format (GT) of the country in which the subscriber’s VLR / MSC is located. MSRN is issued at the time of the call, then again falls into the pool of MSRN numbers.
After the MSRN has been allocated, it is sent to the HLR; The HLR in turn sends this MSRN to the GMSC. The GMSC routes this MSRN call to the VLR / MSC serving subscriber B by sending an ISUP IAM message to the dedicated MSRN.
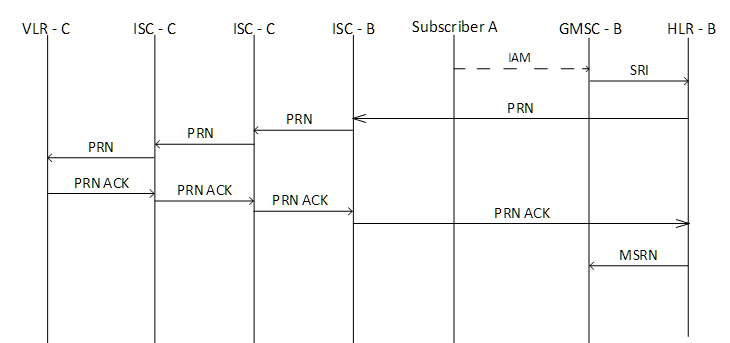
The article will not consider the paging and call setup procedure by ISUP.
Subscriber A, while roaming, calls Subscriber B. For an outgoing call, the Authorization and Update Location procedures described above take place first. First of all, the VLR / MSC in which the subscriber A is registered sends the message “sendRoutingInfo” (which contains the MSISDN of the caller B) to the GMSC. The GMSC, in turn, sends an IAM to the MSISDN number via ISUP. If MSISND belongs to the wired network, then the call goes to the serving PBX number. If the MSISDN belongs to the cellular operator, then the IAM message goes to the GMSC of subscriber B. Then the GMSC sends the “sendRoutingInfo” request to the HLR to find out the address of the VLR / MSC serving the subscriber B and its IMSI. After the HLR has provided this information, the GMSC sends the IAM to this VLR / MSC.
Subscriber A, while roaming, sends an SMS to subscriber B. After the VLR / MSC has received a message from the subscriber, sends it via the SCCP provider to the SMSC of the home network via the GMSC. The SMSC sends the “sendRoutingInfoForSM” message to the subscriber B's HLR, after which the HLR responds with the VLR / MSC address (in which the subscriber B is located) and the IMSI to the SMS center. The SMSC then sends the “forward SM” message to the VLR / MSC of subscriber B.
Subscriber A sends an SMS to subscriber B who is roaming. The principle is similar to that described in the outgoing message. From the SMSC of subscriber A via the SCCP provider, the message “sendRoutingInfoForSM” is sent to the GMSC, and then to the VLR / MSC, in the zone of which subscriber B. is located. After that, the VLR / MSC responds to the IMSI and its address. After this procedure, a forwardSM message is sent from the SMSC of subscriber A. The VLR / MSC, upon receiving this message, attempts to deliver the message to the subscriber. If the message is delivered, the VLR / MSC replies "forwardSM END".
Home routing
On “homerouting”, the HLR issues a fake IMSI and a VLR / MSC address. SMS is sent to the virtual MSC, and then the virtual MSC sends the SMS to the real MSC.
About the service
Roaming is a service that allows subscribers to make calls, use data transfer service, use other services provided by the operator, being in the networks of other operators, including foreign ones, with which the subscriber operator has a roaming agreement. In this case, the phone number of the subscriber remains unchanged.
National roaming r - is the ability to use the services of a "foreign" network within the same country.
International roaming is an opportunity to use the services of a mobile network of a foreign operator with which there is an agreement. The article will describe this type of roaming.
Authorization
The first action that occurs when trying to register on the network of a foreign partner is to check the subscriber for “validity”. This is done by the VLR / MSC, in which the MS is located. After the guest VLR / MSC receives the “Location Update” command from MS, knowing the subscriber’s IMSI, sends the message “Send Authentication Info” to the HLR via MAP; he in turn checks that the MS and the received IMSI are valid. If the verification is successful and the subscriber is “valid”, the HLR sends the IMSI to the AUC. AUC generates a triplet (SRES, RAND, Kc) and sends it to the HLR, then the HLR sends this data to the VLR / MSC that serves the MS. After the VLR / MSC has received this data, the VLR / MSC sends the RAND to the MS. Upon receiving the RAND request, MS substitutes the received RAND and Ki (recorded on the SIM card) and calculates SRES, which is sent to the VLR / MSC. If the SRES received from the MS is the same as the SRES received from the AUC, then the MS is considered authorized.

')
Update Location
After VLC / MSC has authorized MS, it sends an Update Location message to the home HLR. This message is sent so that the HRL knows which VLR / MSC is in range of the subscriber. The message “Update Location” contains the subscriber's IMSI and the GT VLR / MSC. The HLR, after receiving the data, will check if the roaming service is connected. If the subscriber does not have a ban, the HLR will delete the subscriber profile from the VLR / MSC where the subscriber was registered prior to this procedure, by sending the message “Cancel Location”. The HLR also sends the subscriber profile to the VLC / MSC requesting this information using the “Insert Subscriber Data” message. After the VLR / MSC receives this information, the “Update location” will be completed, and the HLR will keep the VLR / MSC address that requested the Update location in the subscriber profile. At this stage, the “Update Location” is finished. When a call or SMS arrives, the HLR knows which VLR / MSC to send it to.
After these procedures, the subscriber is considered to be registered in the network, i.e. he can make and receive calls, SMS, use other available services. Let us consider in more detail the procedures of incoming and outgoing call.

Incoming call
From subscriber A, a call is received to subscriber B who is in roaming. Subscriber A dials the number of subscriber A (MSISDN). If it is a call from the city network, the ISUP IAM message will go to the GMSC, then the GMSC will determine the HLR address based on the received MSISDN and send the message “sendRoutingInfo” using the MAP protocol to the HLR. The HLR, having received MSISND, determines the IMSI of subscriber B, as well as which VLR / MSC the subscriber is in. The HLR then sends the ProvideRoamingNumber message via the MAP protocol to the VLR / MSC which contains the IMSI of the subscriber B. The ProvideRoamingNumber message is used to request a temporary MSRN number from the pool of numbers registered on the VLR / MSC. MSRN has the format (GT) of the country in which the subscriber’s VLR / MSC is located. MSRN is issued at the time of the call, then again falls into the pool of MSRN numbers.
After the MSRN has been allocated, it is sent to the HLR; The HLR in turn sends this MSRN to the GMSC. The GMSC routes this MSRN call to the VLR / MSC serving subscriber B by sending an ISUP IAM message to the dedicated MSRN.

The article will not consider the paging and call setup procedure by ISUP.
Outgoing call
Subscriber A, while roaming, calls Subscriber B. For an outgoing call, the Authorization and Update Location procedures described above take place first. First of all, the VLR / MSC in which the subscriber A is registered sends the message “sendRoutingInfo” (which contains the MSISDN of the caller B) to the GMSC. The GMSC, in turn, sends an IAM to the MSISDN number via ISUP. If MSISND belongs to the wired network, then the call goes to the serving PBX number. If the MSISDN belongs to the cellular operator, then the IAM message goes to the GMSC of subscriber B. Then the GMSC sends the “sendRoutingInfo” request to the HLR to find out the address of the VLR / MSC serving the subscriber B and its IMSI. After the HLR has provided this information, the GMSC sends the IAM to this VLR / MSC.
Outgoing sms
Subscriber A, while roaming, sends an SMS to subscriber B. After the VLR / MSC has received a message from the subscriber, sends it via the SCCP provider to the SMSC of the home network via the GMSC. The SMSC sends the “sendRoutingInfoForSM” message to the subscriber B's HLR, after which the HLR responds with the VLR / MSC address (in which the subscriber B is located) and the IMSI to the SMS center. The SMSC then sends the “forward SM” message to the VLR / MSC of subscriber B.
Incoming SMS
Subscriber A sends an SMS to subscriber B who is roaming. The principle is similar to that described in the outgoing message. From the SMSC of subscriber A via the SCCP provider, the message “sendRoutingInfoForSM” is sent to the GMSC, and then to the VLR / MSC, in the zone of which subscriber B. is located. After that, the VLR / MSC responds to the IMSI and its address. After this procedure, a forwardSM message is sent from the SMSC of subscriber A. The VLR / MSC, upon receiving this message, attempts to deliver the message to the subscriber. If the message is delivered, the VLR / MSC replies "forwardSM END".
Home routing
On “homerouting”, the HLR issues a fake IMSI and a VLR / MSC address. SMS is sent to the virtual MSC, and then the virtual MSC sends the SMS to the real MSC.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/228527/
All Articles