IT guy on vacation: gadgets to the telescope
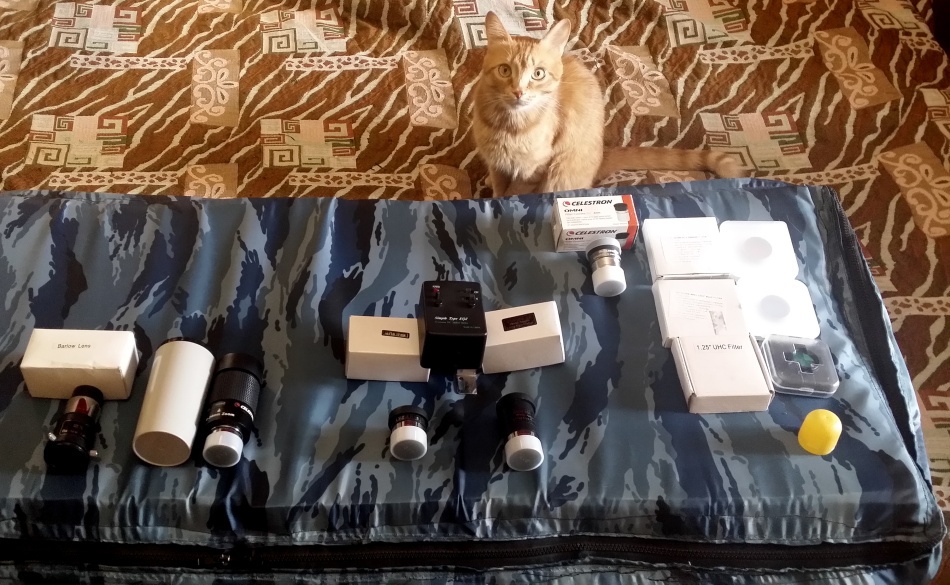

So, you became interested in astronomy , purchased a telescope and thought about a different body kit to improve the quality and convenience of observations. This post is devoted to the issues of retrofitting - eyepieces, light filters, and other gadgets.
Slight warning
In the get-together of astronomy lovers, the subject of eyepieces and other body kit is very holivarnaya. Here I present my experience of two years of lazy fascination with amateur visual astronomy. In case you categorically disagree with what has been written below, or if you are told the opposite opinion, please treat with calm and understanding.
Eyepieces

')
Some theory
Eyepieces, like telescopes, have long evolved from primitive devices with an abundance of distortions at the dawn of telescopes to advanced sophisticated optical systems with anti-reflective coatings and computer modeling during development. There is no special reason to consider optical schemes of eyepieces, because there are a lot of optical schemes now, they are complex, their own from different companies, and, in fact, the most important properties of eyepieces become:
Focal length . It determines the final magnification of the telescope with the eyepiece installed. To calculate the magnification, you need to divide the focal length of the telescope by the focal length of the eyepiece. For example, a telescope with a focal length of 900 mm and a 24 mm eyepiece mounted will give an increase of 900/24 = 37.5x. Eyepieces from 4 to 30 mm are common, eyepieces of 2-3 mm or more than 30 mm are more rare. Eyepieces with extreme focal values are more expensive, complex and have their drawbacks.
Field of view . This parameter determines how large the visible area in the eyepiece will be and how the object will look in it. Usually the field of view is in the range of 40-60 degrees. The larger the field of view, the better.
Removal of the pupil . This parameter indicates how close you need to bring your eye to the eyepiece. If you are forced to use glasses, then you need an eyepiece with a pupil of 12-20 mm. Eyepieces with a very small removal of the pupil will not be very comfortable for people without glasses.
Landing diameter . There are two standards for eyepiece seats - 1.25 "and 2". Focus points are 2 "better and are usually placed on more expensive telescopes. Some eyepieces are equipped with adapters for both diameters.
Weight The heavier the eyepiece, the greater the load on the mount and its drive. The heaviest eyepieces weigh about half a kilo.
In addition to the eyepieces with a fixed focal length there is a so-called. zoom eyepieces with variable focal length. Available focal lengths usually lie in the region of 7-24 mm, the usual field of view of 40-60 degrees. But there are unusual representatives, for example, a zoom of 2-4 mm.
The number of working focal lengths available eyepieces can be doubled using the so-called. Barlow's lens. This is a diffusing lens that is placed in front of the eyepiece, reducing its focal length, usually by half (there are 3x lenses and others).
How the object will look in the eyepiece
The easiest way to see how the object will be visible in the eyepiece with parameters of interest is the Eyepiece plugin for Stellarium. The plugin is included and included in the parameters:
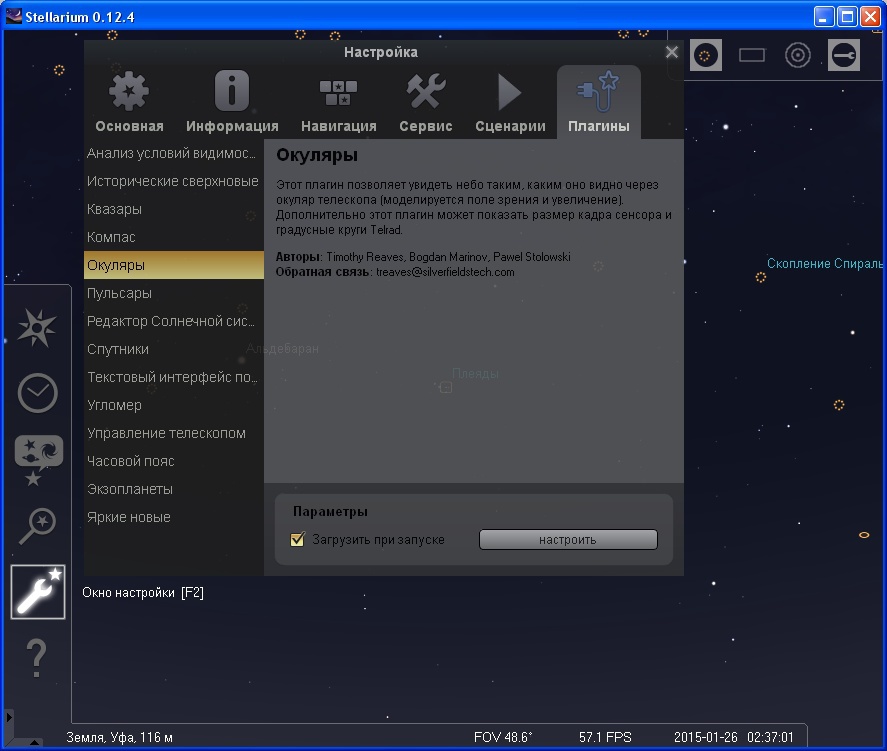
Let us consider how the field of view of the eyepiece affects the visibility of an object using the example of the Pleiades at low magnification: 900 mm telescope focal length, all 20 mm eyepieces, the field of view changes with a step of 20 degrees - 40.60.800.00 degrees. Do not forget that Stellarium draws many objects more beautifully than they look visually through a telescope, you will not see such luxurious nebulae in reality.
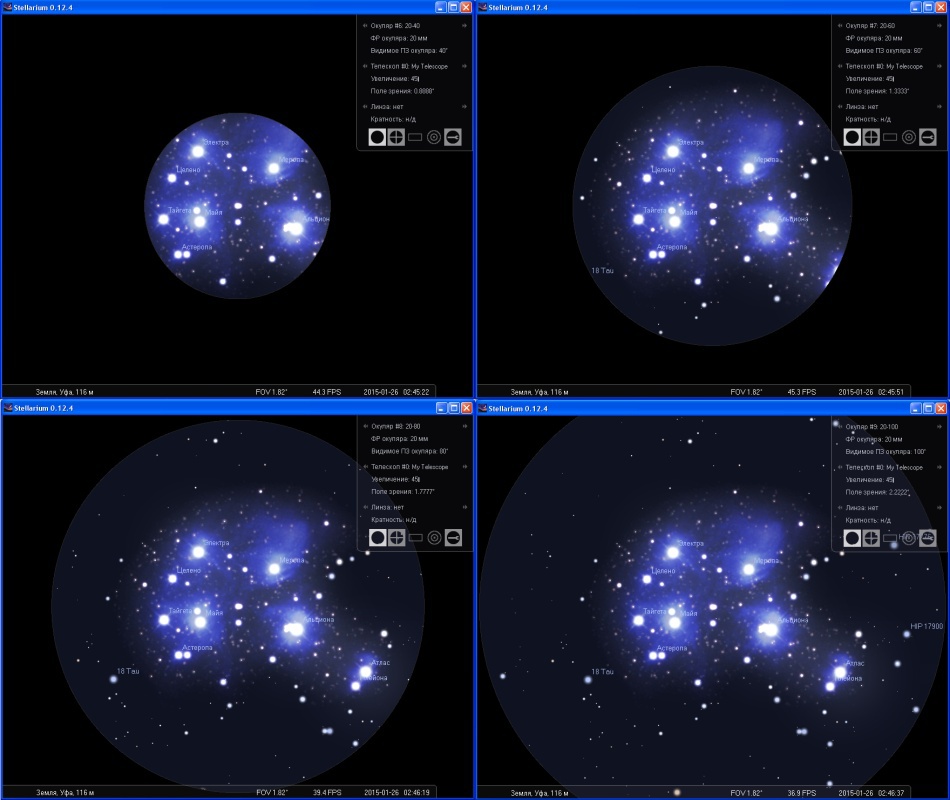
Let us consider how the focal length of the eyepiece affects the visibility of an object using the example of the Pleiades. Telescope with a focal length of 900 mm, eyepieces all with a field of view of 60 degrees, the focal length varies with a step of 5 mm - 30,25,20,15,10,5,5 mm.
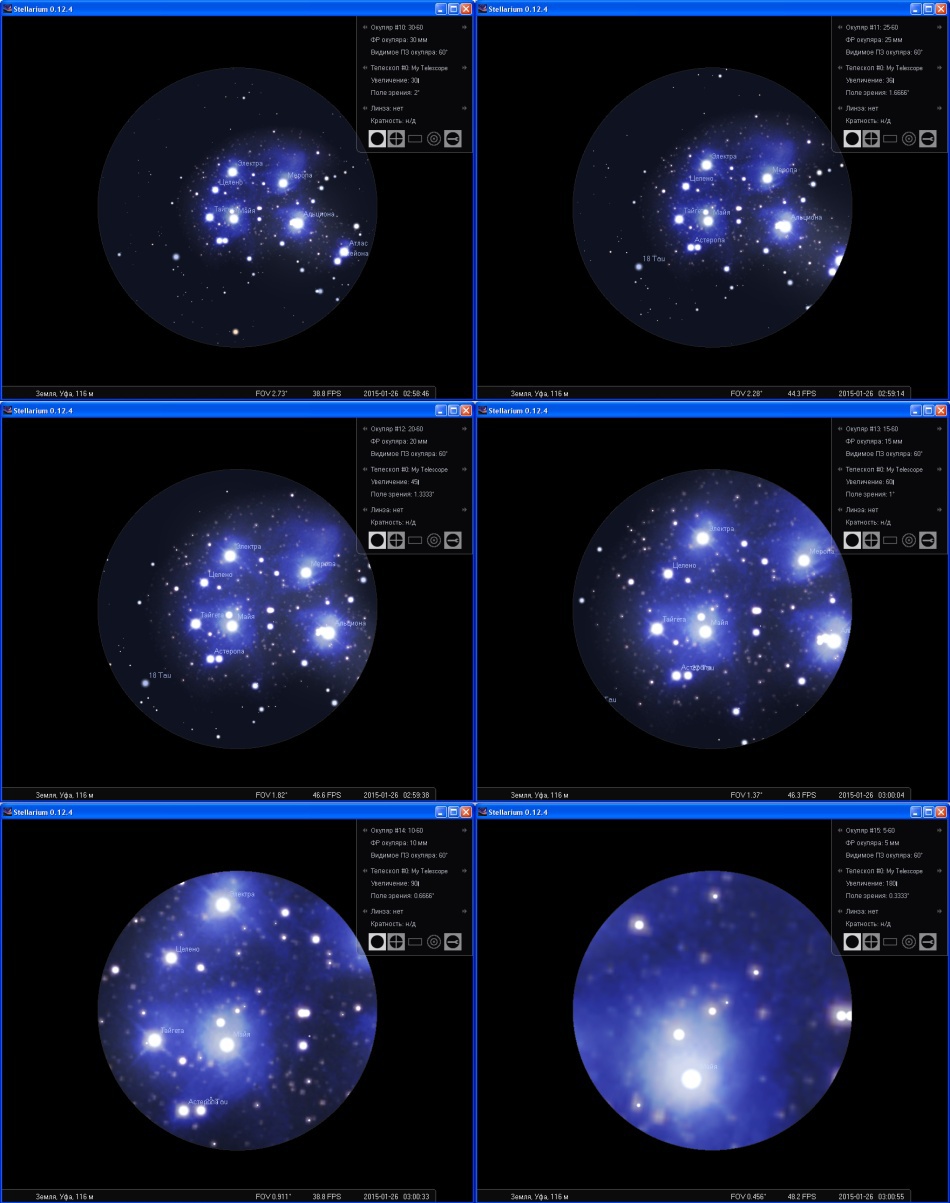
If you want to buy an eyepiece, it is highly desirable to substitute its characteristics into this plugin and walk through the objects of interest.
Eyepiece Planning
Manufacturers usually complete telescopes with one or two eyepieces and sometimes with a Barlow lens. If you took the telescope in a “generous” configuration with two eyepieces and a Barlow lens, you have four available magnifications with which it is possible to live the first months, slowly choosing an additional body kit. Possible increases for the telescope can be divided into:
Small It is 20-50x. On this magnification, it is good to look at the whole Moon, large objects like the same Pleiades, as well as objects for which maximum brightness and contrast are required. The fact is that as the magnification increases, the telescope decreases brightness and contrast, and for weak objects like nebulae, greater brightness may be more important than size.
Average . 50-120x. At this increase, you can peer into the craters of the moon and look at the planets.
Great . This is what is more than 120x. Typically, such increases are close to the limit for amateur telescopes, so the image quality gradually degrades, plus the dependence on the atmosphere increases. On the moon, there are small details, but I personally don’t like lowering the brightness and contrast, and I rarely use it. At this magnification, you can try to find a balance between magnification and image quality for the planets, and also strive to see nearby binary stars.
My experience
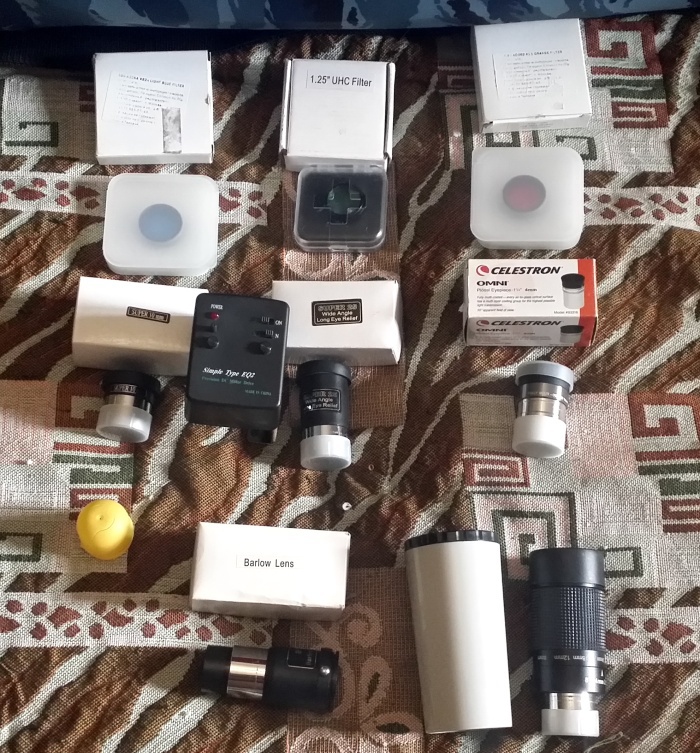

My eyepiece, like the other telescope gadgets, obeys the Pareto principle — 20% of the eyepieces are used 80% of the time. I would even say 20% percent is used almost 100% of the time. I have eyepieces 25 mm (complete), 10 mm (complete), zoom 8-24 mm, 4 mm, Barlow lens (complete). An 8-24 mm zoom is almost always used because of its versatility. Without changing the eyepiece, you can smoothly approach the Moon or pick a balance between magnification and quality for other objects. The ability to smoothly change the magnification is extremely convenient - you can look at the Moon at maximum brightness and minimum magnification, then place it entirely in the eyepiece, and, finally, switch to the maximum zoom for the eyepiece to observe craters. Very comfortably. If necessary, put a Barlow lens and I get a range of 4-12 mm for the planets. Unfortunately, the Barlow lens noticeably degrades the image quality, so it is not used very often. If necessary, to maximize without a long and heavy ligament zoom + Barlow lens is used eyepiece 4 mm - for planets or double stars. But it is quite rare, in reality it is almost always more comfortable to observe in the range of 37-112x, which gives me a zoom eyepiece.
Not eyepieces
Light filters
Light filters provide improved image quality by filtering excessive light flux or unnecessary parts of the spectrum. By design, the filters are divided into solar, hydrogen (H-Alpha) lines, lunar, polarization, color, dipscai, and others.

Solar filters are metallized film or special coated glass. They are placed on the inlet / lens of the telescope instead of the cap and allow you to observe the sun in the eyepiece, similar to night objects. With the help of solar filters you can see sunspots, flare fields, granulation on the sun.

Hydrogen line filters are a thin diffraction grating that cuts off almost all light except the spectrum of hydrogen lines. It allows you to observe prominences on the sun. In the market of amateur astronomy, there is actually one manufacturer - Coronado. They produce solar telescopes with built-in filters and filters for conventional telescopes. Due to the complexity of production, these filters are very expensive - telescopes from $ 600, filters in the region of $ 1000.

Moon filters reduce the overall brightness of the moon, making it comfortable to observe. At full moon, the moon is so bright that it can cause discomfort during observations.
Polarization is a subspecies of lunar filters that allow you to adjust the decrease in brightness on the go, for example, reducing the brightness from 5% to 25%.
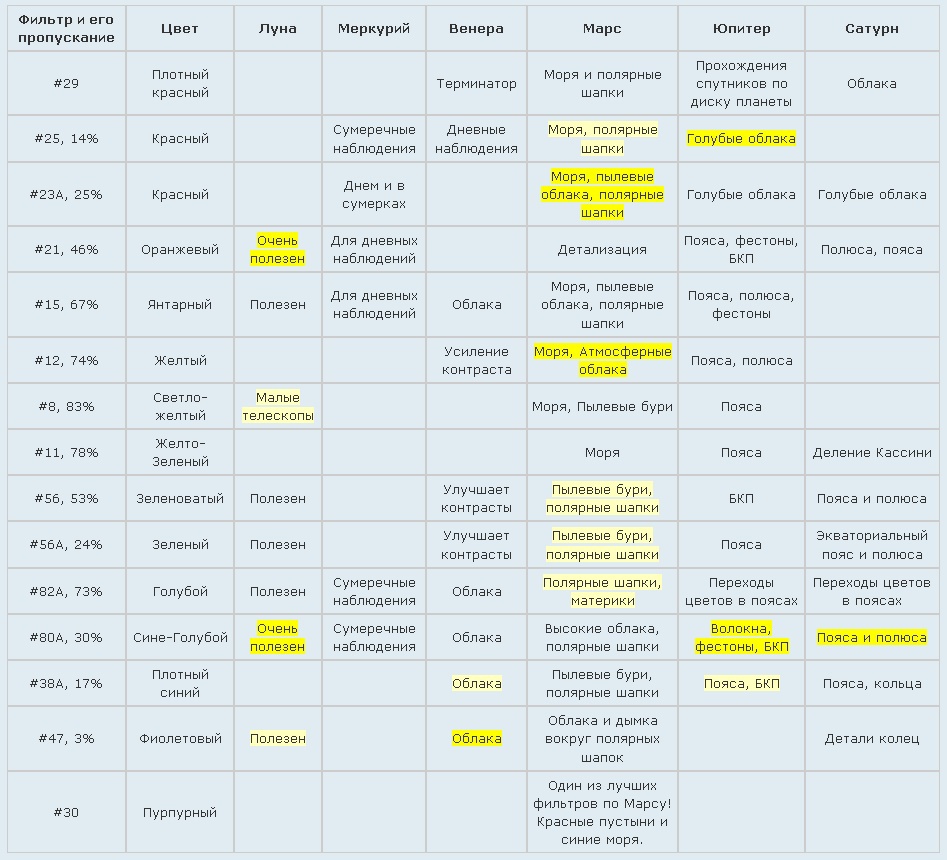
Color filters filter out different areas of the visible area. There is an excellent article on color filters , a table from which I quote here:

Dipskay filters are special filters for observing nebulae. There are UHC (Ultra-High Contrast - ultra-high contrast), O-III (spectral lines of oxygen), H-beta (lines of hydrogen). On the same resource with educational materials on astronomy there is a table of filter tests (shown in part):

Other filters are filters for reducing chromatism in achromates (Fringe killer), filters for reducing urban illumination, enhancing contrast, etc.
My experience using light filters
I have two color filters - # 21 orange and # 82A blue and UHC filter. I did not notice a serious improvement in quality, in my opinion, the decrease in brightness turns out to be stronger than the improvement in image. Color filters were used on Jupiter, there is no noticeable improvement. UHC was used by the M57 and the Great Orion Nebula - the loss of brightness outweighed any benefit from the filter. But my observations were balcony, in good country conditions I did not test the filters, maybe it will be better there. Color filters should have been checked on Mars, it was very solid this year, but, alas, I forgot.
Not eyepieces at all
Mount drive

On the equatorial mount EQ1 and EQ2 from Sky-Watcher, you can buy a drive mount - a small motor that will rotate the telescope with the speed of rotation of the Earth. A very handy thing in single observations and invaluable on astratovyezde with friends - you can aim the telescope at the object and not accompany it manually, during the passage of the queue of those interested, the tip will remain.
Alignment accessories
Half Kindersurprise is an accessory for alignment. The fact is that it has a landing diameter of 1.25 "and fits very well into the knob of the focuser. Interestingly, the alignment has already survived two aster races, probably small Newtons retain it better.
A bag
If you plan to travel outside the balcony with a telescope, the bag will be very helpful. I have a homemade, thanks to my wife. In principle, nothing complicated, fabric, foam rubber and anything solid such as linoleum.
Torch

It is very useful to think in advance and make an astro flashlight from a cheap Chinese headlamp, adding red plastic from a folder or something like that in front of the glass. These flashlights are often removed front glass and it is not difficult.
Eye cup
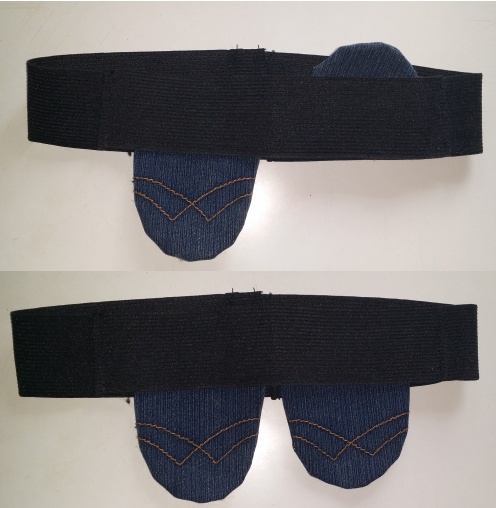

Closing the eye, looking into the eyepiece to others is not very convenient. Over time, you get used to and filter the image from the second eye with the brain, but for the first time you can make your life easier with the eyecup - from a simple dressing to special hand-made equipment, again, thanks to my wife.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a small astrosecrete, a convenient and well-organized observation site, increases the permeability of the telescope by half the magnitude. Good observations!
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/226219/
All Articles