R * -tree or geospatial indexing
Greetings to you, habrazhiteli!
In this post we will talk about geo-space indexing, namely about such data structure as R * -tree and how I implemented my first project.
So let's get started. Immediately after graduating from university, I received an offer from teachers who hold an office that provides GPS car monitoring services, which I accepted. Here it is! Finally, real interesting projects! My joy and enthusiasm knew no bounds. The very first task that was given to me had something like the following wording:
The source codes of the application for 160,000 lines were given to me and that's all. No documentation, nothing. The only source of information was these same teachers and rare comments in the source code of the plan “Removed n * x at Vasya's request”. The project is more than 10 years old, the office is very loyal and flexible in approaching the requests of customers in the shortest possible time to finish drawing all the desires and whistles almost on their knees, which have not been documented. Monstrous negligence! But such projects help to pump the skills of parsing someone else's code.
Well, the task was set, the material for the work was. Having rummaged in the code, having asked questions I clarified for myself a little the state of affairs current at that moment:
The drawing of maps of small size (city, region) occurred tolerably. What happened when you loaded maps the size of a region / country, containing hundreds of thousands of vector objects consisting of millions of points, you can imagine. Googling and reading a lot of material on the topic, I selected for myself 2 options of how to do everything “correctly”:
After a bit of thought, I threw away the first option. it would be necessary to be attached to a certain number of scale levels and for each to build a grid. The second option gave the advantage of unlimited scaling, and in general seemed more universal. In order not to reinvent the wheel, I decided to look for existing libraries under Delphi, since The project was written on it. The libraries were never found and I decided to implement the indexing myself.
What is an R-tree? This structure was proposed by Antonin Guttman for indexing spatial data, is a balanced tree and was developed based on empirical observations. The tree splits the space into many nested rectangles. Each tree node has a minimum ( minCount ) and maximum ( maxCount ) number of objects. For the correct operation of the tree building algorithms, it is necessary that 2 <= minCount <= maxCount / 2 . Each object has its own bounding rectangle - MBR (minimum bounding rectangle). An MBR node is a rectangle that describes the rectangles of the child nodes \ objects.
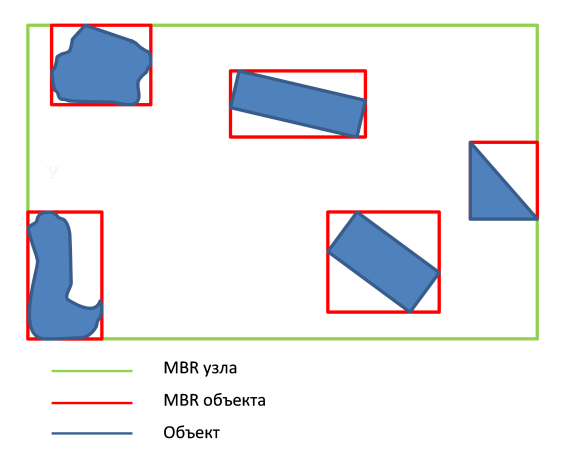
The tree is built by alternately inserting objects into it. When the node is full, it is divided and all parent nodes are divided if necessary. The effectiveness of search queries for a given data structure depends on several criteria:
')
There are different types of R-trees, differing only in the way of choosing the end and dividing the overflowed node.
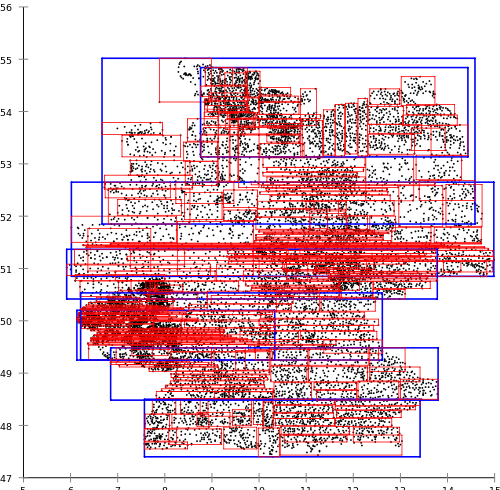
Why did I choose R * -tree? The classical approach proposed by Antonin Gutmann (R-trees), according to my subjective assessment, is absolutely not suitable for use in real projects. As an example, I will cite material from Wikipedia , namely the R-tree, built for the German post offices:
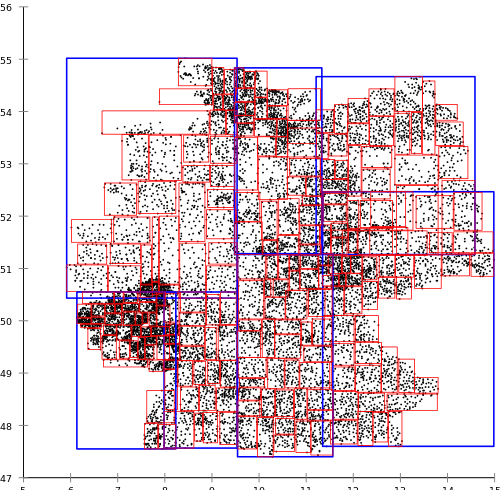
When, at the same time, the R * -tree algorithms proposed by Norbert Beckmann, Hans-Peter Kriegel, Ralf Schneider, and Bernhard Seeger give the following result:
R * -tree is more resource-intensive when building, but gives better results for search queries than regular R-tree.
Let us consider how the insertion takes place: it includes algorithms for selecting a branch (subtree) / node, and an algorithm for separating a node when it overflows.
To find the option of division, R * - the tree uses the following method: nodes are sorted along each of the coordinate axes along the left and right borders. For each sorted version, the nodes are divided into 2 groups in such a way that for k = [1 ... (maxCount - 2 * minCount + 2)] the first group includes (minCount - 1) + k nodes remaining in the second. For each such distribution, the following indicators are calculated:
The authors of the R * -tree in their article state that the best performance of this structure is achieved with minCount = maxCount * 40% .
That's all. Our tree is built, and now it’s easy to find the necessary objects in a given area:
Next, simply call
In order to more clearly demonstrate the work of the basic algorithms, let's look at the code:
After implementation, all that remained to be done was to split the vector map objects into layers, set these layers to the maximum scale at which they would be displayed and construct R * -tree for each layer.
The results can be seen on the video:
In this post we will talk about geo-space indexing, namely about such data structure as R * -tree and how I implemented my first project.
So let's get started. Immediately after graduating from university, I received an offer from teachers who hold an office that provides GPS car monitoring services, which I accepted. Here it is! Finally, real interesting projects! My joy and enthusiasm knew no bounds. The very first task that was given to me had something like the following wording:
There is a desktop application in which, apart from any reports on mileage, fuel spent on cars, etc., vector maps are displayed, with a drawing of the position of these cars in real time, tracks of the history of car movements and all sorts of other buns. Now it all works incorrectly and inefficiently. How to implement correctly, no one knows. Need to rewrite...
The source codes of the application for 160,000 lines were given to me and that's all. No documentation, nothing. The only source of information was these same teachers and rare comments in the source code of the plan “Removed n * x at Vasya's request”. The project is more than 10 years old, the office is very loyal and flexible in approaching the requests of customers in the shortest possible time to finish drawing all the desires and whistles almost on their knees, which have not been documented. Monstrous negligence! But such projects help to pump the skills of parsing someone else's code.
Well, the task was set, the material for the work was. Having rummaged in the code, having asked questions I clarified for myself a little the state of affairs current at that moment:
- Maps are an array of points and objects with links to these points.
- Objects that fall into the screen area are determined by brute force.
- To display an object or not, it was determined “on the fly” by calculating the size of the object on the screen (there is no point in wasting system resources on displaying a 1 pixel house)
The drawing of maps of small size (city, region) occurred tolerably. What happened when you loaded maps the size of a region / country, containing hundreds of thousands of vector objects consisting of millions of points, you can imagine. Googling and reading a lot of material on the topic, I selected for myself 2 options of how to do everything “correctly”:
- Split the entire area of the map into squares of fixed size, split the objects falling on the joints, assign an index of each square to each object, sort the data and calculate the necessary objects on the go;
- Use R-tree.
After a bit of thought, I threw away the first option. it would be necessary to be attached to a certain number of scale levels and for each to build a grid. The second option gave the advantage of unlimited scaling, and in general seemed more universal. In order not to reinvent the wheel, I decided to look for existing libraries under Delphi, since The project was written on it. The libraries were never found and I decided to implement the indexing myself.
What is an R-tree? This structure was proposed by Antonin Guttman for indexing spatial data, is a balanced tree and was developed based on empirical observations. The tree splits the space into many nested rectangles. Each tree node has a minimum ( minCount ) and maximum ( maxCount ) number of objects. For the correct operation of the tree building algorithms, it is necessary that 2 <= minCount <= maxCount / 2 . Each object has its own bounding rectangle - MBR (minimum bounding rectangle). An MBR node is a rectangle that describes the rectangles of the child nodes \ objects.

The tree is built by alternately inserting objects into it. When the node is full, it is divided and all parent nodes are divided if necessary. The effectiveness of search queries for a given data structure depends on several criteria:
- Minimizing the area of MBR nodes (minimizing the empty space between objects);
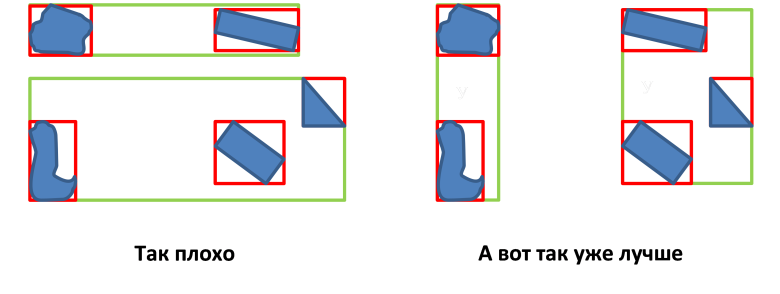
- Minimizing the overlap area of MBR nodes;
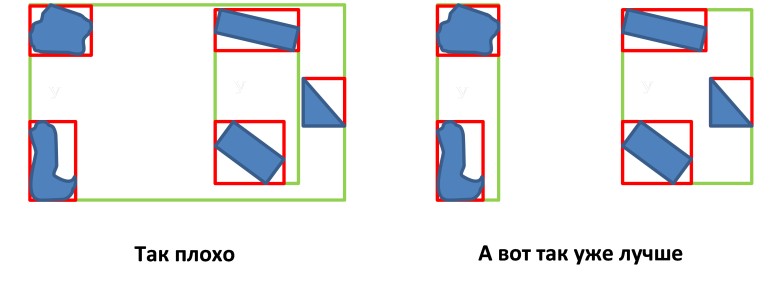
- Minimizing the perimeter of the MBR node;
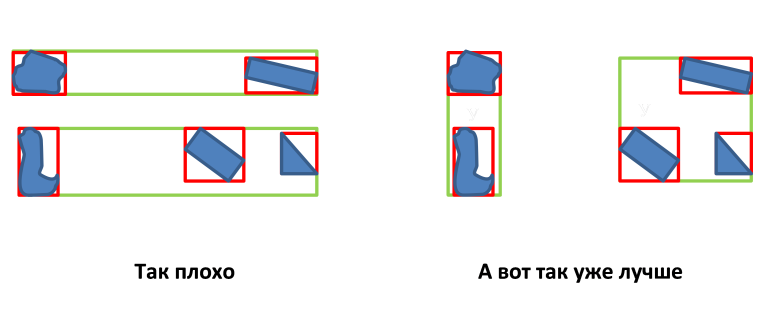
')
There are different types of R-trees, differing only in the way of choosing the end and dividing the overflowed node.
Why did I choose R * -tree? The classical approach proposed by Antonin Gutmann (R-trees), according to my subjective assessment, is absolutely not suitable for use in real projects. As an example, I will cite material from Wikipedia , namely the R-tree, built for the German post offices:

When, at the same time, the R * -tree algorithms proposed by Norbert Beckmann, Hans-Peter Kriegel, Ralf Schneider, and Bernhard Seeger give the following result:

R * -tree is more resource-intensive when building, but gives better results for search queries than regular R-tree.
Let us consider how the insertion takes place: it includes algorithms for selecting a branch (subtree) / node, and an algorithm for separating a node when it overflows.
Subtree selection algorithm (chooseSubtree)
1. Install N by root node 2. If N is an end node, return N 3.Other 4. If the child nodes of N are end nodes (leaves), 5. Select the child node N, whose MBR requires the least increase in overlap when inserting object to node 6. If there are several nodes with the smallest overlap, choose the one which requires the smallest increase in area 7. If there are several nodes with the smallest increase in area, select a node from them. with the smallest area 8. Otherwise 9. Select the child node N, whose MBR requires the least increase in area 10. If there are several nodes with the smallest increase in area, select the node with the smallest area. 11. Set N selected node. 12. Repeat steps from step 2.
Node division algorithm (splitNode)
To find the option of division, R * - the tree uses the following method: nodes are sorted along each of the coordinate axes along the left and right borders. For each sorted version, the nodes are divided into 2 groups in such a way that for k = [1 ... (maxCount - 2 * minCount + 2)] the first group includes (minCount - 1) + k nodes remaining in the second. For each such distribution, the following indicators are calculated:
- Area: Area = Area (MBR of the first group) + Area (MBR of the second group)
- Perimeter: Margin = Margin (MBR of the first group) + Margin (MBR of the second group)
- Overlap: Overlap = Area (MBR of the first group ∩ MBR of the second group)
The best distribution is determined by the following algorithm:
1. Call chooseSplitAxis to determine the axis on which the distribution will occur 2. Call chooseSplitIndex to determine the best distribution on the selected axis 3. Distribute objects on the 2nd nodes
chooseSplitAxis
1. For each of the axes 2. Sort the nodes along the left and then along the right edges of their MBR. Distribute nodes as described above, calculate S - the sum of all perimeters of each of the distributions. 3. Select the axis, with a minimum of S.
chooseSplitIndex
1. Select the distribution along the selected axis with the minimum overlap parameter 2. If there are several distributions with a minimum overlap parameter, select the distribution with the smallest area.
Actually the insert itself (insertObject)
1. Call chooseSubStree, passing the root node as a parameter to determine the node N, in which the object E will be inserted 2. If the number of objects in N is less than maxCount, 3. Paste E to N 4. Update MBR for N and all its parent nodes 5. Otherwise call splitNode for N and E.
The authors of the R * -tree in their article state that the best performance of this structure is achieved with minCount = maxCount * 40% .
That's all. Our tree is built, and now it’s easy to find the necessary objects in a given area:
Algorithm for finding objects in a given area (findObjectsInArea)
1. If the current node N is finite, 2. For each child object E in node N, determine 3. If E intersects with the search area, add E to the search result R. 4. Otherwise 5. For each child node n in node N, determine 6. If n intersects with the search area, call for n findObjectsInArea
Next, simply call
findObjectsInArea , passing it the root node, and the search area.In order to more clearly demonstrate the work of the basic algorithms, let's look at the code:
Sortsy
// R*-tree unit RStar_tree; interface uses Windows, SysUtils, Math; const MAX_M = 16; // MIN_M = Round(MAX_M * 0.4); // type TObjArr = array of Integer; // TAxis = (X, Y); // chooseSplitAxis - TBound = (Left, Right); // (\) TGpsPoint = record // GPS (X = lon\Y = lat) X, Y: Double; end; TMBR = record // \\ MBR = Minimum Bounding Rectangle Left, Right: TGpsPoint; // left - right - end; TRObject = record // R-. mbr: TMBR; // idx: Integer; // , end; TRNode = class // private fmbr: TMBR; // FParent: Integer; // , - FChildren: array of Integer; // FObjects: array of TRObject; // . ( () (, , ) FisLeaf: Boolean; // () FLevel: Integer; // (0=) protected function getIsLeaf: Boolean; // FisLeaf function getChild(Index: Integer): Integer; // function getObject(Index: Integer): TRObject; // procedure setChild(Index: Integer; node_id: Integer); // procedure setObject(Index: Integer; obj: TRObject); // procedure setParent(parent_id: Integer); // - Procedure copy(node: TRNode); // Procedure clearObjects(); // Procedure clearChildren(); // public constructor Create; overload; constructor Create(node: TRNode); overload; destructor Destroy; override; property mbr: TMBR read fmbr write fmbr; // property isLeaf: Boolean read FisLeaf; // property Children[Index: Integer]: Integer read getChild write setChild; // property Objects[Index: Integer]: TRObject read getObject write setObject; // property Parent: Integer read FParent write setParent; // property Level: Integer read FLevel write FLevel; // function isIntersected(mbr1, mbr2: TMBR): Boolean; overload; // mbr1, mbr2 function isIntersected(mbr: TMBR): Boolean; overload; // MBR mbr function Overlap(mbr_ovrl: TMBR): Double; // MBR function Area: Double; overload; // MBR function Area(mbr: TMBR): Double; overload; // MBR function margin: Double; // MBR end; TRtree = class // private FNodeArr: array of TRNode; // FRoot: Integer; // FHeight: Integer; // Procedure QuickSort(var List: array of TRObject; iLo, iHi: Integer; axe: TAxis; bound: TBound); overload; // MBR. axe - , bound - (/) procedure QuickSort(var List: array of Integer; iLo, iHi: Integer; axe: TAxis; bound: TBound); overload; // MBR. axe - , bound - (/) Procedure splitNodeRStar(node_id: Integer; obj: TRObject); overload; // 2 R*-tree (page 325:: The R*-tree: An Efficient and Robust Access Method for Points and Rectangles+) node_id = obj = Procedure splitNodeRStar(splited_Node_Id, inserted_Node_Id: Integer); overload; // 2 R*-tree (page 325:: The R*-tree: An Efficient and Robust Access Method for Points and Rectangles+) splited_Node_Id = , inserted_Node_Id = Procedure updateMBR(node_id: Integer); overload; // MBR Procedure updateMBR(node: TRNode); overload; // MBR Procedure chooseSubtree(obj: TRObject; var node_id: Integer); // node_id obj. function chooseSplitAxis(obj: TRObject; node_id: Integer): TAxis; overload; // ( R*-tree) function chooseSplitAxis(nodeFather, nodeChild: Integer): TAxis; overload; // ( R*-tree) Procedure findObjectsInArea(mbr: TMBR; node_id: Integer; var obj: TObjArr); overload; // mbr function isRoot(node_id: Integer): Boolean; // node_id function newNode(): Integer; // . protected public constructor Create; destructor Destroy; override; Procedure insertObject(obj: TRObject); // Procedure findObjectsInArea(mbr: TMBR; var obj: TObjArr); overload; // mbr. (. .. , ) property Height: Integer read FHeight; // end; function toRObject(lx, ly, rx, ry: Double; idx: Integer): TRObject; overload; function toRObject(mbr: TMBR; idx: Integer): TRObject; overload; implementation function toRObject(lx, ly, rx, ry: Double; idx: Integer): TRObject; begin Result.mbr.Left.X := Min(lx, rx); Result.mbr.Left.Y := Min(ly, ry); Result.mbr.Right.X := Max(lx, rx); Result.mbr.Right.Y := Max(ly, ry); Result.idx := idx; end; function toRObject(mbr: TMBR; idx: Integer): TRObject; begin Result.mbr := mbr; Result.idx := idx; end; { TRNode } function TRNode.Area: Double; begin Result := (fmbr.Right.X - fmbr.Left.X) * (fmbr.Right.Y - fmbr.Left.Y); end; function TRNode.Area(mbr: TMBR): Double; begin Result := (mbr.Right.X - mbr.Left.X) * (mbr.Right.Y - mbr.Left.Y); end; procedure TRNode.clearChildren; begin SetLength(FChildren, 0); end; procedure TRNode.clearObjects; begin FisLeaf := False; SetLength(FObjects, 0); end; procedure TRNode.copy(node: TRNode); var i: Integer; begin SetLength(FObjects, Length(node.FObjects)); SetLength(FChildren, Length(node.FChildren)); if Length(FObjects) > 0 then begin for i := 0 to High(node.FObjects) do begin FObjects[i].idx := node.FObjects[i].idx; FObjects[i].mbr.Left.X := node.FObjects[i].mbr.Left.X; FObjects[i].mbr.Left.Y := node.FObjects[i].mbr.Left.Y; FObjects[i].mbr.Right.X := node.FObjects[i].mbr.Right.X; FObjects[i].mbr.Right.Y := node.FObjects[i].mbr.Right.Y; end; FisLeaf := True; end else begin for i := 0 to High(node.FChildren) do begin Children[i] := node.Children[i]; end; FisLeaf := False; end; fmbr.Left.X := node.fmbr.Left.X; fmbr.Left.Y := node.fmbr.Left.Y; fmbr.Right.X := node.fmbr.Right.X; fmbr.Right.Y := node.fmbr.Right.Y; FParent := node.Parent; FLevel := node.Level; end; constructor TRNode.Create(node: TRNode); begin Create; FParent := -10; copy(node); end; constructor TRNode.Create; begin inherited; FParent := -10; end; destructor TRNode.Destroy; begin SetLength(FObjects, 0); SetLength(FChildren, 0); inherited; end; function TRNode.getChild(Index: Integer): Integer; begin if High(FChildren) >= Index then begin Result := FChildren[Index]; end; end; function TRNode.getIsLeaf: Boolean; begin if Length(FObjects) > 0 then Result := True else Result := False; end; function TRNode.getObject(Index: Integer): TRObject; begin if High(FObjects) >= Index then begin Result := FObjects[Index]; end; end; function TRNode.isIntersected(mbr: TMBR): Boolean; begin Result := False; if (fmbr.Left.X <= mbr.Right.X) and (fmbr.Left.Y <= mbr.Right.Y) then begin if (fmbr.Right.X >= mbr.Left.X) and (fmbr.Right.Y >= mbr.Left.Y) then begin Result := True; end; end; end; function TRNode.margin: Double; begin Result := ((fmbr.Right.X - fmbr.Left.X) + (fmbr.Right.Y - fmbr.Left.Y)) * 2; end; function TRNode.Overlap(mbr_ovrl: TMBR): Double; var X, Y: Double; begin X := Min(mbr_ovrl.Right.X, fmbr.Right.X) - Max(mbr_ovrl.Left.X, fmbr.Left.X); if X <= 0 then begin Result := 0; Exit; end; Y := Min(mbr_ovrl.Right.Y, fmbr.Right.Y) - Max(mbr_ovrl.Left.Y, fmbr.Left.Y); if Y <= 0 then begin Result := 0; Exit; end; Result := X * Y; end; function TRNode.isIntersected(mbr1, mbr2: TMBR): Boolean; begin Result := False; if (mbr1.Left.X <= mbr2.Right.X) and (mbr1.Left.Y <= mbr2.Right.Y) then begin if (mbr1.Right.X >= mbr2.Left.X) and (mbr1.Right.Y >= mbr2.Left.Y) then begin Result := True; end; end; end; procedure TRNode.setChild(Index, node_id: Integer); begin if High(FChildren) >= Index then begin FChildren[Index] := node_id; FisLeaf := False; end else begin if ((Index) <= (MAX_M - 1)) and (Index >= 0) then begin SetLength(FChildren, Index + 1); FChildren[Index] := node_id; FisLeaf := False; end; end; end; procedure TRNode.setObject(Index: Integer; obj: TRObject); begin if High(FObjects) >= Index then begin FObjects[Index] := obj; FisLeaf := True; end else begin if ((Index) <= (MAX_M - 1)) and (Index >= 0) then begin SetLength(FObjects, Index + 1); FObjects[Index] := obj; FisLeaf := True; end; end; end; procedure TRNode.setParent(parent_id: Integer); begin if parent_id >= 0 then FParent := parent_id; end; { TRtree } function TRtree.chooseSplitAxis(obj: TRObject; node_id: Integer): TAxis; var arr_obj: array of TRObject; i, j, k, idx: Integer; node_1, node_2: TRNode; perimeter_min, perimeter: Double; begin SetLength(arr_obj, MAX_M + 1); if not FNodeArr[node_id].isLeaf then Exit; for i := 0 to High(FNodeArr[node_id].FObjects) do begin arr_obj[i] := FNodeArr[node_id].FObjects[i]; end; arr_obj[ High(arr_obj)] := obj; node_1 := TRNode.Create; node_2 := TRNode.Create; perimeter_min := 999999; for i := 0 to 1 do // begin perimeter := 0; for j := 0 to 1 do // () begin node_1.clearObjects; node_2.clearObjects; QuickSort(arr_obj, 0, High(arr_obj), TAxis(i), TBound(j)); for k := 1 to MAX_M - MIN_M * 2 + 2 do // begin idx := 0; while idx < ((MIN_M - 1) + k) do // (MIN_M - 1) + k begin node_1.Objects[idx] := arr_obj[idx]; idx := idx + 1; end; for idx := idx to High(arr_obj) do // begin node_2.Objects[idx - ((MIN_M - 1) + k)] := arr_obj[idx]; end; updateMBR(node_1); updateMBR(node_2); perimeter := perimeter + ((node_1.mbr.Right.X - node_1.mbr.Left.X) * 2 + (node_2.mbr.Right.Y - node_2.mbr.Left.Y) * 2); end; end; if perimeter <= perimeter_min then begin Result := TAxis(i); perimeter_min := perimeter; end; perimeter := 0; end; SetLength(arr_obj, 0); FreeAndNil(node_1); FreeAndNil(node_2); end; function TRtree.chooseSplitAxis(nodeFather, nodeChild: Integer): TAxis; var arr_node: array of Integer; i, j, k, idx: Integer; node_1, node_2: TRNode; perimeter_min, perimeter: Double; begin SetLength(arr_node, MAX_M + 1); for i := 0 to High(FNodeArr[nodeFather].FChildren) do begin arr_node[i] := FNodeArr[nodeFather].FChildren[i]; end; arr_node[ High(arr_node)] := nodeChild; perimeter_min := 999999; node_1 := TRNode.Create; node_2 := TRNode.Create; for i := 0 to 1 do // begin perimeter := 0; for j := 0 to 1 do // () begin node_1.clearChildren; node_2.clearChildren; QuickSort(arr_node, 0, High(arr_node), TAxis(i), TBound(j)); for k := 1 to MAX_M - MIN_M * 2 + 2 do // begin idx := 0; while idx < ((MIN_M - 1) + k) do // (MIN_M - 1) + k begin node_1.Children[idx] := arr_node[idx]; idx := idx + 1; end; for idx := idx to High(arr_node) do // begin node_2.Children[idx - ((MIN_M - 1) + k)] := arr_node[idx]; end; updateMBR(node_1); updateMBR(node_2); perimeter := perimeter + node_1.margin + node_2.margin; end; end; if perimeter <= perimeter_min then begin Result := TAxis(i); perimeter_min := perimeter; end; perimeter := 0; end; FreeAndNil(node_1); FreeAndNil(node_2); SetLength(arr_node, 0); end; procedure TRtree.chooseSubtree(obj: TRObject; var node_id: Integer); var i, id_child: Integer; min_overlap_enlargement: Double; // Overlap_enlargement: Double; area_enlargement: Double; idChild_overlap: array of Integer; { . , , MBR } idChild_area: array of Integer; { . , MBR , MBR } id_zero: Integer; { MBR ( MBR) } enlargement_mbr: TMBR; // MBR dx, dy, dspace: Double; // MBR x, y has_no_enlargement: Boolean; // begin if FNodeArr[node_id].isLeaf then // , begin Exit; end; SetLength(idChild_overlap, 1); SetLength(idChild_area, 1); dx := 0; dy := 0; dspace := 9999999; id_zero := 0; has_no_enlargement := False; min_overlap_enlargement := 999999; if FNodeArr[FNodeArr[node_id].Children[0]].isLeaf then // () begin { } for i := 0 to High(FNodeArr[node_id].FChildren) do begin id_child := FNodeArr[node_id].FChildren[i]; Overlap_enlargement := FNodeArr[id_child].Area(obj.mbr) - FNodeArr[id_child].Overlap(obj.mbr); if Overlap_enlargement <= min_overlap_enlargement then begin if Overlap_enlargement = min_overlap_enlargement then // begin SetLength(idChild_overlap, Length(idChild_overlap) + 1); idChild_overlap[ High(idChild_overlap)] := i; end else // begin min_overlap_enlargement := Overlap_enlargement; if Length(idChild_overlap) = 1 then // idChild_overlap[0] := i else begin SetLength(idChild_overlap, 1); // , 1 idChild_overlap[0] := i end; end; end; end; if Length(idChild_overlap) = 1 then // 1 begin node_id := FNodeArr[node_id].Children[idChild_overlap[0]]; chooseSubtree(obj, node_id); // Exit; end; end else // begin SetLength(idChild_overlap, Length(FNodeArr[node_id].FChildren)); for i := 0 to High(FNodeArr[node_id].FChildren) do // idChild_overlap, ( , idChild_overlap ) idChild_overlap[i] := i; end; { } for i := 0 to High(idChild_overlap) do begin id_child := FNodeArr[node_id].FChildren[idChild_overlap[i]]; enlargement_mbr.Left.X := Min(obj.mbr.Left.X, FNodeArr[id_child].mbr.Left.X); enlargement_mbr.Left.Y := Min(obj.mbr.Left.Y, FNodeArr[id_child].mbr.Left.Y); enlargement_mbr.Right.X := Max(obj.mbr.Right.X, FNodeArr[id_child].mbr.Right.X); enlargement_mbr.Right.Y := Max(obj.mbr.Right.Y, FNodeArr[id_child].mbr.Right.Y); area_enlargement := FNodeArr[id_child].Area(enlargement_mbr) - FNodeArr[id_child].Area; if area_enlargement <= dspace then begin if area_enlargement = dspace then // begin SetLength(idChild_area, Length(idChild_area) + 1); idChild_area[ High(idChild_area)] := i; end else // begin dspace := area_enlargement; if Length(idChild_area) = 1 then // idChild_area[0] := i else begin SetLength(idChild_area, 1); // , 1 idChild_area[0] := i end; end; end; end; if Length(idChild_area) = 1 then // , MBR begin node_id := FNodeArr[node_id].Children[idChild_area[0]]; chooseSubtree(obj, node_id); // end else // ( MBR ) MBR begin dspace := 999999; for i := 0 to High(idChild_area) do begin id_child := FNodeArr[node_id].Children[idChild_area[i]]; if FNodeArr[id_child].Area < dspace then begin id_zero := idChild_area[i]; dspace := FNodeArr[id_child].Area; end; end; node_id := FNodeArr[node_id].Children[id_zero]; chooseSubtree(obj, node_id); end; end; constructor TRtree.Create; begin inherited; SetLength(FNodeArr, 1); FNodeArr[0] := TRNode.Create; FRoot := 0; FNodeArr[FRoot].FisLeaf := True; end; destructor TRtree.Destroy; var i: Integer; begin for i := 0 to High(FNodeArr) do FreeAndNil(FNodeArr[i]); SetLength(FNodeArr, 0); inherited; end; procedure TRtree.findObjectsInArea(mbr: TMBR; node_id: Integer; var obj: TObjArr); var i: Integer; begin if isRoot(node_id) then SetLength(obj, 0); if not FNodeArr[node_id].isLeaf then begin for i := 0 to High(FNodeArr[node_id].FChildren) do begin if FNodeArr[FNodeArr[node_id].Children[i]].isIntersected(mbr) then findObjectsInArea(mbr, FNodeArr[node_id].Children[i], obj); end; end else begin for i := 0 to High(FNodeArr[node_id].FObjects) do begin if FNodeArr[node_id].isIntersected(mbr, FNodeArr[node_id].Objects[i].mbr) then begin SetLength(obj, Length(obj) + 1); obj[ High(obj)] := FNodeArr[node_id].Objects[i].idx; end; end; end; end; procedure TRtree.findObjectsInArea(mbr: TMBR; var obj: TObjArr); begin findObjectsInArea(mbr, FRoot, obj); end; procedure TRtree.insertObject(obj: TRObject); var node_id: Integer; begin node_id := FRoot; chooseSubtree(obj, node_id); if Length(FNodeArr[node_id].FObjects) < MAX_M then // begin FNodeArr[node_id].Objects[ High(FNodeArr[node_id].FObjects) + 1] := obj; updateMBR(node_id); end else // begin splitNodeRStar(node_id, obj); // end; end; function TRtree.isRoot(node_id: Integer): Boolean; begin if node_id = FRoot then Result := True else Result := False; end; function TRtree.newNode: Integer; begin SetLength(FNodeArr, Length(FNodeArr) + 1); FNodeArr[ High(FNodeArr)] := TRNode.Create; Result := High(FNodeArr); end; procedure TRtree.QuickSort(var List: array of TRObject; iLo, iHi: Integer; axe: TAxis; bound: TBound); var Lo: Integer; Hi: Integer; T: TRObject; Mid: Double; begin Lo := iLo; Hi := iHi; case bound of Left: case axe of X: Mid := List[(Lo + Hi) div 2].mbr.Left.X; Y: Mid := List[(Lo + Hi) div 2].mbr.Left.Y; end; Right: case axe of X: Mid := List[(Lo + Hi) div 2].mbr.Right.X; Y: Mid := List[(Lo + Hi) div 2].mbr.Right.Y; end; end; repeat case bound of Left: case axe of X: begin while List[Lo].mbr.Left.X < Mid do Inc(Lo); while List[Hi].mbr.Left.X > Mid do Dec(Hi); end; Y: begin while List[Lo].mbr.Left.Y < Mid do Inc(Lo); while List[Hi].mbr.Left.Y > Mid do Dec(Hi); end; end; Right: case axe of X: begin while List[Lo].mbr.Right.X < Mid do Inc(Lo); while List[Hi].mbr.Right.X > Mid do Dec(Hi); end; Y: begin while List[Lo].mbr.Right.Y < Mid do Inc(Lo); while List[Hi].mbr.Right.Y > Mid do Dec(Hi); end; end; end; if Lo <= Hi then begin T := List[Lo]; List[Lo] := List[Hi]; List[Hi] := T; Inc(Lo); Dec(Hi); end; until Lo > Hi; if Hi > iLo then QuickSort(List, iLo, Hi, axe, bound); if Lo < iHi then QuickSort(List, Lo, iHi, axe, bound); end; procedure TRtree.QuickSort(var List: array of Integer; iLo, iHi: Integer; axe: TAxis; bound: TBound); var Lo: Integer; Hi: Integer; T: Integer; Mid: Double; begin Lo := iLo; Hi := iHi; case bound of Left: case axe of X: Mid := FNodeArr[List[(Lo + Hi) div 2]].mbr.Left.X; Y: Mid := FNodeArr[List[(Lo + Hi) div 2]].mbr.Left.Y; end; Right: case axe of X: Mid := FNodeArr[List[(Lo + Hi) div 2]].mbr.Right.X; Y: Mid := FNodeArr[List[(Lo + Hi) div 2]].mbr.Right.Y; end; end; repeat case bound of Left: case axe of X: begin while FNodeArr[List[Lo]].mbr.Left.X < Mid do Inc(Lo); while FNodeArr[List[Hi]].mbr.Left.X > Mid do Dec(Hi); end; Y: begin while FNodeArr[List[Lo]].mbr.Left.Y < Mid do Inc(Lo); while FNodeArr[List[Hi]].mbr.Left.Y > Mid do Dec(Hi); end; end; Right: case axe of X: begin while FNodeArr[List[Lo]].mbr.Right.X < Mid do Inc(Lo); while FNodeArr[List[Hi]].mbr.Right.X > Mid do Dec(Hi); end; Y: begin while FNodeArr[List[Lo]].mbr.Right.Y < Mid do Inc(Lo); while FNodeArr[List[Hi]].mbr.Right.Y > Mid do Dec(Hi); end; end; end; if Lo <= Hi then begin T := List[Lo]; List[Lo] := List[Hi]; List[Hi] := T; Inc(Lo); Dec(Hi); end; until Lo > Hi; if Hi > iLo then QuickSort(List, iLo, Hi, axe, bound); if Lo < iHi then QuickSort(List, Lo, iHi, axe, bound); end; procedure TRtree.splitNodeRStar(splited_Node_Id, inserted_Node_Id: Integer); var axe: TAxis; parent_id, new_child_id: Integer; node_1, node_2, node_1_min, node_2_min: TRNode; i, j, k: Integer; arr_node: array of Integer; area_overlap_min, area_overlap, // area_min, Area: Double; // begin if FNodeArr[splited_Node_Id].isLeaf then Exit; if isRoot(splited_Node_Id) then begin parent_id := newNode; // id FNodeArr[FRoot].Parent := parent_id; // id , FNodeArr[parent_id].Children[0] := FRoot; // id FNodeArr[parent_id].Level := FNodeArr[FNodeArr[parent_id].Children[0]].Level + 1; // 1 FRoot := parent_id; // id id FHeight := FHeight + 1; // end else begin parent_id := FNodeArr[splited_Node_Id].Parent; end; SetLength(arr_node, MAX_M + 1); for i := 0 to High(arr_node) - 1 do arr_node[i] := FNodeArr[splited_Node_Id].Children[i]; arr_node[ High(arr_node)] := inserted_Node_Id; node_1_min := TRNode.Create; node_2_min := TRNode.Create; node_1 := TRNode.Create; node_2 := TRNode.Create; axe := chooseSplitAxis(splited_Node_Id, inserted_Node_Id); area_overlap_min := 9999999; area_min := 9999999; for i := 0 to 1 do begin QuickSort(arr_node, 0, High(arr_node), axe, TBound(i)); for k := MIN_M - 1 to MAX_M - MIN_M do begin node_1.clearChildren; node_2.clearChildren; j := 0; while j <= k do begin node_1.Children[j] := arr_node[j]; j := j + 1; end; for j := k to High(arr_node) - 1 do begin node_2.Children[j - k] := arr_node[j + 1]; end; updateMBR(node_1); updateMBR(node_2); area_overlap := node_1.Overlap(node_2.mbr); if area_overlap < area_overlap_min then begin node_1_min.copy(node_1); node_2_min.copy(node_2); area_overlap_min := area_overlap; end else begin if area_overlap = area_overlap_min then // begin Area := node_1.Area + node_2.Area; // if Area < area_min then begin node_1_min.copy(node_1); node_2_min.copy(node_2); area_min := Area; end; end; end; end; end; node_1_min.Level := FNodeArr[splited_Node_Id].Level; node_2_min.Level := FNodeArr[splited_Node_Id].Level; FNodeArr[splited_Node_Id].copy(node_1_min); // () FNodeArr[splited_Node_Id].Parent := parent_id; new_child_id := newNode; // FNodeArr[new_child_id].copy(node_2_min); // FNodeArr[new_child_id].Parent := parent_id; // id parent FreeAndNil(node_1); FreeAndNil(node_2); FreeAndNil(node_1_min); FreeAndNil(node_2_min); for i := 0 to High(FNodeArr[new_child_id].FChildren) do // Parent id begin FNodeArr[FNodeArr[new_child_id].Children[i]].Parent := new_child_id end; if Length(FNodeArr[parent_id].FChildren) < MAX_M then // begin FNodeArr[parent_id].Children[ High(FNodeArr[parent_id].FChildren) + 1] := new_child_id; // id updateMBR(parent_id); end else // begin splitNodeRStar(parent_id, new_child_id); // end; end; procedure TRtree.splitNodeRStar(node_id: Integer; obj: TRObject); var axe: TAxis; parent_id, new_child_id: Integer; node_1, node_2, node_1_min, node_2_min: TRNode; i, j, k: Integer; arr_obj: array of TRObject; area_overlap_min, area_overlap, // area_min, Area: Double; // begin if not FNodeArr[node_id].isLeaf then Exit; if isRoot(node_id) then begin parent_id := newNode; // id FNodeArr[FRoot].Parent := parent_id; // id , FNodeArr[parent_id].Children[0] := FRoot; // id FNodeArr[parent_id].Level := FNodeArr[FNodeArr[parent_id].Children[0]].Level + 1; // 1 FRoot := parent_id; // id id FHeight := FHeight + 1; // end else begin parent_id := FNodeArr[node_id].Parent; end; SetLength(arr_obj, MAX_M + 1); for i := 0 to High(arr_obj) - 1 do arr_obj[i] := FNodeArr[node_id].Objects[i]; arr_obj[ High(arr_obj)] := obj; node_1_min := TRNode.Create; node_2_min := TRNode.Create; node_1 := TRNode.Create; node_2 := TRNode.Create; axe := chooseSplitAxis(obj, node_id); area_overlap_min := 9999999; area_min := 9999999; for i := 0 to 1 do begin QuickSort(arr_obj, 0, High(arr_obj), axe, TBound(i)); for k := MIN_M - 1 to MAX_M - MIN_M do begin node_1.clearObjects; node_2.clearObjects; j := 0; while j <= k do begin node_1.Objects[j] := arr_obj[j]; j := j + 1; end; for j := k to High(arr_obj) - 1 do begin node_2.Objects[j - k] := arr_obj[j + 1]; end; updateMBR(node_1); updateMBR(node_2); area_overlap := node_1.Overlap(node_2.mbr); if area_overlap < area_overlap_min then begin node_1_min.copy(node_1); node_2_min.copy(node_2); area_overlap_min := area_overlap; end else begin if area_overlap = area_overlap_min then // begin Area := node_1.Area + node_2.Area; // if Area < area_min then begin node_1_min.copy(node_1); node_2_min.copy(node_2); area_min := Area; end; end; end; end; end; node_1_min.Level := 0; node_2_min.Level := 0; FNodeArr[node_id].copy(node_1_min); // () FNodeArr[node_id].Parent := parent_id; updateMBR(node_id); new_child_id := newNode; // FNodeArr[new_child_id].copy(node_2_min); // FNodeArr[new_child_id].Parent := parent_id; // id parent updateMBR(new_child_id); FreeAndNil(node_1); FreeAndNil(node_2); FreeAndNil(node_1_min); FreeAndNil(node_2_min); if Length(FNodeArr[parent_id].FChildren) < MAX_M then // begin FNodeArr[parent_id].Children[ High(FNodeArr[parent_id].FChildren) + 1] := new_child_id; // id updateMBR(parent_id); end else // begin splitNodeRStar(parent_id, new_child_id); // end; end; procedure TRtree.updateMBR(node: TRNode); var i, idx: Integer; changed: Boolean; begin changed := False; node.fmbr.Left.X := 9999; node.fmbr.Left.Y := 9999; node.fmbr.Right.X := 0; node.fmbr.Right.Y := 0; if node.isLeaf then begin for i := 0 to High(node.FObjects) do begin if node.FObjects[i].mbr.Left.X < node.mbr.Left.X then begin node.fmbr.Left.X := node.FObjects[i].mbr.Left.X; changed := True; end; if node.FObjects[i].mbr.Left.Y < node.mbr.Left.Y then begin node.fmbr.Left.Y := node.FObjects[i].mbr.Left.Y; changed := True; end; if node.FObjects[i].mbr.Right.X > node.mbr.Right.X then begin node.fmbr.Right.X := node.FObjects[i].mbr.Right.X; changed := True; end; if node.FObjects[i].mbr.Right.Y > node.mbr.Right.Y then begin node.fmbr.Right.Y := node.FObjects[i].mbr.Right.Y; changed := True; end; end; end else begin for i := 0 to High(node.FChildren) do begin idx := node.FChildren[i]; if FNodeArr[idx].mbr.Left.X < node.mbr.Left.X then begin node.fmbr.Left.X := FNodeArr[idx].mbr.Left.X; changed := True; end; if FNodeArr[idx].mbr.Left.Y < node.mbr.Left.Y then begin node.fmbr.Left.Y := FNodeArr[idx].mbr.Left.Y; changed := True; end; if FNodeArr[idx].mbr.Right.X > node.mbr.Right.X then begin node.fmbr.Right.X := FNodeArr[idx].mbr.Right.X; changed := True; end; if FNodeArr[idx].mbr.Right.Y > node.mbr.Right.Y then begin node.fmbr.Right.Y := FNodeArr[idx].mbr.Right.Y; changed := True; end; end; end; if changed then begin if node.Parent >= 0 then updateMBR(node.Parent); end; end; procedure TRtree.updateMBR(node_id: Integer); var i, idx: Integer; changed: Boolean; begin changed := False; FNodeArr[node_id].fmbr.Left.X := 9999; FNodeArr[node_id].fmbr.Left.Y := 9999; FNodeArr[node_id].fmbr.Right.X := 0; FNodeArr[node_id].fmbr.Right.Y := 0; if FNodeArr[node_id].isLeaf then begin for i := 0 to High(FNodeArr[node_id].FObjects) do begin if FNodeArr[node_id].FObjects[i].mbr.Left.X < FNodeArr[node_id].mbr.Left.X then begin FNodeArr[node_id].fmbr.Left.X := FNodeArr[node_id].FObjects[i].mbr.Left.X; changed := True; end; if FNodeArr[node_id].FObjects[i].mbr.Left.Y < FNodeArr[node_id].mbr.Left.Y then begin FNodeArr[node_id].fmbr.Left.Y := FNodeArr[node_id].FObjects[i].mbr.Left.Y; changed := True; end; if FNodeArr[node_id].FObjects[i].mbr.Right.X > FNodeArr[node_id].mbr.Right.X then begin FNodeArr[node_id].fmbr.Right.X := FNodeArr[node_id].FObjects[i].mbr.Right.X; changed := True; end; if FNodeArr[node_id].FObjects[i].mbr.Right.Y > FNodeArr[node_id].mbr.Right.Y then begin FNodeArr[node_id].fmbr.Right.Y := FNodeArr[node_id].FObjects[i].mbr.Right.Y; changed := True; end; end; end else begin for i := 0 to High(FNodeArr[node_id].FChildren) do begin idx := FNodeArr[node_id].FChildren[i]; if FNodeArr[idx].mbr.Left.X < FNodeArr[node_id].mbr.Left.X then begin FNodeArr[node_id].fmbr.Left.X := FNodeArr[idx].mbr.Left.X; changed := True; end; if FNodeArr[idx].mbr.Left.Y < FNodeArr[node_id].mbr.Left.Y then begin FNodeArr[node_id].fmbr.Left.Y := FNodeArr[idx].mbr.Left.Y; changed := True; end; if FNodeArr[idx].mbr.Right.X > FNodeArr[node_id].mbr.Right.X then begin FNodeArr[node_id].fmbr.Right.X := FNodeArr[idx].mbr.Right.X; changed := True; end; if FNodeArr[idx].mbr.Right.Y > FNodeArr[node_id].mbr.Right.Y then begin FNodeArr[node_id].fmbr.Right.Y := FNodeArr[idx].mbr.Right.Y; changed := True; end; end; end; if changed then begin if FNodeArr[node_id].Parent >= 0 then updateMBR(FNodeArr[node_id].Parent); end; end; end. After implementation, all that remained to be done was to split the vector map objects into layers, set these layers to the maximum scale at which they would be displayed and construct R * -tree for each layer.
The results can be seen on the video:
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/224965/
All Articles