HD-Voice for cellular communication - Khariton, Dmitry, Vladimir, Oleg, Irina, Glory!

We enabled HD-Voice on the Beeline network in Moscow. Below are sound recordings before and after, as well as technical details.
The HD-voice mode is based on AMR-WB technology (Adaptive Multi Rate Rate Wadeband) - a broadband adaptive coding with variable speed, also this codec is known as the G.722.22 standard. In theory, a person can hear sounds in the range of 20 Hz - 20 kHz, but in practice it is enough to transmit sound in a much narrower range. When encoding speech in AMR-WB, a frequency band of 50Hz-7kHz is used, which is absolutely enough for full voice transmission. For example, the AMR codec uses a range of 300-3 kHz. The method can be used in 2G and 3G networks.
')
Simply put, now the human voice will sound more natural , because it will cease to “squeeze” into a rather narrow band, the need of which was once dictated by the limitations of infrastructure. In addition, with HD coding, ambient noise has less of an effect on speech intelligibility.
How did we get to HD-Voice, and how does it work?
A person is able to hear a certain band of sound frequencies, usually it is assumed to be equal to 20Hz-20kHz. Transmitting the entire spectrum over wireless communication channels without compression is difficult, so the voice without cutting the band is transmitted only in wired systems. For speech compression, voice codecs or vocoders are used. Their side effect is the distortion of the transmitted voice by limiting the frequency band of the voice message.
The very first voice codec used in mobile networks was “Full Rate” - FR. Simultaneously with the FR, the Half Rate codec was introduced, the only purpose of which is to increase the number of simultaneously served subscribers, and, as its name implies, it occupies half of the FR codec band in the radio channel. However, the voice quality after transcoding to FR was not very high, and for some countries (for example, Arabic, where speech speed is high and many high-frequency sounds), it is completely unacceptable. Therefore, the FR codec has been reworked, and the “Enhanced Full Rate” appeared, providing significantly better voice quality, with a lower bitrate being created.
With the increasing penetration of mobile networks, the requirements for the quality of voice services began to grow, and a problem appeared with the deterioration of voice quality, with a low radio signal level from the base station. To solve this problem, a new codec was developed - “Adaptive Multi Rate”, which used the same frequency range for analysis and compression, but the algorithm was implemented in such a way that the codec bitrate dynamically changed, depending on the quality of the received signal. Due to this, an opportunity to provide excellent voice quality under good radio conditions, and for bad ones, to keep the conversation even where FR / EFR codecs could not work at all.
All 3G networks work only with the use of the AMR codec or its subsequent implementations, for example AMR-WB. But since the network remains a large number of subscribers using phones that support only work with EFR / HR codecs, the 2G network continues to work with all codecs (FR / EFR / HR / AMR FR / AMR HR) at once, providing voice to any phone.
Currently, voice quality requirements in mobile networks continue to grow, and the time has come to use AMR-WB technology. All the codecs described above use the frequency range up to 200Hz-3.4kHz for compression, while AMR-WB uses the voice message band at 50Hz-7kHz for coding. AMR-WB allows you to transmit twice the bandwidth, which gives an increase in the quality and saturation of the high and low frequencies of the transmitted voice.
Some characteristics of codecs are listed in the table:
Codec | Standard | Year of creation | Compressible frequency range | Generated bitrate |
Full Rate - FR | GSM 06.10 | 1990 | 13 kbit / s | |
Half Rate - HR | GSM 06.20 | 1990 | 5.6 kbit / s | |
Enhanced Full Rate - EFR | GSM 06.60 | 1995 | 12.2 kbit / s | |
Adaptive Multi Rate - AMR | 3GPP TS 26.071 | 1999 | 4.75 - 12.20 kbit / s | |
Adaptive Multi Rate - WideBand - AMR-WB | 3GPP TS 26.190 | 2001 | 6.60 - 23.85 kbit / s | |
Adaptive Multi Rate-WideBand + - AMR-WB + | 3GPP TS 26.290 | 2004 | 6 - 36 kbit / s (mono) 7 - 48 kbit / s (stereo) |
Hint for curious programmers: a sample of the implementation of the AMR codec in the C language is available in the 3GPP TS 26.073 standard (you can easily find it, download it and try to implement it).
In the diagram below you can see a comparison of voice quality, according to the MOS (Mean Opinion Score) scale, depending on the codec used. The MOS scale is a subjective assessment of voice quality from 0 to 5, where 0 is a total lack of audibility, and 5 is live speech. G.711 codec is used in wired telephony, that is, this is the quality that you should hear from your landline phone (if it is, of course, not transferred to the IP channel, but this is a completely different topic).
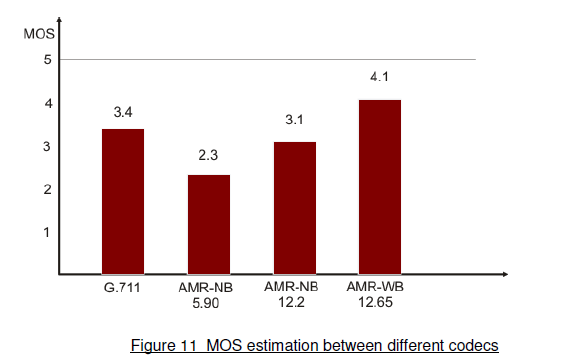
Update: The comments rightly indicated that the average MOS score for the G.711 codec is about 4.1, this picture distorts reality a little.
As can be seen from the diagram (and taking into account the information from the Update), the AMR-WB codec provides, under good radio conditions, the voice quality is similar to the one we are used to when using a wired home phone.
For example, two fragments of a musical composition, which were compressed by AMR and AMR-WB codecs, you can compare the sound quality yourself and visually assess the difference in the sound picture created by different codecs.
AMR coded top track
Bottom track encoded in AMR-WB
Tests
We are not the first to launch this technology in Russia, so some developments have already been made. Our first part of the network with HD-Voice was built within the Moscow Ring Road, on the equipment of Ericsson. Activating AMR-WB took a long time: first, it was tested on one controller (with numerous drive tests to measure speech quality). And even after everything was tested on one controller, the subsequent activation proceeded in stages, controller by controller. The whole activation process took almost half a year.
Here are the sample samples from the final tests , which were evaluated by hardware using accurate measurements at different times.
Does it already work?
Yes, now the technology is implemented in the 3G network for Moscow. In order to use the mode, you do not need to make additional settings, it is activated itself, if both subscribers are in the 3G network and both their phones support the work of the codec.
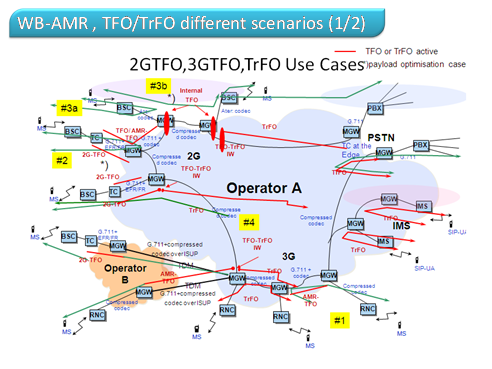
The diagram shows the conditions that are necessary for the operation of AMR-WB. Now, as mentioned above, the codec is running on the 3G network, the next stage is to ensure the codec works between the 2G and 3G networks, then between the networks and between the operators.
What devices are supported?
List. Carefully, under the spoiler a lot of letters.
Alcatel One Touch 903
Alcatel One Touch 916 / 916D
Alcatel One Touch 918
Alcatel One Touch 983
Alcatel One Touch 985 / 985D
Alcatel One Touch 991 / 991D / 991T
Alcatel One Touch 992D
Alcatel One Touch 993 / 993D
Alcatel One Touch 995/996
Alcatel One Touch Idol
Alcatel One Touch Idol Ultra
Alcatel One Touch Scribe Easy
Alcatel One Touch Scribe HD
Alcatel One Touch Star
Alcatel One Touch Tribe
Alcatel One X'POP
Apple iPhone 5
Apple iPhone 5S
Apple iPhone 5C
Blackberry q10
Blackberry q5
BlackBerry Torch 9810
Blackberry z10
Blackberry z30
HTC Desire 500
HTC ChaCha
HTC Desire C
HTC Desire HD
HTC Desire S
HTC Desire X
HTC Desire Z
HTC EVO 3D
HTC Incredible
HTC One
HTC One mini
HTC One S
HTC One SV
HTC One V
HTC One X
HTC One X +
HTC One XL
HTC One (M8)
HTC Radar
HTC Raider
HTC Rhyme
HTC Sensation
HTC Sensation XE
HTC Sensation XL
HTC Titan
HTC Touch HD
HTC Wildfire S
HTC Windows Phone 8X
HTC Windows Phone 8S
Huawei Ascend D Quad
Huawei Ascend D2 LTE (VoLTE)
Huawei Ascend G510
Huawei Ascend G740
Huawei Ascend P1 U9200
Huawei Ascend P2
Huawei Ascend P6
Huawei Boulder U8350
LG A310
LG Nexus 4 E960
LG Nexus 5
LG Optimus 3D
LG Optimus G
LG Optimus G Pro
LG Optimus L4 II
LG Optimus L5
LG Optimus L5 II
LG Optimus L7
LG Optimus L7 II
LG Optimus L9
LG Optimus LTE2 F160LV (VoLTE)
LG Optimus F7
LG Optimus F180S (VoLTE)
LG Optimus Vu2 F200 (K, L, S) (VoLTE)
LG Optimus Vu3 F300 (K, L, S) (VoLTE)
LG Optimus GX F310L (VoLTE)
LG Optimus G2 F320S (VoLTE)
LG Optimus G Pro F240S (VoLTE)
LG Optimus LTE III F260S (VoLTE)
LG Optimus G Flex F340S (VoLTE)
LG Optimus 3D Max (P720)
LG Optimus 3D (P920)
LG Optimus 4X HD (P880)
LG Prada (P940)
LG Prada 3.0
Motorola quench
Motorola RAZR (XT910)
Motorola RAZR i (XT890)
Motorola Moto G
Nokia 300
Nokia 301
Nokia 302
Nokia 500
Nokia 515
Nokia 600
Nokia 603
Nokia 700
Nokia 701
Nokia 808 PureView
Nokia 5230
Nokia 5330 Mobile TV Edition
Nokia 5530 XpressMusic
Nokia 5630 XpressMusic
Nokia 5730 XpressMusic
Nokia 6260 Slide
Nokia 6600i slide
Nokia 6700 classic
Nokia 6700 slide
Nokia 6710 Navigator
Nokia 6720 classic
Nokia 6760 slide
Nokia 6790 slide
Nokia 7230
Nokia Asha 300
Nokia Asha 301
Nokia Asha 302
Nokia Asha 303
Nokia Asha 311
Nokia C2-01
Nokia C3-01 Touch and Type
Nokia C5-03
Nokia C5-04
Nokia C6-00
Nokia C6-01
Nokia C7-00
Nokia E5-00
Nokia E52
Nokia E55
Nokia E6-00
Nokia E63
Nokia E7 Communicator
Nokia E7-00
Nokia E71x
Nokia E72
Nokia E73 Mode
Nokia Lumia 510
Nokia Lumia 520
Nokia Lumia 520.2
Nokia Lumia 521
Nokia Lumia 610
Nokia Lumia 610 NFC
Nokia Lumia 620
Nokia Lumia 625
Nokia Lumia 710
Nokia Lumia 720
Nokia Lumia 800
Nokia Lumia 810
Nokia Lumia 820
Nokia Lumia 822
Nokia Lumia 900
Nokia Lumia 920
Nokia Lumia 920T
Nokia Lumia 925
Nokia Lumia 925 Superman Edition
Nokia Lumia 925T
Nokia Lumia 928
Nokia Lumia 929 LTE-A (Cat 4)
Nokia Lumia 1020.2
Nokia Lumia 1020 3G
Nokia Lumia 1020 LTE
Nokia Lumia 1520
Nokia N7
Nokia N8
Nokia N86 8MP
Nokia N9
Nokia N97
Nokia N97 mini
Nokia X3-02
Nokia X5
Nokia X6-00
Nokia X7-00
Samsung Galaxy Star
Samsung Galaxy Light
Samsung Ativ S
Samsung galaxy ace
Samsung Galaxy Ace 2
Samsung Galaxy Express
Samsung Galaxy Fame
Samsung Galaxy Mini
Samsung Galaxy Mini 2
Samsung Galaxy Nexus
Samsung Galaxy Note
Samsung Galaxy Note II
Samsung Galaxy Note 3
Samsung Galaxy Note 10.1
Samsung Galaxy S II
Samsung Galaxy S III
Samsung Galaxy S4
Samsung Galaxy S4 Mini
Samsung Galaxy S5
Samsung Galaxy S Advance
Samsung Galaxy S Plus
Samsung Galaxy W
Samsung Galaxy Y
Samsung Omnia 7
Samsung Omnia Pro B7350
Samsung S5610
Samsung Wave 3
Samsung Trend Plus
Sony Ericsson Elm
Sony Ericsson Hazel
Sony Ericsson Live with Walkman
Sony Ericsson Xperia X8
Sony Ericsson Xperia X10 Mini
Sony Ericsson Xperia X10 mini pro
Sony Ericsson Xperia acro
Sony Ericsson Xperia active
Sony Ericsson Xperia Arc
Sony Ericsson Xperia arc S
Sony Ericsson Xperia mini
Sony Ericsson Xperia Mini Pro
Sony Ericsson Xperia neo
Sony Ericsson Xperia Neo V
Sony Ericsson Xperia Play
Sony Ericsson Xperia ray
Sony Ericsson W995
Sony Xperia A SO-04E
Sony xperia acro s
Sony xperia e
Sony Xperia E dual C1605
Sony Xperia Go (ST27i)
Sony Xperia i1 HSPA + C6902
Sony Xperia i1 LTE
Sony xperia ion
Sony xperia j
Sony xperia l
Sony xperia m
Sony Xperia M35t (VoLTE)
Sony xperia miro
Sony Xperia P
Sony xperia s
Sony xperia sola
Sony Xperia SP
Sony xperia t
Sony xperia tipo
Sony Xperia Tipo Dual
Sony xperia u
Sony xperia v
Sony Xperia Z
Sony Xperia ZL
Sony Xperia ZR
Sony Xperia Z1
Sony Xperia Z1S (T Mobile US only)
Sony Xperia Z1 Compact LTE-A D5503
Sony Xperia Z2 LTE-A D6543 / D6503
TechFaith Wildfire 80
ZTE Blade V880
ZTE Crescent (San Francisco 2 on Orange)
ZTE Era
ZTE F160 Atlanta
ZTE Grand X
ZTE Grand X IN
ZTE Orbit
ZTE R252 / Orange Tara
ZTE Kis Pro / Orange Zali
ZTE Skate (Monte Carlo on Orange)
ZTE Smart Netphone 701
ZTE Tania
ZTE TMN smart A15
Alcatel One Touch 916 / 916D
Alcatel One Touch 918
Alcatel One Touch 983
Alcatel One Touch 985 / 985D
Alcatel One Touch 991 / 991D / 991T
Alcatel One Touch 992D
Alcatel One Touch 993 / 993D
Alcatel One Touch 995/996
Alcatel One Touch Idol
Alcatel One Touch Idol Ultra
Alcatel One Touch Scribe Easy
Alcatel One Touch Scribe HD
Alcatel One Touch Star
Alcatel One Touch Tribe
Alcatel One X'POP
Apple iPhone 5
Apple iPhone 5S
Apple iPhone 5C
Blackberry q10
Blackberry q5
BlackBerry Torch 9810
Blackberry z10
Blackberry z30
HTC Desire 500
HTC ChaCha
HTC Desire C
HTC Desire HD
HTC Desire S
HTC Desire X
HTC Desire Z
HTC EVO 3D
HTC Incredible
HTC One
HTC One mini
HTC One S
HTC One SV
HTC One V
HTC One X
HTC One X +
HTC One XL
HTC One (M8)
HTC Radar
HTC Raider
HTC Rhyme
HTC Sensation
HTC Sensation XE
HTC Sensation XL
HTC Titan
HTC Touch HD
HTC Wildfire S
HTC Windows Phone 8X
HTC Windows Phone 8S
Huawei Ascend D Quad
Huawei Ascend D2 LTE (VoLTE)
Huawei Ascend G510
Huawei Ascend G740
Huawei Ascend P1 U9200
Huawei Ascend P2
Huawei Ascend P6
Huawei Boulder U8350
LG A310
LG Nexus 4 E960
LG Nexus 5
LG Optimus 3D
LG Optimus G
LG Optimus G Pro
LG Optimus L4 II
LG Optimus L5
LG Optimus L5 II
LG Optimus L7
LG Optimus L7 II
LG Optimus L9
LG Optimus LTE2 F160LV (VoLTE)
LG Optimus F7
LG Optimus F180S (VoLTE)
LG Optimus Vu2 F200 (K, L, S) (VoLTE)
LG Optimus Vu3 F300 (K, L, S) (VoLTE)
LG Optimus GX F310L (VoLTE)
LG Optimus G2 F320S (VoLTE)
LG Optimus G Pro F240S (VoLTE)
LG Optimus LTE III F260S (VoLTE)
LG Optimus G Flex F340S (VoLTE)
LG Optimus 3D Max (P720)
LG Optimus 3D (P920)
LG Optimus 4X HD (P880)
LG Prada (P940)
LG Prada 3.0
Motorola quench
Motorola RAZR (XT910)
Motorola RAZR i (XT890)
Motorola Moto G
Nokia 300
Nokia 301
Nokia 302
Nokia 500
Nokia 515
Nokia 600
Nokia 603
Nokia 700
Nokia 701
Nokia 808 PureView
Nokia 5230
Nokia 5330 Mobile TV Edition
Nokia 5530 XpressMusic
Nokia 5630 XpressMusic
Nokia 5730 XpressMusic
Nokia 6260 Slide
Nokia 6600i slide
Nokia 6700 classic
Nokia 6700 slide
Nokia 6710 Navigator
Nokia 6720 classic
Nokia 6760 slide
Nokia 6790 slide
Nokia 7230
Nokia Asha 300
Nokia Asha 301
Nokia Asha 302
Nokia Asha 303
Nokia Asha 311
Nokia C2-01
Nokia C3-01 Touch and Type
Nokia C5-03
Nokia C5-04
Nokia C6-00
Nokia C6-01
Nokia C7-00
Nokia E5-00
Nokia E52
Nokia E55
Nokia E6-00
Nokia E63
Nokia E7 Communicator
Nokia E7-00
Nokia E71x
Nokia E72
Nokia E73 Mode
Nokia Lumia 510
Nokia Lumia 520
Nokia Lumia 520.2
Nokia Lumia 521
Nokia Lumia 610
Nokia Lumia 610 NFC
Nokia Lumia 620
Nokia Lumia 625
Nokia Lumia 710
Nokia Lumia 720
Nokia Lumia 800
Nokia Lumia 810
Nokia Lumia 820
Nokia Lumia 822
Nokia Lumia 900
Nokia Lumia 920
Nokia Lumia 920T
Nokia Lumia 925
Nokia Lumia 925 Superman Edition
Nokia Lumia 925T
Nokia Lumia 928
Nokia Lumia 929 LTE-A (Cat 4)
Nokia Lumia 1020.2
Nokia Lumia 1020 3G
Nokia Lumia 1020 LTE
Nokia Lumia 1520
Nokia N7
Nokia N8
Nokia N86 8MP
Nokia N9
Nokia N97
Nokia N97 mini
Nokia X3-02
Nokia X5
Nokia X6-00
Nokia X7-00
Samsung Galaxy Star
Samsung Galaxy Light
Samsung Ativ S
Samsung galaxy ace
Samsung Galaxy Ace 2
Samsung Galaxy Express
Samsung Galaxy Fame
Samsung Galaxy Mini
Samsung Galaxy Mini 2
Samsung Galaxy Nexus
Samsung Galaxy Note
Samsung Galaxy Note II
Samsung Galaxy Note 3
Samsung Galaxy Note 10.1
Samsung Galaxy S II
Samsung Galaxy S III
Samsung Galaxy S4
Samsung Galaxy S4 Mini
Samsung Galaxy S5
Samsung Galaxy S Advance
Samsung Galaxy S Plus
Samsung Galaxy W
Samsung Galaxy Y
Samsung Omnia 7
Samsung Omnia Pro B7350
Samsung S5610
Samsung Wave 3
Samsung Trend Plus
Sony Ericsson Elm
Sony Ericsson Hazel
Sony Ericsson Live with Walkman
Sony Ericsson Xperia X8
Sony Ericsson Xperia X10 Mini
Sony Ericsson Xperia X10 mini pro
Sony Ericsson Xperia acro
Sony Ericsson Xperia active
Sony Ericsson Xperia Arc
Sony Ericsson Xperia arc S
Sony Ericsson Xperia mini
Sony Ericsson Xperia Mini Pro
Sony Ericsson Xperia neo
Sony Ericsson Xperia Neo V
Sony Ericsson Xperia Play
Sony Ericsson Xperia ray
Sony Ericsson W995
Sony Xperia A SO-04E
Sony xperia acro s
Sony xperia e
Sony Xperia E dual C1605
Sony Xperia Go (ST27i)
Sony Xperia i1 HSPA + C6902
Sony Xperia i1 LTE
Sony xperia ion
Sony xperia j
Sony xperia l
Sony xperia m
Sony Xperia M35t (VoLTE)
Sony xperia miro
Sony Xperia P
Sony xperia s
Sony xperia sola
Sony Xperia SP
Sony xperia t
Sony xperia tipo
Sony Xperia Tipo Dual
Sony xperia u
Sony xperia v
Sony Xperia Z
Sony Xperia ZL
Sony Xperia ZR
Sony Xperia Z1
Sony Xperia Z1S (T Mobile US only)
Sony Xperia Z1 Compact LTE-A D5503
Sony Xperia Z2 LTE-A D6543 / D6503
TechFaith Wildfire 80
ZTE Blade V880
ZTE Crescent (San Francisco 2 on Orange)
ZTE Era
ZTE F160 Atlanta
ZTE Grand X
ZTE Grand X IN
ZTE Orbit
ZTE R252 / Orange Tara
ZTE Kis Pro / Orange Zali
ZTE Skate (Monte Carlo on Orange)
ZTE Smart Netphone 701
ZTE Tania
ZTE TMN smart A15
Recognition problems
Human speech is such that in the radio and on a narrow band of the audio spectrum, the sounds of “C” and “F” are poorly distinguished. Couples “T” and “P”, “M” and “H” also suffer. Hence the mnemonic system with the names: “I dictate, number two-zero-zero, three Olga, as I understand it, reception?”. From here, things like the assignment of the most critical parts of the call sign to “p” grow up - for example, a sniper who in no case should confuse his call sign will most likely be “thirty-third” because it is very well discernible on air in narrow conditions. stripes.
Voice recognition is also growing with HD-Voice. This is important both for personal communication and for additional voice authentication gaining popularity, for example, in banks.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/228231/
All Articles