Cloud Encryption Backup
Many of us have already appreciated the benefits of cloud technologies that today set the fashion for working on the Internet and storing files. Depending on the size of the occupied space, the user has the opportunity, for a fee or for free, to store rather large amounts of data on remote servers. At the same time, access to stored information is possible from anywhere in the world - from anywhere, where there is access to the Internet, from any device (local computer, tablet, smartphone) and from any OS.

Also interesting is the ability to synchronize data , allowing you to always have on hand updated information. For example, it becomes necessary for you to finish work as soon as possible with a specific document, which is located in the backup folder. You work with him in the office, but, not having time to finish, continue to work on the way home on the tablet (where the document will open with all the changes) and finish on your home computer, where all the information, after synchronization with the cloud copy of this document, also will update.
')
In addition, installing applications on the computer that we all used to working on almost daily is not necessary now either. For example, the entire set of office applications from Microsoft is now available to work straight through the browser using Office Online , from where the created documents can be immediately saved to OneDrive and, if necessary, used to be shared with other users. You can also work with documents through Google Docs , Google Sheets, etc.
Thus, cloud technologies provide fairly extensive and interesting opportunities and, apparently, the transition from using the contents of a personal computer to using cloud services, where resources and computing technologies are distributed among all, is not so far away. After all, all that is needed to make full use of cloud technologies is stable high-speed Internet access.
At the same time, there is another side. By sending their files to the cloud, the user, in fact, trusts their stranger - the provider of the service and falls into a certain dependency. Is there any guarantee that tomorrow the owner of the cloud will not raise the prices for his services or will not deny access at all without knowing you about it, as a result of which you will lose all your files? In addition, not a single cloud service is insured against failures (recall at least cases with the fall of Amazon ES2 ).
Equally important is the issue of protecting information in the clouds from access by third parties. Whether to fully trust the holders of cloud services, relying on the measures taken by them to protect information - a personal matter. And even if this is the case, is it possible to be sure that the staff of the service itself will not have access to your information?
Of course, you feel much more confident and calm if the files are encrypted by you personally on your computer, using the method, program and algorithm that you chose yourself.
Which approach in this case to choose? Abandoning the use of cloud technologies, of course, is unwise. But relying on cloud resources is also hardly worth it. You can, for example, store non-confidential large-sized files (video, audio, and photos) on the cloud, trusting the provider’s protection tools and not keeping them on your computer, thereby unloading it from a significant amount of data. At the same time, it will be better to keep all confidential documents on your hard drive, and send their encrypted backup copies to the cloud.
CyberSafe provides the ability to encrypt files on any cloud storage: Google Drive, Dropbox, Microsoft OneDrive, Apple iCloud (PC version of the client), Box, etc. At the same time, the application you use for backup can be any and perform copying files not only on the “cloud”, but also over the local network, in network storage, RAID-array or using any other technology and storage location.
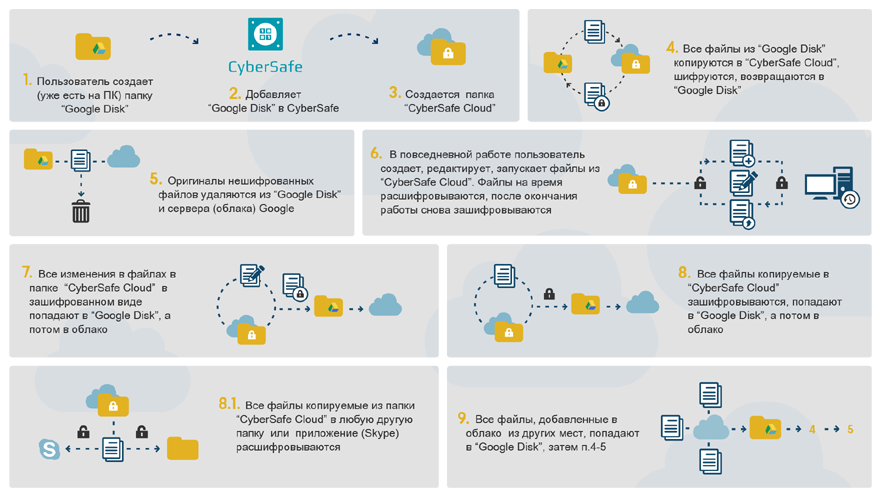
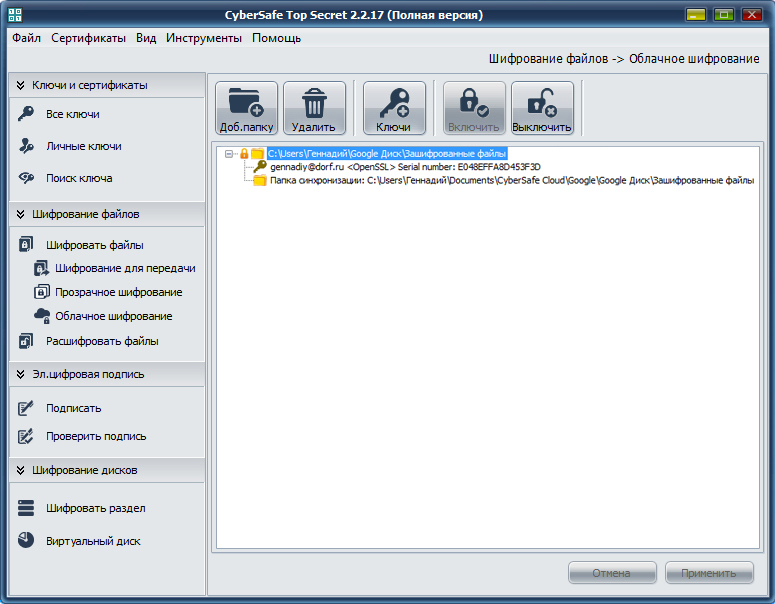
When adding a local backup folder in CyberSafe, the program creates a mirror copy of it. After that, all files added to the mirror-folder are encrypted and transferred to the backup folder in an already encrypted form. Then, the encrypted data gets to the remote resource (cloud). All work with encrypted files occurs from a mirrored folder in transparent encryption mode.
CyberSafe has the following advantages over Boxcryptor, a program for encrypting cloud services:
1. While Boxcryptor stores the user's private keys on its server, in CyberSafe your private key is only on your computer and, if desired (using the CryptoPro software built-in provider), can be created and stored on a token.
2. In Boxcryptor, encrypted files are stored on a cryptodisk, which is also vulnerable . CyberSafe protects files using transparent encryption with a system of trusted applications that provides additional protection for your files.
3. Boxcryptor charges users for a one-year subscription, which can lead to account blocking if it is not renewed, while in CyberSafe the license is not limited to time.
Thus, when working with CyberSafe , the data sent to the cloud resource is encrypted on the user's side, after which the encrypted files are always available for any operations on the fly. All the important information that you store on the cloud service, is reliably protected and, at the same time, at any time available for use.

Also interesting is the ability to synchronize data , allowing you to always have on hand updated information. For example, it becomes necessary for you to finish work as soon as possible with a specific document, which is located in the backup folder. You work with him in the office, but, not having time to finish, continue to work on the way home on the tablet (where the document will open with all the changes) and finish on your home computer, where all the information, after synchronization with the cloud copy of this document, also will update.
')
In addition, installing applications on the computer that we all used to working on almost daily is not necessary now either. For example, the entire set of office applications from Microsoft is now available to work straight through the browser using Office Online , from where the created documents can be immediately saved to OneDrive and, if necessary, used to be shared with other users. You can also work with documents through Google Docs , Google Sheets, etc.
Thus, cloud technologies provide fairly extensive and interesting opportunities and, apparently, the transition from using the contents of a personal computer to using cloud services, where resources and computing technologies are distributed among all, is not so far away. After all, all that is needed to make full use of cloud technologies is stable high-speed Internet access.
At the same time, there is another side. By sending their files to the cloud, the user, in fact, trusts their stranger - the provider of the service and falls into a certain dependency. Is there any guarantee that tomorrow the owner of the cloud will not raise the prices for his services or will not deny access at all without knowing you about it, as a result of which you will lose all your files? In addition, not a single cloud service is insured against failures (recall at least cases with the fall of Amazon ES2 ).
Equally important is the issue of protecting information in the clouds from access by third parties. Whether to fully trust the holders of cloud services, relying on the measures taken by them to protect information - a personal matter. And even if this is the case, is it possible to be sure that the staff of the service itself will not have access to your information?
Of course, you feel much more confident and calm if the files are encrypted by you personally on your computer, using the method, program and algorithm that you chose yourself.
Which approach in this case to choose? Abandoning the use of cloud technologies, of course, is unwise. But relying on cloud resources is also hardly worth it. You can, for example, store non-confidential large-sized files (video, audio, and photos) on the cloud, trusting the provider’s protection tools and not keeping them on your computer, thereby unloading it from a significant amount of data. At the same time, it will be better to keep all confidential documents on your hard drive, and send their encrypted backup copies to the cloud.
Backup Encryption with CyberSafe
CyberSafe provides the ability to encrypt files on any cloud storage: Google Drive, Dropbox, Microsoft OneDrive, Apple iCloud (PC version of the client), Box, etc. At the same time, the application you use for backup can be any and perform copying files not only on the “cloud”, but also over the local network, in network storage, RAID-array or using any other technology and storage location.
When adding a local backup folder in CyberSafe, the program creates a mirror copy of it. After that, all files added to the mirror-folder are encrypted and transferred to the backup folder in an already encrypted form. Then, the encrypted data gets to the remote resource (cloud). All work with encrypted files occurs from a mirrored folder in transparent encryption mode.


CyberSafe has the following advantages over Boxcryptor, a program for encrypting cloud services:
1. While Boxcryptor stores the user's private keys on its server, in CyberSafe your private key is only on your computer and, if desired (using the CryptoPro software built-in provider), can be created and stored on a token.
2. In Boxcryptor, encrypted files are stored on a cryptodisk, which is also vulnerable . CyberSafe protects files using transparent encryption with a system of trusted applications that provides additional protection for your files.
3. Boxcryptor charges users for a one-year subscription, which can lead to account blocking if it is not renewed, while in CyberSafe the license is not limited to time.
Thus, when working with CyberSafe , the data sent to the cloud resource is encrypted on the user's side, after which the encrypted files are always available for any operations on the fly. All the important information that you store on the cloud service, is reliably protected and, at the same time, at any time available for use.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/226393/
All Articles