Mars rover Curiosity completed the main scientific mission
Curiosity - year. I already wrote this phrase, but today the Martian year has passed, which lasts a little less than two Earth years. The rover's clock counted 668 solos (Martian days) and this means that you can celebrate the anniversary of the Martian epic in the Gale crater.
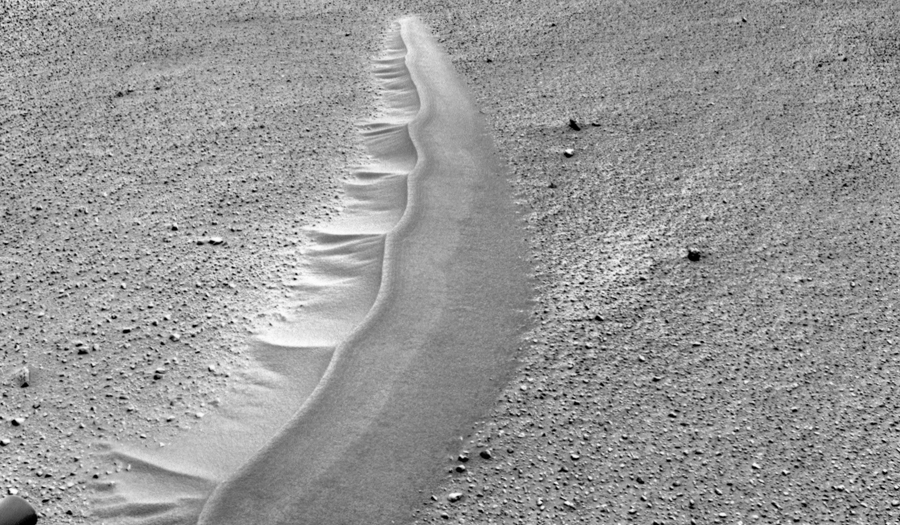

Over the entire journey, more than 8 kilometers was covered, but the rover did not reach the main goal of its journey - Mount Eolid (Sharp), although it diligently walks toward it for over a year. Therefore, his main research and probable discoveries are still ahead.
')
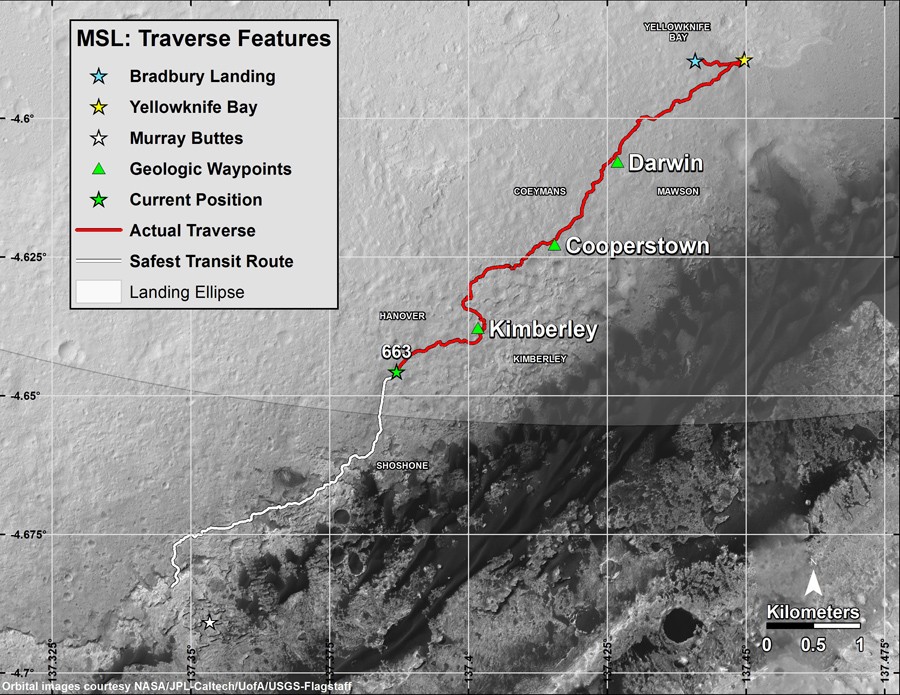
Initially, the term of the main scientific mission was called in one Martian year. That is, today Curiosity has realized the minimum for which it was sent to Mars, and even now NASA can report that the work of the rover has been successfully completed. Of course, no one will disconnect him, and he will continue research until the full development of his resource, which can be enough for 10-15 Earth years. Earlier, for Mars rovers of the previous generation, NASA called the term of the main scientific program 90 days, but Opportunity exceeded these plans more than 40 times, we wish the same efficiency and Curiosity.
On the anniversary it would be good to traditionally sum up the work. But the journey to the mountain led to the fact that much time was spent on scientific research than in the first months after landing. Therefore, new information has been added a little since the time when we did surveys on the anniversary of landing or on the basis of 2013 . Since then, the rover drilled a new well, and is now on the road engaged in analyzing the collected samples.
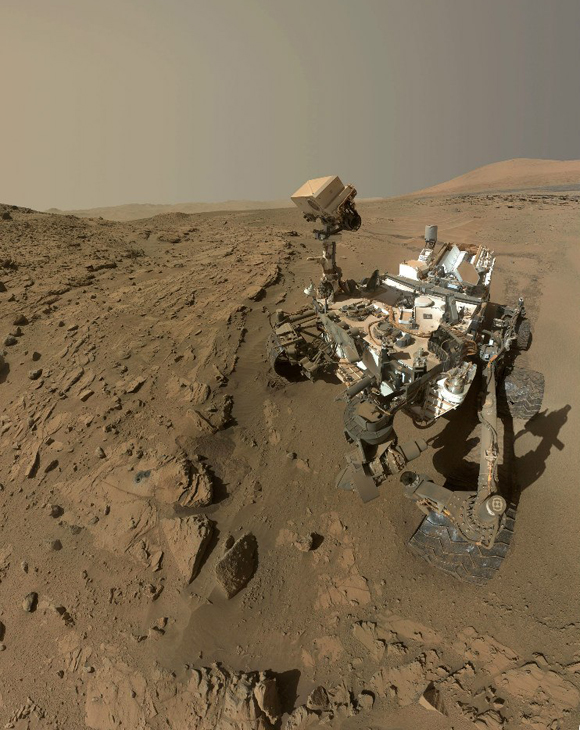

So far we have only been told that we have drilled a rock with a high content of feldspar, which means that the geological history of the Martian crust may be more complicated than it had been previously thought.
Let me briefly remind you of why everything was started.
After Spirit and Opportunity found obvious evidence of the warm and humid past of Mars, science asked itself a new question: were the conditions on Mars suitable for the origin and maintenance of life? To answer this, and a number of other questions, we have assembled a new powerful and heavy rover Curiosity. The answer he gave unexpectedly quickly for everyone - just six months after the start of work: yes, there were times on Mars when the atmosphere was denser, on a planet that had not yet become Red, rivers flowed, and the water there was potable.
Was life on Mars? Not yet known. Curiosity can only detect traces of organic compounds in the soil. Unfortunately, during landing, the SAM device was contaminated with an organic solvent, so now scientists cannot say for sure which organic material was found on Mars and which one was brought with them. It is hoped that subsequent studies will allow more accurate calibration of the device and speak more confidently about the traces of organic compounds in the Martian soil.
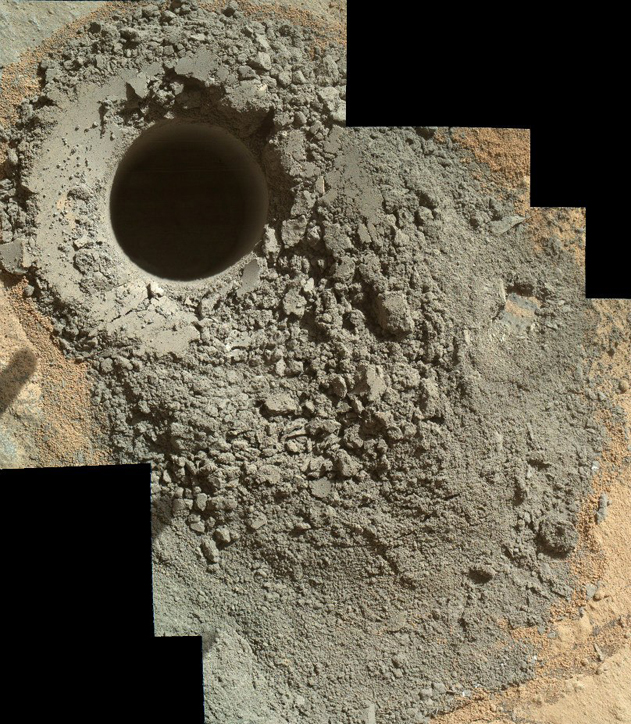

Along the way, Curiosity did a very useful job for future manned flights to Mars - measured radiation in flight and on the surface. The results are encouraging: the background during the flight was about twice as high as on the International Space Station, and on the surface - as on the ISS. In other words, it is possible to live and not necessarily dig in bunkers under multi-meter stratum of soil. With the flight is more difficult, but also real.
In addition, the rover collected abundant information about the climate of Mars, the isotopic composition of the atmosphere and the minerals of the soil, conducted astronomical observations. But I tried to talk about it as new data became available.
Many media outlets told about the anniversary of Curiosity, so now I would like to draw attention to various interesting trivia that can be observed with Curiosity, and which, as a rule, do not fall from official press releases or news agency publications.
Let's talk about dust. Perhaps this is the only object whose movement we can observe on Mars. Apart from the rovers themselves, naturally.
For a year, the dust covered the dense "fur coat" of the body of the rover.

Unlike Opportunity, which is regularly cleaned by local tornadoes, Curiosity sweeps more and more. As it turned out, there are no more or less strong tornadoes in the Gale crater, apparently the conditions are not the same. Small gusts of wind were recorded, but the dust devil was never observed, like in Opportunity.
Another interesting example of movement on Mars can be observed when the vibration from the rover is transmitted along the ground. There are micro-creeps on the sandy slopes, which confirm that Mars is seismically a dead planet. If he had even shaken a little, that sand had slipped even earlier.
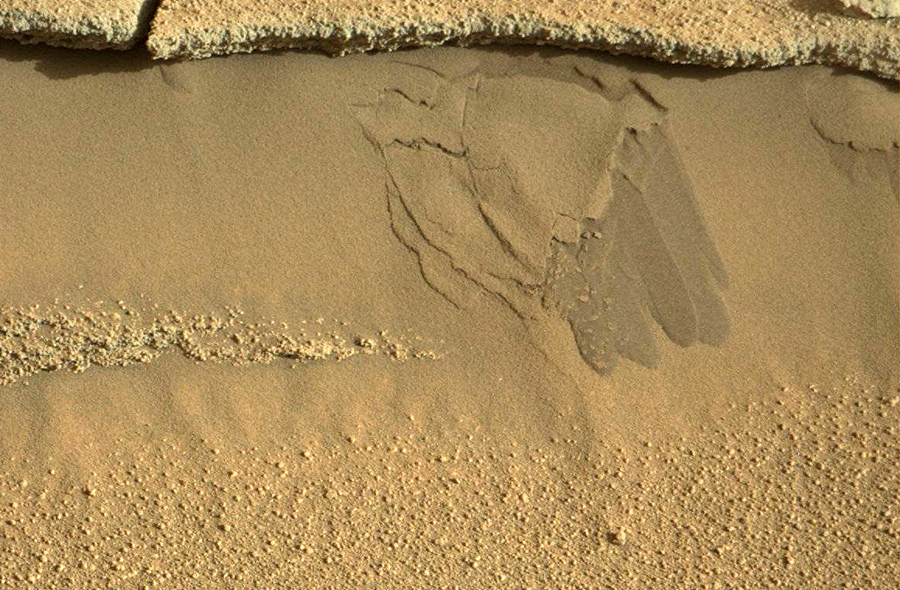

In fact, what makes up the oncoming Martian dunes is not the usual sand, but something between sand and dust. American geologists have a corresponding term "silt", which is different from sand and dust. Under certain conditions, this silt acquires properties comparable to a thick liquid. This became very noticeable when Curiosity began new drilling operations two months ago.

The Curiosity drill is a hammer drill, not just a drill. The inclusion of a vibrator on the manipulator not only caused a landslide and microearthquake, but also had a very beneficial effect on the degree of dustiness of the cameras. Particularly lucky camera MARDI, which was installed only for shooting landing. She was the only one who did not close the dust cover when the landing jet raised clouds of dust. As a result, MARDI issued frames of very mediocre quality.
After two round holes were made in Mars, MARDI began to show pictures better.
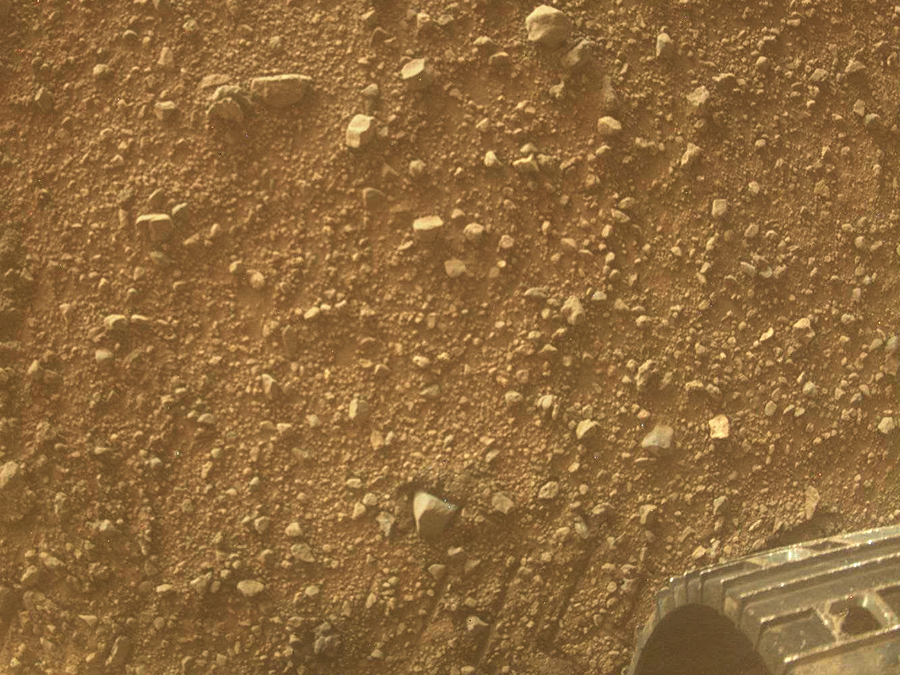

To celebrate, NASA has shot a new video that will show the sweeping surface of Mars, under the wheels of Curiosity. While it is available to us only in the preview.

Full records will have to wait a few weeks or months.
If we talk about the quality of shooting mast cameras, then dust also sits on their lenses, but only slightly, and begins to affect the image only if Curiosity stays in one place for a long time. While moving, shaking effectively cleans the glass. A more significant impact on image quality is influenced by dust, which is constantly hanging in the atmosphere. Thanks to the opportunity to look at the mountains 30-50 kilometers from the rover, we can observe the transparency of the local "air". Once, in the Martian winter, the conditions were such that it was possible to examine the incredibly small details on the ridge 25 kilometers from the rover.
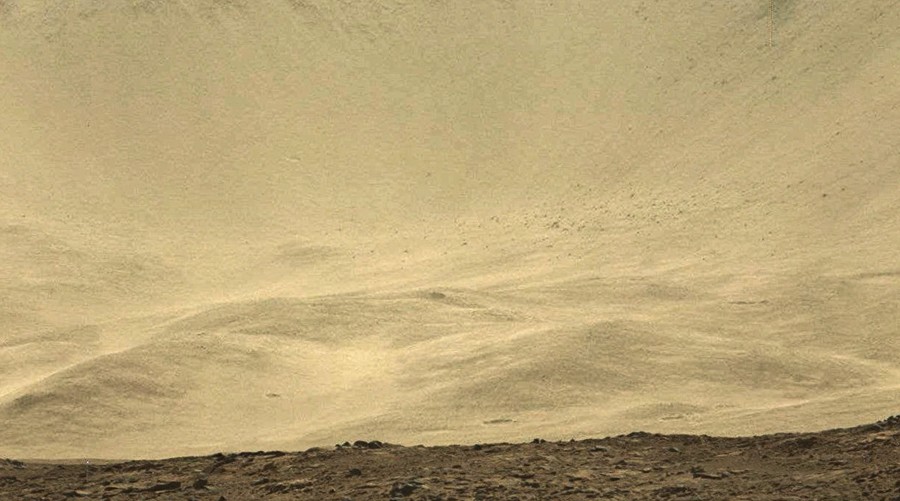

I have never seen such a quality of these slopes, and, apparently, we will not see another year until next winter.
Three hefty metallic meteorites have become the most recent recent discovery of Curiosity:
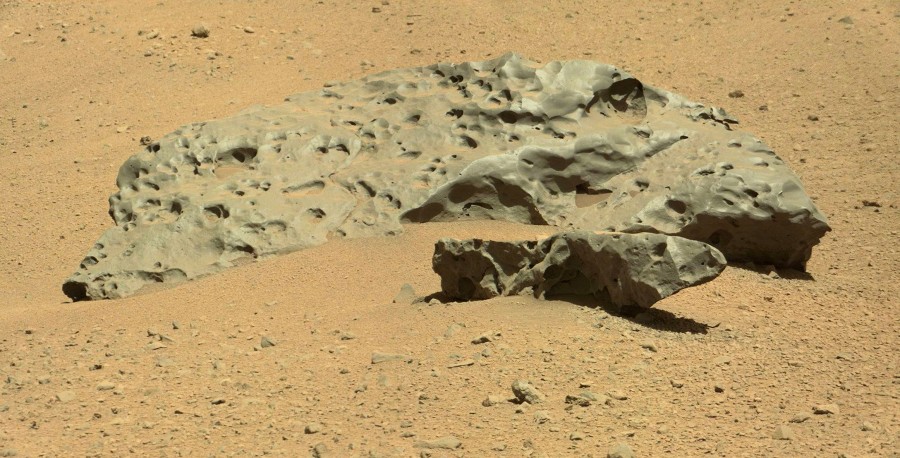

I expected them to undergo serious research, but, oddly enough, NASA limited itself to a cursory inspection from 10 meters, and then the rover moved on. It seems that geologists are so attracted to Sharpe's mountain that they do not want any delays.
To the credit of the drivers of the rover is to say that now they have picked up a good pace. A kilometer in two months is very cool. The truth is now lucky with the surface, which allows you to drive, without worrying about the condition of the wheels. The holes continue to grow, but rather slowly compared to the previous pace.
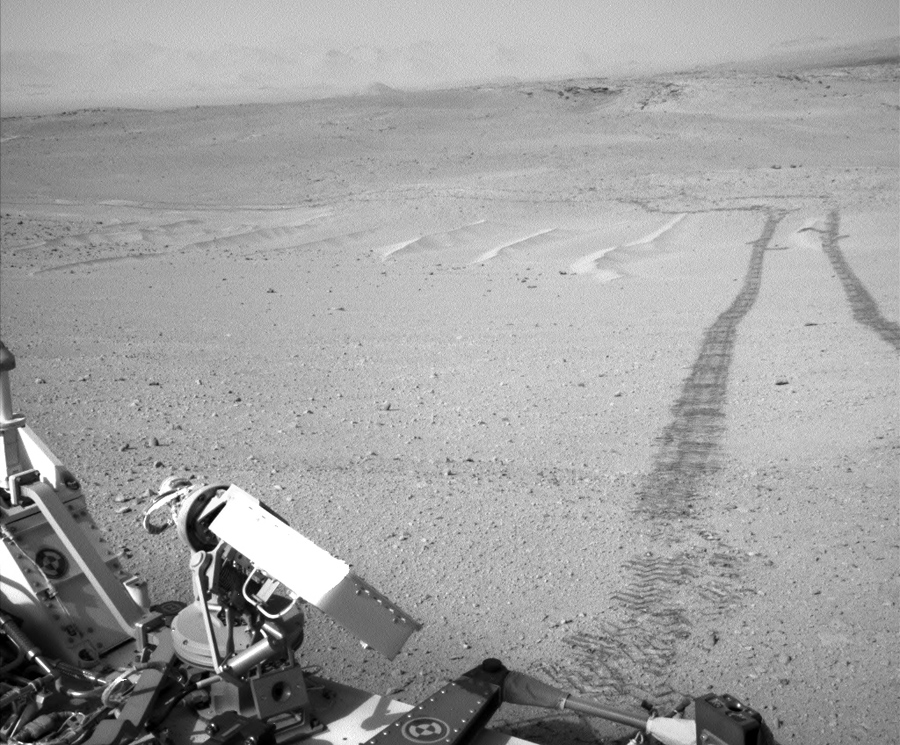

Such a sandy beach will continue for about a kilometer, and then a new type of surface will begin, which is still unfamiliar, but most likely will be very tough. But the dull plains will end, slopes and ravines will begin, and therefore interesting finds at their bottom.

Over the entire journey, more than 8 kilometers was covered, but the rover did not reach the main goal of its journey - Mount Eolid (Sharp), although it diligently walks toward it for over a year. Therefore, his main research and probable discoveries are still ahead.
')

Initially, the term of the main scientific mission was called in one Martian year. That is, today Curiosity has realized the minimum for which it was sent to Mars, and even now NASA can report that the work of the rover has been successfully completed. Of course, no one will disconnect him, and he will continue research until the full development of his resource, which can be enough for 10-15 Earth years. Earlier, for Mars rovers of the previous generation, NASA called the term of the main scientific program 90 days, but Opportunity exceeded these plans more than 40 times, we wish the same efficiency and Curiosity.
On the anniversary it would be good to traditionally sum up the work. But the journey to the mountain led to the fact that much time was spent on scientific research than in the first months after landing. Therefore, new information has been added a little since the time when we did surveys on the anniversary of landing or on the basis of 2013 . Since then, the rover drilled a new well, and is now on the road engaged in analyzing the collected samples.

So far we have only been told that we have drilled a rock with a high content of feldspar, which means that the geological history of the Martian crust may be more complicated than it had been previously thought.
Let me briefly remind you of why everything was started.
After Spirit and Opportunity found obvious evidence of the warm and humid past of Mars, science asked itself a new question: were the conditions on Mars suitable for the origin and maintenance of life? To answer this, and a number of other questions, we have assembled a new powerful and heavy rover Curiosity. The answer he gave unexpectedly quickly for everyone - just six months after the start of work: yes, there were times on Mars when the atmosphere was denser, on a planet that had not yet become Red, rivers flowed, and the water there was potable.
Was life on Mars? Not yet known. Curiosity can only detect traces of organic compounds in the soil. Unfortunately, during landing, the SAM device was contaminated with an organic solvent, so now scientists cannot say for sure which organic material was found on Mars and which one was brought with them. It is hoped that subsequent studies will allow more accurate calibration of the device and speak more confidently about the traces of organic compounds in the Martian soil.

Along the way, Curiosity did a very useful job for future manned flights to Mars - measured radiation in flight and on the surface. The results are encouraging: the background during the flight was about twice as high as on the International Space Station, and on the surface - as on the ISS. In other words, it is possible to live and not necessarily dig in bunkers under multi-meter stratum of soil. With the flight is more difficult, but also real.
In addition, the rover collected abundant information about the climate of Mars, the isotopic composition of the atmosphere and the minerals of the soil, conducted astronomical observations. But I tried to talk about it as new data became available.
Many media outlets told about the anniversary of Curiosity, so now I would like to draw attention to various interesting trivia that can be observed with Curiosity, and which, as a rule, do not fall from official press releases or news agency publications.
Let's talk about dust. Perhaps this is the only object whose movement we can observe on Mars. Apart from the rovers themselves, naturally.
For a year, the dust covered the dense "fur coat" of the body of the rover.

Unlike Opportunity, which is regularly cleaned by local tornadoes, Curiosity sweeps more and more. As it turned out, there are no more or less strong tornadoes in the Gale crater, apparently the conditions are not the same. Small gusts of wind were recorded, but the dust devil was never observed, like in Opportunity.
Another interesting example of movement on Mars can be observed when the vibration from the rover is transmitted along the ground. There are micro-creeps on the sandy slopes, which confirm that Mars is seismically a dead planet. If he had even shaken a little, that sand had slipped even earlier.

In fact, what makes up the oncoming Martian dunes is not the usual sand, but something between sand and dust. American geologists have a corresponding term "silt", which is different from sand and dust. Under certain conditions, this silt acquires properties comparable to a thick liquid. This became very noticeable when Curiosity began new drilling operations two months ago.

The Curiosity drill is a hammer drill, not just a drill. The inclusion of a vibrator on the manipulator not only caused a landslide and microearthquake, but also had a very beneficial effect on the degree of dustiness of the cameras. Particularly lucky camera MARDI, which was installed only for shooting landing. She was the only one who did not close the dust cover when the landing jet raised clouds of dust. As a result, MARDI issued frames of very mediocre quality.
After two round holes were made in Mars, MARDI began to show pictures better.

To celebrate, NASA has shot a new video that will show the sweeping surface of Mars, under the wheels of Curiosity. While it is available to us only in the preview.

Full records will have to wait a few weeks or months.
If we talk about the quality of shooting mast cameras, then dust also sits on their lenses, but only slightly, and begins to affect the image only if Curiosity stays in one place for a long time. While moving, shaking effectively cleans the glass. A more significant impact on image quality is influenced by dust, which is constantly hanging in the atmosphere. Thanks to the opportunity to look at the mountains 30-50 kilometers from the rover, we can observe the transparency of the local "air". Once, in the Martian winter, the conditions were such that it was possible to examine the incredibly small details on the ridge 25 kilometers from the rover.

I have never seen such a quality of these slopes, and, apparently, we will not see another year until next winter.
Three hefty metallic meteorites have become the most recent recent discovery of Curiosity:

I expected them to undergo serious research, but, oddly enough, NASA limited itself to a cursory inspection from 10 meters, and then the rover moved on. It seems that geologists are so attracted to Sharpe's mountain that they do not want any delays.
To the credit of the drivers of the rover is to say that now they have picked up a good pace. A kilometer in two months is very cool. The truth is now lucky with the surface, which allows you to drive, without worrying about the condition of the wheels. The holes continue to grow, but rather slowly compared to the previous pace.

Such a sandy beach will continue for about a kilometer, and then a new type of surface will begin, which is still unfamiliar, but most likely will be very tough. But the dull plains will end, slopes and ravines will begin, and therefore interesting finds at their bottom.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/227669/
All Articles