Traffic Inspector in action: monitor network activity via VPN
Introduction
As you know, VPN technology is used to organize a direct secure connection between clients (the end user and the corporate office) or two local networks through a public Internet channel. Using VPN, remote users can access enterprise servers and communicate with various offices of their company.
VPN does not need dedicated lines, so anyone who has access to the Internet can use it. Once the connection is established, the employee can work with all network resources as if he were in the office. But perhaps the most important advantage of this technology is that, despite the public infrastructure, a direct VPN connection (the so-called VPN tunnel) is so securely protected that it is almost impossible to steal data or gain unauthorized access to a geographically distributed network.
In this article, we will look at how, with the help of Traffic Inspector, we can monitor VPN collaboration in a corporate network and track network activity.
')
Configuration
Let our company have a head office in Moscow and a branch in St. Petersburg. Suppose we need to combine the St. Petersburg office with the Moscow office into a single corporate network through a VPN, as well as organize Internet access through the Moscow office and monitor network activity in both offices. Suppose also that a VPN is created programmatically and that each client machine connects separately.
General principle
In the most general form, the tuning algorithm will be as follows:
- Create and configure a VPN server at the head office.
- Create and configure VPN connections to the head office from the branch.
- Check work on VPN.
- Install and activate Traffic Inspector on the gateway in the head office.
- Create permissions in Traffic Inspector in the external firewall for VPN.
- Add branch users to Traffic Inspector.
- Assign rules to individual users and their groups (for example, deny access to certain resources, set up accounting and charging for day-time traffic, etc.).
- Check the operation of the rules and the correctness of the settings.
Configure the VPN server
So, now we know the general order of adjustment and we can proceed to the description of specific actions. For example, we took Windows Server 2012, but the same applies to earlier versions (Windows 2003 and 2008).
In the Routing and Remote Access service, right-click your server and select Configure and Enable Routing and Remote Access.
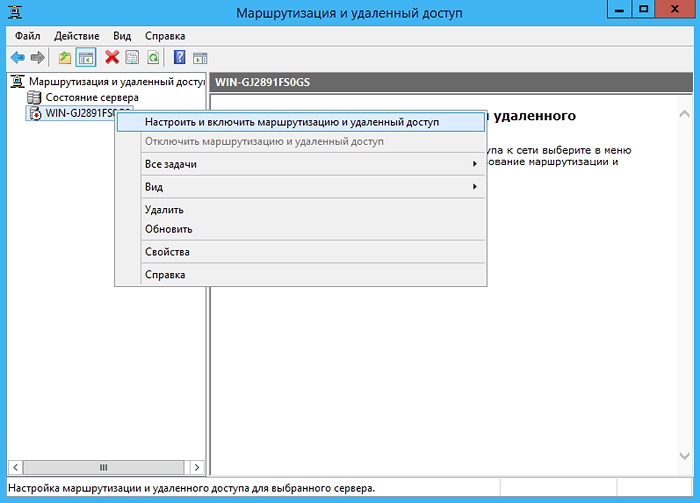
- In the Routing and Remote Access Server Setup Wizard that opens, click Next and select Special configuration.
- In the next window, select Virtual Private Network Access (VPN), Network Address Translation (NAT), LAN Routing and click Next.
- In the final wizard window, click Finish and start the service.
- Now go to the server properties:
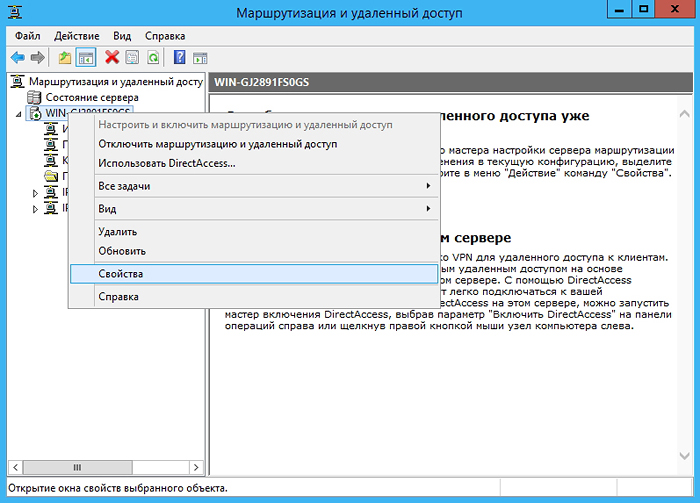
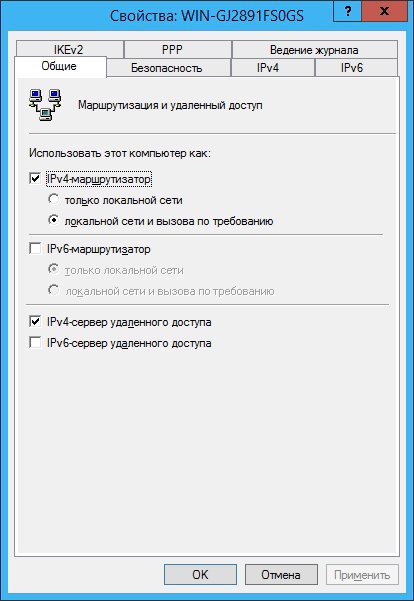
and on the General tab , set the following parameters:
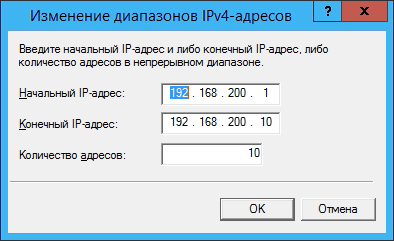
Go to the IPv4 tab and select the static address pool: 4
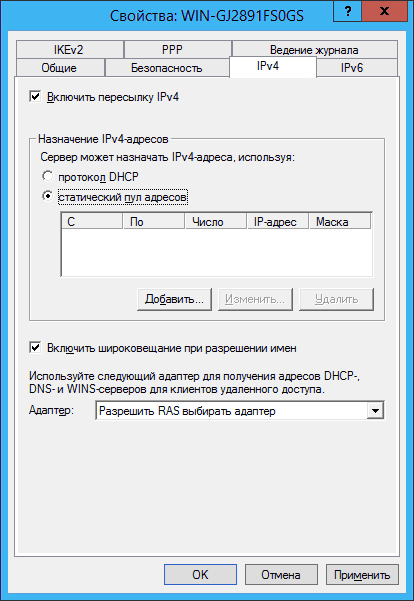
Click the Add button and assign an address pool (in this case, the subnet 192.168.200.1-192.168.200.10 is selected, consisting of 10 addresses, and the server receives the address 192.168.200.1):
Click the Logging tab and check the Log errors and warnings box .
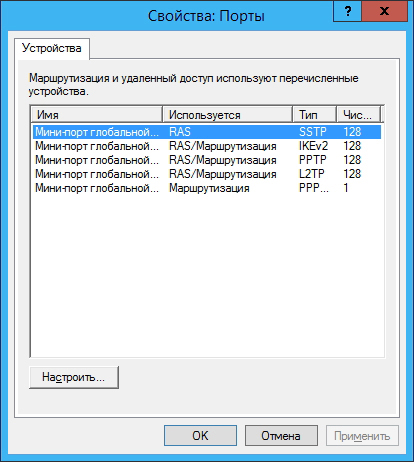
Right-click Ports and select Properties:

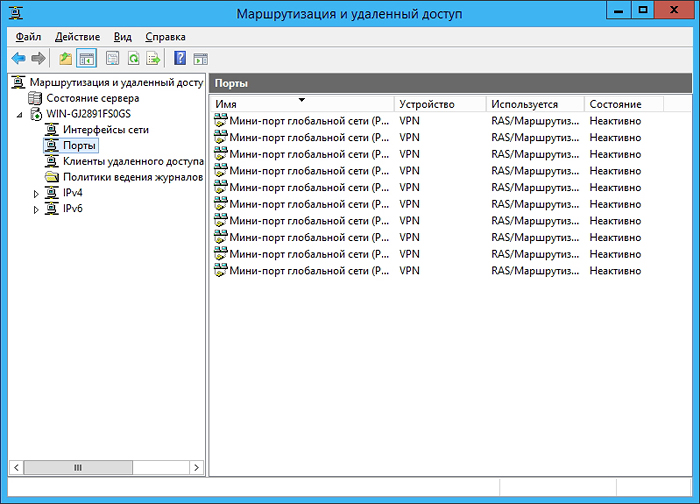
For stable server operation, it is recommended to remove unnecessary ports (SSTP, PPOE, L2TP, IKEv2) and create the required number of PPTP ports (in our case, you need 10 such ports):
Go to Network Address Translation (NAT) and add a new interface:
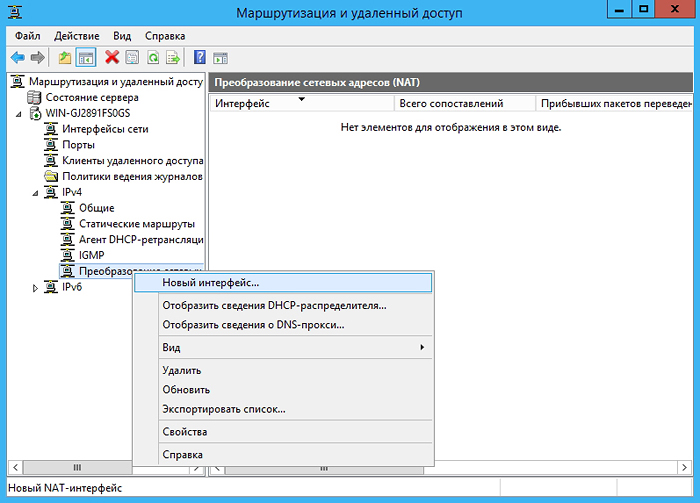
Select an Internet connection and check the boxes under the common interface connected to the Internet and Enable NAT on this interface.
Then mark the local network interface as “ Private interface connected to private network ”, and the internal interface as Private interface connected to private network. It turns out about the following:
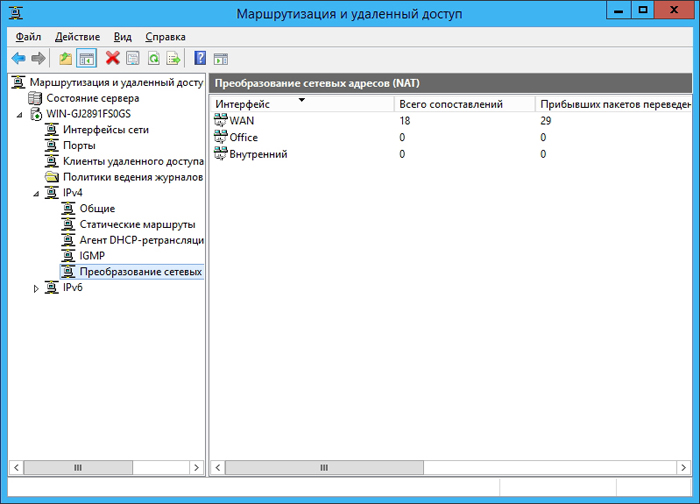
This completes the configuration of the VPN server at the head office and completes the configuration of VPN clients in the branch office.
Configure VPN Clients
On the server side, start computer management:
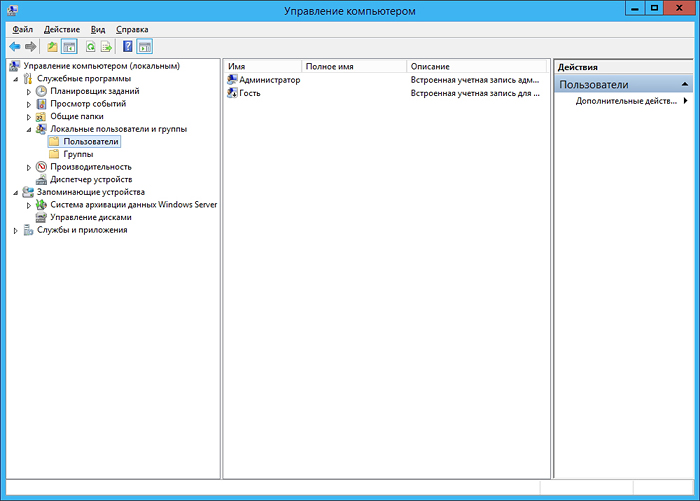
and in the section Local Users and Groups - Users add a new user and provide his credentials:
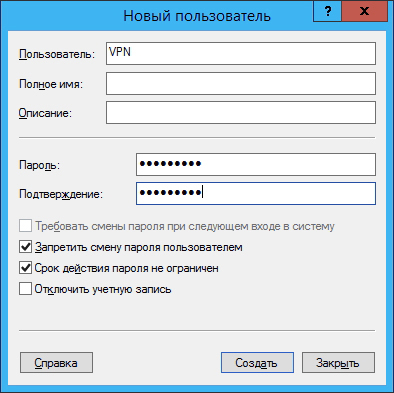
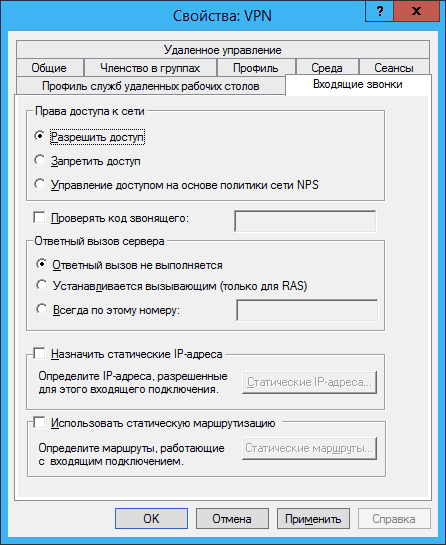
Go to the user properties on the Incoming Calls tab and specify the settings as shown in the figure (you can also assign a static IP to the user):
Now, on the client side, create a VPN connection using the operating system (for example, take Windows 8). To do this, in the Network and Sharing Center, select the Configure a new connection or network option, and in the opened wizard, select Connect to a workstation:

Select Use my Internet connection (VPN) and click Next :

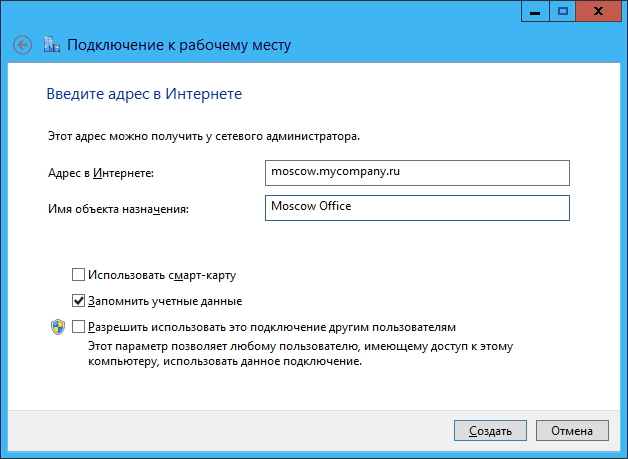
Then enter the URL or IP address of the VPN server, specify the name of its location and click the New button:
Configuring Traffic Inspector on the VPN server
After configuring the VPN server and clients, you can proceed to installing and configuring Traffic Inspector itself. Please note that Traffic Inspector is installed only at this stage, so the performance of the VPN should be checked in advance using standard Windows tools (ping, netstat, tracert, etc.).
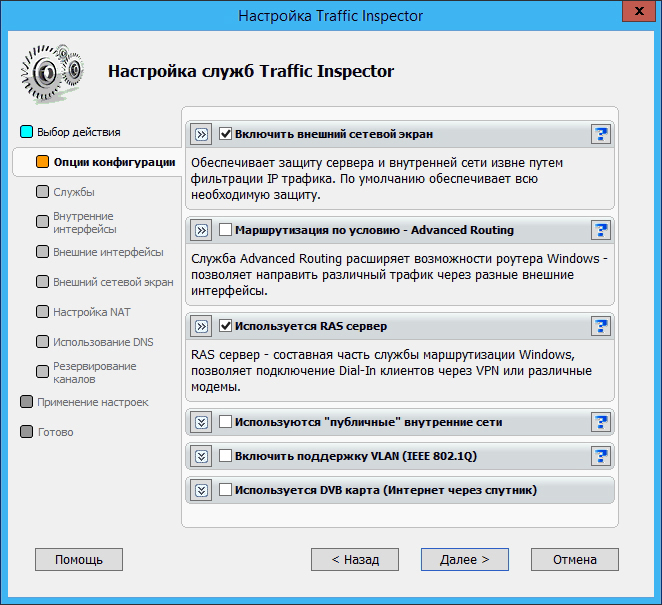
In the Traffic Inspector configurator in the service settings, check the Use RAS server checkbox:
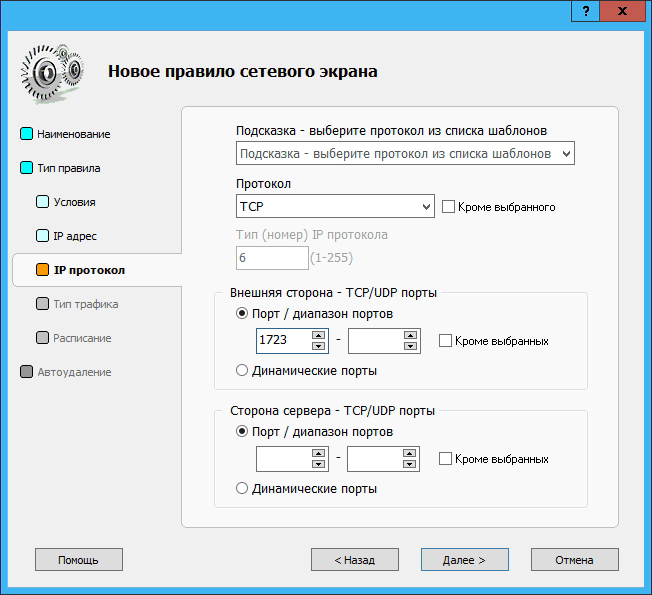
In the External Firewall Rules section in Traffic Inspector, create two rules — in one rule, allow TCP connections to port 1723 for external clients, and in the second rule, allow connections using the GRE protocol (option Specified IP type , number 47 ):
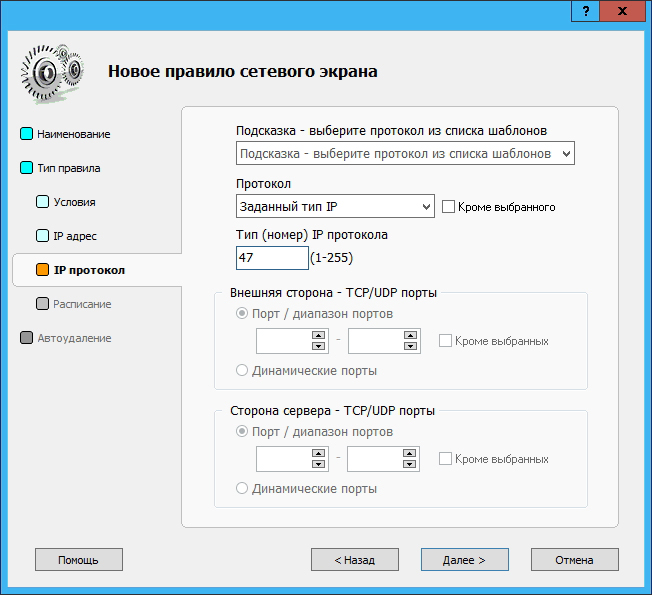
The remaining parameters can be not changed and leave the default values.
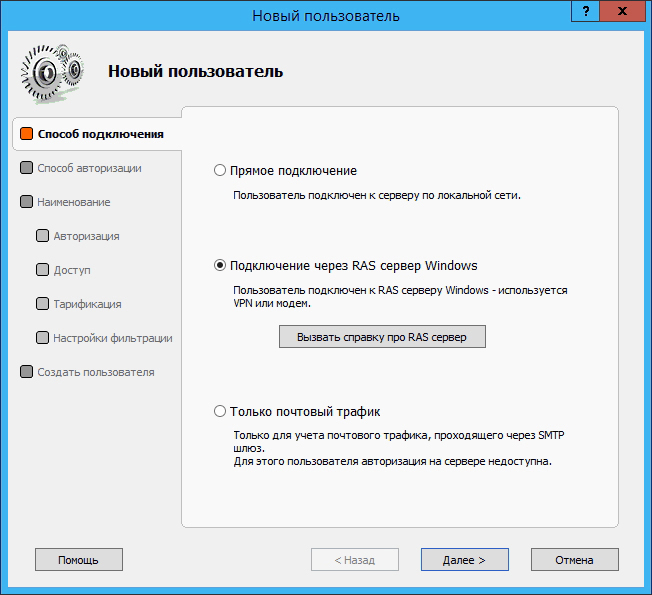
Add a new client to the program and specify the connection method. Connect via Windows RAS server :
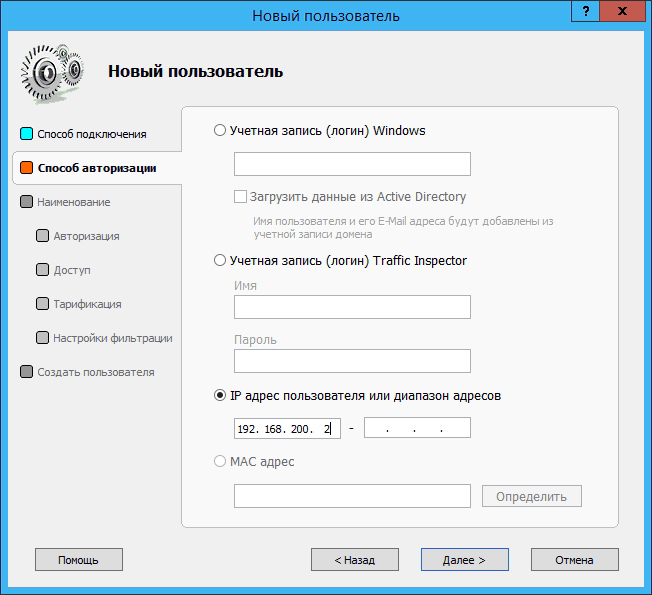
The remaining settings are similar to the settings of the program clients. In this case, IP authorization is used:
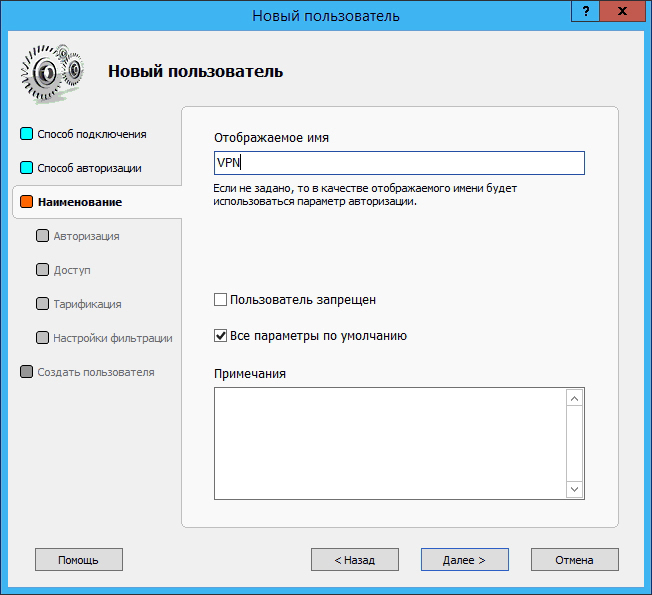
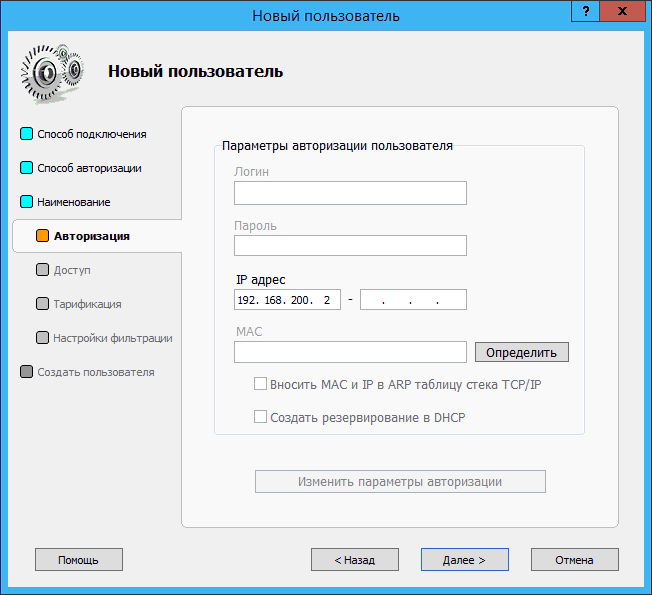
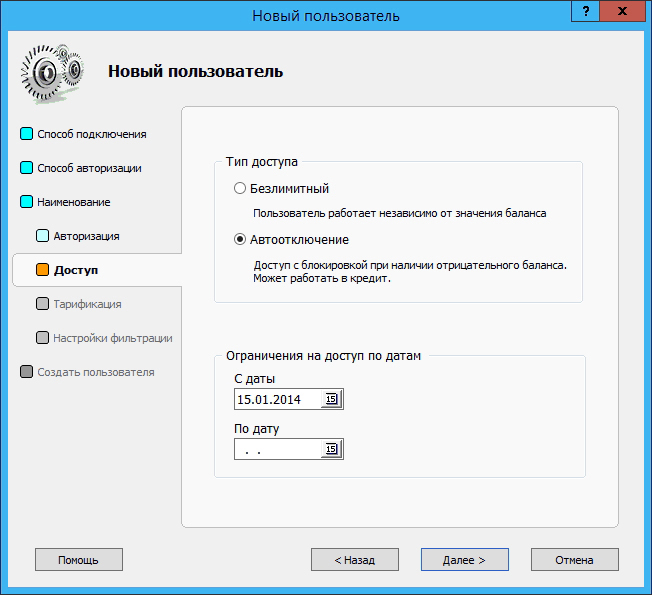
If necessary, you can configure automatic shutdown of the client in case of exceeding the allowable balance, or you can deny access to the server on certain days:
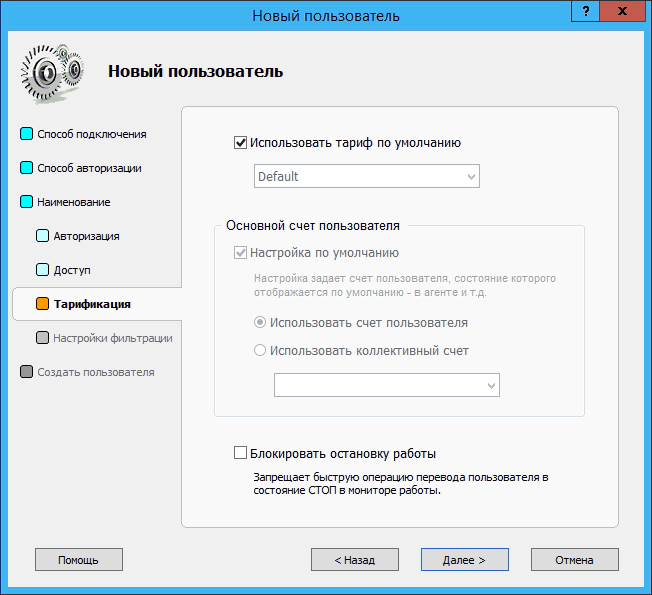
Traffic Inspector provides 4 levels of traffic filtering for users - banners, multimedia, graphics and text only. To select one of them, select the Set individual minimum filtering level for user checkbox :

In addition, the user can be allocated a certain quota of traffic (for example, 100 MB):
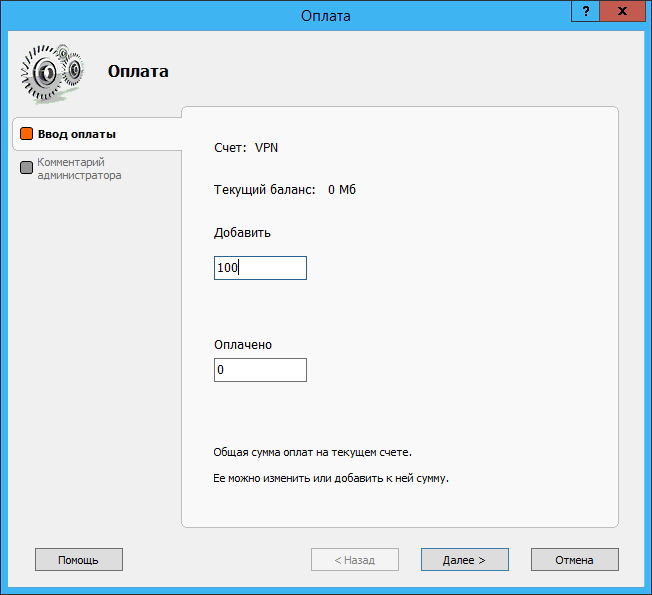
After the settings are completed, a new RAS server (dial in) network will appear in the main Traffic Inspector window:
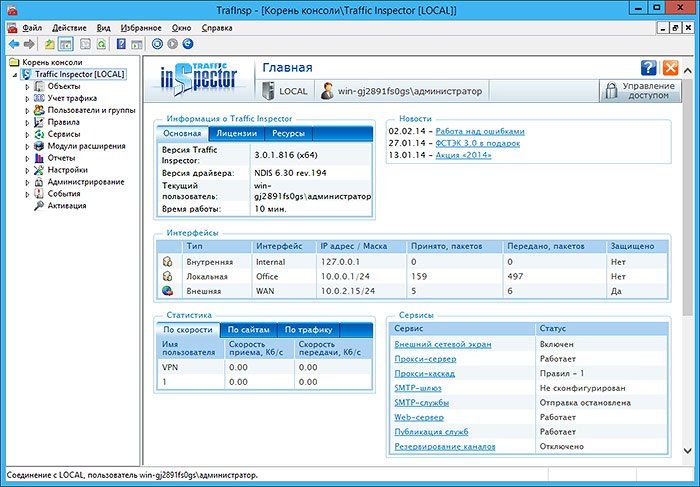
Conclusion
The organization of a VPN tunnel can provide high-speed and secure connections in the corporate network, guaranteed bandwidth, and cost savings on the network infrastructure. However, the problem of network security remains relevant for VPN. Traffic Inspector fills this gap, allowing you to quickly monitor users on the Internet and connect to the corporate server, including setting quotas for traffic , limit access to certain resources, adjust various levels of filtering for users, and much more. In this case, the system administrator does not require any special knowledge - all configuration is done in the Windows Management Console (MMC) using convenient step-by-step wizards.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/227247/
All Articles