42 yoctonewton
42 yoctonewtons, or 42 * 10 -24 Newtons, is a force that affects a cloud of 1200 rubidium atoms cooled to almost zero kelvins in a unique experiment conducted by scientists from Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory. This is the weakest force ever measured by man. It is only four times the theoretical minimum ( standard quantum limit ), below which no force can be measured due to the fundamental limitations of quantum mechanics. The previous “weakness record” (174 yoktonyuton) was set in 2010.
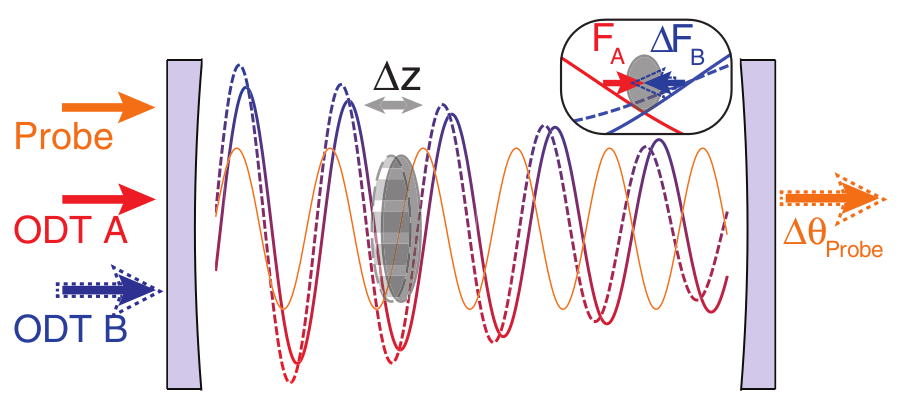
The scheme of the experiment is shown in the figure. A cloud of rubidium atoms is used as a mechanical oscillator. Atoms are held in an optical trap — between the fronts of a standing light wave, which is supported by lasers A and B with wavelengths of 860 and 840 nm. Such a trap allows you to keep a cloud of atoms in the right place without heating them. By modulating the amplitude of laser B, you can make the oscillator oscillate with a certain frequency. Oscillations are recorded by changing the phase of the third light wave passing through the cloud. Knowing the oscillator mass and the magnitude of its deflection under the influence of an external force, we can calculate this force.
The measurement of such small forces is of great practical importance for the development of scientific instruments. A new measurement method can be used in gravitational wave detectors and in scanning atomic-force microscopes . Scientists who have made a record measurement say that it will be possible to come even closer to the standard quantum limit if it is possible to cool the oscillator even more and improve the sensitivity of the optical detector.
')

The scheme of the experiment is shown in the figure. A cloud of rubidium atoms is used as a mechanical oscillator. Atoms are held in an optical trap — between the fronts of a standing light wave, which is supported by lasers A and B with wavelengths of 860 and 840 nm. Such a trap allows you to keep a cloud of atoms in the right place without heating them. By modulating the amplitude of laser B, you can make the oscillator oscillate with a certain frequency. Oscillations are recorded by changing the phase of the third light wave passing through the cloud. Knowing the oscillator mass and the magnitude of its deflection under the influence of an external force, we can calculate this force.
The measurement of such small forces is of great practical importance for the development of scientific instruments. A new measurement method can be used in gravitational wave detectors and in scanning atomic-force microscopes . Scientists who have made a record measurement say that it will be possible to come even closer to the standard quantum limit if it is possible to cool the oscillator even more and improve the sensitivity of the optical detector.
')
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/228077/
All Articles